Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Doc 2018-07-25
New Doc 2018-07-25
Uploaded by
akshay gopal100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
132 views27 pagesFuel Injector
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFuel Injector
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
132 views27 pagesNew Doc 2018-07-25
New Doc 2018-07-25
Uploaded by
akshay gopalFuel Injector
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Contents
Page
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
1. Function a
2. Dis-assembly 5
8, Inspection of parts 7
4. Assembly 8
5. Calibration 10
SNUBBER VALVE
1. Function 2
NOZZLE HOLDER AND NOZZLE
1. Function 13
2, Removal ofinjector from engine oyinderhead uy
8. Functional tests onnozze test stand “
4. Dissastembly 15
5. Inspection ofparts 16
6. Assembly ”
7. _ Installation of injector on engine a
‘SPARE PARTS LIST FOR FUEL INJECTION PUMPS. 20
EXPLODED VIEW OF FUEL INJECTION PUMP a
PF 1 WV...
‘SPARE PARTS LIST FOR NOZZLE HOLDER 2
EXPLODED VIEW OF NOZZLE HOLDER 23
KBA 242...
COMPARISON OF MICO/ ABC/ ALCO 24
FUEL INJECTION EQUIPMENT SPARES
‘TEST SPECIFICATIONS 26
‘SERVICE TOOLS FOR INJECTOR 27
Scanned with CamScanner
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
10 Function
MICO fuel injection pumps aro of singlo acting,
Constant stroke and plunger typo with tho
effective working stroke, however, boing
adjustable. The pump consists primarily of a
housing, delivery valve and spring, delivery valve
holder, element (plunger and barrel assembly),
Plunger spring, a geared control sleeve and
ccontrol rack (rod) assembly. Tho pump element
‘comprises a barrel and a plunger, which are
match assembled oa very close tolerance.
‘The fuel injection pump has three functions:
+ to raise the fuel oil pressure to a value, which
willeficiently atomise the fuel
+ to supply the correct quantity of fuel to the
injection nozzle commensurate with the
power and speedrequiement ofthe engine.
* to accurately time the delivery of the fuel for
éfficient and economical operation of engine.
Detvery Valve Holder
Nut — ORing
Delivery Valve Spring oma
Delivery Valve
Pump Housing
Element
Baffle Ring
Control Rod Assembly
Regulating Sleeve
Upper Spring Plate
‘Screw
Plunger Spring
Plunger Guide
Lower Spring Plate Suse
Fig. 1. Cut section of fuel injection pump (ALCO/DLW Locomatives)
Scanned with CamScanner
nee
Fuol ail ontors the pump fom tho {vl ol hoador
a file tho sump surrounding tho plungor
barrel, Whon the plungor i a the bottom ofits
soko (position 1), fuol lows through the barrel
pors filing th spaco above the plungor and the
cutaway area the helt.
‘As the plunger moves upward, fuel is pumped
pack to the sump until barrel ports are closed.
Further upward movement of plunger (position
2) raises the pressure ofthe rapped fuel. When
pressure is sufficient to overcome the force
fxerted on the delivery valve by the valve spring,
the delivery valve opens and fuel is discharged
into: the high-pressure pipe, leading to the
injector. Further upward movement of the
plunger increases fuel pressure to enable the
injection to ocour: Delivery of fuel ceases when
plunger helix opens the barrel ports (position 3).
During the remaining movement of plunger, fuel
spils into the sump. This termination of fuel
delivery by he helix controls the quantity of fuel
dolvered per stroke. The angular position of @
plunger, with respect to the barrel ports,
determines the effective stroke and therefore,
the quantity of fuel injected. The total length of
the plunger stroke remains constant regardless
of engine speed orload.
‘When the plunger is rotated to a position (8)
where the vertical groove is aligned with the
control port, no pressure can build up and
‘consequently, no uel willbe delivered,
Tre angular postion ofthe plunger, with respect
to the bare, is altered by a control sleeve, the
lower end of the sleeve being slotted to engage
the flange (vane) ofthe plunger. The upper end
of control sleeve has an integral gearing, which
‘engages with the control rack. Movement ofthe
‘control rack by the engine governor rotates the a
plunger, thereby varying the quantity of fuel
delveredby the pump.
1. Barel 2
Barrel Port
A
Commencement
[Maximum detivery
"8-2. Control of fuel delivery by rotation of plunger
Scanned with CamScanner
2.0
21
Tho dolivory valvo provonts oxcoss draining of
{uo from the dischargo lino. As tho plungor holix
Uncovers the barrel ports, thore is a suddon
pressure drop in the barrel resulting in tho
closure of the valve due to higher pressure in the
delivery pipe and delivery valve spring force. As
the valve snaps into its seat, the prossuro ia
reduced in the injection tubing to lower the
‘opening pressure of the nozzle. This action of
the valve eliminates the possibilty of secondary
injection (after dribble) from the nozzle,
Tho sudden drop in pressure in the injection
tubing is achieved by providing an accurate
‘ali piston atthe upper end ofthe delivery vale
pin Fig. 3)
When the plunger heli first uncovers the barel
ports, the lower edge of the rele piston slides
into the valve body and traps all fuel in the
injection tube. Further movement of the valve to
its seat increases the space available for fel in
the tube and therefore reduces the fuel
pressure,
‘The metered quantity of fuel from the injection
pump passes through a shubber valve and high-
pressure line, entering the nozalo holder at the
pressure tube inlet connection. Drilled
passages in the nozzle holder conduct fuel to
the pressure chamber ofthe nozzle,
‘When the pressure of fuel acting on the
pressure chamber exceeds the spring pressure,
the nozzle valves forced fromits seat. Fuel then
flows through the nozale spray holes until the
fuel pump coases to deliver fuel. Fuel flow is
then instantaneously and positively cut off, as
the spring snaps the vale shut.
