Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ebp Poster Presentation
Uploaded by
api-5001763700 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views1 pageOriginal Title
ebp poster presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views1 pageEbp Poster Presentation
Uploaded by
api-500176370Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
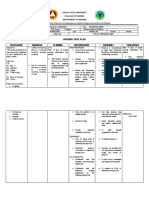
Basin Bed Baths vs. Disposable Bath Wipes: Which method is best?
Kevin Gross
Old Dominion University
Findings Nursing Implications
Introduction
• Understand personal hygiene
• Personal Hygiene: What is it, and why is it Study 1: requirements of patients
important?
• Bed baths: What is it, and why are they • Of the 60 nurses involved more than half were less than 25 years old. • Understand how spread of contaminants
important? • Two thirds of them had a BSN. from one area of the body to another can
increase risk of infection
• Traditional practice: Basin with soap and • Two thirds had more than 5 years of ICU experience • Know how hospital acquired infections
water • More than three quarters of the nurses had improper bath techniques (HAIs) occur and work to reduce
• Current Standards: American Academy of
Critical Nurses suggest disposable bath • Study revealed that there was a significant gap between what is currently being done and what should be done occurrences.
with regard to EBP recommendations. • Understand time on task for bathing
wipes
patient and work to reduce amount.
• Showed that bath time should be patient centered and should aim to complete them at a time that doesn’t • Understand how poor hygiene can affect
interrupt sleep. It should be done efficiently so that sleep schedules are not interrupted (AACN recommends self-esteem and patient satisfaction and
avoiding the hours between midnight and 0600 for that reason) (El-Soussi, A., Asfour, H., 2016) work to improve upon it.
Purpose
Study 2:
The purpose of this presentation is to
discuss current practice in bathing patients • Consisted of 40 patients
in the clinical environment as well as • Majority of patients were men with an average age of 60.7 years
introduce an alternative method in order to • Average number of days in the hospital before study took place was 21 days Conclusion
keep up with current standards. • Average number of days on antibiotics before study took place was 15.2 days • Traditional basin bed baths have been
• No significant difference between disposable bath wipes and traditional basin baths when measured for time and shown to increase risk of HAIs
• Current changes in practice indicate use
quality and microbial counts
of disposable bath wipes.
• Significant differences were noticed between disposable bath wipes and traditional basin baths when measured 1. Reduce time on task
on cost savings and nurses’ satisfaction. 2. Save money
Methods
❖Cost savings were related to a reduction in total supplies used and time it took to complete the task. 3. Decrease patient
• Study 1: Descriptive design. 60 discomfort
nurses were observed. Graded
(Larson, E., Ciliberti, T., Chantler, C., Abraham, J., Lazaro, E., Venturanza, M., Pancholi, P., 2004).
4. Increase patient
using “assessment sheet” satisfaction
Study 3:
• Study 2: Observational study. • Consisted of two studies that were systematically reviewed and deemed to be of high quality.
40 patients were involved.
Independent variables:
• No significant difference was noticed in microbial counts between the two methods (bathing without water and
disposable wipes and traditional basin baths. References
traditional basin bath. • Bathing without water did show a reduction in skin discoloration, erythema, and skin breakdown. El-Soussi, A., Asfour, H. (2016). Examining
Dependent variables: time and • Limited evidence found to make a solid recommendation to follow with regard to policy change. (Groven, F., bed-bath practices of critically ill
quality, microbial counts,
nurses satisfaction, and costs.
Zwakhalen, S., Odekerken-Schröder, G., Joosten, E., Hamers, J., 2017) patients. Journal of Nursing Education
and Practice, 6(12), 1-11.
Study 3: Systematic review: 2 Groven, F., Zwakhalen, S., Odekerken-
studies were reviewed. Schröder, G., Joosten, E., Hamers, J.
