Professional Documents
Culture Documents
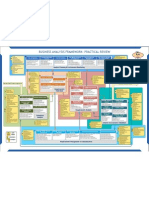
Nataliemoore Business-Analysisguide (BABOK)
Nataliemoore Business-Analysisguide (BABOK)
Uploaded by
Shruti GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nataliemoore Business-Analysisguide (BABOK)
Nataliemoore Business-Analysisguide (BABOK)
Uploaded by
Shruti GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
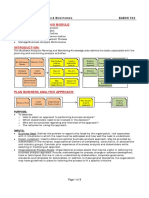
What is Business Analysis? Role of BA in project phases (cont) What is a Business Goal? (cont)
The practice of enabling change in an Processing new requirements (new - It allows the organization to understand and
organizational context, by defining needs and regulations, standards, etc.) maintain a commitment to the business’
recommending solutions that deliver value to main objectives
Processing the requests to fulfill new needs
stakeholders.
requested by the customer or user - It provides a metric against which to
disciplined approach measure the organization’s progress
Business analysts identify and define the What is an artefact? SMART
solutions that will maximize the value delivered
Final or intermediate work products that are SMART is a system and a tool that is used to
by an organization to its stakeholders
produced and used during a project establish goals and define their quality
Business analysts work across all levels of an objectives. SMART requires that all goals have
Might describe the function, architecture, and
organization and may be involved in everything the following characteristics
design of software
from defining strategy, to creating the
- Specific
Might be concerned with the process of
enterprise architecture, to taking a leadership
development itself, such as project plans, - Measurable
role by defining the goals and requirements for
business cases and risk assessments - Attainable
programs and projects or supporting continuous
improvement in its technology and processes. Should use version control - Relevant
Business Analysis is the set of tasks, Should be correctly traced to their origin - Timely
knowledge, tools and techniques required to
identify business needs and determine What is a Business Goal? What is a requirement?
solutions to business problems [BABOK]
A Business Goal is a short- or long-term A condition or capability needed by a
BA Solutions may include:
objective of an organization. Business Goals stakeholder to solve a problem, or achieve an
- Development of software systems should be characterized by the following objective.
- Development of software components qualities
A condition or capability that must be met or
- Extensions of existing software - Specificity possessed by a system or system component,
- Optimism to satisfy a contract, standard, specification, or
- Improvements to the business process
other formally imposed documents
- Changes to the organization - Realism
A documented representation of a condition or
- Both short- and long-term scope
capability
Role of BA in project phases Setting Business Goals is important because:
Requirements are the foundation of systems, or
Supporting implementation work in order to - The organization needs to have a vision of
system components. They can be obligatory
ensure developers understand and implement what it wants to accomplish. This is (required functions, constraints, etc.), essential
the requirements properly facilitated by having clearly stated goals, for the software to perform its functions, and
Business Analyst supports the project from the along with establishing time periods in meet the expectations and needs of the
which they need to be achieved
beginning through the system deployment (and intended stakeholders
sometimes to the system retirement). - It keeps a clear picture of what the Requirements should be placed into one of the
Supporting testing, for example by validating organization is trying to do with the following categories
business, and helps focus motivation
test cases in order to ensure that testing will
- Business requirements
adequately cover all the requirements
- User requirements
Analyzing and documenting change requests
- Functional requirements
for the requirements
- Non-functional requirements
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 1 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
What is a requirement? (cont) Requirement Analysis Requirement Analysis (cont)
Purpose of requirements: Elaborate the solution definition in order to Validate that a requirement will satisfy a
enable the project team to design and build a business need.
- Provide a foundation for assessment,
solution that will meet the needs of the
planning, execution and monitoring of the Outputs: Validated requirements
business and stakeholders
project activities
Task: Organize Requirements Elicitation
- Define customer expectations (expressed
as real requirements and stakeholder’s Structure and organize a set of requirements
Business Requirements Elicitation is defined as
value of those requirements) into logical sets. The organization may be
a set of approaches, techniques, activities, and
based on defining multiple “levels” of
- Serve as a component of agreements, tasks used to capture the business
orders, project plans requirements, packaging related functions requirements of a planned solution from the
together, and so forth. stakeholders and other available sources [
- Establish system boundaries, scope of
Inputs: Business Case, Solution Scope,
delivery, and the services classification of Purpose: Explore, identify and document
the requirements Requirements stakeholder needs. Orienting the requirements
Outputs: Structured requirements toward the project vision. Excluding features
Requirement classifications
that the customer does not want and need
Task: Prioritize Requirements
Process requirements
Describes how we work with stakeholders to
- describe needs and limitations of the Determine the business priority of
find out what their needs are and ensure that
business processes requirements (including voting, ranking, benefit
we have correctly and completely understood
analysis and so forth). Identify logical
- Costs their needs.
dependencies between requirements and
- Marketing requirements packages. Task: Prepare for Elicitation
- Processing time Inputs: Requirements, Business Case Purpose: Prepare for elicitation by ensuring all
- Sales and distribution Outputs: Prioritized requirements needed resources are organised and
scheduled for conducting the elicitation
- Organisation Task: Specify and Model Requirements
activities
- Documentation Describes standard practices for writing textual
Outputs
Product requirements requirements and creating models or diagrams.
- Scheduled resources
Specific models are addressed as techniques.
- functional and non-functional product
Includes capturing the requirements attributes - Supporting materials
requirements
Inputs: Requirements Task: Conduct Elicitation
- POV of customer and team
Outputs: Specified or modeled Requirements Meet with stakeholder(s) to elicit information
Types of requirement
Task: Determine Assumptions and regarding their needs
- Customer requirements
Constraints Outputs
- Solution or system requirements
Identify stakeholder requests that are not Elicitation activity results
- Product or component requirements
properly requirements but based on Assumptions, constraints, risks, issues
assumptions regarding what the solution team
Documentation based on technique (e.g.,
is capable of delivering
interview notes, workshop results, survey
Capture and assess these requests responses, etc.)
Outputs: Assumptions and Constraints Task: Document Elicitation Results
Task: Verify Requirements Purpose: Record stakeholder info for use in
Outputs: Verified requirements analysis.
