Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloud Computing and Security Issues: June 2017
Uploaded by
praneshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloud Computing and Security Issues: June 2017
Uploaded by
praneshCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/317908867
Cloud Computing and Security Issues
Article · June 2017
DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138
CITATIONS READS
0 3,567
2 authors, including:
DHANAMMA SHANKAR JAGLI
Vivekanand Education Society's Institute of Technology
20 PUBLICATIONS 27 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
E-SaaS Cloud: Smart Service for Educational Institute View project
All content following this page was uploaded by DHANAMMA SHANKAR JAGLI on 30 January 2018.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS
Cloud Computing and Security Issues
Rohan Jathanna*, Dhanamma Jagli**
*(Department of Mca, VESIT, Mumbai
Email: rohan.jathanna@ves.ac.in)
** (Department of Mca, VESIT, Mumbai
Email: dsjagli.vesit@gmail.com )
ABSTRACT
Cloud computing has become one of the most interesting topics in the IT world today. Cloud model of
computing as a resource has changed the landscape of computing as it promises of increased greater reliability,
massive scalability, and decreased costs have attracted businesses and individuals alike. It adds capabilities to
Information Technology’s. Over the last few years, cloud computing has grown considerably in Information
Technology. As more and more information of individuals and companies are placed in the cloud, there is a
growing concern about the safety of information. Many Companies that are considered to be giants in software
industry like Microsoft are joining to develop Cloud services [1]. Despite the hype about the cloud, customers
are reluctant to deploy their business in the cloud. Security issues is one of the biggest concerns that has been
affecting the growth of cloud computing .It adds complications with data privacy and data protection continues
to affect the market. Users need to understand the risk of data breaches in the cloud environment. The paper
highlights issues related to cloud computing.
Keywords - Cloud computing, security Issue
Service (PaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). A
I. INTRODUCTION cloud service is used by clients as and when needed,
Software Developers describe Cloud in a usually on hourly basis. This pay as you go approach
different way than a System Administrator, while a has made the cloud flexible such that where end user
Database Administrator may have different can have services the way they desire at any point
definition. Cloud means a wide range of scalable of time and the cloud services is entirely monitored
services that users can access via an Internet by the provider. There are some of the basic security
connection. Providers like Microsoft, Amazon, threats that have exploited the usage of Cloud
Google and many more provide various cloud-based Computing. An example of security threat is botnets,
services for which users can pay on the basis of the use of botnets to spread spam and malware. Of
service subscription and consumption. Many the 761 data breaches investigated in 2010 by the
providers offer a wide range of Cloud services like U.S. Secret Service, almost 63% occurred at
Messaging, Social Computing, Storage, CRM, companies with 100 or fewer employees. And a
Identity management, Content Management etc. 2011 survey by security systems provider Symantec
Cloud computing is dependent on resource sharing. Corp. around 2,000 plus small and midsize
Using these internet enabled devices, cloud enterprises indicated that close to 73% had been
computing permits the function of application breached by a cyber-attack. One of the best features
software. Cloud computing is also known as the of cloud computing is pay-as-you-go model of
cloud. Cloud computing serves a wide range of computing as a resource. This model of computing
functions over the Internet like storage. Taking has enabled businesses and organizations in need of
advantage of resource sharing, cloud computing is computing power to purchase as many resources as
able to achieve consistency and economies of scale. they need without the need to put forth a large
Types of cloud computing can be classified on basis capital investment in the IT infrastructure. Other
of two models. Cloud computing service models and advantages of cloud computing are scalability and
cloud computing deployment models. It is a file increased flexibility for a relatively constant price.
backup shape. It also allows working on the same [2]. Cloud is the new trend in the evolution of the
document for several jobs of different types .Cloud distributed systems. The user does not need
computing simplifies usage by allowing overcoming knowledge or expertise to control the infrastructure
the limitations of traditional computer. Cloud of clouds, it provides abstraction. Cloud providers
computing also provides more agility because it deliver common online business applications which
allows faster access. These hosted services are are accessed from servers through web browser [3].
normally separated into three broad categories:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 31 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
II. CLOUD COMPUTING MODELS of private, public or community cloud that is bound
Cloud hosting deployment models are together but remain individual entities. Hybrid
classified by the proprietorship, size and access. It clouds are capable of crossing isolation and
tells about the nature of the cloud. Most of the overcoming boundaries by the provider; therefore, it
organizations are willing to implement cloud since it cannot be simply categorized into public, private or
reduces the expenditure and controls cost of community cloud. It allows the user to increase the
operation capacity as well as the capability by assimilation,
aggregation and customization with another cloud
2.1Cloud computing deployment models package / service. In a hybrid cloud, the resources
2.1.1 Public Cloud are managed either in-house or by external
It is a type of cloud hosting in which the providers. It is an adaptation between two platforms
cloud services are delivered over a network that is in which the workload exchanges between the
open for public usage. This model is actually true private cloud and the public cloud as per the needs
representation of cloud hosting. In this the cloud and demand of organization. Resources which are
model service provider provides services and non-critical like development and test workloads can
infrastructure to various clients. Customers do not be housed in the public cloud that belongs to a third-
have any control over the location of the party provider. While the workloads that are critical
infrastructure. There may be very little or no or sensitive should be housed internally.
difference between public and private clouds Organizations may use the hybrid cloud model for
structural design except the level of security that are processing big data. Hybrid cloud hosting has
offered for various services given to the public cloud features like scalability, flexibility and security.