Independent variables: Bath (2017). How does washing without water
without water and traditional perform compared to the traditional bed
basin bath. Dependent variables: bath: a systematic review. BMC
physiologic outcomes, stakeholder Geriatrics, 17(31), 1-16.
outcomes, and organizational Larson, E., Ciliberti, T., Chantler, C.,
outcomes.
Abraham, J., Lazaro, E., Venturanza, M.,
Pancholi, P. (2004). Comparison of
traditional and disposable bed baths in
critically ill patients. American Journal of
Critical Care, 13(3), 235-241.
You might also like
- Course PlanDocument7 pagesCourse PlanSAMRAH FARIDINo ratings yet
- CHN 1Document2 pagesCHN 1Pankaj WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Using Paplau Theory of Inter Personal Relations To Guide The Teaching of Patient Undergoing Urinary DiversionDocument10 pagesUsing Paplau Theory of Inter Personal Relations To Guide The Teaching of Patient Undergoing Urinary DiversionarunNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Bed Bath Proper Positioning OutlinedDocument18 pagesWeek 2 Bed Bath Proper Positioning OutlinedNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
- Virginia Henderson Nursing Needs TheoryDocument4 pagesVirginia Henderson Nursing Needs TheoryBangtan SeonyodanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing Research and Importance of The Course in NursingDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Nursing Research and Importance of The Course in NursingAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Credentials AND Background of The Theorist: OutlineDocument7 pagesCredentials AND Background of The Theorist: OutlineMa. Goretti Jica GulaNo ratings yet
- Abdellah's TheoryDocument25 pagesAbdellah's TheorySimran ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanKatherine BellezaNo ratings yet
- EBP PersntaionDocument17 pagesEBP PersntaionMo7med YasserNo ratings yet
- The ABC Towards Proper Personal Care: Always Be Clean!: Presented By: Balita, Gamboa, Lejero, Sulit, TenorioDocument31 pagesThe ABC Towards Proper Personal Care: Always Be Clean!: Presented By: Balita, Gamboa, Lejero, Sulit, TenorioAngelou RosalesNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Practice With Nurses in Incontinence CareDocument25 pagesCollaborative Practice With Nurses in Incontinence Caresingle_ladyNo ratings yet
- How Much Time Do Nurses Spend On Patient CareDocument4 pagesHow Much Time Do Nurses Spend On Patient CareSean CabralesNo ratings yet
- Zuwena Presentation For WaterAid India Workshop March 2016 - CGHEWebDocument32 pagesZuwena Presentation For WaterAid India Workshop March 2016 - CGHEWebBonita SugehaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing PDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Papi-26587879100% (4)
- 0733464815574094.full 2 2Document24 pages0733464815574094.full 2 2jay jayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research RefresherDocument73 pagesNursing Research RefresherJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAmple CasaclangNo ratings yet
- Katharine KolcabaDocument4 pagesKatharine KolcabaimmajinbuxoxoNo ratings yet
- GokulDocument17 pagesGokulSumaiya ParvinNo ratings yet
- NCP Leptospirosis - NewDocument5 pagesNCP Leptospirosis - Newglaiza_requintoNo ratings yet
- Psych - Chapter 23 Into To Milieu ManagementDocument4 pagesPsych - Chapter 23 Into To Milieu ManagementKaren かれんNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Collection of Mucus in The Airways (Pneumonia) andDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange Related To Collection of Mucus in The Airways (Pneumonia) andBetina De JesusNo ratings yet
- NCP Actual 1Document2 pagesNCP Actual 1Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationMina SumaoangNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument6 pagesNCP LeptospirosisJean Marie DavidNo ratings yet
