Professional Documents
Culture Documents
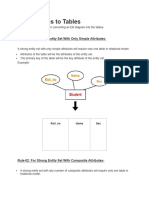
DBMS Joins We Understand The Benefits of Cartesian Product of Two Relation
Uploaded by
abcOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DBMS Joins We Understand The Benefits of Cartesian Product of Two Relation
Uploaded by
abcCopyright:
Available Formats
DBMS Joins We understand the benefits of Cartesian product of two relation, which gives us all the
possible tuples that are paired together. But Cartesian product might not be feasible for huge relations
where number of tuples are in thousands and the attributes of both relations are considerable large.
Join is combination of Cartesian product followed by selection process. Join operation pairs two tuples
from different relations if and only if the given join condition is satisfied. Following section should
describe briefly about join types: Theta (θ) join θ in Theta join is the join condition. Theta joins combines
tuples from different relations provided they satisfy the theta condition. Notation: R1 ⋈θ R2 R1 and R2
are relations with their attributes (A1, A2, .., An ) and (B1, B2,.. ,Bn) such that no attribute matches that
is R1 ∩ R2 = Φ Here θ is condition in form of set of conditions C. Theta join can use all kinds of
comparison operators. Student SID Name Std 101 Alex 10 102 Maria 11 [Table: Student Relation]
Subjects Class Subject 10 Math 10 English 11 Music 11 Sports [Table: Subjects Relation] Student_Detail =
STUDENT ⋈Student.Std = Subject.Class SUBJECT Student_detail SID Name Std Class Subject 101 Alex 10
10 Math 101 Alex 10 10 English 102 Maria 11 11 Music 102 Maria 11 11 Sports [Table: Output of theta
join] Equi-Join When Theta join uses only equality comparison operator it is said to be Equi-Join. The
above example conrresponds to equi-join Natural Join ( ⋈ ) Natural join does not use any comparison
operator. It does not concatenate the way Cartesian product does. Instead, Natural Join can only be
performed if the there is at least one common attribute exists between relation. Those attributes must
have same name and domain. Natural join acts on those matching attributes where the values of
attributes in both relation is same. Courses CID Course Dept CS01 Database CS ME01 Mechanics ME
EE01 Electronics EE [Table: Relation Courses] HoD Dept Head CS Alex ME Maya EE Mira [Table: Relation
HoD] Courses ⋈ HoD Dept CID Course Head CS CS01 Database Alex ME ME01 Mechanics Maya EE EE01
Electronics Mira [Table: Relation Courses ⋈ HoD] Outer Joins All joins mentioned above, that is Theta
Join, Equi Join and Natural Join are called inner-joins. An inner-join process includes only tuples with
matching attributes, rest are discarded in resulting relation. There exists methods by which all tuples of
any relation are included in the resulting relation. There are three kinds of outer joins: Left outer join ( R
S ) All tuples of Left relation, R, are included in the resulting relation and if there exists tuples in R
without any matching tuple in S then the S-attributes of resulting relation are made NULL. Left A B 100
Database 101 Mechanics 102 Electronics [Table: Left Relation] Right A B 100 Alex 102 Maya 104 Mira
[Table: Right Relation] Courses HoD A B C D 100 Database 100 Alex 101 Mechanics --- --- 102 Electronics
102 Maya [Table: Left outer join output] Right outer join: ( R S ) All tuples of the Right relation, S, are
included in the resulting relation and if there exists tuples in S without any matching tuple in R then the
R-attributes of resulting relation are made NULL. Courses HoD A B C D 100 Database 100 Alex 102
Electronics 102 Maya --- --- 104 Mira [Table: Right outer join output] Full outer join: ( R S) All tuples of
both participating relations are included in the resulting relation and if there no matching tuples for both
relations, their respective unmatched attributes are made NULL. Courses HoD A B C D 100 Database 100
Alex 101 Mechanics --- --- 102 Electronics 102 Maya --- --- 104 Mira [Table: Full outer join output]
Source: http://www.tutorialspoint.com/dbms/database_joins.htm
You might also like
- Dbms 23Document3 pagesDbms 23Chrispine OtienoNo ratings yet
- Dbms Joins: Theta (θ) joinDocument5 pagesDbms Joins: Theta (θ) joinWendy MarieNo ratings yet
- Relational Algebra PDocument9 pagesRelational Algebra PkamalgaihreNo ratings yet
- Dbms Relational AlgebraDocument16 pagesDbms Relational AlgebraRitesh VermaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Joins Types and ExamplesDocument5 pagesDBMS Joins Types and ExamplesJosef GirmaNo ratings yet
- RDBMS MSTDocument13 pagesRDBMS MSTNisha ChouhanNo ratings yet
- DBMS ASSIGNMENT CA3Document17 pagesDBMS ASSIGNMENT CA3Ritesh VermaNo ratings yet
- 12-Joins Operation in DbmsDocument32 pages12-Joins Operation in DbmsMohit SainiNo ratings yet