subscribers by the cloud hosting providers. Public
cloud is suited for business which require managing 2.1.4 Community Cloud
load. Due to the decreasing capital overheads and It is a type of cloud hosting in which the
operational cost the public cloud model is setup is mutually shared between a lot of
economical. Dealers may provide the free service or organizations which belong to a particular
license policy like pay per user. The cost is shared community like banks and trading firms. It is a
by all the users in public cloud. It profits the multi-tenant setup that is shared among many
customers by achieving economies of scale. Public organizations that belong to a group which has
cloud facilities may be available for free an e.g. of a similar computing apprehensions. Theses
public cloud is Google. community members usually share similar
performance and security concerns. The main
2.1.2 Private Cloud intention of the communities is to achieve business
It is also known as internal cloud. This related objectives. Community cloud can be
platform for cloud computing is implemented on managed internally or can be managed by third party
cloud-based secure environment and it is providers and hosted externally or internally. The
safeguarded by a firewall which is governed by the cost is shared by specific organizations within the
IT department that belongs to a particular corporate. community, therefore, community cloud has cost
Private cloud permits only the authorized users and saving capacity. Organizations have realized that
gives the organization greater control over their data. cloud hosting has a lot of potential. To be the best
The physical computers may be hosted internally or one must select the right type of cloud hosting
externally they provide the resources from a distinct Therefore, one need to know the business and
pool to the private cloud services. Businesses having analyze his/her demands. Once the appropriate type
unanticipated or dynamic needs, assignments which of cloud hosting is selected, one can achieve
are critical management demands and uptime business related goals easily.
requirements are better suited to adopt private cloud.
In private cloud there is no need for additional 2.2: Cloud computing service models
security regulations and bandwidth limitations that
can be present in a public cloud environment.
Clients and Cloud providers have control of the
infrastructure and improved security, since user’s
access and the networks used are restricted. One of
the best examples is Eucalyptus Systems [4].
2.1.3 Hybrid Cloud
It is a type of cloud computing, which is
integrated. It could constitute an arrangement of two
or more cloud servers, i.e. either of the combination
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 32 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
2.2.1: Software as a Service (SaaS) III. SECURITY ISSUES
Software as a Service (SaaS) is growing Cloud service models not only provide
rapidly. SaaS makes uses the web to provide different types of services to users but they also
applications which are managed by a third-party reveal information which adds to security issues and
vendor and whose interface is accessed on the client risks of cloud computing systems. IaaS which is
side. SaaS applications can be run from a web located in the bottom layer, which directly provides
browser without the need to download or the most powerful functionality of an entire cloud.
installation, but these require plugins. The cloud IaaS also enables hackers to perform attacks, e.g.
provider provides the consumer with the ability to brute-forcing cracking, that need high computing
deploy an application on a cloud infrastructure power. Multiple virtual machines are supported by
[5].Because of this web delivery model SaaS IaaS, gives an ideal platform for hackers to launch
removes the need to install and run applications on attacks that require a large number of attacking
individual computers. In this model it is easy for instances. Loss of data is another security risk of
enterprises to improve their maintenance and cloud models.
support, because everything can be managed by Data in cloud models can be easily
vendors: applications, runtime, data, middleware, accessed by unauthorized internal employees, as
OS, virtualization, servers, storage and networking. well as external hackers. The internal employees can
Popular SaaS services include email and easily access data intentionally or accidently.
collaboration, healthcare-related application. SaaS External hackers may gain access to databases in
providers usually offer browser-based interfaces. such environments using hacking techniques like
APIs are also normally made available for session hijacking and network channel
developers. The key benefit of SaaS is that it eavesdropping. Virus and Trojan can be uploaded to
requires no advance investment in servers or cloud systems and can cause damage [6].It is
licensing of software. The application developer, important to identify the possible cloud threats in
have to maintain one application for multiple clients. order to implement a system which has better
security mechanisms to protect cloud computing
2.2.2: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) environments.
Infrastructure as a Service, are used for monitoring,
and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, 3.1Threats in cloud computing
such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, 3.1.1Compromised credentials and broken
Users can purchase IaaS based on consumption, authentication
similar to other utility billing. IaaS users have the Organizations/companies at times struggle
responsibility to be in charge applications, data, with identity management as they try to grant
runtime and middleware.. Providers can still manage permissions appropriate to the user’s job role. They
virtualization, servers, storage, and networking. IaaS sometimes forget to remove user access when a job
providers offer databases, messaging queues, and function changes or a user leaves the organization.
other services above the virtualization layer as well. The Anthem breach exposed more than 80 million
customer records, was the result of stolen user
2.2.3: Platform as a Service (PaaS) credentials. Anthem had failed to deploy multifactor
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a kind of authentication, so when the attackers obtained the
cloud computing services that provides a platform credentials, it was all over. Many deSvelopers have
that allows customers to develop, run, and manage made the mistake of embedding credentials and
applications without the problem of building and cryptographic keys in source code and have them in
maintaining the infrastructure. One need not be public-facing repositories [7].