Task: Validate Requirements Outputs: Stated requirements
Task: Confirm Elicitation Results
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 2 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Elicitation (cont) What is a stakeholder (cont) Business Analysis Communication
Planning (cont)
Purpose: Play back the requirements to Installation and Operations personnel
validate that the stakeholder’s intentions have Stakeholders on the customer side Outputs from the Business Analysis are also
been correctly captured and understood. inputs to system acceptance testing, which is
Customer representatives (i.e., “Business”) the final check before the production release.
Outputs: Validated stated requirements
Project sponsors
Techniques System acceptance testing is conducted to
End users (from the customer company) verify that the software is working as expected,
Questionnaires
Installation and Operations personnel and is needed in order to realize its goals (i.e.,
Interviews improving efficiency of performing the business
External stakeholders may be:
process
Self-recording
End users who are not a part of the customer’s
Reviewing existing documents BA provides info to the following
organization
Reusing a specification from a previous project - Project management (scope planning,
Other organizations (e.g., regulatory entities) scheduling, and estimating development
Brainstorming
and testing)
Field observation Stakeholder Identification Problems
- Systems analysis
Apprenticing A lack of understanding of the real operators of - Design (system specification and
Conducting workshops to refine the the business processes in the organization architecture)
requirements after each iteration Unclear definition of responsibilities within the - Implementation
Requirements Elicitation should apply to customer’s organization
- Testing
enterprise requirements as well as user or Excluding stakeholders who are not clearly and
Common methods of communication include:
customer requirements. directly related to the process
Requirement characteristics - Workshops
Incomplete analysis resulting in missing
processes and activities, and the related - Presentations
Functionality
stakeholders - Reviews
Reliability
Factors to be Considered
Usability Business Analysis Communication
- Type of project
Efficiency Planning
- Communication formality
Maintainability The main purpose of planning the Business
- Communication frequency
Portability Analysis communication is to define how to
receive, distribute, access, update and - Geographical location
What is a stakeholder escalate information to and from the project
- Culture
stakeholders, as well as how to organize the
Any person involved in, or with an interest in, a schedule and structure of the communication
project Common BA techniques
within a project.
Stakeholders on the vendor side Brainstorming
Business Analysis is the starting point for
Project Managers designing and implementing a software CATWOE (Clients, Actors, Transformation,
solution. Its deliverables are inputs to many Worldview, Owner, Environmental constraints)
Business and System Analysts
other project phases and processes, such as Data Flow Diagrams
Developers and Architects establishing the system architecture that will
Five Why’s
Database designers allow meeting the business goals, creating
detailed functional and non-functional system Functional decomposition
GUI designers
specifications, and planning and executing QA Interviews
Technical writers
activities.
MoSCoW
Testers and Quality Assurance staff
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 3 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Common BA techniques (cont) Acceptance and Evaluation Criteria Acceptance and Evaluation Criteria (cont)
PESTLE (P for Political, E for Economic, S for Acceptance criteria are used to define the - represent a meaningful and agreed-upon
Social, T for Technological, L for Legal and E requirements, outcomes, or conditions that decomposition of the value proposition into
for Environmental) must be met in order for a solution to be its constituent parts, which can be
considered acceptable to key stakeholders. described as qualities that the solution
MOST (Mission, Objectives, Strategies, Tactics)
Evaluation criteria are the measures used to should either possess or avoid
Prototyping
assess a set of requirements in order to
examples
Requirements Workshops choose between multiple solutions
ability to provide specific information
Risk Analysis Define measures of value attributes to be used
ability to perform or support specific operations
Scenarios and Use Cases for assessing and comparing solutions and
alternative designs performance and responsiveness
SWOT
characteristics
Measurable and testable criteria allow for the
User stories
objective and consistent assessment of applicability of the solution in specific situations
solutions and designs and contexts
Principles for Successful Requirements
Acceptance criteria describe the minimum set availability of specific features and capabilities
1. Understand the top level critical of requirements that must be met in order for a usability, security, scalability, and reliability
objectives particular solution to be worth implementing.
~ Assessment ~
2. Think stakeholders, not just users and They may be used to determine if a solution or
solution component can meet a requirement. In order to assess a solution against
customers
acceptance or evaluation criteria, it must be
3. Focus on the required system quality, not Acceptance criteria are typically used when
constructed in a measurable format
just its functionality only one possible solution is being evaluated,
and are generally expressed as a pass or fail Evaluation criteria provide a way to determine if
4. Quantify quality requirements as a basis features provide the value necessary to satisfy
for software engineering. Valuation criteria define a set of
stakeholder needs.
measurements which allow for ranking of
5. Don’t mix ends and means
solutions and alternative designs according to The criteria are presented as parameters that
6. Capture explicit information about value. their value for stakeholders. can be measured against a continuous or
discrete scale.
7. Ensure there is “rich specification”; Attributes that cannot be measured directly are
requirement specifications need much evaluated using expert judgment or various Acceptance criteria are expressed in a testable
more information than just the scoring technique form
requirement itself.
Elements Acceptance criteria are presented in the form of
8. Carry out specification quality control statements which can be verified as true or
~ Value attributes ~
(SQC). false. This is often achieved through user
- are the characteristics of a solution that acceptance testing (UAT)
9. Consider the total lifecycle and apply
determine or substantially influence its value
systems-thinking, not just a focus on Usage Considerations
for stakeholders
software
Agile methodologies may require that all
10. Recognize that requirements change; requirements be expressed in the form of
use feedback and update requirements testable acceptance criteria
as necessary.
Acceptance criteria are necessary when the
requirements express contractual obligations
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 4 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Acceptance and Evaluation Criteria (cont) Why is Business Analysis Necessary? Why is Business Analysis Necessary?
