Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
DumaluOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheat Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
DumaluCopyright:
Available Formats
A.
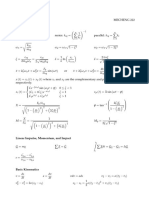
2 Semiconductor Equations
Semiconductor carrier concentrations
Thermal equilibrium
n = Nc e-(Ec-Ef)/kT = ni e(Ef-Ei)/kT p = Nv e-(Ef-Ev)/kT = ni e(Ei-Ef)/kT
2π me* kT 3/2 2π mh* kT 3/2
Nc = 2 [ ] Nv = 2 [ ]
h2 h2
1
n p = ni2 = NcNv e-Eg/kT f(E) =
1 + e(E-Ef)/kT
N -N (Nd-Na)2 N -N (Na-Nd)2
n= d a+ + ni2 p= a d+ + ni2
2 4 2 4
Not in thermal equilibrium
n = Nc e-(Ec-Fn)/kT = ni e(Fn-Ei)/kT p = Nv e-(Fp-Ev)/kT = ni e(Ei-Fp)/kT
p n = ni2 e(Fn-Fp)/kT= NcNv e(-Eg/2+Fn-Fp)/kT
Field, potential and energy
dφ dEc dEv dEi
q =-q = = = q = - q ∇ φ = ∇ Ec = ∇ Ev = ∇ Ei
dx dx dx dx
d ρ q ρ q
= = (p - n + Nd+ - Na-) ∇. = = (p - n + Nd+ - Na-)
dx εs εs εs εs
Q
⌠
⌡ dA = εs
Poisson's equation
∂2φ ∂2φ ∂2φ -ρ
∇2φ = + + =
∂x2 ∂y2 ∂z2 εs
1 ∂ ∂φ 1 ∂2φ ∂2φ -ρ
cylindrical coordinates: [r ] + 2 2 + 2 =
r ∂r ∂r r ∂θ ∂z εs
1 ∂ 2 ∂φ 1 ∂ 2 ∂φ 1 ∂2φ -ρ
spherical coordinates: 2 [r ]+ 2 [r sinθ ] + 2 =
r ∂r ∂r r sinθ ∂θ ∂θ r sinθ ∂ϕ2 εs
Current relations including drift and diffusion
Principles of Electronic Devices A2.1 © Bart J. Van Zeghbroeck 1996
∂n
Jn = q n µn + q Dn Jn = q n µn + q Dn ∇n Dn = µn Vt
∂x
∂p
Jp = q p µp - q Dp Jp = q p µp - q Dp ∇n Dp = µp Vt
∂x
Minority carrier rate (continuity) equations
∂np 1 ∂Jn ∂pn 1 ∂Jp
= + (Gn-Rn) =- + (Gp-Rp)
∂t q ∂x ∂t q ∂x
∂np 1 (n - n ) ∂pn 1 (p - p )
∇. p - p p0 + Gn
= ∇.J ∇. n - n n0 + Gp
= - ∇.J
∂t q τn ∂t q τp
Gn = Gp = generation due to light, avalanche multiplication, etcetera.
(np - np0) (pn - pn0)
Rn = Rp =
τn τp
Generation-Recombination equations
∂n ∂p P (x)
Gn = light = Gp = light = α q opt
∂t ∂t A Eph
Ub-b = b (np - ni2)
(pn - ni2) 1
USHR = , with = Nt vth σ
[n + p + 2 ni cosh((Ei-Et)/kT)] τ0 τ0
Us = s p' with s = Nst vth σ
UA = Γn n (np - ni2) + Γp p (np - ni2)
Diffusion equations
d2n np - np0
0 = Dn - , x < -xp , Dn = µn Vt
dx2 τn
d2p pn - pn0
0 = Dp - , x > xn , Dp = µp Vt
dx2 τp
(np - np0) (pn - pn0)
0 = Dn ∇2n - 0 = Dp ∇2p -
τn τp
Metal-semiconductor junction
Principles of Electronic Devices A2.2 © Bart J. Van Zeghbroeck 1996
1 q Nd xn2
φi - Va = ΦM - χ - (Ec - Efn) -Va = (n-type)
q 2εs
1 q Na xp2
φi - Va = χ + (Ec - Efp) - ΦM -Va = (p-type)
q 2εs
p-n junction relations (abrupt junction)
φi - Va = q Nd xn2/2εs + q Na xp2/2εs
max = q Nd xn/εs = q Na xp/εs
N N 2εs 1 1
φi = Vt ln( a 2 d) xd = ( + ) (φi-Va)
ni q Na Nd
2εs Na 1 2εs Nd 1
xn = (φ -V ) xp = (φ -V )
q Nd Na+Nd i a q Na Na+Nd i a
Dp Dn
J = J0 (eVa/Vt - 1), J0 = q ni2 ( + ) (ideal current for a short diode)
NdWn' NaWp'
np(-xp) = np0 eVa/Vt pn(-xn) = pn0 eVa/Vt
D p D n q x' ni V /2V
Jt = q ( p n0 + n p0 + xd ni2 b) (eVa/Vt - 1) + (e a t - 1)
Lp Ln 2τ0
Principles of Electronic Devices A2.3 © Bart J. Van Zeghbroeck 1996
BJT relations (npn with short emitter, base and collector)
IE = a11 (eVBE/Vt - 1) + a12 (eVBC/Vt - 1)
IC = a21 (eVBE/Vt - 1) + a22 (eVBC/Vt - 1)
where for short quasi-neutral regions (short compared to the diffusion length)
DE DB
a11 = -IES = - q A ni2 ( + )
NEwE NBwB
D
a12 = a21 = αF IES = αR ICS = - q A ni2 ( B )
NBwB
D DB
a22 = -ICS = - q A ni2 ( C + )
NCwC NBwB
1
α=
w N D
1+ B B E
wENEDB
wB2
αT = 1 -
2DBτB
q A ni2wB V /2V
IrB = (e BE t - 1)
2NBτB
Principles of Electronic Devices A2.4 © Bart J. Van Zeghbroeck 1996
Miscellaneous Fundamental Relations
F = Q ( + v x B) , Q = charge of the particle
dQ εs
C= =
dV xd
dv h dk
F = m* =
dt 2π dt
1 4π2 ∂2E
=
m* h2 ∂k2
2π ∂E
vg =
h ∂k
8π2 m*
∇2 Ψ + (E - V(x)) Ψ = 0
h2
ρ
∇2 φ = −
ε
Principles of Electronic Devices A2.5 © Bart J. Van Zeghbroeck 1996