Dis-assembly
Before attempting to disassemble a fuel
injection pump, make certain that the work
bench and the tools are clean. Cover the bench
with clean paper. Rinse the parts, as they are
removed, in clean fuel oll. SOVASOL or white
kerosene could also be used as an alternate
cleaning medium.
Number in brackets indicates the exploded view
reference number frindividual components.
Removal of plunger guide cap
(7), plunger control sleeve (4)
Place the pump in a dismanting fixture in an
inverted position and force the plunger guide
cup into the pump housing. Insert a piece of drill
rod or heavy wire in the hole on the inside ofthe
‘pump bod to hold the plunger guide cup down,
(Fig. 4)
Remove the plunger guide cup retaining ring
(Fig. 5) and force the plunger guide cup downto
5
Fi. 8. Removing the guide cup retaining ring
Insert: Close-up of retaining ring
Scanned with CamScanner
{oreo on tho guide ls
20 tho
corr io Oe gar guteCP
cx at), pe and
A the pump housing
ig with upper spring
plunger and keep it
Lincthe lower seri
unger sping (8) out e
Remove contol seve a
cxat (Fg. 6 Wash We
separately ioprvert daa
Delivery valve (21)
anling fature in an
the pump on a dis
Peta poston. Wiha socket wrench, 1082”
ry wae Pksing nut (8) (ig 7). While
Teosning the nut oxet asirongand steady ul
onthe wrench,
Remove holding nut (Fig. 8) and delivery valve
holder (20),Removethe delivery valve and valve
body sa uni Ths unit can belted out ofthe
purmphousing.
Wash the delivery valve and valve body
separately o prevent them from being damaged
bycomingin contact with other parts.
Caution:
Never use a hammer to loosen or tighten the
dalveryvae holding nut (18).
Plunger barrel
Remove plunger barrel by pushing tout through
the deivery valve opening. The barrel is held in
Position by means of a locating pin and
corresponding slot on the barrel. The locating
pin should not be removed. Wash barrel
separately to prevent it from being damaged by
coming in contact with other parts. Now
‘assemble the plunger and barrel fr protection
against possible damage.*
“Caution:
Protection sleeve to be placed in between the
‘Plunger vane and the barrel to avoid damage to
{he plunger top, Damage to the plunger top can
‘Cause seizure! stickiness ofthe element,
Control rack (29) and bushings
Remove control rack stop screw (27). Pu
ontrolrack outofts bushings (Fig 9)
'm case bushings need 1
Suitable mandrel
Allow i to fal
replacement, using a
Push in one side bushing and
Ot HHOUGh the opening in the
"© Pump housing, Remove the
a
ond bushingalsointhe same manner,
Fig. 8-Removing delivery valve holding nut
Scanned with CamScanner
3.0
34
3.2
3.3
3.4
Inspection of parts
Plunger guide cup (7)
Replace plunger guide cup (7) ifthe indentation
on the plunger and tappet seating surlace is
more than 0.126 mm (0.005"),
‘The clearance between guide cup and the pump
housing has no effect on pump performance.
Replacement however, should be based on
mechanical judgement.
Plunger spring and spring seats
Replace plunger spring it
+ cracked! nicked
+ corroded
+ surface coating damaged.
Replace spring seat worn-out/ damaged.
Plunger and barrel assembly
(element)
With constant use and abrasive action of
extremely minute impurities in fue, the plunger
‘wears out, thus affecting the tightness of
clement. Particularly ifthe wear! scoring mark is
‘considerably above the helix region of element
plunger, the specified delivery quantity cannot
be obtained and this will afect the engine
performance.
If there is considerable wear! scoring in the
region above the helix ofthe element plunger
and if specified values as per the Calibration
Chart cannot be obtained, the element requires
replacement.
Occasionally, dark discolouration and pitting
marks may be seen on the delivery valve seating
surface bf the barrel f the surface shows only
discolouration and no wear is noticed, the
seating surface may be polished by using
‘mutton tallow’ or ‘clover compound A. After
polishing, wash thoroughly in clean et ol It
wearis observed, replace element.
Element plunger and barrel are ‘match
assembled’ and cannot be replaced
individually.
Delivery valve holding nut (18)
Examine delvery valve holding nut for damaged
threads orseat. Replace, fnecessary.
Fig, 8. Removing the contol rack
Scanned with CamScanner
3.5
3.6
fap
3.8
3.9
4.0
41
Delivery valve holder (20)
Examine for damage to high-prossure
connecting threads. Examino tho seating
surface. H necessary, lap the seating surface to
remove any discolouration marks using ‘clover
compound A\. After lapping, thoroughly wash
dlvery valve holderin clean fuel oil
Delivery valve spring (19)
‘The delivery valve spring must not be pitted or
‘racked nicked. Replaceit, necessary.
Delivery valve (21)
Examine the seating surfaces ofthe valve body
that come into contact with barrel and delivery
valve holder. Discolouration marks can be
emoved by polishing with mutton tallow.
4 either the valve or valve body cannot be
reused, the delivery valve assembly must be
replaced. The valve and valve body are ‘match
assombled’ and must never be replaced
individual
Control rack and sleeve
Check the clearance between control rack and
bushings. It shouldbe within 0.5 mm (0.020%).
necessary, replace bushings/ control rack.”
Move control rack by holding the sleeve firmly.