bothered about lower level elements of
Infrastructure, Network Topology, Security all this is 3.1.2Data breaches
done for you by the Cloud Service Provider. With Cloud environments face many of the same
this technology, third-party providers can manage threats as traditional corporate networks, but since a
OS, virtualization, and the PaaS software itself. large amount of data is stored on cloud servers,
Developers manage the applications. Applications providers have become an attractive target. The
using PaaS inherit cloud characteristic such as severity of the damage tends to depend on the
scalability, multi-tenancy, SaaS enablement, high- sensitivity of the data that is exposed. Personal
availability and more. Enterprises benefit from this financial information grabs the headlines, but
model because it reduces the amount of coding, breaches involving government information, trade
automates business policy, and help in migrating secrets can be more devastating. When a data breach
applications to hybrid model. takes place, a company may be subjected to legal
action. Breach investigations and customer
notifications can rack up significant costs. Indirect
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 33 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
effects may include brand damage and loss of customer may encrypt data before uploading it on
business can impact organizations future for years. the cloud, then that customer has to be careful to
protect the encryption key. If the key is lost then the
3.1.3Hacked interfaces and APIs data will also be lost. Compliance policies many a
Today every cloud service and application times specify how long organizations must retain
now offers APIs. IT teams use these interfaces and records of audit and other documents. Losing such
APIs to manage and interact with cloud services, sensitive data may have serious consequences.
including those that offer cloud provisioning,
management and monitoring. The security and 3.1.7 Inadequate diligence
availability of cloud services depend on the security Organizations accepting cloud computing
of the API. Risk is increased with third parties who without having complete understanding of the
rely on APIs and build on these interfaces, as environment and risks associated with it may
organizations may need to expose more services and encounter a great number of commercial, financial,
credentials. APIs and Weak interfaces may expose technical, legal, and compliance risks. Diligence is
organizations to security related issues such as needed whether the organization is trying to migrate
confidentiality, accountability, availability APIs and to the cloud or merging with another company in the
interfaces are the very much exposed part of the cloud. For example, organizations that fail to
system because they can be accessed from open examine a contract may not be aware of the
Internet [7]. provider’s liability in case of data loss or breach.
Operational and architectural issues could arise if an
3.1.4 Exploited system vulnerabilities organization development team isn’t familiar with
Vulnerabilities in system, exploitable bugs cloud technologies as apps are deployed to a
in programs have become a bigger problem with the particular cloud. An organization should do adequate
advent of multitenancy in cloud computing. research before moving to cloud computing because
Organizations share memory, databases and of the risk associated with it [7].
resources in close proximity to one another, creating
new attack surfaces. The costs of mitigating system 3.1.8 Cloud service abuses
vulnerabilities are relatively small compared to other Cloud services may be used to support
IT expenditures. The expense of putting IT processes activities like using cloud computing resources to
in place to find and repair vulnerabilities is small break an encryption key in order to launch an attack.
when compared to the potential damage. Examples of these attacks include launching DDoS
attacks, sending spam and phishing emails.
3.1.5 Account hijacking Providers need to recognize kind of abuse to
Phishing, fraud, and software exploits are recognize DDoS attacks and offer tools for
highly prevalent today, and cloud services add a new customers to monitor the health of their cloud
dimension to the threat because attackers can environments. Customers should make sure that
eavesdrop on activities, manipulate transactions, and providers offer them a mechanism for reporting
modify data. Attackers may be able to use the cloud abuse. Even though customers may not be direct
application to launch other attacks. Organizations prey for malicious actions, cloud service abuse can
must prohibit sharing of account credentials between still result in unavailability of service and data loss
users and services and must enable multifactor [7].
authentication schemes where available. Accounts,
must be monitored so that every transaction should 3.1.9 DoS attacks
be traced to a human owner. The key is to protect DoS attacks have been around for a long
account credentials from being stolen [7]. time and have gained prominence again thanks to
cloud computing because they often affect
3.1.6 Permanent data loss availability. Systems may run slow or simply time
Hackers have in the past have permanently out. These DoS attacks consume large amounts of
deleted data from cloud to cause harm businesses processing power, a bill the customer may ultimately
and cloud data centers are as vulnerable to natural have to pay. High-volume DDoS attacks are very
disasters as any facility. Cloud providers may common, but organizations should also be aware of
recommend distributing applications and data across asymmetric and application-level DoS attacks,
multiple zones for better protection. Adequate data which target Web server and database
backup measures and disaster recovery are very vulnerabilities. Cloud providers are better poised to
important. Daily data backup and off-site storage are handle DoS attacks than their customers. The key
very important with use of cloud environments. The here is to have a plan to mitigate the attack before it
burden of preventing data loss is not only of cloud occurs, so administrators have access to those
service provider, but also of data provider. A resources when they need them.
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 34 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
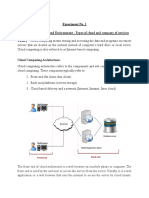
The table below shows represents the schematic the server virtualization increases, an extremely
diagram showing the hierarchy of the cloud difficult problem with backup and storage is created
computing with security challenges on both the [12]. Data de-duplication is one of the solutions to
cloud computing models: Deployment and Service reduce backup and offline storage volumes.
models
4.1.3Service hijacking
Service hijacking is means gaining illegal
control on certain authorized services by
unauthorized users. It can be through various
techniques like phishing, exploitation of software
and fraud. This is as one of the threats. Account
Hijacking has been pointed as one of the most
serious threats [13]. The chances of hijacking
account are incredibly high as no native
4.1.4VM Hopping
The attacker can check the victim/users
VM’s resource procedure, alter the configurations
and can even delete stored data which may be
sensitive, therefore, putting it in danger the VM’s
confidentiality, integrity, and availability. A
requirement for this type of attack is that the two
VMs must be operating on the same host, and the
attacker must be able to recognize the victim VM’s
IP address. Though PaaS and IaaS users have partial
authority, an attacker may get hold of or decide the
IP address using benchmark customer capabilities by
IV. SECURITY CHALLENGES OF using various tricks and combinational inputs to
CLOUD MODEL fetch user’s IP. Thus it can be said that VM hopping
is a rational threat in cloud computing.