(cont)
Acceptance criteria provide the ability to assess Problems with requirements can cause projects
requirements based on agreed-upon criteria to fail. In most cases those problems are - Unclear requirements, or low quality
caused by poor or incorrectly conducted business design of the solution, can lead to
Evaluation criteria provide the ability to assess
Business Analysis (especially Requirements confusion and questions regarding the
diverse needs based on agreed-upon criteria,
Engineering, a part of the Business Analysis intended software product or process
such as features, common indicators, local or
knowledge area). solution
global benchmarks, and agreed ratios
Evaluation criteria assist in the delivery of Common problems - risk of the project’s failure increases
expected return on investment (ROI) or - Ambiguous, under-specified, unclear, - Requirements are imprecise
otherwise specified potential value impossible, contradictory business
- Requirements are ambiguous
requirements
Evaluation criteria helps in defining priorities
- Requirements are contradictory
Limitations - Instability of the requirements (frequent and
- Requirements do not fulfill the agreed
uncontrolled changes in requirements)
Acceptance criteria may express contractual criteria
- Poor translation of the business needs to
obligations and as such may be difficult to - Requirements are missing
requirements (incomplete, inconsistent, or
change for legal or political reasons
not measurable requirements) - Business processes and artifacts are not
Achieving agreement on evaluation criteria for covered by requirements or are described
- Unclear objectives of the initiative
different needs among diverse stakeholders incompletely
can be challenging. - Communication problems
- All stakeholders are not identified
- Language barriers
What is a business analyst? - Business goals or needs are not identified
- Knowledge barriers
causing the designed solution to fail to meet
A person responsible for: - Vague wording the organization’s needs and not achieve
identifying the business needs of the customer - Overly formal wording the business goals
(external or internal) and other stakeholders Common reasons for neglecting BA
- Redundancy
determining solutions to business problems - Time pressure
- Gold plating (adding unnecessary scope)
BA activities include identifying, analyzing, - Exclusive focus on fast results
- Insufficient user involvement
developing and managing the requirements.
- Exclusive fixation on costs
- Overlooked user classes
Business Analyst is not responsible for
- Minimal specification - Perceiving documentation or the analysis
determining the solution implementation
and understanding of the business
(creating the product’s design) Consequences of low quality BA
processes within an organization as a cost,
The Business Analyst acts as a bridge between - Problems during during scope definition not an added value
the customer and other stakeholders (e.g., the - Planning difficulties
project team), identifying, negotiating and Requirements Elicitation
- Implementation problems
achieving a consensus between the needs of
- Testing problems Requirements Elicitation is the collection of
the various representative individuals and
groups. activities, approaches, tools and techniques for
capturing the requirements for a planned
software system (or other business solution)
from the stakeholders\
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 5 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Traceability What is Enterprise Analysis? (cont) What is Enterprise Analysis? (cont)
Traceability is an association that exists Fully define business problem/opportunity - Inputs: Business Architecture, Business
between different types of requirements and the Goal(s), Defined Business
Output: Defined Problem/Opportunity
following items: Problem/Opportunity Solution Scope
Task: Determine Solution Approach
- Requirements (mapping the higher level - Outputs: Business Case
Purpose:
requirements that defined the needs and
features to the more detailed requirements) - Identify potential solutions Solution Assessment and Validation
- Detailed requirements to design models - Analyze feasibility of options
How to assess proposed solutions to determine
- Detailed requirements to test cases - Recommend viable business solution which solution best fits the business need,
- High level requirements to test cases - Validate with decision makers identify gaps and shortcomings in solutions,
and determine necessary workarounds or
- Requirements to release/code Output: Solution Approach
changes to the solution
branch/version Task: Define Solution Scope
How we assess deployed solutions to see how
Allows BA to ensure all business requirements
Projects inevitably struggle at some point or the well they met the original need in order to
have been met.
other if the scope is not defined properly enable businesses to assess the performance
Important from the change management and effectiveness of projects.
Solution scope may be determined using the
perspective, to determine the impact of a
following techniques Purpose: Assess solutions to ensure that
change on the system or process
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) - a strategic goals are met and requirements are
For the testers and developers, traceability satisfied.
decomposition of the work that is required
ensures that the requirements coverage has
to complete a project, and accomplish the Task: Assess Requirements Coverage
been achieved
business objectives
Purpose: Determine how well possible options
- Product Breakdown Structure (PBS) - a for solution designs will meet the
What is Enterprise Analysis?
decomposition of the components of the requirements. The assessment may include a
Purpose: Identify and propose projects that product recommendation of a particular solution,
meet strategic needs and goals. rejection of all solutions, or an assessment of
- System Interface Analysis - a definition of
Task: Identifying business processes the work required to integrate the new possible trade-offs.
performed in the organization solution into the existing business and Examples: RFI/RFP responses, Internal
technical environments designs, Manual procedures
Purpose: Evaluate the internal and external
environment Context diagram Inputs: Solution Design Option(s)
Conducting feasibility studies to determine the Product Breakdown Structure Outputs: Solution Design Assessment
optimum business solution Output: Solution Scope Task: Allocate Requirements
Define/refine current/future business Task: Develop the Business Case Purpose: Allocate requirements among
architecture
- Define project objectives and expected releases and/or solutions components. Ensures
Assess the current state of technology business benefits that the possible release options are designed
(infrastructure and applications) in a way to maximize the possible business
- Develop project scope
Benchmark analysis value given the options and alternatives
- Estimate time, cost, resources generated by the design team.
Competitive studies
- Analyze cost vs. benefit Activities
- Evaluate risk Allocate requirements to hardware, software,
manual procedures, etc.
Recommend the release/delivery strategy
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 6 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Solution Assessment and Validation (cont) Solution Assessment and Validation (cont) Business Case Definition (cont)
Understand trade-offs between different - Compare actual vs. expected costs and May be in form of
implementation approaches benefits.