‘The control rack movement should be within
0.226 mm (0.008") Similarly move control rack
by holding element plunger stationary
Tho control rack movement should be within
0.38 mm (0.018"), necessary, replace control
rack! sleeve.
Baffle ring (22)
‘The baffle ring surrounds the barrel to prevent
erosion of the pump housing as a result of a
‘sudden oil pressure when barrel ports are
uncovered,
Inspect batle ting for erosion. If excessive,
replace bate ring
ee
Assembly
Before assembling a fuel injection pump, wash
all parts in clean fuel and assemble them when
wet. Protective grease from new element
‘and delivery valve should be removed in petrol
‘thoroughly. Dip the element plunger and delivery
valepinin clean fitered fuel before assembly
Control rack bush tings
Place the pump housing on an arby
Dress in one bushing at a time
tool (Fig. 10).
oF press,
with @ suitable
Fig. 10. Pressingrin the control rack bushing
Scanned with CamScanner
Alter both tho bushings havo boon insorted,
ream the bushings 10 18.25 to 18.27 mm
(0.7185 to 0.7102"), Use areamer with euitablo
guide (Fig 11). After roaming, thoroughly clean
bushings and pump housing,
4.2 Plunger barrel
Examine the barel seat in the pump housing.
Donotattempt to refinish the barrel seat but
remove dirt if there is any. The barrel seat
must be tight, 50 that during pump operation,
fue wil not leak past the seat into the spring
cchamber. lace pump housing in a dismantling
fiature in an upright postion. Insert element
bartelinto pumphousing.
Caution:
Protection sleeve to be placed in between the
plunger vane and the barrel to avoid damage to
the plunger top. Damage to the plunger top can
° Gause seizure stickiness of the pump.
‘The element barrel is located by means of a pin
pressed into the housing and a slot outside the
barrel indicated by arrows in Fig. 12). After the
barrels lowered fits seat, move the barrel up
and down and rotate itsightly to ensure that itis,
propery located. Thereafter, insert baffle ring
around the element. Install delivery valve
assembly and delivery valve spring into pump
housing. Insert rubber 'O' ring (11) over the
delvery valve holder. Place 'O' ring (12) on
dolvery valve holding nut. Before insertion of ei
“O'ring, smear a small quantty of vaseline or Fig. 12. Locating the element barre
petroleum jelly onthe surface of'O'rings. Screw
the holding nut into pump housing and then
tighten it to a torque of 620-690 Nim (62-69
kgfm.or 450-500bs. ft) withatorque wrench
Control rack and control sleeve
Pace:the pump in the dismantling fiure in an
inverted position. Slide control rack into its
bushings rotating it, until
the notched tooth is
visible through the
bottom opening of
pump. Screw in the
control rack stop screw
and engage it with the
| slot in the rack. Tighten
the stop screw and put
thelock-wire.
Lower the control sleeve
into the pump housing
‘and engage the rack so
| that the notches on the
| sleeve and rack are in
line (Fig. 13),
Fig. 18. Aligning marks
9
Scanned with CamScanner
RE9 pungerandplngerguidecup ==
Install uppor spring eoat and plungor opring in
pump housing. Position tho lowor spring saat to
plungorand nsor plungorinto tho barrol go that
thonotches on plungor flango (vano) and control
sleovoarainine,
Slide tho plungor guido cup into pump housing.
Force the guide cup down against the spring
pressure making certain thatthe plunger flange
(ane) engages inthe slots in the control sleeve,
Insert piece of dillrod or heavy wire inthe hole
of the pump housing to hold the guide cup
down, Install guide cup retaining ring; again
force guide cup down and remove the dil rod.
Release guide cup.
General
After the pump is completely assembled, check
for free movement of control rack. The rack
should slide freely. The pump is now ready for ®
calibration,
5.0 Calibration
‘AI MICO fuel injection pumps are thoroughly
tested for function, mounting dimensions,
dativry values, ec, before despatch,
‘The calibration values specified for pumps (refer
supplement - page 26) will hold good only if
tested on Bosch calibration test bench with a
suitable cambox. At the time of calioration of
pump, the point of port closure is also marked
ie, a matk is provided on pump plunger guide
fang an aligning mark on the pump housing. On
Pumps assembled with shorter plunger guide
‘cups, no separate matkng is provided on the
cup, but the top edge of the plunger guide cup
will serve as reference mark. The inspection
windows coveredby a cover.
51 Procedure
Mount the fuel injection pump on test bench
(Fig. 14). Run the test bench and ensure that
Airfreefuelis delivered through the test injector
Increase the speed to 500 min’ (rpm), direction
of rotation throughout calibration remaining
Clockwise as viewed from the driving end, With
Suitable scale and contol rack holding device,
Push control rack towards'stop' and ensure that
‘here is no further movement. Thereatter, move
{he control rack towards delivery postion by
20 mm inthe case of pump type PF 1 WV 180/53
nd 28 mm in the case of pump type PF 1 WV
{17018 ignoring the marking on the control rack,
1 Check deivery quanti the value, as specied
0
Scanned with CamScanner
eS
5.2
ienot obtained, vary the position of control rack
til pump dalvers specified quantiy. Holding the
contol rack in this postion, add shims to tho
pointe sothattindicatos:
‘30 mm on pump type PF 1 WV 150/65
‘28 mm on pump type PF 1 WV 170/6
‘Without making any further adjustment, check
dalivery at a contol rack travel of 9 mm (idle
positon). The pump should deliveras specified.
‘Stamp the total thickness of shims used on the
pump housing near the pointer, after having
erased the earlier stamping.
Checking fuel delivery at zero
control rack travel
Move the control rack towards stop position and
‘engage the latch with the slot provided on the
control rack. Run test bench at 200 min (rpm).
