Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMP Cheat Sheet PDF
PMP Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
Dildar SainiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP Cheat Sheet PDF
PMP Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
Dildar SainiCopyright:
Available Formats
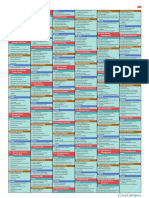
42 Project Management Processes
PMP Cheat Sheet and Study Notes
Based on PMBOK V4 Project Integration Management
The reader is responsible to verify and confirm all information presented herein. 1. Develop Project Charter
2. Develop Project Management Plan
Processes Human Resource Management
3. Direct / Manage Project Execution
Initiation Organizational Structures: Functional, Matrix (weak, balanced,
strong) , Projectized, Composite 4. Monitor / Control Project Work
Planning
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Physiological, Safety, Social, Self 5. Perform Integrated Change Control
Execution -esteem, Self-actualization. 6. Close Project or Phase
Monitor and Control McGregor: Theory X, Theory Y. Project Scope Management
Closing Ouchi: Theory Z. Motivated by commitment, opportunity advancement.
7. Collect Requirements
Knowledge Areas Herzberg’s Theory of Motivation: Hygiene factors, Motivating Agents.
8. Define Scope
Integration Leadership Styles: Directing, Facilitating, Coaching, Supporting,
Autocratic, Consultative, Consensus. 9. Create WBS
Scope Management
Project Manager Powers: Formal (legitimate,) Reward, Penalty 10. Verify Scope
Time Management
(coercive), Expert, Referent. 11. Control Scope
Cost Management Conflict Management: Withdraw (avoid), Smooth (accommodate), Project Time Management
Quality Management Compromise, Force, Collaborate, Confront (problem solving.)
12. Define Activities
HR Management Quality Management
13. Sequence Activities
Communications Management Ishikawa = Fishbone Diagram: cause and effect.
14. Estimate Activity Resources
Procurement Management Pareto Diagram: Identify problems and frequency. 80/20 Rule.
Flow Charts; Control Charts. 15. Estimate Activity Durations
Risk Management
Just in Time: Reduces inventory; requires additional quality control. 16. Develop Schedule
Professional Responsibility
Quality Theories: Kaizen (continuous improvement,) Six Sigma, TQM 17. Control Schedule
(total quality management.) Project Cost Management
Earned Value Management
Kaizen: Small improvements to reduce costs and improve consistency. 18. Estimate Costs
BAC = Budget At Completion
Deming Cycle: Plan, Do Check, Act. 19. Determine Budget
EV = Actual % * BAC
Cost Management
PV = Planned % * BAC 20. Control Costs
Cost Estimating - Accuracy
AC = Sum of all incurred costs Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM): -50% to +100% Project Quality Management
CV = EV - AC Budgetary: -10% to +25% 21. Plan Quality
Definitive: -5% to + 10% 22. Perform Quality Assurance
SV = EV - PV
Risk Management 23. Perform Quality Control
CPI = EV / AC
Risk Strategies (threats): Avoid, Transfer, Mitigate, Accept. Project Human Resource
< 1 = Over Budget
Risk Strategies (opportunities): Exploit, Share, Enhance, Accept. Management
> 1 = Under Budget
Qualitative Risk Analysis: Chance and impact of risk occurrence 24. Develop Human Resource Plan
SPI = EV / PV Results in prioritized list of risks; risk ranking.
< 1 = Behind Schedule 25. Acquire Project Team
Quantitative Risk Analysis: Numerical analysis of probability
> 1 = Ahead of Schedule and impact. 26. Develop Project Team
EAC = BAC / CPI Tools: Interviews, Sensitivity Analysis, Decision Tree Analysis, 27. Manage Project Team
EAC = AC + ETC Simulation, Monte Carlo Analysis. Project Communications
EAC = AC + (BAC + EV) / CPI Closing Management
ETC = EAC - AC Contract Close: Before project close 28. Identify Stakeholders
Project or Phase Close: Lessons Learned
VAC = BAC - EAC 29. Plan Communications
PMI Code of Ethics: Respect, Fair, Honest.