You might also like
- App 02 PDFDocument5 pagesApp 02 PDFGalindo JoldanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- A.2 Semiconductor Equations Semiconductor Carrier ConcentrationsDocument5 pagesA.2 Semiconductor Equations Semiconductor Carrier ConcentrationsaqilatulfitriNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EDocument9 pagesWeek 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EInstituto Centro de Desenvolvimento da GestãoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Solar Cell FundamentalsDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Solar Cell FundamentalsZeina FarhatNo ratings yet
- 2011-02-Elliptic Functions - Fourier SeriesDocument4 pages2011-02-Elliptic Functions - Fourier Seriesdawson zhaoNo ratings yet
- Mcde S16Document30 pagesMcde S16puceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-L14Document22 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-L14LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis On Second Order Neutral Delay Difference EquationsDocument6 pagesQualitative Analysis On Second Order Neutral Delay Difference EquationsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument3 pagesSummaryKHÁNH NGÔ ĐÌNH BẢONo ratings yet
- Final FormulasDocument2 pagesFinal FormulasVoici101No ratings yet
- Qualifying Fall 202 0Document9 pagesQualifying Fall 202 0Saswata MandalNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Problem Set 1Document13 pagesSolutions To Problem Set 1Vinícius FernandoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-L18Document22 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-L18LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- List of FormulaDocument3 pagesList of FormulaaqaazNo ratings yet
- Est Bloque IIDocument2 pagesEst Bloque IIm4nu.k1r0No ratings yet
- STA222 Week7Document14 pagesSTA222 Week7Kimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Problem4 07Document3 pagesProblem4 07Fábio TakahashiNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series of Periodic Discrete-Time SignalsDocument36 pagesFourier Series of Periodic Discrete-Time SignalsBruce MarshallNo ratings yet
- Carrier Action II S16Document18 pagesCarrier Action II S16puceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Introductory Pages PDFDocument23 pagesIntroductory Pages PDFHitlar MamaNo ratings yet
- 03 PN JunctionsDocument25 pages03 PN Junctions陳浚維No ratings yet
- Chap7_part2(DFT)Document11 pagesChap7_part2(DFT)김민성No ratings yet
- Son2Document6 pagesSon2PUSHPA SAININo ratings yet
- ExpandedAppendixChapter12 PDFDocument4 pagesExpandedAppendixChapter12 PDFfunam2No ratings yet
- Quadratic ReciprocityDocument5 pagesQuadratic ReciprocityAntonio FangNo ratings yet
- STAT-1501-final-exam-formulae-December 2020Document1 pageSTAT-1501-final-exam-formulae-December 2020Huy DiecNo ratings yet
- IdealDiodeDiscussion S16Document19 pagesIdealDiodeDiscussion S16puceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Formulae Sheet - StatisticsDocument1 pageFormulae Sheet - StatisticsIshmael WoolooNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: MotionDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: MotionfarujoyNo ratings yet
- ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗDocument3 pagesΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗtrelofysikosNo ratings yet
- Some Useful DistributionsDocument19 pagesSome Useful DistributionsfaizazohraNo ratings yet
- Decimation in Frequency (DIF) FFT AlgorithmDocument9 pagesDecimation in Frequency (DIF) FFT AlgorithmGaag JssjNo ratings yet