‘There should beno delivery
Note that the calibration values shown on
page 1 of supplement ae for reference purpose
only In diesel service stations, where master
pumps for ull fue’ and ‘ile fuel are availabe,
before any repaired pump is taken for testing,
the master pump values should be obtained on
the test bench. After that the repaired pump
shouldbe re-settothe same limits.
IFitis not possible to calibrate the pump within
the specified limits, the element or delivery valve
‘assembly may need replacement. The
replacement of either or both of the above
should providetheneeded correction. +
Adjusting shims
‘The adjusting shims for control rack pointer are
available in various thickness (refer page 22)
"
Scanned with CamScanner
1.0
SNUBBER VALVE
Function
A snubber valve assembly is fitted on the fuel
injection pump at the top of the delivery valve
holderusing atubing union sleeve and nut,
Itis basically a check valve that restricts fuel flow
in the reverse direction through a small orice.
Its function isto dampen shock waves traveling
through the high-pressure line resulting from
sudden closure of the delivery valve and the
nozzle valve.
Inspection and replacement of
snubber valve
+ Visually inspect forcracks
+ Check or ree movement ofdiscby shaking
+ Examine the disc to see that itis not broken
(by holding snubber valve assembly near a
light source and looking through the snubber
valve bore). Note that the office in the disc is
considerably smaller than the bore in the
snubber valve.
‘The snubber valve should be replaced if male
and female cones are damaged/ worn out and/
orthe valve discis found broken.
Replace complete assembly as individual parts
arenot marketed.
———|
NN
in
WSJ
<<
QZ
Snubber valve - part no.
Scanned with CamScanner
ee NL a
1.0
1
1.2
NOZZLE HOLDER AND NOZZLE
Function
Nozzle holder
‘Tho fuel injection nozzle holdor conducte fuel
‘rom the pump, srubber valve and high prossuro
discharge tubing to fuel injaction nozzle and
provides a means of adjusting the nozzle valve
‘pening pressure, The nozzle alomises the fucl
and directs it in a definite spray pattem into the
engine combustion chamber. The major
components of the nozzle holder are nozzle
holder body (1), pressure adjusting spring (4),
shims (compensating washers) (2), uide bush
{@), intermediate disc (6) and nozzle capnut (7)
{ee page 19)
To adjust nozzle valve opening pressure, shims
are used between nozzle holder body and guide
‘bush (spring cap), above the spring. The lower
end of nozzle holder is ground and lapped to
provide leak-proof and pressurestght seal with
the lapped upper surface of intermediate
disc (6). The lower surface of intermediate disc
isalsolapped to provide a prossure tight sealing
with the lapped surface of nozzle body. Nozzle
holder and nozzle assembly will hereafter be
referredto-sinjector.
Nozzle
‘The fuel injection nozzles are the closed,
hydraulically operated, differential type
consisting of two parts nozzle body and nozzle
valve (pin). Both these parts are made out of
special heat-treated alloy steel to minimise wear
‘The nozzle valve and nozzle body are matched to
form an assembly. These parts should not be
exchanged individually but replaced only as an
assembly.
[At the tip of nozzle body are 9 spray holes
through which fuel passes into the combustion
‘chamber, The spring loaded nozzle valve
‘controls the flow.
Operation
‘The metered quantity of fuel from the injection
pump enters the nozzle holder through the
high-pressure inlet tube connection and flows
through the drilled passages of nozzle holder
‘and nozzle body to the nozzle pressure chamber.
When fuel pressure acting on the differential
area exceeds the spring force to which the
opening pressure is set, the valves lifted off its
seat, Fuel flows through the nozzle spray holes
ntithe fuel pump coases to deliver fuel.
Figs injection nozle
Scanned with CamScanner
2.0
3.0
31
3.2
Tho fuel flow is then instantaneously and
‘cut off as tho spring pressure forces
bbotween tho nozzle valve and nozzle body is
necessary forlubrication.
‘The "leakage! fuel accumulates in the spring
ccompariment. From the spring compartment,
fuel drains out of the nozzle holder through aleak
off passage, thus preventing the nozzle valve
from becoming hydraulcaly locked.
Removal of injector from
engine cylinder head
*+ Loosen high-pressure fuel line connection at
‘pump andnozzle holder.
+ Remove injector retaining stud nuts.
+ Remove retaining clamp and take out the
injectorwith apuller.
Note: There is no gasket between the nozzle
holder capnut and the rolled sleeve in the
oylinderhead,
Cleaning
Wipe all drt and loose carbon particles from
injector with a clean cloth and clean the nozzle
tipwitha brass wire brush.
ss
Functional tests on nozzle test
‘stand
Mount the injector in a testing fixture and
Connect to nozzle tester using suitable high-
pressure pipe. Put the pressure gauge of nozzle
{ester out of circuit by screwing in the shut off
valve knob (clockwise direction).
To flush the nozzle, operate the hand lever of
{ester for about 10-12 strokes at the fastest
possible lever speed,
Tho nozsle should repeat (chatter) with a
whistling tone and/ or spray in a well atomised
form,
Opening pressure test
To check the opening pressure, bring the
Pressure gauge in circuit by screwing out the
Shut off valve knob (anticlockwise direction),
Stowiy depress the hand lever until the nozse
‘sets the test oil and the pressure gauge
Trading suddenly drops. At this stage, note
own the pressure gauge reading,
"indicates the injector opening pressure
Fig. 2. Nozzle test stand
Scanned with CamScanner
3.3
3.4
4.0
HF tho opening prossure los botweon 266
kg(/om* (8600 psi) and 270 kgl/cm’ (8800 pai
itisnot necessary tor0-s0t, ,
Seat tightness test
Slowly operate tho hand lever of nozzle testor
until the pointer in prossure gauge indicates 20
kgf/cm? less than the
pening pressure
recorded above, .