- Structured document
Inputs: Solution Design, Validated Outputs: Cost/Benefit Analysis
- Short argument
Requirements
- Presentation
Outputs: Allocated Requirements Stakeholder Identification Techniques
Topics may include
Task: Determine Organizational Readiness Investigating the business domain
- Information about the opportunity (market
Purpose: Identifying owners of the business processes trends, competitors)
Determine organizational readiness to Analyzing the structure of the customer’s - Qualitative and quantitative benefits
effectively operate the new solution organization
- Estimates of cost and time to breakeven
- Conduct organizational readiness Exploring the target market of the customer’s
- Profit expectations
assessment organization
- Follow-on opportunities
- Recommend ways to optimize the Analyzing relationships with external
organizational deployment organizations (suppliers, etc.) - Cash flow consequences of the action, over
time, and the methods used for quantifying
Outputs: Organizational Readiness
Stakeholder Needs and Expectations benefits and costs
Assessment, Organizational Change
Recommendations - The impact of the proposed project on the
Different stakeholders may have different
business operations or business process
Task: Validate Solution needs and expectations regarding the planned
solution. It is very important to identify all the - The impact of the proposed project on the
Purpose:
stakeholders and their needs, and to find a technology infrastructure
Validate the verified and deployed solution
common understanding of the purpose of a - Constraints associated with the proposed
meets the business need
solution, in order to avoid the situation where project
Define acceptance criteria (including what level the final product may meet the requirements of
- Estimated budget
of conformance to requirements is acceptable) only a selected group of stakeholders.
- Alignment with priorities established by the
Identify defects/shortcomings (this should be Ensure that the features to be implemented will
business
distinguished from functional testing) not conflict with the requirement of other
stakeholders Procedure of Building the Business Case
Analyze impact
- Identify and quantify the benefits
Define corrective actions One of the responsibilities of a Business
Analyst is to identify all the stakeholders and - Identify and quantify the costs
Validate corrective actions
define their requirements and expectations - Prepare the Business Case
When a problem is identified with the deployed
Determines the initial scope and requirements
solution determine what is the most - Define the procedures that will be used to
of the system
appropriate response measure the costs and benefits
Outputs: Validated Solution, Defect Impact
Business Case Definition
Analysis, Validated Corrective, Actions
Provides the reasoning for initiating a project
Task: Evaluate Solution
Describes a justification for the project in terms
Purpose:
of the value added to the business as a result
- Assess the value of the solution as of the project outcomes, in comparison to the
deployed to the business (to determine if cost of developing the new solution
the original goals are met).
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 7 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Requirements Documentation Requirements Documentation (cont) Modelling (cont)
Follow common standards and guidelines Trivialities - Lengthy descriptions of commonly - simplified expression of real processes
known issues should not be included
Important guidelines - describe a complex system in the most
Information out of scope clear and unambiguous way.
- Each requirement must be unambiguous,
precise, and understandable Thinking in solutions - The requirements - Models present the whole system and its
specification should discuss the problem to be context in a single diagram and therefore
- Superfluous information should be avoided
solved not the technical design of the solution help to look at the problem from the overall
- Templates should be used as an aid
perspective.
Redundant details
- Models and diagrams should be used to
Common techniques
Lacking rationale
make the specification document clear and
more understandable for readers. - UML notation to express requirements as
Modelling use case diagrams, activity diagrams,
- Formal graphical notation should be used
component diagrams, state machine
as a method for presenting complex Modeling is a way of expressing requirements
diagrams, etc.
requirements, dependencies, and by representing parts, or the whole, of the
- BPMN
relationships proposed solutions
- Using prototyping as a technique of GUI
A requirements document may include Way of presenting complex requirements and
modeling
- Introduction relationships in the form of a model, especially
some graphical form such as diagrams, helps - Using SysML notation to develop
- Secrecy clause
ensure the solution is understood by other specifications, analysis, design, verification
- Regulations stakeholders and validation documentation for systems
- Standards and systems-of-systems. The
Easier to read and comprehend than written
specifications may include hardware,
- Stakeholders text
software, information, processes, personnel
- Purpose of the product Not mandatory but very helpful in big projects and facilities.
- Overall description Can skip modeling in the following situations
Quality criteria for business process models
- Functional requirements - The solution is fully understood by the
- Correctness (syntactic and semantic
stakeholders and is easy to implement.
- Non-functional requirements correctness)
- The requirements are mostly non-
- Limitations and assumptions - Relevance (no irrelevant details)
functional and difficult to express in the form
- Dependencies - Economic efficiency (designed for a
of a model
particular purpose)
- Risks - The problem domain is well known
- Clarity (understandable by the audience)
- Safety requirements - The solution is dedicated to use by very
- Comparability (based on the same
- Document acceptance few people
modeling conventions within and between
When creating a requirements document, the - The scope is declared as constant and
models)
Business Analyst should remember that there is a low probability of changes in the
requirements specifications must be complete, scope resulting from future requirements or
consistent, modifiable, and traceable [Wiegers]. needs.
Common Mistakes - model representation would be less
understandable by the key stakeholders
than written text
Benefits of modeling
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 8 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Modelling (cont) Tools and Techniques of Facilitation (cont) Process Improvement (cont)
- Systematic design (contains well-defined Tools Capability Maturity Model
interfaces to other types of models) Integration/Capability Maturity Model
Gap analysis
(CMMI/CMM)
Flipcharts
Domain Knowledge ISO 9000
Checklists
The goal of a Business Analyst is to provide IT Governance
Multi-voting
business solutions to business issues by Just In Time manufacturing
assessing business problems, and identifying Root cause analysis
Lean manufacturing
and analyzing root causes. Brainstorming
Performance improvement
The success of Business Analysis is Managing conflicts tips sheet
determined by the benefit that the solution Process management
Focus group framework
provides to the business either in terms of Process Improvement and Management
savings in costs, improvement in productivity, (PI&M)
Process Improvement
and/or increase in customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma
To be able to provide a business solution that Process Improvement supports the
Total Quality Management (TQM)
provides a measurable benefit to the introduction of change into the current process
organization, the Business Analyst must have in order to improve quality, reduce costs and/or
BA Knowledge Areas
knowledge of the business domain. accelerate schedules
Importance Supporting Process Improvement is one of the 1. Business Analysis Planning and
tasks of a Business Analyst. Monitoring (Orange)
Domain knowledge makes it easier for the
Business Analyst to connect and communicate The Business Analyst models and analyzes 2. Enterprise Analysis (Dark Green)
with Business Users. business processes used within an 3. Elicitation (Light blue)
organization in order to discover any
Domain knowledge makes understanding and 4. Requirement Analysis (light pink)
ineffective elements.