- DE Module2 RelationalModel PPTDocument71 pagesDE Module2 RelationalModel PPTwowafer745No ratings yet
- Relation AlgebraDocument39 pagesRelation Algebraspacely.iqNo ratings yet
- Query Tree Generation and OptimizationDocument25 pagesQuery Tree Generation and OptimizationEDWIN RIOBANo ratings yet
- Natural join (⋈) explainedDocument2 pagesNatural join (⋈) explainedParul RajpalNo ratings yet
- A1, A2, A3R2Document45 pagesA1, A2, A3R2NamanNo ratings yet
- Relation Algebra OperationDocument32 pagesRelation Algebra Operationeumine100% (4)
- Relational Algebra (Autosaved)Document45 pagesRelational Algebra (Autosaved)mishrasudhakant0No ratings yet
- Relational Algebra To SQLDocument15 pagesRelational Algebra To SQLSushma NayakNo ratings yet
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya College Database Management System Relational Algebra and Relational CalculusDocument28 pagesDeen Dayal Upadhyaya College Database Management System Relational Algebra and Relational CalculusPRATIKSHA 20MTS5721No ratings yet
- Database Design, Implementation, and ValidationDocument8 pagesDatabase Design, Implementation, and Validationbaluchandrashekar2008No ratings yet
- Cbse Xii Volume 1 - Formulae and ConceptsDocument50 pagesCbse Xii Volume 1 - Formulae and ConceptsAdarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Relations and Partial Orders ExplainedDocument25 pagesRelations and Partial Orders ExplainedphilipyapNo ratings yet
- About Database Management System: Sachin Kumar Asst. Professor IIMT College of Management, Greater NoidaDocument38 pagesAbout Database Management System: Sachin Kumar Asst. Professor IIMT College of Management, Greater NoidaM10 FFNo ratings yet
- Relational Data Model and Relational AlgebraDocument34 pagesRelational Data Model and Relational AlgebraDevika HarikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Query LanguagesDocument78 pagesUnit 3 Query Languagesvedantbailmare22No ratings yet
- Relational Algebra: Muhammad QasimDocument16 pagesRelational Algebra: Muhammad QasimSyeda Areeba RashidNo ratings yet
- DB Relational Algebra v2Document67 pagesDB Relational Algebra v2Babu100% (1)
- Unit-III NotesDocument33 pagesUnit-III NotesathirayanpericseNo ratings yet
- Databases 2 Exercise Sheet 4Document2 pagesDatabases 2 Exercise Sheet 4Shivam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Relational - Algebra ExamplesDocument35 pagesRelational - Algebra ExamplesImranNo ratings yet
- 4 - Relational AlgebraDocument20 pages4 - Relational AlgebragauravNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 12 Mathematics Part 1Document289 pagesNCERT Class 12 Mathematics Part 1md1sabeel1ansariNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - Relational Database ConceptsDocument55 pagesUnit-2 - Relational Database ConceptsharshitpanwaarNo ratings yet
- Unit-III (Functional Dependencies and Normalization, Relational Data Model and Relational Algebra) Important Questions Section A: (2 Marks)Document12 pagesUnit-III (Functional Dependencies and Normalization, Relational Data Model and Relational Algebra) Important Questions Section A: (2 Marks)Jayaseelan JayaseelanNo ratings yet
- Unit4 SQL and Database Project at Students NotesDocument29 pagesUnit4 SQL and Database Project at Students Notesashrafsmith272No ratings yet
- Lecture-36-37: ER to Relational ConversionDocument36 pagesLecture-36-37: ER to Relational ConversionManu KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Dbms 2Document54 pagesDbms 2Pooja Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- 16mis0350 VL2017181000858 Da02Document7 pages16mis0350 VL2017181000858 Da02Chitturi Arun Krishna 16MIS0350No ratings yet
- DB brt Chapter 6 2015Document41 pagesDB brt Chapter 6 2015yonasante2121No ratings yet
- Realtional Model - Relational AlgebraDocument67 pagesRealtional Model - Relational AlgebraneetunarwalNo ratings yet
- Jesus Saves Integrated School Foundation, Inc. Mabuco, Hermosa, Bataan General Mathematics Introduction To FunctionDocument6 pagesJesus Saves Integrated School Foundation, Inc. Mabuco, Hermosa, Bataan General Mathematics Introduction To FunctionNick GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design Algorithms and Normal FormsDocument6 pagesRelational Database Design Algorithms and Normal Formsachaparala4499No ratings yet
- Relational Algebra RupinderDocument18 pagesRelational Algebra Rupinderapurva manchanda 7010No ratings yet
- CH - 6 Algebra OperationDocument39 pagesCH - 6 Algebra OperationelijahtafereNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Relational AlgebraDocument41 pagesUnit2 Relational Algebramanasailla666No ratings yet