- Formulario I ParcialDocument1 pageFormulario I Parcialseca cacaNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Properties and Linear ConvolutionDocument13 pagesFourier Transform Properties and Linear ConvolutionZenPhiNo ratings yet
- La Place 5Document1 pageLa Place 5api-3821702No ratings yet
- Lecture # 23: Subject No. PH11003 (Physics of Waves) Duration: 2 HRDocument14 pagesLecture # 23: Subject No. PH11003 (Physics of Waves) Duration: 2 HRdomagix470No ratings yet
- CH3 PDFDocument41 pagesCH3 PDFOliver PerezNo ratings yet
- EquationSheet TestB 2023Document2 pagesEquationSheet TestB 20231218doyoungNo ratings yet
- Coulombic Interaction in Magnetic Field: 1 Traditional Electronic SystemDocument5 pagesCoulombic Interaction in Magnetic Field: 1 Traditional Electronic SystemRaymond AdamsNo ratings yet
- Proof Mean and Variance of BINOMIAL and POSSIONDocument4 pagesProof Mean and Variance of BINOMIAL and POSSIONJia Yuan ChngNo ratings yet
- Fomulario Y Tablas: Istribuciones de Robabilidad Istribuci ONDocument3 pagesFomulario Y Tablas: Istribuciones de Robabilidad Istribuci ONSebastian SandovalNo ratings yet
- Panel method for constant potential (2DDocument4 pagesPanel method for constant potential (2Ddrkarimaa3791No ratings yet
- 02 DistributionsDocument19 pages02 DistributionsgpaswathyNo ratings yet
- Physics 4201 - 5Document36 pagesPhysics 4201 - 5fitchmicahNo ratings yet
- Unit II 1Document60 pagesUnit II 1dharanidec15No ratings yet
- Chap6 PDFDocument40 pagesChap6 PDFBouhafs AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Fizikos Vbe Pagrindinės FormulėsDocument2 pagesFizikos Vbe Pagrindinės FormulėsxGytis3xNo ratings yet
- 5 L L EC533: Digital Signal Processing: DFT and FFTDocument20 pages5 L L EC533: Digital Signal Processing: DFT and FFTDalia Abou El MaatyNo ratings yet
- 2011-11-Elementary Approach To Modular Equations - Ramanujans Theory 1Document7 pages2011-11-Elementary Approach To Modular Equations - Ramanujans Theory 1dawson zhaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 103 Even and Odd Functions and Half-Range Fourier SeriesDocument12 pagesChapter 103 Even and Odd Functions and Half-Range Fourier SeriesBaibhav MohantyNo ratings yet
- Lap Inv 4Document1 pageLap Inv 4api-3821702No ratings yet
- MATH4333 Solution To Homework 3Document4 pagesMATH4333 Solution To Homework 3John ChanNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: B, Where (A, B) Can Be (Or X (T)Document6 pagesDigital Signal Processing: B, Where (A, B) Can Be (Or X (T)Mrinal MitraNo ratings yet
- EF in n-type and p-type materials definedDocument4 pagesEF in n-type and p-type materials definedphambam90No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 2021Document1 pageFormula Sheet 2021goldduckieadNo ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Random Walks and Semiflexible Polymers Part (I) : StaticsDocument24 pagesLecture Notes On Random Walks and Semiflexible Polymers Part (I) : StaticsBJI ALUMNINo ratings yet
- Radial Functions and The Fourier Transform: 1 Area of A SphereDocument4 pagesRadial Functions and The Fourier Transform: 1 Area of A SphereLeonardo BossiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 PDFDumaluNo ratings yet
- Springer FlyerDocument1 pageSpringer FlyerDumaluNo ratings yet
- Lorex SpecsDocument5 pagesLorex SpecsDumaluNo ratings yet
- Lorex SpecsDocument5 pagesLorex SpecsDumaluNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Meixnerite (Mg-Al-OH) Type Layered Double Hydroxide by A Mechanochemical RouteDocument6 pagesPreparation of Meixnerite (Mg-Al-OH) Type Layered Double Hydroxide by A Mechanochemical RouteDAVID LUCAS LIMA BARROSONo ratings yet
- List of Chemical Compound FormulaDocument12 pagesList of Chemical Compound FormulaJuanmiguel Ocampo Dion SchpNo ratings yet