- Personal hygiene..H.EDocument6 pagesPersonal hygiene..H.EJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- NCM THEORIES Nightingale RoyDocument16 pagesNCM THEORIES Nightingale RoyAeizaNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-Template - PDF p2Document3 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-Template - PDF p2Franz keannu Libunao GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment in NCM 106 LectureDocument6 pagesAssignment in NCM 106 LectureJeanessa Delantar QuilisadioNo ratings yet
- Nightingale's Environmental TheoryDocument49 pagesNightingale's Environmental Theoryankita guptaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Care PlansDocument7 pagesCare PlansFirenze Fil100% (6)
- KKKKDocument22 pagesKKKKMARY CLAIRE SUMILHIGNo ratings yet
- NCM 118a OBWard (Bernales, JLE)Document10 pagesNCM 118a OBWard (Bernales, JLE)Jan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- Ebm Therapeutics Lecture For MsucomDocument51 pagesEbm Therapeutics Lecture For MsucomKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- " Nursing Ought To Signify The Proper Use of Fresh Air, Light, Warmth, Cleanliness, Quiet, and Proper Selection and Administration of Diet-All at Least Expense of Vital Power To The PatientDocument44 pages" Nursing Ought To Signify The Proper Use of Fresh Air, Light, Warmth, Cleanliness, Quiet, and Proper Selection and Administration of Diet-All at Least Expense of Vital Power To The PatientALLEYAH JAIRA D LORENZONo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale: Nursing TheoryDocument44 pagesFlorence Nightingale: Nursing TheoryJirah Mae GavinoNo ratings yet
- Imogene KingDocument21 pagesImogene KingAlyssa MercadoNo ratings yet
- Professional Meeting Reflective JournalDocument5 pagesProfessional Meeting Reflective Journalapi-353656227No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument21 pagesMedical Surgical NursingSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanLei KeneptNo ratings yet
- Nanda, Nic, and Noc Linkages: Home CareDocument2 pagesNanda, Nic, and Noc Linkages: Home CareLisa YusidaNo ratings yet
- Building Solutions: Improving Mental Healthcare EnvironmentsDocument16 pagesBuilding Solutions: Improving Mental Healthcare Environmentsjanice19899No ratings yet
- Florence andHendersonTheoryDocument61 pagesFlorence andHendersonTheoryankita guptaNo ratings yet
- Cauti103 508Document56 pagesCauti103 508Yahia HassaanNo ratings yet
- Relos, Kristel Joyce D. Bsn2e - NCPDocument3 pagesRelos, Kristel Joyce D. Bsn2e - NCPKristel Joyce RelosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Constipationbmrose3783% (12)
- Wash Me Without WaterDocument6 pagesWash Me Without Waterjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing Related Learning Experience Plan Course Title: NCM 109: Sample of Alternative Activities For Clinical Practice (RLE Equivalent 8 Hours)Document5 pagesCollege of Nursing Related Learning Experience Plan Course Title: NCM 109: Sample of Alternative Activities For Clinical Practice (RLE Equivalent 8 Hours)Danica Yen PagalNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Asepsis: Module EDocument37 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Asepsis: Module EmalindaNo ratings yet
- Basic Science and Technology PDFDocument10 pagesBasic Science and Technology PDFpromiseisemin59No ratings yet
- Cauti102 508Document75 pagesCauti102 508Yahia HassaanNo ratings yet
- Prelim Outline - Bioethics BSNDocument11 pagesPrelim Outline - Bioethics BSNSheenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetPrincess Mildred AbdonNo ratings yet
- Health Asses PrelimsDocument41 pagesHealth Asses PrelimsJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- CRITIQUEDocument29 pagesCRITIQUEManisha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Manual for Iv Therapy Procedures & Pain Management: Fourth EditionFrom EverandManual for Iv Therapy Procedures & Pain Management: Fourth EditionNo ratings yet
- Practice Summary Paper Intro PageDocument5 pagesPractice Summary Paper Intro Pageapi-500176370No ratings yet
- Death and Dying Intro PageDocument2 pagesDeath and Dying Intro Pageapi-500176370No ratings yet
- Practice Summary PaperDocument15 pagesPractice Summary Paperapi-500176370No ratings yet