4.1SECURITY CHALLENGES OF SERVICE
MODEL
4.1.1Malicious attacks 4.2 Security challenges of deployment model
Security threats can occur from both 4.2.1Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) security issues
outside of and within organizations. According to PaaS allows deployment of cloud-based applications
the 2011 Cyber Security Watch Survey 21% of without the cost of buying and maintaining the
cyber-attacks were caused by insiders. 33% of the underlying hardware and software layers [14]. PaaS
respondents thought the insider attacks were more depends on a secure and reliable network. PaaS
costly and damaging to organizations. Generally, application security constitutes two software layers:
inside attacks were unauthorized access to and use of Security of the PaaS platform itself and Security of
corporate information (63 %), and theft of customer applications deployed on a PaaS platform.
intellectual property (32%). Malicious users can gain
access to certain sensitive data and thus leading to 4.2.2Third-party relationships
data breaches. Farad Sabah [11] has shown PaaS along with traditional programming
malicious attacks by the unauthorized users on the languages also offers third-party web services
victim’s IP address and physical server. The components such as mashups [15]. Mashups can
malicious agenda can vary from data theft to combine more than one source element into a single
revenge. In a cloud scenario, an insider can destroy integrated unit. Therefore PaaS models have security
whole infrastructures or manipulate or steal data. issues which are related to mashups [16]. PaaS
Systems that depend solely on the cloud service users are dependent on both the security of web-
provider for security are at greatest risk. hosted development tools and third-party services.
4.1.2 Backup and Storage 4.2.3Development Life Cycle
The cloud vendor should ensure that regular From the point of view of the application
backup of data is implemented that even ensure development, developers may face the complexity of
security with all measures. But the backup data is building secure applications that may be hosted in
generally found in unencrypted form which can lead the cloud. The speed at which applications change in
to misuse of the data by unauthorized people. Thus the cloud will affect both the security and System
data backups lead to various security threats. More Development Life Cycle (SDLC) [17]. Software
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 35 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
Developers have to keep in mind that PaaS 4.5 Authentication and Identity Management
applications must be upgraded frequently hence they With the use of cloud, a user is facilitated to
have to make sure that their application development access private data and makes it available to various
processes are flexible enough to keep up with services across the network. Identity management
changes. However, software developers should helps in authenticating the users through their
understand that any change in PaaS components can credentials. A key issue, concerned with Identity
compromise the security of the applications. Other Management (IDM), is its disadvantage of
than secure development techniques, developers interoperability resulting from different identity
need to be educated and informed about data legal tokens and identity negotiation protocols as well as
issues as well, so that data is not stored in the architectural pattern [20].
inappropriate locations. Data may be stored in
different places with different legal regimes that can 4.6Network Issues:
include its privacy and security. Cloud computing relies on internet and
remote computers so that it can maintain data for
4.2.4 Underlying infrastructure security running various applications. This network is used to
In PaaS, software developers do not upload all information. H.B. Tabakki [21] has stated
normally have access to the underlying layers, so security issues with network on cloud as a prime
providers are therefore responsible for securing the focus. It provides virtual resources, high bandwidth
underlying infrastructure and the applications and software to the consumers on demand. In reality,
services. Even if developers are in control of the the network structure of this cloud is vulnerable to
security, they do not have the assurance that the various attacks and security issues like cloud
development environment tools provided by a PaaS malware injection attack, browser security issues,
provider are secure. flooding attacks, locks-in, incomplete data deletion,
data protection and XML signature element
4.3 Cloning and Resource Pooling wrapping.
Cloning means with replicating or
duplicating the data.. Cloning can lead to data 4.6.1XML Signature Element Wrapping
leakage problems which reveal the machine’s It is a very renowned web service attack.
authenticity. While Wayne A. Pauley [18] describes This protects identity value and host name from
resource pooling as a service provided to the users illegal party but cannot protect the position in the
by the provider to use various resources and share documents [22]. The attacker targets the host
the same according to their application demand. computer by sending SOAP messages and putting
Resource Pooling means unauthorized access due to scrambled data which the user of the host computer
sharing through the same network. Studies on will not understand. The XML Signature wrapping
Virtual and Cloud Computing by researchers state attack changes the content of the signed part of a
that a Virtual Machine can quite easily be message and does not tamper the signature. This
provisioned, they can also be inversed to previous would not let the user to understand.
cases, paused and easily restarted and migrated
between two servers, leading to non-auditable 4.6.2 Browser Security
security threats Client uses browser to send the information
on network. These browsers use SSL technology to
4.4Unencrypted Data encrypt user’s identity and credentials. But hackers
Data encryption is a process that helps to from the intermediary host may obtain these
solve various external and malicious threats. credentials by using sniffing packages installed on
Unencrypted data is very vulnerable for susceptible the intermediary host. One should have a single
data, as it does not provide any security mechanism. identity but this credential must allow different
Unencrypted data can very easily be accessed by levels of assurance which can be achieved by
unauthorized users. Unencrypted data risks the user obtaining approvals digitally.
data which leads to cloud server to escape various
data information to unauthorized users [19]. For 4.6.3Flooding Attacks
example, the famous file sharing service Drop box In this type of attack the invader sends large
was accused for using a single encryption key for all number of requests for resources on the cloud
user data the company stored. These unencrypted, rapidly so that the cloud gets flooded with the large
insecure data encourage the malicious users to number of requests. As per the study carried out by
misuse the data one or the other way. IBM [23] cloud has a property to expand on the
basis of amount of request. It will expand in so that
it fulfills the requests of invader making the
resources inaccessible for the normal users.