analyzing business issues easier
5. Solution Assessment and Validation
Techniques
Lack of domain knowledge may lead to delays
6. Requirements Management and
in providing the solution, since the business - Manually re-design processes on the basis
Communication
process and business rules must first be of experience and domain knowledge with
understood the goal of eliminating bottlenecks and
Common Objectives of Business Analysis
making the execution times shorter and
Tools and Techniques of Facilitation more efficient Collect and document the requirements
- Introduce tools, including software, to Design business solutions to resolve the
Applying engagement strategies
optimize the business processes in the business problems
Creating participation organization (e.g., SAP, ERP, CRM
Assist in the timely completion of the project by
Generating and organizing data software)
providing accurate requirements identification
Initiating reflection - Simulate and optimize processes and analysis
Mobilizing energy - Adopt a selected methodology or strategy Improve efficiency by increasing the quality of
Igniting action Methods: requirements identification and analysis and
therefore reducing the need for rework and
Recording information Benchmarking
fixes in the later stages of the project
Applying SWOT analysis Business process improvement
Business process reengineering
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 9 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Business Analysis influences other project What is a business process? (cont) BA in Phases of the Software Life Cycle
areas
focuses on how the work is done within an Analysis phase
Significant impact on project management organization, the way of organizing work,
- Identifying and evaluating the current
(especially scope and time management) activities, relationships and the dependencies
business processes in an organization (“as
between them. A process can be considered as
Design – Business Analysis determines the is” analysis)
the ordering of work activities across time and
required business architecture and scope of the
- Gathering initial requirements for the
place, with a beginning, an end, and clearly
solution
needed business solution (“to be” analysis)
defined inputs and outputs [
Development – The Systems Analyst (who
- Creating and analyzing the business case
determines detailed requirement A business process must have the following
characteristics - Conducting a feasibility study
specifications) uses the Business Analysis to
determine what has to be implemented. - Has a goal - Preparing ideas for the business solution
Testing and other Quality Assurance activities – - Has specific inputs Specification phase
Products of Business and Systems Analysis
- Has specific outputs - Identifying and documenting business
are a basis for testing
- Uses resources requirements on a more detailed level
- Has a number of activities that are - Supporting the Systems Analyst in
Business needs
performed in some order preparing the detailed system
A Business Need describes the business specifications (e.g., covering such items as
- Affects at least one organisational unit
problem or opportunity which the Business data, mapping, integration issues, user
Analyst must understand and analyze in order - Creates value for the customer (both interfaces)
to recommend appropriate solutions internal and external)
- Validating the proposed software design
before a project starts, the Business Need Identification of processes allows the Business with the customer and other stakeholders
(understood as a problem or an opportunity) Analyst to understand the organization’s goals,
- Managing any requirements changes
and Business Case (understood as costs vs. Helps determine the activities and the flow
Development phase
benefits) are defined, either formally or required to achieve future planned business
informally. and strategic goals - Supporting the development team during
implementation (e.g., clarifying issues
for the projects that help the organization reach Identification of business processes helps find
related to the requirements, validating
its vision, strategic goals, and business possible gaps and ineffective parts of the
business rules to be applied in the code)
objectives. process, which may then be improved via
process optimisation - Validating the evolving solution according to
Business Analysts are often supported by
Project Managers and Product Managers in the intended requirements and needs
If business processes are not established and
(when possible)
defining Business Needs understood, then the organization may have a
One of the responsibilities of a Business low maturity level, which makes measuring and
Analyst is to cooperate with the person or group controlling processes very difficult. In addition,
requesting the project, including users or proxy there are likely to be significant problems with
users, and to help them articulate the real the definition of the business goals and needs.
need.
What is a business process?
set of activities aimed at producing a specific
output for a particular customer or market.
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 10 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
BA in Phases of the Software Life Cycle BA Planning and Monitoring (cont) BA Planning and Monitoring (cont)
(cont)
- determining appropriate stakeholders for - metrics that can be used for monitoring
- Supporting testers in preparing test cases the project or project phase, and analyzing business analysis work are determined.
and test scripts at the business level and stakeholder influence, authority (approve,
- helps in improving future business analysis
validating the resulting work products sign off, veto), and project attitude.
plans
- Managing any required changes to the Outputs: Stakeholder list, Stakeholder roles - performance measures, reporting and
requirements (resulting from detected and responsibility designation
corrective actions
defects, regulatory or legal changes, needs
- RACI matrix (also known as RASCI matrix)
Plan Business Analysis Activities
for new or extended functionality, etc.)
plays very important role in this process.
- Determine which activities are required to
Testing phase
- Scope of the tasks and the dependency
define the solution to a business problem,
- BA role varies can be defined easily how those activities will be carried out, the
- verifying test results - estimates related to cost, timings and work effort involved, and an estimate of
resources how long the activities will take.
- resolving issues related to defects or gaps
in the requirements Communication Planning - Determine tasks in the Knowledge Areas:
- Participating in the preparation of test cases - Determine what information the various - Identifies task dependencies
for User Acceptance Testing stakeholders need to be provided about the - Develop estimates for BA work (time, skill
results of business analysis and the forms it
- Supporting the acceptance testers by level, complexity of tasks, etc.)
should take (verbal, written, etc). It includes
answering questions during test execution - Inputs: Stakeholder list, Stakeholder roles
considerations for, as well as constraints,
and responsibility designation,
impacts, durability and trade-offs of
BA Planning and Monitoring Organizational Standards
different communications media
The parameters which are defined and set - Outputs: Business Analysis Plans for each
- Communication plays very important role in
during the planning phase should retain their KA
any stage of project life-cycle and in order
validity throughout the project phases and it to avoid ambiguity or conflicts in the Plan Requirements Management Process
becomes the responsibility of the business requirements and end results, the - Describes how to determine the
analyst to perform the activities classified under communication should be precise and appropriate requirements process for a
this knowledge area precisely. controlled. particular initiative
Activities - Each stakeholder should understand the - Consider whether and how requirements
Identify the stakeholders details of the requirements are changed
- Identify stakeholders who may be impacted - WHAT, WHO and WHEN are the important - Which stakeholders need to approve
by a proposed initiative or who share a questions related to communication
- Who will be consulted on, or informed of
common business need. Monitoring BA work changes,
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 11 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
BA Planning and Monitoring (cont) Requirements Management and Change Management process
Communication (cont)
- includes the approach to requirements Identifying a potential change
traceability and determining which Outputs: Approved Requirements, Decision
Requesting new functionality
requirements attributes we will capture Record
Analyzing the change request
- Output: Requirements Management Plan Task: Manage Requirements Traceability
Evaluating the change
RASCI: R- Responsible (does the work), A- Purpose:
Planning the change
Accountable (decision maker, only one), S- Trace requirements (update and maintaining
Support (provides support during any phase of Implementing the change
relationships between requirements
lifecycle), C- Consulted (consulted prior to the components) Reviewing and closing the change request
work and provides input), I- Informed (informed
Perform impact analysis when changes are Potential changes might be a result of:
about the work progress).