For example, if opening pressure in as is
condition is 260 kgf/cm’, hold the pressure at
240 kgf/cm’ for 10 seconds by slowly operati
the hand lever, a
‘The nozzle is considered tight (good) ifno drop
falls from the nozzle within 10 seconds,
Wetness or formation of oil drop (which does
‘ot fall in 10 seconds) at the nozzle tip is
acceptable.
Spray pattern/ atomisation
Put the pressure gauge out of circuit by
screwing in the shut off valve (clockwise
direction). Operate the nozzle tester hand lever
at the fastest possible speed (4-6 strokes per
‘second). At this speed the spray should be well
‘atomised, the nozzle may or may not repeat
audibly.
If injector is satisfactory for seat tightness,
spray pattern/ atomisation and opening
pressure is lower than 256 kgl/om’ (3600 psi)
re-set the opening pressure to 260-270 kgt/em*
(8700 to 3800 psi) by changing the thickness of
shims between nozzle holder body and the
‘guide bush (spring cap). Repeat seat tightness
and spray pattern/atomisation tests.
Absolute cleanliness is essential during
.ssembly/ dis-assembly and testing of
injectors. The working space must be free
from dirtand chips.
Dis-assembly
Mount the itjector in a bench vice or suitable
fixture, Unscrew the nozzle, capnut using @
socket wrench part no. HS! KDEP 77
(@ 689 034 038). Do not use a pipe wrench
Lift the nozzle off the nozzle holder taking care
that nozzle Aeedle does not drop out of the
nozzle body.
If nozzle is stuck in capnut due to excessive
carbon formation, dive the nozzle out carefully
with a brass rod, whose end conforms to the
contour of nozzle tip. In order to protect the
lapped surface of nozzle holder, screw on the
‘capnut to nozzle holder.
8
Scanned with CamScanner
44
4.2
4.3
5.0
51
hholderbody and clean themin clean fuel oil,
Cleaning of nozzle
Soak nozzle in clean fuel oil/ kerosene and
withdraw the nozzle valve (needle pin) from
nozzle body. If the needle cannot be withdrawn
easily, soak nozzle in kerosene for a few hours. If
nozzle needle is stil sticky, it is advisable to
scrap the nozzle. Such nozzles may not function
satisfactorily even if the needle is removed
somehow. Examine nozzle needle for damaged
or rough nozzle needle seat. Also examine the
nozzle body for damaged or carboned seat and
clogged spray hole. fnocessary, soak nozzle in
kerosene.
Clogged nozzle spray holes
Blow clean and dry compressed air into nozzle
body. If necessary clean the spray holes (Fig, 3)
with nozzle cleaning wire (refer supplement for
details) The cleaning wire should not break into
the hole because it is difficult to remove the
broken piece.
Nozzle body
To clean the nozzle body use an oil collecting
groove cleaner and nozzle seat scraper
available innozze cleaning kit (Fig. 4).
—
Inspection of parts
Nozzleslide test
‘After having removed all traces of foreign
material rinse nozzle needle and body in fitered
test ol, Holding the nozzle body almost vertical,
pullout nozzle needle by one third ofits engaged
(Guide) length. When released, the nozzle
needle should slide down to the seat with its
own weight (Fig. 6).
"nozzle needle sticks in the body, smear a tle
mutton tallow on the needle guide and hold it in
the chuck of a lapping motor. Run the lapping
‘motor and move nozzle body over the needle,
imparting ‘back and forth’ and rotary motion.
While carrying out this operation nozzle, needle
should not touch its seat in the body. Wash
ozzle needle and body in clean test oll and
‘epeatthe slidetest.
Nozzle holder body (1)
The lapped pressure surface should be free of
Cracks, Scratches, pitting marks etc, that may
fause an improper seal between the nozzle
holder and the intermediate piece. Clean with
‘est oll and blow with ‘clean and dry’
Fig. 5. Fall test
Scanned with CamScanner
‘compressed air, Chock the
cae hroads for any
5.3 Nozzle capnut (7)
Remove carbon deposits from inner and outer
surfaces. Examine for cracks, damage to
threads and seatn ;
ing surface. Replace, if
peels place, if
5.4 _ Pressure adjusting spring (4)
Replace the spring itis nicked, pitted or worn
ut. If spring is condemned for wear on the
outer surface of the spring col, determine the
cause and rectly.
5.5 Spring seat (3)
Replace spring seat it is rough or badly worn
out.
5.6 Spindle (lower spring seat) (5)
Replace, if broken, cracked or excessively worn
out.
5.7 Intermediate disc (6)
Replace intermediate disc if found cracked or if
indentation at the nozzle seating end exceeds
0.125 mm.
_
6.0 Assembly
61 — Cleaningofnozzle
If using a new nozzle, remove the preservative
coating and wash the nozzle thoroughly in clean
petrol
~Djpthenozzle body and needleinfiteredtest of
andassemble.
Nozzle needle and body are ‘match assembled’.
‘Therefore they should not be interchanged with
those of other nozzles,
6.2 Slidetest
+. Dipthenozzleneedieinfiteredtest oilandineert
+ intonozzle body.
Holdiig the nozzle body almost vertical, pull out
the needle up to maximum one third of its
fengaged (guide) length. When released, the
nozzle should slide down to its seat by its own
weight.