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 36 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
4.6.4SQL Injection Attack the attack. Malware was found to be the culprit
These attacks are known to be malicious act creating havoc on Sony's network. While malware
on the cloud computing in which a malicious code is protection is important and could have certainly
inserted into a SQL code. This attack allows the limited the destruction, it is crucial to have a better
invader to gain unauthorized access to a database understanding of what is taking place on a network
and to other confidential information. SQL injection with in-depth network security intelligence. Network
can be used to attack any type of SQL database. The monitoring can alert businesses in the event of an
reason that SQL injection and other exploits are intrusion, but these alerts are of no use if businesses
possible is because security is insufficiently overlook threats. Cloud was not the issue for the
emphasized in development. Sony hack; it was improper network security
. precautions that ultimately affected the company.
V. REAL LIFE EXAMPLES
5.1 Target: OTHER CASES
Target security breach leaked Google had a big failure in 2011, involving
approximately 70 million customer’s credit card the deletion of around 150,000 Gmail user’s emails,
information during 2013. Similar to iCloud, Target's contact and other information. Google claimed it
network breach revealed that it had many holes in was caused due to a software upgrade which resulted
the company's security strategy. The Target hack unexpected consequences. It took Google around
was the result of access to network via an HVAC four days to completely restore data of the impacted
contractor monitoring store climate systems, so once users, which is quite a long time, given that Google
the Target system was breached, the hackers simply claimed this as impacting less than 1% of its
uploaded a grabber program to mirror payment data accounts. The Microsoft Business Productivity
to Target server which was unused. Hackers Online Suite was reportedly hit with a data breach in
accessed the payment stream -- plump with holiday 2010, customers of BPOS cloud service could
shopper’s information -- for two months. Target download information on other customers of the
faced losses of $400 million -- plus a great deal of suite though inadvertently. The technology giant
customer trust. It cost CEO his jobs. Hackers had claimed it had resolved the issue within couple of
gained access to Target's network for close two hours of its discovery, and claimed only a few
weeks in 2013. Target has now taken measures to customers were involved.
plug any security holes, but the intrusion could have
been avoided. An intrusion detection package had VI. CONCLUSION
warned of this attack on multiple occasions, but Cloud Computing is a new concept that
those warnings were ignored. presents quite a number of benefits for its users. But
it also raises some security problems which may
5.2Home Depot affect its usage. Understanding about the
More than 56 million credit or debit cards vulnerabilities existing in Cloud Computing will
and approximately 53 million emails compromised, help organizations to make the shift towards using
this damage was even more severe from Home the Cloud. Since Cloud Computing leverages many
Depot's attack. A malware accessed a POS system technologies and it also inherits their security issues.
that gave hackers entry into to Home Depot's Traditional web applications, virtualizations have
systems over nearly a six month period. Hackers been looked over but some of the solutions offered
used a third-party vendor's user name and password by cloud are immature or inexistent. We have
to gain access Home Depot's network. The stolen presented security issues for cloud models: IaaS,
information about credentials provided direct access PaaS, and IaaS, which differ depending on the
to the organizations point-of-sale devices, hackers model. As described in this paper, storage and
then acquired greater rights that allowed them to networks are the biggest security concerns in Cloud
navigate portions of Home Depot's network and to Computing. Virtualization that allows multiple users
deploy custom-built malware on its self-checkout to share a physical server is a major concerns for
systems in the US and Canada. These files did not cloud users.. Virtual networks are target for some
contain passwords or other sensitive information, but attacks. We have focused on this distinction, where
phishing scams are a real danger we consider important to understand these issues.
Another core element of cloud computing is
5.3Sony multitenancy.
Hackers, who referred to themselves as the
Guardians of Peace, got access to data ranging from ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
employee information to email’s and unreleased We thank all the people who have contributed
films. In addition to this hackers destroyed many of towards development of our research.
Sony's computers and many of its servers following .
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 37 | P a g e
Rohan Jathanna. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application www.ijera.com
ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 7, Issue 6, ( Part -5) June 2017, pp.31-38
REFERENCES Computer Science and Engineering, ISSN:
[1]. Mohamed Magdy Mosbah, “Current 0975-3397, Vol. 3 No. 3 March 2011, pp:
Services in Cloud Computing: A Survey ,” 1227 – 1231.
International Journal of Computer Science, [14]. Subashini S, Kavitha V: A survey on
Engineering and Information Technology Security issues in service delivery models
(IJCSEIT), Vol.3,No.5,October 2013 of Cloud Computing. J Netw Comput Appl
[2]. Armbrust, M. et. al., (2009), “Above the 2011, 34(1):1–11.
clouds: A Berkeley view of Cloud 10.1016/j.jnca.2010.07.006.
Computing”, UC Berkeley EECS, Feb [15]. Mather T, Kumaraswamy S, Latif S: Cloud
2010. Security and Privacy. Sebastopol, CA:
[3]. Lizhe Wang, Jie Tao, Kunze M., O’Reilly Media, Inc.; 2009.
Castellanos A.C., Kramer D., Karl W., [16]. Keene C: The Keene View on Cloud
“Scientific Cloud Computing: Early Computing. 2009.
Definition and Experience,” 10th IEEE Int. [17]. Rittinghouse JW, Ransome JF: Security in
Conference on High Performance the Cloud. In Cloud Computing.