BCWS = PV 30. Distribute Information
BCWP = EV Key Formulas Time Management 31. Manage Stakeholder Expectations
ACWP = AC Standard Deviation = (P - O) / 6 Precedence Diagramming Method 32. Report Performance
Tips: PERT = (O + 4M + P) / 6 PDM: Activity-on-Node (AON)
Project Risk Management
Negative is bad Total Float = LS—ES or LF –EF Arrow Diagram Method
33. Plan Risk Management
Positive is good ADM: Activity-on-Arrow (AOA)
Comm Channels = N (N-1) / 2 34. Identify Risks
If Variance: EV - Something Where: Conditional Diagram Method
If Index: EV / Something Graphical Evaluation and Review 35. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
P = Pessimistic
If Cost related use AC O = Optimistic Technique (GERT): Allows loop 36. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
If Time related use PV M = Most likely; Realistic Crashing: Add more resources 37. Plan Risk Responses
Most formulas start with EV N = # Project Members Fast Tracking: Tasks in parallel 38. Monitor and Control Risks
Benefit Cost Ratio = Forward Pass: Early start, early Project Procurement Management
Rules Based on Numbers Cost / Benefits finish
BCR < 1 Unfavorable 39. Plan Procurements
80 Hour Rule = Max size of Backward Pass: Late start, late
work packages BCR > 1 Higher is Better 40. Conduct Procurements
finish
80/20 Rule = Pareto’s Law Net Present Value = 41. Administer Procurements
Float; Slack: activity margin off
20% of causes responsible for FV / (1 + r)^n critical path 42. Close Procurements
80% of problems Future Value =
PV (1 + i)^n Free Float: activity margin not
0/50/100 = Work package impacting early start of next de- Copyright © 2009 PMServicesNW
completion. No credit until Internal Rate of Return pendant activity All rights reserved
50% complete. No additional Higher is better
Project Float www.PMServicesNW.com
credit until 100% complete. Six Sigma: 99.99% defect free
You might also like
- Cheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6Document2 pagesCheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6rimrany87% (15)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionFrom EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- PMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- PMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)Document6 pagesPMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)phongbkac46100% (9)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- PMP Study SheetDocument3 pagesPMP Study SheetRobincrusoe88% (26)
- PMP Formulas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Cheat SheetAn Nguyen100% (12)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat SheetoovijaygNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument5 pagesPMP Formulasbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsFrom EverandCAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PMP Exam Prep SummaryDocument5 pagesPMP Exam Prep SummaryAshenafi100% (8)
- PMP Memory SheetsDocument6 pagesPMP Memory Sheets1hass197% (30)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat Sheetyogesh sharma89% (9)
- 60 Days - PMP Study PlanDocument3 pages60 Days - PMP Study PlanShahram Karimi100% (7)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Bolden - What Is Leadership PDFDocument38 pagesBolden - What Is Leadership PDFaolmedoNo ratings yet
- Crack PMP in 45 DaysDocument10 pagesCrack PMP in 45 Daysgolfmaniac48% (21)
- ITTO Trick Sheet 49 Process - Jan 18 V 1.0 PMBOK 6th EditionDocument26 pagesITTO Trick Sheet 49 Process - Jan 18 V 1.0 PMBOK 6th EditionAbdulla Jawad Alshemary84% (25)
- Key Acupoints PDFDocument6 pagesKey Acupoints PDFthouartu50% (2)
- CAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamFrom EverandCAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamNo ratings yet
- PMP Cheat Sheet 6 PagesDocument6 pagesPMP Cheat Sheet 6 PagesSergio Alves100% (11)
- PMP Full ExamDocument51 pagesPMP Full Examrvsreddy197285% (26)
- PMBOK Study Notes PDFDocument83 pagesPMBOK Study Notes PDFshetupuc92% (26)
- PMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookDocument10 pagesPMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookIbrahimSamir100% (9)
- PMP Study SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Study SheetAli Abdelmoniem Ahmed75% (4)
- PMP NotesDocument4 pagesPMP Notesmukesh697No ratings yet
- PMBOK6 EnglishDocument1 pagePMBOK6 Englishbigprice100% (3)
- PMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)Document53 pagesPMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)girishkris92% (25)
- A Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideFrom EverandA Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideNo ratings yet
- IFC2x3 TC1 Entity Hierarchy PDFDocument17 pagesIFC2x3 TC1 Entity Hierarchy PDFthouartuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Developing Strategic Management and Leadership Skill)Document15 pagesUnit 1 (Developing Strategic Management and Leadership Skill)Honey Rajput33% (3)
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamFrom EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- PMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateFrom EverandPMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Earned Value Management: 60 Minutes Compact Knowledge: The Best Methods and Tools to Keep Your Project Under ControlFrom EverandEarned Value Management: 60 Minutes Compact Knowledge: The Best Methods and Tools to Keep Your Project Under ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsFrom Everand50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsNo ratings yet
- PMP Study MaterialsDocument90 pagesPMP Study Materialsamira_salama100% (4)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesPMP Cheat Sheetsachin.nate525782% (11)
- PMP FormulasDocument3 pagesPMP Formulaspolters100% (8)