Wash all the nozzle holder components
= thoroughly incleantestoil.
6.3 Mount nozale holder body () in holding Fate
ale end’ upwards. Insert shims (2),
spring seat (3) and spring (4 in the body. Keep
Spindle with guide bush (6) and intermediate
doe (6) on the protruding end of spring
”
with ‘90%
— Scanned with CamScanner
7.0
‘Assemble nozzle ovor tho intermodiato dive:
sorow on tho nozzlo capnut by hand and
ccentraliso tho nozzle,
Tighten the nozzlo capnut to 130-150 Num (13-
15 kglim of 94-109 Ibs.) torque with a suitable
boxspannerand torque wrench (Fig. 6).
Remove the injector from fiture and carry out
the functional tests.
+ Fitmentand flushing: Same as 3.
+ Opening pressure test: Same as3.2
Ifthe injector is new or new nozzle holder spring
‘and nozzle have been used, set the opening
pressure to 275+10 kgt/cm® (3800 to 4050
psi). Re-setting pressure for injector (with used
nozzle holder spring and nozzle) is 260-270
kat/om (3700 to 3800 psi).
+ Seattightness test: Same as 3.3
+ Repetition (chatter) and spray pattern
test (for new nozzle)
Good repetition in the entire range of attainable
lever speed.
Lowest-test speed is one downward stroke/
second. Occasional/ small non-repeating
anges are of no significance and should not be
the criteria for rejection. At fast lever speeds,
good repetition is indicated by well atomised
spray.
Spray pattern/ atomisation
‘At lower test speeds, the atomisation is coarse
(non-homogeneous).
At fast lever speeds te spray is compact and
finely atomised.
Installation of injector on engine
*+ Clean nozzle hole in cyinder head.
+ Position the rubber 'O' ring around the nozzle
holder.
+ Place the injector in cylinder head and
position itwith the locating dowel.
+ Apply the injector retaining clamp so that the
clamp bearing surface is directly over the
centre line of the nozzle holder. Tighten the
clamp nuts, hand tight until the clamp is
parallelto the head surface.
Insert fuel injection tube at the side, making
sure that upset cone enters conical seat on
the side of the nozzle holder body. Tighten the
clamp nuts, hand tight until the clamp is
parallelto the head surface.
Fig. 6. Tightening the nozzle capnut with torque
wrench
Scanned with CamScanner
7A
Centering of Nozzle
& checking
truerunning
Itis very important that
the injector,
centralised,
uring the assembly of
Care is taken that the nozzle is
To achieve a true running of 0.3 mm, the
centering sleeve (part no, 9 689 084 100) has
beenused (Fig. 7).
Further, using the true running gauge (part no,
F 002 H81 508), check the true running of the
nozzle (Fig. 8).
Note: Failure to follow the above Procedure can
lead to side thrust on the nozzle, which can lead
tothe breakage of nozzle.
Fig. 7. To achieve true running of 0.3 m
coanoco LY
on
e
(F002 H1 608)
Fig. 8. For checking the true running of nozzle
use gauge (part no. F 002 H31 508)
Scanned with CamScanner
SPARE PARTS LIST FOR FUEL INJECTION PUMPS
Types: a. 9410035 000-PF 1 WV 150/5flted to ALCO 251 B-16 Vee Diesel Engine
b, 94100095001 -PF1 WV 170/6 fitted to ALCO 251 D/6 Cylinder Diesel Engine
Fig. Description of spare parts Partno, No.in
ng each
1 Pump housing 9411 085 208 1
>2 Elementfor
-9410035 000 9411 038401 1
-9.410036 001 9411 038 402 1
34 Regulating sleeve 9.411 036300 1 ,
ls Upper spring late 9411 030508 7
é Plunger spring ‘9411 084600 1
Plunger guide cup 19411 030504 1
8 Lower springplate 9411 030104 1
10 Springing 9411 084602 1
>it "Oring 9411 080201 1
>i2 ‘Oring 9411 030 202 1
4 Screw 9411 033.400 1 ®
18 Nut 9411 088302 1
19 Delivery valve spring 94110346011
20 Delivery valve holder 9411 038301 1
>a Delivery valve for
-9410035 000 9411 038503 1
b __-9410035001 9411 038.505 1
22 Baffle ring 9411 030 208 1
24 Sorew 9910501 152 2
25 Pointer 9411 080000 4
26 Latch 19.411 032003 i
20 Screw 9411 038.401 4
8 ‘Shims yi
a -0.1 mmthick 9.411 030 105
b -0.2mmthick 9.411 030 106 Q
© -0.25mmthick ‘9411030107 2
4 -0.5mmthick 9411030108 | asrequired
@ —-O.8mmthick 9411030109
1 mm thick 9411030110
9g -20mmthick 9411030111
329 Controlrackassembly 9411 086 000 1
>20/* Controlrackbushing 9.411 080336 2
30 Screw 2910022 196 2
3t Washer for 30 1410 107 005 2
[32 Inspection cover ‘9411 080002 1
33 Gasketfor32 ‘8411 080008 i
3° Banjoboltforfueliniet ‘9411 088.407 1
*Notilustrated > Parts subject to wear and tear
Scanned with CamScanner
EXPLODED VIEW OF FUEL INJECTION PUMP
PF 1 WV...
9 410 035...
Oo) -OG or a OMD0OO
Scanned with CamScanner
SPARE PARTS LIST FOR NOZZLE HOLDER
Types: 0.431 919 008/ KBA 242 72
19.490 081 902/ KBA 242 T10
Fig. Descriptionofspareparts Spareparts —_-Spareparts, No.in
oy forKBA242T2 for KBA242T10 each
1 Nozzle holder body 9431 035 132 1
2 ‘Compensating washer
2 OSmmthick 2430 100600 -
b 0.35mmthick 2.480 100601 2
cc OAmmthick 2490 100602 : :
6 0.45 mmthick 2490 100603 .