Computing and Communications, pp. 825- Implementation, Management, and
830, Dalian, China, Sep. 2008, ISBN: 978- Security, CRC Press; 2009.
0-7695-3352-0. [18]. Wayne A. Pauley, “Cloud Provider
[4]. B. R. Kandukuri, R. Paturi V, A. Rakshit, Transparency – An empirical evaluation”,
“Cloud Security Issues”, In Proceedings of the IEEE computer and reliability societies,
IEEE International Conference on Services IEEE, November 2010, pp: 32 – 39.
Computing, pp. 517-520, 2009 [19]. Cong Wang, Ning Cao, Kui Ren, Wenjing
[5]. National Institute of Standards and Lou, “Enabling Secure and Efficient
Technology, NIST Definition of Cloud Ranked Keyword Search over Outsourced
Computing, Sept 2011. Cloud Data”, IEEE transactions on parallel
[6]. D. Jamil and H. Zaki, “Security Issues in and distributed systems, IEEE, Digital
Cloud Computing and Countermeasures,” Object Indentifier 10.1109/TPDS.2011.282,
International 2011, pp: 1 – 14.
[7]. Journal of Engineering Science and [20]. Rosa Sánchez, Florina Almenares, Patricia
Technology, Vol. 3 No. 4, pp. 2672-2676, Arias, Daniel Díaz-Sánchez and Andrés
April 2011 Marín, “Enhancing Privacy and Dynamic
http://www.infoworld.com/article/3041078 Federationn IdM for Consumer Cloud
[8]. Rittinghouse JW, Ransome JF: Security in Computing”, IEEE Transactions on
the Cloud. In Cloud Computing. Consumer Electronics, Vol. 58, No. 1,
Implementation, Management, and February 2012, pp: 95 – 103.
Security, CRC Press; 2009. [21]. H. Takabi, J.B.D. Joshi, and G.-J. Ahn,
[9]. Garfinkel T, Rosenblum M: When virtual is “Secure Cloud: Towards a Comprehensive
harder than real: Security challenges in Security Framework for Cloud Computing
virtual machine based computing Environments,” Proc. 1st IEEE Int’l
environments. In Proceedings of the 10th Workshop Emerging Applications for
conference on Hot Topics in Operating Cloud Computing (CloudApp 2010), IEEE
Systems, Santa Fe, NM. volume 10. CA, CS Press, 2010, pp. 393– 398.
USA: USENIX Association Berkeley; [22]. Jamil, D., Zaki, H. “Security issues in cloud
2005:227–229. computing and counter measures”,
[10]. Morsy MA, Grundy J, Müller I: An International Journal of Engineering
analysis of the Cloud Computing Security Science and Technology (IJEST) , Vol. 3
problem. In Proceedings of APSEC 2010 No. 4, pp: 2672-2676.
Cloud Workshop. Sydney, Australia: [23]. Web 2.0/SaaS Security, Tokyo Research
APSEC; 2010. Laboratory, IBM Research.
[11]. Farzad Sabahi, “Cloud Computing Security http://www.trl.ibm.com/projects/web20sec/
Threats and Responses”, 978-1-61284-486- web20sec_e.htm
2, IEEE, 2011, pp: 245 – 249.
[12]. Intel IT Center, “Preparing your Virtualized
Data Center for the Cloud”, pp: 1 – 20
[13]. Rajnish Choubey, Rajshree Dubey, Joy
Bhattacharjee, “A Survey on Cloud
Computing Security, Challenges and
Threats”, International Journal on
www.ijera.com DOI: 10.9790/9622-0706053138 38 | P a g e
View publication stats
You might also like
- Cloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeFrom EverandCloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNo ratings yet
- Data Security in Cloud Oriented Application Using SSL/TLS ProtocolDocument7 pagesData Security in Cloud Oriented Application Using SSL/TLS ProtocolInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDocument17 pagesCloud Computing IntroductionSheshankNo ratings yet
- Differences between private and public cloudDocument6 pagesDifferences between private and public cloudAbhishek RaviNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Cloud Deployment and Service Delivery Models: February 2011Document5 pagesExploring The Cloud Deployment and Service Delivery Models: February 2011Dwdroo DiwokNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Data Security and Privacy in Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesReview Article: Data Security and Privacy in Cloud Computingsagar sagNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Cloud ComputingDocument26 pagesAssignment - Cloud ComputingBiju PoudelNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing PPT 2Document22 pagesCloud Computing PPT 2Maira SohailNo ratings yet
- Ijet V4i3p33 PDFDocument10 pagesIjet V4i3p33 PDFInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Types of Cloud Services: Student - Feedback@sti - EduDocument3 pagesCloud Computing Types of Cloud Services: Student - Feedback@sti - EduEricka JanelleNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesCloud ComputingManal FaluojiNo ratings yet
- Ijettcs 2012 12 21 048Document4 pagesIjettcs 2012 12 21 048International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- unit 3 newDocument24 pagesunit 3 newakramshaik2004No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Research Activities and ChallengesDocument9 pagesCloud Computing: Research Activities and ChallengesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- assg 7Document8 pagesassg 7bhalaninaman7No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Cloud Computing Overview RKSDocument22 pagesUnit 5 Cloud Computing Overview RKSmr yashNo ratings yet
- Cloud Billing Model: A Review: AbstractDocument4 pagesCloud Billing Model: A Review: AbstractManzoorNo ratings yet
- Jetir2211584 PDFDocument3 pagesJetir2211584 PDFpriyaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Cryptography in Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesA Review On Cryptography in Cloud ComputingYashil PatelNo ratings yet
- Innovative Intelligence Over The Internet - "The Cloud"Document3 pagesInnovative Intelligence Over The Internet - "The Cloud"MYTHILI RAMESHNo ratings yet
- B0501 02-0812 PDFDocument5 pagesB0501 02-0812 PDFIJMERNo ratings yet