requested and supply this information to the A defect found in the code, documentation or
change control process requirements
Requirements Management and
Support the allocation of requirements to the System improvement efforts
Communication
solution in Solution Assessment and
External changes (regulatory, legal, etc.)
How we manage conflicts, issues and changes Validation.
and ensure that stakeholders and the project New or changing requirements (resulting from
Outputs: Traced Requirements
team remain in agreement on the solution new regulations, changes within the business
scope Tasks: Maintain Requirements for re-use domain, new features requested by the users,
Purpose: etc.)
Purpose
Select which implemented requirements will be Business process improvement initiatives
Recognise that communication takes places
throughout all knowledge areas and is important maintained after solution implementation Change Request
for managing requirements Name the responsible party who will maintain When the need for a change appears, there
Manage the approved solution and the requirements should be a Change Request raised by a
requirements scope Facilitate ongoing use of requirements for stakeholder requesting new or modified
Ensure stakeholders have access to business impact analysis and solution maintenance functionality. Important elements of a change
analysis work products request are a unique identifier, the author, the
Facilitate re-use of requirements on related
deadline (if applicable), an indication whether
Prepare and communicate requirements to projects to encourage enterprise consistency of
the change is required or optional, the change
stakeholders business models
type, and an abstract, or description, of the
Task: Manage Solution and Requirements Inputs: Implemented requirements
proposed change
Scope Outputs: Maintained/re-used requirements
All changes should be tracked in a Change Log
Baseline and manage changes to business Task: Prepare Requirements Package or Change List
case, solution and requirements
Determine appropriate format for Changes should be managed by the Change
Approve requirements (according to the requirements, Create a requirements package Control Board (CCB). The CCB is not allowed
approval authority stated in the Requirements to submit, approve, reject, or implement
Outputs: Requirements package (e.g.,
Management Plan) changes without discussion with the other
executive summary, formal documentation,
stakeholders.
Control multiple versions of requirements work RFI, RFP, etc.)
products may have significant impact on other elements
Task: Communicate requirements
of the system, such as components,
Manage requirements conflicts and issues
Interaction with all stakeholders before, during interfaces, functionality, etc.
Inputs: Stakeholder roles and responsibility and after projects.
designation, Requirements, Requirements Impact analysis should be performed
Interaction with solution team to assure that
management plan
requirements are correctly understood and
implemented
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 12 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
Change Management process (cont) Requirements Organization (cont) Acceptance and Evaluation Criteria
Impact analysis includes analysis of the - an abstraction of the solution of the problem
changes needed in the project schedule or expressed at a high-level
budget that would be necessitated if the change
- A feature is developed into completely
were to be implemented described functional and supplemental
The planning of change implementation requirements
includes: Functional decomposition
Updating plans as needed depending on the - breakdown of a list of items into
phase of the project (e.g., Project Plan, classifications or groups based on the
Development Plan, and Test Plan) function each item performs or the use it
Updating business and system documentation provides
(e.g., specifications, architecture design, user - identifies the high-level functions of the
manuals) proposed solution, or the organization itself,
Updating test cases and test scripts and then breaks them down into sub-
processes and activities.
Implementing the change (coding)
- usually performed by a Systems Analyst
Testing by vendor or/and customer test team
Deploying the change to the production
Quality Assurance
environment
Quality Assurance is a process of systematic
Requirements Organization monitoring and evaluation of the various
aspects of a project or solution. The goal is to BA necessary skills
Requirements can be organized (structured) maximize the probability that the solution has
into packages. This packaging conforms to the achieved a desired standard of quality Analytical skills
boundaries (limitations) and solution scope
Quality Criteria for Requirements Financial analysis
established during Enterprise Analysis and
Allocatable Feasible Statistical analysis
helps to further define those boundaries
Complete Measurable Operations research
BA decomposes the problem model to make
each requirement more detailed Consistent Necessary Requirements analysis
Ensure that the model correctly reflects the Correct Prioritized Systems analysis
boundaries for the business problem
Testable Traceable Technical skills
Ensure proper level of detail is achieved
Unambiguous Understandable Working knowledge of technology
Types of decomposition
Does not determine solution Understanding of engineering principles
Goal decomposition
Checklists Ability to apply financial principles to feasibility
- Goals are business requirements studies
One of the most common techniques for
- Goal decomposition helps to ensure the requirements’ quality control is the use of Managerial skills
solution will satisfy stakeholder’s needs checklists. Project management capabilities
Feature list decomposition
Understanding of organizational behavior
- A feature is a service that the solution
Soft skills
provides to fulfill one or more stakeholder
need Negotiation skills
- Ability to negotiate to obtain data
- Ability to negotiate with stakeholders to
implement projects
Communication and writing skills
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 13 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
Business Analysis Cheat Sheet
by Natalie Moore (NatalieMoore) via cheatography.com/19119/cs/9837/
BA necessary skills (cont) BA necessary skills (cont) BA necessary skills (cont)
- Ability to communicate with all levels of - Providing processes to support members of - Helps the group to listen and draw logical
management the group to help them use their time conclusions
effectively and to make high-quality
- Ability to communicate with stakeholders of - Runs meetings
decisions
various knowledge levels
- Manages people’s expectations
- Guiding group discussions to ensure
- Precision in articulating ideas and thoughts
- Understands and explains the process
objectives are met, and noting any ideas
- Ability to relate with line workers
and concepts raised by members during the
- Good technical writing skills discussion
- Strong communication skills in all forms - Supporting members of the group in
(verbal, non-verbal, written, etc.) assessing their current skills and building
- Public speaking skills new skills
Facilitation skills - Using consensus to enable the group to
make decisions
Facilitation can be defined as a process of
- Managing conflicts using a collaborative
enabling groups to work cooperatively and
approach
effectively. Facilitation provides leadership
- Helping the group to communicate
Facilitation serves to improve the following skills
effectively and to access resources needed
- Leading
to make decisions
- Solving issues
The facilitator must always stay neutral, listen
- Building team and community actively and ask questions that allow the group
- Empowering to identify and collect ideas and concepts. One
of the facilitator’s tasks is to note and
- Resolving conflicts
summarize all ideas raised by the members of
- Transforming the group.
