Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASEPSIS
Uploaded by
teabagmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ASEPSIS
Uploaded by
teabagmanCopyright:
Available Formats
ASEPSIS
MEDICAL SURGICAL
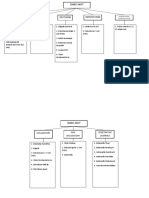
-Principle of Following the Sterile Technique:
Tier I Tier II Sterile in sterile
AKA AKA transmission based prec Sterile is unsterile if touched with
Standard latter
precautio Waist down, table, out if sight(back)
ns unsterile
When When applicable: when client is infected Prolonged exposure to airborn
applicable micro=unsterile(prepping sterile
: field)
When in Fld flows by gravity (forceps down)
contact Moisture
with body Skin cannot be sterilized
tissues Edges (1in are unsterile)
and fld
HH and Airborne Droplet Contact
PPE dissemination of either Large particle droplet involves skin-to-skin
airborne droplet nuclei >5micron contact and physical
(5micronorless) Siptheria, pertussis, transfer
measles,varicella,tb mumps
(-) air pres rum Travel 3 feet or less Private rm or cohort if DON PPE REMOVE PPE
6-12changes per -wear a mask none
minute -private rm if none No sharing of utensils Gown Gloves
Keep room door closed cohort equip Mask Goggles
Wear N95 respirator -if no cohort, 3 feet Gloves Goggles Gown
distance Gloves Mask
-mask pt wen
transported
SP: HH, PPE,(Gloves, gown, goggles, Mask)
Standard precautions apply to all patients regardless of their diagnosis or presumed infection status. Standard
precautions must be used in the handling of:
• blood (including dried blood)
• all other body fluids/substances (except sweat), regardless of whether they contain visible blood
• non-intact skin
• mucous membranes.
Standard precautions consist of the following practices:
• hand hygiene before and after all patient contact
• the use of personal protective equipment, which may include gloves, impermeable gowns, plastic aprons, masks,
face shields and eye protection
• the safe use and disposal of sharps
• the use of aseptic “non-touch” technique for all invasive procedures, including appropriate use of skin
disinfectants
• reprocessing of reusable instruments and equipment
• routine environmental cleaning
• waste management
• respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette
• appropriate handling of linen.
Standard precautions are the minimum infection prevention and control practices that must be used at all times for all
patients in all situations.
Transmission-based precautions (TBPs) are used in addition to standard precautions when standard precautions alone
may be insufficient to prevent transmission of infection. TBPs are used for patients known or suspected to be infected or
colonised with epidemiologically important or highly transmissible pathogens that can transmit or cause infection.
TBPs are not required for patients with bloodborne viruses, such as HIV, hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus.
The type of TBPs applied is based upon the mode of transmission of the pathogen. For diseases that have multiple
routes of transmission, more than one TBP category is applied. The following are the routes of transmission.
• airborne transmission, e.g., pulmonary tuberculosis, chickenpox, measles
• droplet transmission, e.g., influenza, pertussis (whooping cough), rubella
• contact transmission (direct or indirect), e.g., viral gastroenteritis, Clostridium difficile, MRSA, scabies
Infection Route of transmission
control
measure Airborne Droplet Contact
Gloves As per As per For all manual contact with
standard standard patient, associated devices and
precautions precautions immediate environmental
surfaces
Impermeable As per As per When healthcare worker's
apron/gown standard standard clothing is in substantial
precautions precautions contact with the patient, items
in contact with the patient, and
their immediate environment
P2 Respirator Yes Not Not required
required
Refer to
AS/NZS 1715
for additional
information
Mask No (P2 Yes As per standard precautions
(surgical- respirator)
style)
Refer to AS
4381:2015 for
additional
information
Goggles/face As per As per As per standard precautions
shields standard standard
precautions precautions
Infection Route of transmission
control
measure Airborne Droplet Contact
Standard No Yes or Yes or cohort patients with
single room (negative cohort same infection
with own pressure patients
ensuite ventilation with same
required) infection
Door closed
Negative Essential Not Not required
pressure required
ventilation
room
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Quiz BioethicsDocument1 pageQuiz Bioethicsteabagman50% (2)
- Quiz BioethicsDocument1 pageQuiz Bioethicsteabagman50% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Benner's 5 Stages of Nursing CompetenceDocument1 pageBenner's 5 Stages of Nursing CompetenceMagilas S. SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1st GradingDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Exam 1st Gradingteabagman100% (2)
- Madeleine Leininger's Culture Care TheoryDocument5 pagesMadeleine Leininger's Culture Care Theoryteabagman100% (1)
- XVII Making Hospital Baby FriendlyDocument18 pagesXVII Making Hospital Baby FriendlyteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment LectureDocument16 pagesHealth Assessment LectureteabagmanNo ratings yet
- VaccinationDocument28 pagesVaccinationM AQIB ASLAMNo ratings yet
- VII Milk SupplyDocument28 pagesVII Milk SupplyteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Nursing TheoriesDocument5 pagesClassification of Nursing Theoriesteabagman70% (10)
- Globe Mackay and Radio Corporation V CA: Civil CodeDocument2 pagesGlobe Mackay and Radio Corporation V CA: Civil CodeteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Spillover: Animal Infections and The Next Human Pandemic by David QuammenDocument5 pagesSpillover: Animal Infections and The Next Human Pandemic by David QuammenSouthern California Public Radio40% (5)