- Shri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiDocument19 pagesShri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiAaqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesIntroduction of Cloud ComputinggeetsainisNo ratings yet
- Real World Challenges of Cloud ComputingDocument23 pagesReal World Challenges of Cloud ComputingVarsha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Use of Cryptography in Cloud Computing: November 2013Document7 pagesUse of Cryptography in Cloud Computing: November 2013Ashish jangid CS-A 19EARCS026No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: On-Demand Access to Shared Computing ResourcesDocument8 pagesCloud Computing: On-Demand Access to Shared Computing ResourcesMUTHIREDDY ASHWITHANo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Security Issues and Challenges: Pranita P. Khairnar, Prof. V.S. UbaleDocument13 pagesCloud Computing Security Issues and Challenges: Pranita P. Khairnar, Prof. V.S. Ubalewww.irjes.comNo ratings yet
- Use of Cryptography in Cloud Computing: November 2013Document7 pagesUse of Cryptography in Cloud Computing: November 2013Ashish jangid CS-A 19EARCS026No ratings yet
- Backpack MergedDocument410 pagesBackpack MergedNEELIM SAHARIAHNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing A Review PaperDocument6 pagesCloud Computing A Review PaperIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document45 pagesChapter 1Mandara ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Types and ModelsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Types and ModelsDivyasriNo ratings yet
- The Management of Security in Cloud Computing: September 2010Document8 pagesThe Management of Security in Cloud Computing: September 2010Fernando SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Keyword Specific Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesKeyword Specific Cloud ComputingIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Enterprise-level benefits achieved from Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesEnterprise-level benefits achieved from Cloud ComputingMis MaliNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Data Breach Challenges in Cloud Computing Security: Issues and ThreatsDocument8 pagesA Survey On Data Breach Challenges in Cloud Computing Security: Issues and ThreatsDr StrangeNo ratings yet
- Secure Data Storage Approach for Cloud EnvironmentsDocument4 pagesSecure Data Storage Approach for Cloud EnvironmentsPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Cloud AtmDocument26 pagesCloud AtmNagesh LakshminarayanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing JUNE 2022Document12 pagesCloud Computing JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Cloud Deployment Models Service Models and Cloud ArchitectureDocument19 pagesCloud Deployment Models Service Models and Cloud ArchitectureTech MateNo ratings yet
- CC Lab 1 Roll No. 10Document15 pagesCC Lab 1 Roll No. 10Revathi DusaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesCloud Computingshariful islamNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing' - Scenarios and The Concerned IssuesDocument9 pagesCloud Computing' - Scenarios and The Concerned IssuesArunNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Platform and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesCloud Computing - Platform and ApplicationsIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Cse PDF Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesCse PDF Cloud Computingshivani.cs1995No ratings yet
- Business Implementation of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesBusiness Implementation of Cloud ComputingQuaid Johar SodawalaNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Cloud Computing and Mobile Cloud Computing: Kusum Lata, Sugandha SharmaDocument5 pagesA Survey On Cloud Computing and Mobile Cloud Computing: Kusum Lata, Sugandha SharmaArthee PandiNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Cloud Security using Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECCDocument5 pagesEnhancing Cloud Security using Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECCNati ManNo ratings yet
- Is Cloud Computing Finally Beginning To Mature?Document4 pagesIs Cloud Computing Finally Beginning To Mature?Hengky CungNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingmadhavNo ratings yet
- Use of Cryptography in Cloud Computing: November 2013Document7 pagesUse of Cryptography in Cloud Computing: November 2013E-533 Kangane machhidranath subhashNo ratings yet
- Cloud Os and Security Protocols: AbstractDocument4 pagesCloud Os and Security Protocols: Abstractnirmala velumaniNo ratings yet
- Clod Cryptography 1Document7 pagesClod Cryptography 1Garima PariharNo ratings yet
- Practical For MCA ProgramDocument17 pagesPractical For MCA ProgramDevendra Kumar Chandrabahadur YadavNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security ChallangeDocument5 pagesCloud Security ChallangeAdil RashidNo ratings yet
- I Jsa It 01222013Document9 pagesI Jsa It 01222013warse1No ratings yet
- A Survey On Data Security in Cloud Computing Issues and Mitigation TechniquesDocument5 pagesA Survey On Data Security in Cloud Computing Issues and Mitigation TechniquesInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Opportunities For The Cloud in The Enterprise: Sam SomashekarDocument16 pagesOpportunities For The Cloud in The Enterprise: Sam Somashekarsvnbadrinath8335No ratings yet
- Rsa SecurityDocument6 pagesRsa SecuritySumana SikdarNo ratings yet