- Theory ApplicationDocument9 pagesTheory Applicationapi-500176370No ratings yet
- Position Paper Intro PageDocument5 pagesPosition Paper Intro Pageapi-500176370No ratings yet
- Personal Philosophy of NursingDocument8 pagesPersonal Philosophy of Nursingapi-500176370No ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: AuthorsDocument9 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: AuthorsRam Kumar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Speech Language Concerns Teacher HandoutDocument12 pagesSpeech Language Concerns Teacher HandoutUsamah HussainNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Perdarahan ObstetriDocument10 pagesTatalaksana Perdarahan ObstetriAfiani JannahNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Organizing Categorical Variables: SolutionDocument34 pagesProblem 1: Organizing Categorical Variables: SolutionArgieshi GCNo ratings yet
- National Rural Health Mission AssignmentDocument12 pagesNational Rural Health Mission AssignmentFaceless BubbiesNo ratings yet
- Peer Facilitator Action Plan Anger ManagementDocument2 pagesPeer Facilitator Action Plan Anger ManagementChristine Joy MarananNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 TrialsDocument289 pagesCovid 19 TrialsPaulo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- BRM - Investment in Healthcare SectorDocument37 pagesBRM - Investment in Healthcare SectorChandan moreNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Section 1 - Product & Company IdentificationDocument8 pagesSafety Data Sheet Section 1 - Product & Company IdentificationBoyet BaldeNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology-QuestionDocument4 pagesGeneral Pharmacology-Questionlina amjadNo ratings yet
- Psycho Social Theoretical FrameworkDocument14 pagesPsycho Social Theoretical FrameworkSieg AguillonNo ratings yet
- iTT MANUALDocument80 pagesiTT MANUALGerencia Rigar Colombia SASNo ratings yet
- PrescriptionDocument24 pagesPrescriptionCrazy BrainNo ratings yet
- Hypertrophy Max - Primer PhaseDocument21 pagesHypertrophy Max - Primer PhaseRV810100% (6)
- VEINDOCANOL English PresentationDocument9 pagesVEINDOCANOL English PresentationSOLOSCOPE MEDICALNo ratings yet
- The History, Current Role, and Future of Music Therapy in IndiaDocument9 pagesThe History, Current Role, and Future of Music Therapy in IndiaDaniele PendezaNo ratings yet
- 2159-Article Text-4965-1-10-20230310Document7 pages2159-Article Text-4965-1-10-20230310najwaazzahra2121No ratings yet
- Air Quality Index and ExplanationDocument4 pagesAir Quality Index and ExplanationPrarthana DasNo ratings yet
- A Multiple Intelligences Road To An EST ClassroomDocument15 pagesA Multiple Intelligences Road To An EST ClassroomAndreia PintoNo ratings yet
- Praxis CBTinPractice ODCEpacketDocument4 pagesPraxis CBTinPractice ODCEpacketJ.C. GarzaNo ratings yet
- Case Report - SAHDocument41 pagesCase Report - SAHNeni NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Control of Nonconforming Work019 Af.r4Document6 pagesControl of Nonconforming Work019 Af.r4Massimiliano PorcelliNo ratings yet
- Black White PA Brochure 1 PDFDocument2 pagesBlack White PA Brochure 1 PDFWendy ChausseeNo ratings yet
- Community Service Sites Fall 2023Document5 pagesCommunity Service Sites Fall 2023Nixon MarkNo ratings yet
- Management of Blunderbuss CanalsDocument11 pagesManagement of Blunderbuss CanalsNitesh PatilNo ratings yet
- National Immunization Policy Pakistan 2022Document30 pagesNational Immunization Policy Pakistan 2022Mk AbbNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0160252722000693 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0160252722000693 MainjohnsmithdosNo ratings yet
- Essay On Technology 3 Selected Essays On TechnologyDocument1 pageEssay On Technology 3 Selected Essays On TechnologyMuradNo ratings yet
- Political SelfDocument53 pagesPolitical SelfMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- List of Personnel Benefits Granted by The SchoolDocument8 pagesList of Personnel Benefits Granted by The SchoolAspci Assumption Passi100% (1)