- PMP Notes FinalDocument24 pagesPMP Notes Finalumerillias89% (9)
- Memory Aids For PMP ExamDocument7 pagesMemory Aids For PMP ExamMustafa100% (18)
- Integration Management: - Develop Project Charter Process - Project Selection MethodsDocument2 pagesIntegration Management: - Develop Project Charter Process - Project Selection MethodsAbhijith VJ50% (2)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationFrom EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationNo ratings yet
- PgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- How to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptFrom EverandHow to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PMP Practice Makes Perfect: Over 1000 PMP Practice Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP Practice Makes Perfect: Over 1000 PMP Practice Questions and AnswersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- PMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasFrom EverandPMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasNo ratings yet
- Aspect of Prana Prana Apana Udana Samana VyanaDocument3 pagesAspect of Prana Prana Apana Udana Samana VyanathouartuNo ratings yet
- Acu Chakra ConnectionflowDocument2 pagesAcu Chakra ConnectionflowthouartuNo ratings yet
- Using A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamDocument28 pagesUsing A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamthouartuNo ratings yet
- World Religious Views of Health and HealingDocument34 pagesWorld Religious Views of Health and HealingthouartuNo ratings yet
- The Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlDocument27 pagesThe Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlthouartuNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondDocument14 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondthouartuNo ratings yet
- MongodbDocument66 pagesMongodbthouartuNo ratings yet
- MX Injection TestingDocument24 pagesMX Injection TestingthouartuNo ratings yet
- Helm ClashdetectionDocument7 pagesHelm ClashdetectionMayouran WijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Goldsmith MOJO ScorecardDocument3 pagesGoldsmith MOJO ScorecardthouartuNo ratings yet
- Elem Am 98 RepeatabilityDocument13 pagesElem Am 98 RepeatabilitythouartuNo ratings yet
- 6 Packet Spring13Document6 pages6 Packet Spring13thouartuNo ratings yet
- Aryabhateeya: Trivandrum 695 018, India (0471-2490149)Document27 pagesAryabhateeya: Trivandrum 695 018, India (0471-2490149)thouartuNo ratings yet
- The Science of Hindu SpiritualityDocument12 pagesThe Science of Hindu SpiritualitythouartuNo ratings yet
- SPI-Software Process ImprovementDocument24 pagesSPI-Software Process ImprovementthouartuNo ratings yet
- SanskritDocument8 pagesSanskritthouartu0% (2)
- Final MCQ OBDocument43 pagesFinal MCQ OBYadnyesh Khot100% (2)
- Management Motivation EOMDocument18 pagesManagement Motivation EOMI AM LEGENDNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management: By: Mayank Pandey Assistant Professor Niet Business ShoolDocument51 pagesIndustrial Management: By: Mayank Pandey Assistant Professor Niet Business ShoolDaman100% (1)
- EBM2063 Group Assignment FULLDocument30 pagesEBM2063 Group Assignment FULLAdrian GohNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Theories and ControversiesDocument12 pagesLeadership: Theories and ControversiesAhmed LarhmamNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Evolution of Management Thoughts 1Document32 pagesAssignment On Evolution of Management Thoughts 1Mahjabin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 4 MsDocument19 pages4 MsMaryrose VasquezNo ratings yet
- SLM-III Sem BBA Human Resource ManagementDocument79 pagesSLM-III Sem BBA Human Resource ManagementMing Bhutia NuppaazzNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy ManagementDocument31 pagesPharmacy Managementradya mosadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument28 pagesLesson 2 Evolution of Management TheoriesVon Violo BuenavidesNo ratings yet
- HRM-Study MaterialDocument19 pagesHRM-Study MaterialGreeshma SharathNo ratings yet
- Human Relations TheoriesDocument28 pagesHuman Relations TheoriesHarold100% (1)
- Organization Theories and ApplicationDocument30 pagesOrganization Theories and ApplicationjediNo ratings yet
- Employee Motivation and Level of SatisfactionDocument63 pagesEmployee Motivation and Level of Satisfactionarvindchandru098No ratings yet
- Leadership Theories: For SEBI Grade A & RBI Grade BDocument18 pagesLeadership Theories: For SEBI Grade A & RBI Grade Bomesh gehlot100% (1)
- M&e NotesDocument183 pagesM&e NotesAravind SureshNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of LeadershipDocument112 pagesThe Art and Science of LeadershipGohar SaeedNo ratings yet
- OB Full NOTESDocument143 pagesOB Full NOTESrushipavan5No ratings yet
- WM Test Bank AutoRecoveredDocument70 pagesWM Test Bank AutoRecoveredMerlajoy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Behavioural Approach To ManagementDocument13 pagesBehavioural Approach To ManagementRishab MehraNo ratings yet
- 1-Contribution of Management ThinkersDocument35 pages1-Contribution of Management ThinkersSwapnil Gopal Mahajan100% (1)
- Ch2-The Evolution of Management ThinkingDocument31 pagesCh2-The Evolution of Management ThinkingRakshith Reddy TNo ratings yet
- The CaseDocument16 pagesThe Casepoint clickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2bladehero10100% (1)
- Leadership and Management 2003Document46 pagesLeadership and Management 2003Ciella Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Administrators Are Born Not TrainedDocument9 pagesAdministrators Are Born Not TrainedRONNEL SECADRONNo ratings yet
- Motivate Your Team CLUBDocument40 pagesMotivate Your Team CLUBYusuf BatawalaNo ratings yet
- Session 7-8Document39 pagesSession 7-8KANIKA GORAYANo ratings yet