- Evoking wise democracy Facilitator competancies
- Building personal effectiveness - Communicates well
Facilitator - Processes ideas from people
facilitator is a person who contributes structure - Shows a natural interest
and process to interactions so that groups are
- Listens well
able to function effectively and make high-
- Maintains control
quality decisions. The facilitator’s goal is to
support others and enable them to achieve high - Empowers the group
performance
- Handles uncertainty
Tasks and activities
- Connects with the group quickly
- Helping the group to define its goals and
- Focuses on the business not on personal
objectives solutions
- Negotiates between parties
- Understands group dynamics
By Natalie Moore Published 16th November, 2016. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
(NatalieMoore) Last updated 16th November, 2016. Measure your website readability!
cheatography.com/nataliemoore/ Page 14 of 14. https://readability-score.com
www.speedwell.com.au/
You might also like
- Business Analysis PosterDocument1 pageBusiness Analysis Posterhamed93% (14)
- CBAP Ebook PDFDocument1,061 pagesCBAP Ebook PDFPeeyush Modi100% (12)
- CBAP Exam Top MnemonicsDocument2 pagesCBAP Exam Top Mnemonicshareesh.ganapathy7804100% (5)
- Business Analyst Handbook PDFDocument152 pagesBusiness Analyst Handbook PDFOlalekan Fagbemiro100% (20)
- BABOK Knowledge Areas Cheat SheetDocument37 pagesBABOK Knowledge Areas Cheat Sheetskumarites100% (1)
- Business Analyst Role GuidelineDocument4 pagesBusiness Analyst Role GuidelineVijayakanth100% (1)
- Business Analysis Book of Knowledge Version Three PDFDocument3 pagesBusiness Analysis Book of Knowledge Version Three PDFiloveshms100% (1)
- Business Analyst TrainingDocument58 pagesBusiness Analyst Trainingprashant_padte100% (2)
- 1 - BABOK 3 - Cheat Sheet - Tasks Vs Techniques V2Document1 page1 - BABOK 3 - Cheat Sheet - Tasks Vs Techniques V2luavanloc100% (1)
- Business Analysis - How To Gather and Document User RequirementsDocument0 pagesBusiness Analysis - How To Gather and Document User Requirementsnataliazi8910No ratings yet
- BABOK Techniques Knowledge Areas V2Document1 pageBABOK Techniques Knowledge Areas V2ashmah24100% (2)
- Business Analysis and The IIBA Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK)Document214 pagesBusiness Analysis and The IIBA Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK)Alan McSweeney100% (11)
- Cert Handbook CTSDocument61 pagesCert Handbook CTSJesse Adkins50% (2)
- Business AnalysisDocument37 pagesBusiness AnalysisPraveen Kanwar100% (2)
- Seven Steps To Mastering Business Analysis - SummaryDocument15 pagesSeven Steps To Mastering Business Analysis - SummaryValentino DoriaNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst TrainingDocument3 pagesBusiness Analyst TrainingMuniswamaiah Mohan100% (2)
- Top 50 Business Analyst Interview QuestionDocument9 pagesTop 50 Business Analyst Interview QuestionLony80% (5)
- Babok OverviewDocument1 pageBabok OverviewSérgio ViegasNo ratings yet
- Agile Business Analysis - Developing Product Backlog Into Business CapabilitiesDocument42 pagesAgile Business Analysis - Developing Product Backlog Into Business CapabilitiesVinita Bhatia50% (2)
- BABOKV3 Tasks Input&OutputDocument1 pageBABOKV3 Tasks Input&OutputSmith And Y100% (1)
- Business Analysis Lecture SeriesDocument6 pagesBusiness Analysis Lecture SeriesJune Sung ParkNo ratings yet
- SBR Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSBR Cheat SheetParvathi Nair0% (1)
- Business Analysis Book of KnowledgeDocument44 pagesBusiness Analysis Book of KnowledgeParveen Kumar Jain100% (1)
- 101 Business Analysis TechniquesDocument119 pages101 Business Analysis TechniquesBhushan Waykole100% (7)
- Examples of Business AnalysisDocument81 pagesExamples of Business Analysistahsin çetinkaya100% (2)
- Business Analysis Masterclass.Document6 pagesBusiness Analysis Masterclass.Brent Elliott100% (1)
- BABOK 2 Big PictureDocument1 pageBABOK 2 Big PictureCBAPMaster100% (3)
- Business AnalysisDocument50 pagesBusiness Analysissrimkb82% (11)
- CBAP HandbookDocument19 pagesCBAP HandbookarunkumarsNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Plan Business Analysis ApproachDocument4 pages3.1 Plan Business Analysis ApproachSushmita RoyNo ratings yet
- CBAP Question Bank v62 - Sample ChapterDocument42 pagesCBAP Question Bank v62 - Sample Chapterketi kociNo ratings yet
- 1 Understanding Business Analyst RoleDocument26 pages1 Understanding Business Analyst RoleMohamed Abrar100% (1)
- Use Cases and ActivityDocument52 pagesUse Cases and ActivityracringandhiNo ratings yet
- 1 Requirement Gathering and Analysis (1,2,3)Document41 pages1 Requirement Gathering and Analysis (1,2,3)Ayan SheikhNo ratings yet
- International Institute of Business Analysis Standard RequirementsFrom EverandInternational Institute of Business Analysis Standard RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis Planning and MonitoringDocument2 pagesBusiness Analysis Planning and MonitoringAbi SanNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis Fundamentals BACCMDocument8 pagesBusiness Analysis Fundamentals BACCMskumaritesNo ratings yet
- CBAP HandbookDocument20 pagesCBAP Handbookeceeyes100% (2)
- Final BA Book PDFDocument129 pagesFinal BA Book PDFSwapnilSaurav50% (2)