- Library Management System: 1) IntroductionDocument13 pagesLibrary Management System: 1) IntroductionpraneshNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2: 1) Explain Classification With Logistic Regression and Sigmoid FunctionDocument6 pagesAssignment-2: 1) Explain Classification With Logistic Regression and Sigmoid FunctionpraneshNo ratings yet
- Impact Ready Analytics: Google Data StudioDocument6 pagesImpact Ready Analytics: Google Data Studiopranesh100% (1)
- Assignment 1: Aim-To Draw The Different Icons Using Figma ToolDocument1 pageAssignment 1: Aim-To Draw The Different Icons Using Figma ToolpraneshNo ratings yet
- College Library ManagementDocument73 pagesCollege Library ManagementTashongedzwa DhliwayoNo ratings yet
- Plan Each Day With Purpose and Action.: A Higher Degree of PurposeDocument2 pagesPlan Each Day With Purpose and Action.: A Higher Degree of PurposepraneshNo ratings yet
- ChildstoreyDocument1 pageChildstoreypraneshNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: 1. Title of The Project: 2. Objective of The ProjectDocument2 pagesSynopsis: 1. Title of The Project: 2. Objective of The ProjectpraneshNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: 1. Title of The Project: 2. Objective of The ProjectDocument2 pagesSynopsis: 1. Title of The Project: 2. Objective of The ProjectpraneshNo ratings yet
- StoreyDocument2 pagesStoreypraneshNo ratings yet
- CampusDocument3 pagesCampuspraneshNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: 1. Title of The Project: 2. Objective of The ProjectDocument2 pagesSynopsis: 1. Title of The Project: 2. Objective of The ProjectpraneshNo ratings yet
- BBS en 2015 02 Dzomira PDFDocument9 pagesBBS en 2015 02 Dzomira PDFobiad83No ratings yet
- Different Types of Computer VirusesDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of Computer Virusesrohanr18No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Computer Software - SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Computer Software - SummaryNyana4395No ratings yet
- CyberSecurity UNIT 2Document5 pagesCyberSecurity UNIT 2shivamvr371No ratings yet
- Cisco Annual Cybersecurity Report 2018Document68 pagesCisco Annual Cybersecurity Report 2018Tanat TonguthaisriNo ratings yet
- How To Detect and Remove MalwareDocument8 pagesHow To Detect and Remove MalwareIruma 入間No ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Deteksi Malware Dengan Metode Hybrid Analysis Menggunakan Framework MobsfDocument11 pagesAnalisis Dan Deteksi Malware Dengan Metode Hybrid Analysis Menggunakan Framework MobsfAgung Tri LaksonoNo ratings yet
- CySA (CS0-001) Practice ExamDocument26 pagesCySA (CS0-001) Practice ExamJoker JrNo ratings yet
- Info Security Quiz 2Document4 pagesInfo Security Quiz 2asmal.saarahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 E-Commerce Security and Payment SystemsDocument8 pagesChapter 5 E-Commerce Security and Payment SystemsSivanathan KanistanNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Icons IconLibrary 19 August PublicDocument38 pagesFortinet Icons IconLibrary 19 August PublicburhanNo ratings yet
- Embedded Operating SystemsDocument3 pagesEmbedded Operating SystemsElisha Lois ManluluNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity HandbookDocument9 pagesCybersecurity HandbookseuNo ratings yet
- Annexes To The PSDSRC Final ReportDocument53 pagesAnnexes To The PSDSRC Final ReportNicholasFCheongNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Assingnment1 - Template (1) (1) - Copy 1 1Document19 pagesUnit 7 - Assingnment1 - Template (1) (1) - Copy 1 1JwsNo ratings yet
- A Study On Awareness of Cyber Crime and Security: Anupreet Kaur Mokha AbstractDocument6 pagesA Study On Awareness of Cyber Crime and Security: Anupreet Kaur Mokha AbstractJohn Lloyd ZaluagaNo ratings yet
- Sophos Endpoint DsnaDocument2 pagesSophos Endpoint DsnaKevin DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Resume IT ManagerDocument3 pagesResume IT ManagerImran Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Avira AntiVir Premium 10.0.0.603Document13 pagesAvira AntiVir Premium 10.0.0.603aksandaniNo ratings yet
- B GRADE 12 EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY Q3M1 LearnerDocument25 pagesB GRADE 12 EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY Q3M1 LearnerDanisse Casanova75% (8)
- Unit 4 Acquiring HostBased EvidenceDocument24 pagesUnit 4 Acquiring HostBased EvidenceBrain WasherNo ratings yet
- Emtech q1 Module FullDocument72 pagesEmtech q1 Module FullMarlyn GuiangNo ratings yet
- Final Examination QuestionsDocument6 pagesFinal Examination QuestionsCarlos Baul DavidNo ratings yet
- Essay Cohesion Coherence and Unity WorksheetDocument6 pagesEssay Cohesion Coherence and Unity WorksheetPhương VũNo ratings yet
- Doc. Tech. - Cylance - CylancePROTECT Admin Guide 2.1 Rev34Document226 pagesDoc. Tech. - Cylance - CylancePROTECT Admin Guide 2.1 Rev34etienne CuretNo ratings yet
- Instructions - YES ACTUALLY READ THEMDocument12 pagesInstructions - YES ACTUALLY READ THEMsandragNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crimes Guide: Types, Definitions and ExamplesDocument68 pagesCyber Crimes Guide: Types, Definitions and ExamplesMercy NamboNo ratings yet
- TitusElian SBACyberOps FGADTS2019 Batch2Document4 pagesTitusElian SBACyberOps FGADTS2019 Batch2Titus Elian50% (2)
- Gateprotect Gpa 250: Designed For Small EnterprisesDocument4 pagesGateprotect Gpa 250: Designed For Small EnterprisesfreakorioNo ratings yet
- Website: Vce To PDF Converter: Facebook: Twitter:: 220-1002.vceplus - Premium.Exam.82QDocument33 pagesWebsite: Vce To PDF Converter: Facebook: Twitter:: 220-1002.vceplus - Premium.Exam.82QArun kumarNo ratings yet