© OSmmthick 2490100604 9431090125"
{ 08Smmthick 2.430 100608 : ssrequired|] BO @
@ 0.6mmthick 2.430 100606 :
hh 1Ommthick 2490103008 9431 080126"
i 20mmthick 2.430 103.006 :
k 04 mmthick @ 2430100607 9431030 123"
w | ate = earanoe
° 3 Springseat 2480120000 9491080128" 1
(Washer) or 9.431 030 129" 1
4 Spring 2434619008 —9.431034601* ’
| 38 Intermediate dise 2430136000 9431030120 1
7 Nozzle capnut 2433314087 9.431 083320 1 .
>B Nozzlefor
a -251B 16Veeengine 9430083800 9490039300. 1
DLIS7T1194 —DL1S7T 1194 9
b +251 D6 CyLengine 9490033901 9430033301 1
DLIS7TH41 LAST Hat
“Interchangeable with corresponding ABC parts
Nozzle is not supplied along with the nozzle holder ané
f ‘number engraved on the nozzle.
>Parts subject to wearand tear
id hence to be ordered separately, Please state order
—
Scanned with CamScanner
EXPLODED VIEW OF NOZZLE HOLDER
KBA 242...
Pray
Ci
S 2
@e °
“eo
Ss
iS 4
=e ©
i
Wy
UW)
Scanned with CamScanner
COMPARISON OF MICO/ABC/ALCO FUEL INJECTION EQUIPMENT SPARES
- iCOequivaiont SSCS
: Fig.no.asshown Partnumber Description
nico asm, Has eto
view drawing
922008 GATEIG at 1410 107008 Washer
26200162 APFACO 150 A
T4016 941035000 Pump for 251 8
T520016S _APFICO 150 PFW 18015
T4016F
2921267 __8C76286-2A 2 9.411 038.401 Pump elementfor 2518
2321294 GU 76106 |
Gu76153 7 9411 080604 Plunger guide cup
72821904 GU76114
+2922384_ +WA7646 9 9411 030 104 Lower spring plate 7
2921316 _GU76144 5 9411 080503 Upper spring plate
2321326 GA1060 2 9411030202 “O'ring between housing :
2321927 GA76214 and nut
+2821325_ +RG 1047 7 9411 080201 "Oring between nutand
delivery valve holder ® o
2821688 HG761142A 7 ‘9417 085 208 Pumphousing
togetherwith
18 11No.9411 033.302 Nut J Inividualparts of
4 2Nos.2910501 152 Screw | ABC pump housing
27 1No.9411033.401 Screw }eannotbe replaced
30 2Nos.2910022196 Screw | withcorresponding
14 1No.9411 033.400 _ Screw | MICO parts
282184941 _HP-76356 20 (9411 083301 Delivery valveholder
2321955 PO76I0 25 (9411 080000 Pointer
2821968 VA76I98A 21 9414 038505 Delivery vale for251D
2321983 SP76114 18 9411 034601 Delivery valve spring
2921878 RD 76205A 29 9411036000" Controlrackassembly
23214451 SV7656 4 9411086300" __Reguiatingsloeve
2921464 RG7624 10 8411 034602 ‘Spring ring
292153 OV76203 32 ‘9411 030002 Inspection cover o:e@
2922088 _GA76269 33 9411 030003, Gasket :
2922084 SP 76141 8 9.411 034600 Piungerspring
23001641 8G 7678 - 9411 030836 ‘Controlrackbushing
2922662 _ LH762 26 9.411 032003, Latch
2402466__VATEI94A 9.411037 400 ‘Snubbervalve
4231051-1 ADL I67 (0430039301 Nozzle for 251 D
TM822-6 DLAs7 T1141
4820021 APFICQH7O
50488 9410035001
4920021-1 APF1CQ170 PF1WV170/6 ——_ Pumpfor251D
T5048C
4321001 BC 76356A 2 (9411 088 402 Elementfor251D
223102189 ADL 167 19430033300
TMe21-6 DLIB7T 1194 Nozzlefor2518 ">
22372410-2. AKK242 0431 519003
T5700 KBA24272
or Nozale holder for 251 B&D
9430031 302
—
Scanned with CamScanner
COMPARISON OF MICO/ABC/ALCO FUEL INJECTION EQUIPMENT SPARES
MICO equivalent
ALCO ABCno. Fig.no.asshown Partnumber Description
Cat.no. inthe exploded
view drawing
23210318 SR7629-2 28 ‘9.411 030106
23210319 SR7629-7 28 9.411.030 111
23210321 SR7629-1 28 9411 030 105
23210822 SR7629-3 28 9.411 030107
23210323 SR7629-4 28 9411 080 108
23210324 SR7629-5 28 ‘9411 030109
[23210325 SR7629-6 28 9411 030 110 Shim
23213611 VA76196A a 9411 038503 Delivery valve for 2518
24010442 : (9411 033407 Banjo bolt
MICO baffle ring 9.411 030 208 cannot be used with ABC pump housing but ABC ring can be used with
MICO pump housing,
+ If MICO control rack assembly has to be used on ABC pump, regulating sleeve should also be replaced with
that of MICO and vice-versa.