- Communicable DiseasesDocument7 pagesCommunicable DiseasesteabagmanNo ratings yet
- CW Puzzle MuscleDocument3 pagesCW Puzzle MuscleteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Endometab Exam 2018Document8 pagesEndometab Exam 2018teabagmanNo ratings yet
- Live MicroorganismsDocument3 pagesLive MicroorganismsteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Cordillera Career Development College Biostatistics Final ExaminationDocument3 pagesCordillera Career Development College Biostatistics Final ExaminationteabagmanNo ratings yet
- ConflictDocument2 pagesConflictteabagmanNo ratings yet
- XV Ongoing Support For MothersDocument19 pagesXV Ongoing Support For MothersteabagmanNo ratings yet
- XVI Maternal Health OutcomesDocument12 pagesXVI Maternal Health OutcomesteabagmanNo ratings yet
- XIV Infants With Special NeedsDocument23 pagesXIV Infants With Special NeedsteabagmanNo ratings yet
- XIII If Baby Cannot Feed at The BreastDocument23 pagesXIII If Baby Cannot Feed at The BreastteabagmanNo ratings yet
- XII Breast and Nipple ConditionsDocument23 pagesXII Breast and Nipple ConditionsteabagmanNo ratings yet
- VIII Birth Practices and Breast FeedingDocument35 pagesVIII Birth Practices and Breast FeedingteabagmanNo ratings yet
- XI Helping With A BreastfeedDocument32 pagesXI Helping With A BreastfeedteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument2 pagesCleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia TrachomatisteabagmanNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Endo Meta GI SyllabusDocument8 pagesNCM 103 Endo Meta GI SyllabusteabagmanNo ratings yet
- MOA Sample 1Document3 pagesMOA Sample 1teabagmanNo ratings yet
- Joyce Ardiente VDocument2 pagesJoyce Ardiente VteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding and LactationDocument36 pagesBreastfeeding and LactationteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Sample Speech As Guest Speaker in Elem GraduationDocument1 pageSample Speech As Guest Speaker in Elem GraduationteabagmanNo ratings yet
- BacteriophageDocument16 pagesBacteriophageJames FranklinNo ratings yet
- Flu Specimen Collection PosterDocument1 pageFlu Specimen Collection Poster568563No ratings yet
- Philippine Children's Medical Center: Covid-19 Testing Laboratory Molecular Pathology Result FormDocument1 pagePhilippine Children's Medical Center: Covid-19 Testing Laboratory Molecular Pathology Result FormRica RegorisNo ratings yet
- Pathology Important Solved BCQs 5th Semester MBBS + 3rd Semester BDS LUMHSDocument57 pagesPathology Important Solved BCQs 5th Semester MBBS + 3rd Semester BDS LUMHSNaheed Jatoi100% (1)
- PGI MANIMTIM - Reaction Paper - Family Medicine - COVID-19Document1 pagePGI MANIMTIM - Reaction Paper - Family Medicine - COVID-19Kim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- ABH NanoMack Details R CDocument6 pagesABH NanoMack Details R CrajasajjadNo ratings yet
- Covid - 19 - v4 2Document47 pagesCovid - 19 - v4 2dori aarlevNo ratings yet
- En Oie Asf Poc Tests Guide FinalDocument13 pagesEn Oie Asf Poc Tests Guide Finaljefry ManurungNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy - Promises, Problems and ProspectsDocument4 pagesGene Therapy - Promises, Problems and ProspectsLordsam B. ListonNo ratings yet
- Philippines COVID Response AllianceDocument4 pagesPhilippines COVID Response AllianceEloise Dorothy PatiñoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Article 1738Document19 pages2023 Article 1738Murillo Pyaia Alves PaixãoNo ratings yet
- BT503 Assignment 2Document2 pagesBT503 Assignment 2Umair AfzalNo ratings yet
- Funding Vaccines For Emerging Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesFunding Vaccines For Emerging Infectious Diseasesfadfdafade uohdajufadNo ratings yet
- Immulite: Anti-HDocument28 pagesImmulite: Anti-HpinoponiNo ratings yet
- Caries VaccineDocument30 pagesCaries Vaccinemangesh andhareNo ratings yet
- But I Spoke With My Virologist Friend and He SaidDocument3 pagesBut I Spoke With My Virologist Friend and He SaidBrian DavisNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases (Skin Eyes)Document23 pagesMicrobial Diseases (Skin Eyes)Hazel Mae FestinNo ratings yet
- VAAT 113947 Bovine Leukemia Virus Current Perspectives - 081017Document14 pagesVAAT 113947 Bovine Leukemia Virus Current Perspectives - 081017Mohammad Yusuf AlamudiNo ratings yet
- ID Virus Avian Influenza h5n1 Biologi Molek PDFDocument13 pagesID Virus Avian Influenza h5n1 Biologi Molek PDFArsienda UlmafemaNo ratings yet
- Imse Finals Reviewer - Pacate, Joyce C.Document9 pagesImse Finals Reviewer - Pacate, Joyce C.jcpacate1178qcNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BDocument16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BM7MD AshrafNo ratings yet
- Diare Akut: Adhesi Invasi Sitotoksin EnterotoksinDocument4 pagesDiare Akut: Adhesi Invasi Sitotoksin EnterotoksinVeronica Yosita AnandaNo ratings yet
- Group Number: 10A Group MembersDocument5 pagesGroup Number: 10A Group Membersmnukwa wendieNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Oral RevalidaDocument22 pagesInfectious Diseases Oral RevalidaShella Mae UsquisaNo ratings yet
- Perbedaan Kadar Hbsag Sampel Serum Dan Plasma Metode Clia Pada PendonorDocument7 pagesPerbedaan Kadar Hbsag Sampel Serum Dan Plasma Metode Clia Pada PendonorAAK DHGRiski MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0306452222004444 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0306452222004444 MainAdinda AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Toxoigg ArcDocument8 pagesToxoigg Arctesteste testeNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov2 (Covid-19) Real Time RT PCR TestDocument1 pageSars-Cov2 (Covid-19) Real Time RT PCR Testsanjana rohiteNo ratings yet