- Introduction To Business AnalystDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Business AnalystJayna Wampy100% (2)
- Professional Business Analysis HandbookDocument42 pagesProfessional Business Analysis Handbookfatihy73No ratings yet
- BAE Ebook PDFDocument121 pagesBAE Ebook PDFHimanshu ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Babok Framework Overview: BA Planning & MonitoringDocument1 pageBabok Framework Overview: BA Planning & MonitoringJuan100% (1)
- BA Planning GuideDocument37 pagesBA Planning GuideRia100% (1)
- Role of A Business AnalystDocument5 pagesRole of A Business AnalystDiptadeep Karmakar50% (2)
- Business Analyst Interview Question AnswersDocument69 pagesBusiness Analyst Interview Question Answersfaisalaziz27No ratings yet
- CBAP V3 Study Guide-Sample ChapterDocument47 pagesCBAP V3 Study Guide-Sample ChapterAdaptive ProcessesNo ratings yet
- BA Techniques - Flash CardsDocument10 pagesBA Techniques - Flash CardsShruti Gupta100% (3)
- BABOK Cartoons - KAT Tales Strips v1.0 PDFDocument9 pagesBABOK Cartoons - KAT Tales Strips v1.0 PDFMedo MohtasebNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business Analysis Module 1 - IntroductionDocument54 pagesFoundations of Business Analysis Module 1 - IntroductionShivir JainNo ratings yet
- My Journey To CBAPDocument13 pagesMy Journey To CBAPvikram_gajjala0% (1)
- Professional Business Analysis HandbookDocument40 pagesProfessional Business Analysis Handbookdigy23No ratings yet
- Business Analysis ReportDocument13 pagesBusiness Analysis Reporthassan_401651634No ratings yet
- 100+ Business Analyst Interview Questions & Answers in 2022Document17 pages100+ Business Analyst Interview Questions & Answers in 2022Sendil Kumar100% (1)
- Ethics Final ProjectDocument17 pagesEthics Final Projectapi-282483815No ratings yet
- Individual Assignment UNIT 2Document6 pagesIndividual Assignment UNIT 2TusharNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SEM-C4DDocument19 pagesModule 1 SEM-C4DAndrew WongNo ratings yet
- How High Can It Fly?: Examining The Evidence On Information Mapping's Method of High Performance CommunicationDocument22 pagesHow High Can It Fly?: Examining The Evidence On Information Mapping's Method of High Performance CommunicationleeteryiNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Planning Research ProjectDocument54 pagesLec 4 Planning Research ProjectJing WenNo ratings yet
- ED 10 Assessment in Learning 2Document50 pagesED 10 Assessment in Learning 2Danica Beato CaponggaNo ratings yet
- Erp Question Bank (UNIT 1 - 4) : What Is The Impact of Internet and World Wide Web On ERP Products?Document2 pagesErp Question Bank (UNIT 1 - 4) : What Is The Impact of Internet and World Wide Web On ERP Products?Om SarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Clark Umn 0130E 19979Document200 pagesClark Umn 0130E 19979Manna YankiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Program For Education of Religion and EthicsDocument32 pagesTeaching Program For Education of Religion and EthicsQulb e AbbasNo ratings yet
- HCI Term ProjectDocument3 pagesHCI Term ProjectNoman AliNo ratings yet
- ECO-Holder: The Effectiveness of Eco-Friendly Pen and Phone Holder Made Out of Used PaperDocument6 pagesECO-Holder: The Effectiveness of Eco-Friendly Pen and Phone Holder Made Out of Used PaperVicky rederaNo ratings yet
- TESDA Circular No. 118-2019Document2 pagesTESDA Circular No. 118-2019Episode 17No ratings yet
- Project Management Process Chart: PM Knowledge AreasDocument1 pageProject Management Process Chart: PM Knowledge AreasjalejandropinedagNo ratings yet
- ISO/IEC Information & ICT Security and Governance Standards in PracticeDocument19 pagesISO/IEC Information & ICT Security and Governance Standards in PracticeJéferson LucasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document17 pagesUnit 4Aakash RajNo ratings yet
- Checklist For The Monitoring and Evaluation of Local DRRM PlansDocument2 pagesChecklist For The Monitoring and Evaluation of Local DRRM PlansJulibert CastillonNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Decision Making Process DefinedDocument8 pagesDecision Making Decision Making Process DefinedRupert Rosel AmatorioNo ratings yet
- WWW - Ajoysingha.info: ISTQB Question Paper - 1Document9 pagesWWW - Ajoysingha.info: ISTQB Question Paper - 1Ramesh AkulaNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Checklist QACDocument9 pagesInternal Audit Checklist QACdhir.ankur100% (1)
- Standard Review Plan (SRP)Document17 pagesStandard Review Plan (SRP)Aamir Bashir100% (1)
- Training of Military PersonnelDocument17 pagesTraining of Military PersonnelRaymark LaraNo ratings yet
- Job Evaluation Hay GroupDocument58 pagesJob Evaluation Hay GroupᕼᑕNo ratings yet
- Questions 1-50 Taken From Philhealth BenchbookDocument14 pagesQuestions 1-50 Taken From Philhealth BenchbookallanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Pay Now or Pay Later:: Jarred Markel and Susan MinnickDocument34 pagesPay Now or Pay Later:: Jarred Markel and Susan MinnickiqblsatwikaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument160 pagesUntitledPrajwalNo ratings yet
- 3.1descriptin of The Study AreaDocument4 pages3.1descriptin of The Study Areaadamu shumetNo ratings yet
- Resource ManagementDocument23 pagesResource ManagementLou CabantingNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamApril KimNo ratings yet