- Relational Algebra Operations in RDM: Tools Boot CampDocument32 pagesRelational Algebra Operations in RDM: Tools Boot CampSrinivasan SivaramakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Relational AlgebraDocument18 pagesRelational Algebrajeet PandyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document34 pagesUnit 3Mr. Skull EditorNo ratings yet
- 2 Relational Model Part 1of3Document24 pages2 Relational Model Part 1of3co22352No ratings yet
- Rohini 52831092917Document6 pagesRohini 52831092917Gautam KumarNo ratings yet
- Relational Data Model and ConstraintsDocument30 pagesRelational Data Model and ConstraintsMohammad DiabNo ratings yet
- Relational AlgebraDocument9 pagesRelational AlgebraMatoke NahasonNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document16 pagesDBMS Unit 1Harsh OjhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Relational Algebra v2Document82 pagesChapter 5 Relational Algebra v2dragon0962No ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-2 (I)Document35 pagesDBMS Unit-2 (I)ISHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- 数据库原理与实践 Database Systems-Principle and PracticeDocument182 pages数据库原理与实践 Database Systems-Principle and Practicerajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Ncert Math Class 12Document618 pagesNcert Math Class 12Bhaskar Bharati100% (1)
- Definitions of Database TermsDocument7 pagesDefinitions of Database TermsJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Relation AlgebraDocument31 pagesRelation AlgebraVarun GargNo ratings yet
- Transforming Entities and Attributes To RelationsDocument28 pagesTransforming Entities and Attributes To RelationsfanniemayNo ratings yet
- Finance Management SystemDocument32 pagesFinance Management Systemgdhsgjsagdhsa100% (1)
- Exams With Proctorio Students 2603Document1 pageExams With Proctorio Students 2603Nicu BotnariNo ratings yet
- PSP Xenon Operation Manual PDFDocument22 pagesPSP Xenon Operation Manual PDFJaktronNo ratings yet
- Agilent LogicWave OS Compatibility GuideDocument1 pageAgilent LogicWave OS Compatibility Guidecs9816521982No ratings yet
- UNIX NotesDocument4 pagesUNIX NotesAnil Kumar PatchaNo ratings yet
- JDEDocument376 pagesJDEphani87No ratings yet
- Developing With SQLWindowsDocument750 pagesDeveloping With SQLWindowslams_21100% (2)
- Operate Database Application - Lecture NotesDocument169 pagesOperate Database Application - Lecture NotesSamson Girma50% (4)
- Panda Book PDFDocument3,229 pagesPanda Book PDFShubham RanaNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument71 pagesMini ProjectishandeepNo ratings yet
- Archana - Kankam ResumeDocument3 pagesArchana - Kankam ResumeArchanaNo ratings yet
- Apache CXF - Quick Guide - TutorialspointDocument49 pagesApache CXF - Quick Guide - TutorialspointkrkamaNo ratings yet
- Accessdata Mpe+: Quick Install GuideDocument11 pagesAccessdata Mpe+: Quick Install GuideCristhian LopezNo ratings yet
- System Call Handler, Load Control, File System Drivers & Bad SectorsDocument2 pagesSystem Call Handler, Load Control, File System Drivers & Bad SectorsSunita RevaleNo ratings yet
- Re-Flashing A CMG-DCM To Install Platinum FirmwareDocument5 pagesRe-Flashing A CMG-DCM To Install Platinum FirmwareSubodh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 PDFDocument2 pagesExercise 6 PDFviệt lêNo ratings yet
- Capston Project Final FULL PDFDocument19 pagesCapston Project Final FULL PDFRobertNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Atm Management SystemDocument47 pagesProject Report: Atm Management SystemRohit Kumar100% (1)
- SSH Key ImplementationDocument2 pagesSSH Key Implementationkarthikm07No ratings yet
- Upgr Ora UX Guide 19c PDFDocument30 pagesUpgr Ora UX Guide 19c PDFGilmar RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Dolby DigitalDocument5 pagesDolby DigitalPratik pagarNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNotes - FieldTools - 3.2 - (Jan 2020)Document5 pagesReleaseNotes - FieldTools - 3.2 - (Jan 2020)Ronnie TolaneyNo ratings yet
- SQ L Practical FileDocument44 pagesSQ L Practical Fileprogrammer71% (7)
- Serato Sample Software ManualDocument17 pagesSerato Sample Software ManualAnand Davis100% (1)
- X7-2 Datasheet Oracle Servers PDFDocument6 pagesX7-2 Datasheet Oracle Servers PDFHope HimuyandiNo ratings yet
- Oracle® REST Data Services: Installation and Configuration Guide Release 2.0Document38 pagesOracle® REST Data Services: Installation and Configuration Guide Release 2.0Bikash बिकासNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Remote Display (VRDP Support) 1Document1 page1.1. Remote Display (VRDP Support) 1Asad BublooNo ratings yet
- SQR Getting StartedDocument348 pagesSQR Getting StartedFlorian TituNo ratings yet
- Install Android SDK & Create Hello World AppDocument25 pagesInstall Android SDK & Create Hello World AppRaihan FuadNo ratings yet
- CoolGen-Training IDocument40 pagesCoolGen-Training Iapi-1997553275% (4)