Scanned with CamScanner
TEST SPECIFICATIONS
Test equipment
Testbench
Cambox
Testinjector
Nozzle
High pressure pipe
Test conditions
Inlet pressure foréalbration
Ciltemperature
Testoil
MICO/ Bosch make
82421 1900
0681 343 005 (EFEP 218)
0681 443 016
3115 23674
8x 2x950mm
(outer dia x wall thickness x length)
osto1
402°C
isons
Calibration Values (Applicable only when tested on MICO/ Bosch test bench)
Pumptype Testinjector —_Controlrack
‘opening position min’ (rpm) Delivery quantity
pressure (mm) (cm’/300 strokes)
kgt/em*
PFI WV 150/5 17248 9 500 70.5-76.5 (645-825)
9410035000 30 500 999-411 (887-423)
PF1WV170/6 17248 9 500 90-100 (86-104)
9.410035 001 28 500 465-489 (462-492)
Notes:
(a) Values given in brackets are overchecking
values.
(0) Applicable only for MICO and Bosch test
benches,
{(c) Maximum shims at pointer tobe 4 mm.
BDC dimension (a) :6.5 0.05 mm
BDC dimension is the distance from the pump
mounting surface to the top of the pump drive
push rod or roller tappet in BDC position. See
sketch alongside. This dimension must be
maintained while mounting the pump on the
testbench.
Caution:
Teppet
Measurement of BDC dimension
Itis absolutely essential o ensure maintenance of BDC dimension both on the calibration test bench as wollas
onthe pump mounting block on the engine. Failure to adherence willresultin:
+ Damage tothe housing by way of spigot breakage ifthe BDC dimensionis more
+ Damage tothe control sleeve! element plunger in caseitis less
Scanned with CamScanner
SERVICE TOOLS FOR INJECTOR
Sno. Description Designation Application
Nozzle cleaning / testing
1
03-KDEP 2900 Forcleaning ll nozzles
9680034001
2 Nozzlecleaning wire (0.8mm) 03-KDEP 2900/11/1 ForDL157T 1134 nozzles
9681 033.209
3 Nozzle cleaningwire (0.85mm) 03-KDEP.2900/19/1 For DL157T 1141 nozzles
9681 033.210
4 Nozzlesnesdielift gauge H-S/KDEP1 For checking nozzle needle ft
9689035001
+Feeler +H-S/KDEP 1/4
9681033211
5 Dialgauge Range Oto 10mm Forusein conjunction with
Least count 0.01 mm nozzle needle lift gauge
(Tobe procured locally)
[6 Mattontaiow FT19V1 Forgeneraluse
| 5700262000
7 Nozzle centering sleeve HS/KDEP 128 Forcentering the nozzle
9.689034 100 while assembing nthe
| NHbody
|B Twerunninggauge +~—-—«~FOO2HS1508 ‘Go/no go gauge for checking
the truerunning of the nozzle
during injector assembly
| Nozzle testing
1 Nozzle tester Bosch : EFEP 60...
MICO: H-S/KDEP99 or H-S/KDEP 99A
2 High-pressure pipe 03-A1-EF 8040/24 For connecting injector to
(M14x 1.5mm capnutson 9681 030 703 the nozzle tester
both sides)
7 3 Fixture for injector H-S/KDEP 66 For holding the injector |
g 9689033034 while testing |
4 Socketwrench H-S/KDEP 77 For loosening/ tightening
9689034038 nozzle capnut
5 Testoil 9916034004 For testing nozzles |
Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
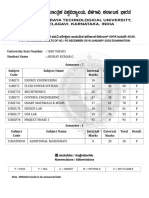
- Acknowledgement: Tejesh Gowda N 1DB16ME477Document1 pageAcknowledgement: Tejesh Gowda N 1DB16ME477akshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Dcet 2018 Exam TimetableDocument1 pageDcet 2018 Exam Timetableakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Contents 430 PDFDocument1 pageContents 430 PDFakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- VTU ResultDocument2 pagesVTU Resultakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Front Sheet 403 PDFDocument2 pagesFront Sheet 403 PDFakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Clutch: Seminar GuideDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Clutch: Seminar Guideakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Contents Technical 430Document2 pagesContents Technical 430akshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Special Finishes To Garment An OverviewDocument18 pagesSpecial Finishes To Garment An Overviewakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Print - ApplicationDocument2 pagesPrint - Applicationakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report 414 PDFDocument22 pagesSeminar Report 414 PDFakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Scope of Work - CNC Milling MachineDocument1 pageScope of Work - CNC Milling Machineakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Contents Technical 414 PDFDocument2 pagesContents Technical 414 PDFakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Contents Technical 403 PDFDocument2 pagesContents Technical 403 PDFakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 ReportDocument13 pagesPhase 1 Reportakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- ON I-Vtec Engine: A SeminarDocument19 pagesON I-Vtec Engine: A Seminarakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- A Seminar: ON I-Vtec EngineDocument19 pagesA Seminar: ON I-Vtec Engineakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Multipurpose 4 in 1 Agriculture Robotic VehicleDocument33 pagesFabrication of Multipurpose 4 in 1 Agriculture Robotic Vehicleakshay gopal100% (1)
- ಕ ಫ ಾಂಶ ಂಬ -೨೦೧೯/ಜನವ -೨೦೨೦. Vtu Provisional Results Of Ug / Pg December-2019/January-2020 ExaminationDocument2 pagesಕ ಫ ಾಂಶ ಂಬ -೨೦೧೯/ಜನವ -೨೦೨೦. Vtu Provisional Results Of Ug / Pg December-2019/January-2020 Examinationakshay gopalNo ratings yet
- Tumble Dryer: en Installation and OperatingDocument36 pagesTumble Dryer: en Installation and Operatingakshay gopalNo ratings yet