- The MOSFET TransistorDocument5 pagesThe MOSFET TransistorsamactrangNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride - English Units: Density, Composition and TCT of 94-97% Cacl Solutions in WaterDocument6 pagesCalcium Chloride - English Units: Density, Composition and TCT of 94-97% Cacl Solutions in WateraliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions-Semiconductor DevicesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions-Semiconductor DevicesGanesh Dhyani0% (1)
- Buku Saku Kimia Analisis DasarDocument13 pagesBuku Saku Kimia Analisis Dasarmarhamatul laiyinahNo ratings yet
- Local Salt Production Problems in East Flores RegencyDocument6 pagesLocal Salt Production Problems in East Flores RegencyTRI CAHYANI ANGGRAININo ratings yet
- CHAP 1 - Semiconductor Material-PADocument31 pagesCHAP 1 - Semiconductor Material-PAvisionNo ratings yet
- Semi 4 Final Prob Sol 5Document14 pagesSemi 4 Final Prob Sol 5steven88995100% (11)
- Introduction To Semiconductor: SemiconductorsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Semiconductor: SemiconductorsadeelNo ratings yet
- Application of SWE To H Like SystemDocument69 pagesApplication of SWE To H Like SystemDhanaswamy Ilangeswaran100% (1)
- Mate1000 Sln21aDocument3 pagesMate1000 Sln21aclearcastingNo ratings yet
- Drishti Physics Project Class 12Document24 pagesDrishti Physics Project Class 12madd4u63% (46)
- Balance The Equations Below:: Chapter 7 Worksheet #1 Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument4 pagesBalance The Equations Below:: Chapter 7 Worksheet #1 Balancing Chemical EquationsFe JanduganNo ratings yet
- Combustrion Sol Gel Ca3co4o9 Suhu 120 CDocument62 pagesCombustrion Sol Gel Ca3co4o9 Suhu 120 CkiraNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations WorksheetDocument4 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations WorksheetRajat SabharwalNo ratings yet
- UNdata - Export - Sri LankaDocument26 pagesUNdata - Export - Sri LankaVijendran SanthirasegaranNo ratings yet
- Working of Semiconductors: DefinitionDocument3 pagesWorking of Semiconductors: Definitionsonali soumyashreeNo ratings yet
- 3 Semiconductors and Insulators 1Document35 pages3 Semiconductors and Insulators 1Dam SonNo ratings yet
- The PN JunctionDocument65 pagesThe PN JunctionHosea MuchiriNo ratings yet
- 3.3 IV Characteristics of PN Junction Diode-ModifiedDocument18 pages3.3 IV Characteristics of PN Junction Diode-Modifiedraunak guptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ionic CompoundDocument12 pagesChemistry Ionic CompoundEden YokNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Semiconductors: Intrinsic vs ExtrinsicDocument2 pagesElectrical Properties of Semiconductors: Intrinsic vs ExtrinsicApril Wilson100% (1)
- Chem 104A Review Session Key ConceptsDocument28 pagesChem 104A Review Session Key ConceptsKate SongNo ratings yet
- Perspective: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Metal-Organic FrameworksDocument10 pagesPerspective: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Metal-Organic FrameworksHa HoangNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Semiconductor-03Document6 pagesModule 4 - Semiconductor-03srinidhiNo ratings yet
- Stark EffectDocument16 pagesStark EffectBharath Manchikodi100% (1)
- Chemical formulas and synonymsDocument30 pagesChemical formulas and synonymsMariaFrancescaBiancoSaenzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Exercises Problems Answers Silicon SemiconductorsDocument5 pagesChapter 5 Exercises Problems Answers Silicon SemiconductorsA Sibiescu100% (1)
- Atomic PhysicsDocument18 pagesAtomic PhysicsAnonymous ffLrUFNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)