Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inheritance Triple 2
Uploaded by
Vlad BratuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inheritance Triple 2
Uploaded by
Vlad BratuCopyright:
Available Formats
Read the information.
1
Insects can be both useful and harmful to crop plants.
Insects such as bees pollinate the flowers of some crop plants. Pollination is needed for
successful sexual reproduction of crop plants.
Some insects eat crops and other insects eat the insects that eat crops.
Corn borers are insects that eat maize plants.
A toxin produced by the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis kills insects.
Scientists grow Bacillus thuringiensis in large containers. The toxin is collected from the
containers and is sprayed over maize crops to kill corn borers.
A company has developed genetically modified (GM) maize plants. GM maize plants contain
a gene from Bacillus thuringiensis. This gene changes the GM maize plants so that they
produce the toxin.
(a) Describe how scientists can transfer the gene from Bacillus thuringiensis to maize plants.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
Rossett School Page 1 of 18
(b) Would you advise farmers to grow GM maize plants?
Justify your answer by giving advantages and disadvantages of growing GM maize plants.
Use the information from the box and your own knowledge to help you.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(Total 7 marks)
(a) Fossils provide evidence for what early life forms were like. From the evidence, scientists
2 think that life began on Earth more than 3 billion years ago.
Many early life forms were soft-bodied.
Explain why this makes it difficult for scientists to be certain about what these early life
forms were like.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
Rossett School Page 2 of 18
(b) The illustration below shows two types of pistol shrimp.
The shrimps live in shallow, tropical seas on opposite sides of Panama.
Panama
Not to scale
Scientists put one Type A shrimp and one Type B shrimp together in a tank of seawater.
The two types of shrimp snapped their claws aggressively at each other.
They did not mate.
The scientists said that this was evidence for the Type A and Type B shrimps being
classified as two different species.
(i) Give one reason why the scientists’ opinion may be correct.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(ii) Suggest two reasons why the scientists’ opinion may not be correct.
1. ____________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
2. ____________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(c) Panama is a narrow strip of land which today joins North America and South America.
It was formed by land moving up from beneath the sea. Panama has separated the Pacific
Ocean and the Caribbean Sea for the past 3 million years.
Rossett School Page 3 of 18
Explain how two different species of pistol shrimp could have developed from an ancestral
species of shrimp.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(6)
(Total 11 marks)
Rossett School Page 4 of 18
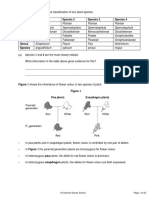
In 1866, Gregor Mendel published the results of his investigations into inheritance in garden pea
3 plants.
The diagram below shows the results Mendel obtained in one investigation with purple-flowered
and white-flowered pea plants.
(a) (i) Calculate the ratio of purple-flowered plants to white-flowered plants in the F2
generation.
Ratio of purple : white = ________________________
(1)
(ii) There was a total of 929 plants in the F2 generation.
Mendel thought that the production of a large number of offspring plants improved the
investigation.
Explain why.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
Rossett School Page 5 of 18
(b) (i) Some of the plants in the diagram are homozygous for flower colour and some are
heterozygous.
Complete the table to show whether each of the plants is homozygous or
heterozygous. For each plant, tick ( ) one box.
Homozygous Heterozygous
Purple-flowered plant in the P generation
White-flowered plant in the P generation
Purple-flowered plant in the F1 generation
(2)
(ii) Draw a genetic diagram to show how self-pollination of the F1 purple-flowered plants
produced mainly purple-flowered offspring in the F2 generation together with some
white-flowered offspring.
Use the following symbols:
N = allele for purple flower colour
n = allele for white flower colour
(3)
(c) When Mendel published his work on genetics, other scientists at the time did not realise
how important it was.
Suggest two reasons why.
1. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
2. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
Rossett School Page 6 of 18
Glyphosate is a herbicide.
4
Crop plants have been genetically modified to make them resistant to glyphosate.
(a) Why is it an advantage to make crop plants resistant to glyphosate?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
Rossett School Page 7 of 18
(b) Figure 1 shows how scientists produce genetically modified (GM) crop plants.
The scientists use a GM-bacterium that can invade plant cells.
(i) The ring of DNA shown in Figure 1 acts as a vector for the resistance gene.
What is the scientific name for this ring of DNA?
______________________________________________________________
(1)
Rossett School Page 8 of 18
(ii) At step 1 in Figure 1, the ring of DNA is cut open.
How do scientists cut open the ring of DNA?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(iii) At step 5 in Figure 1, plant cells and GM-bacteria are put on agar containing
glyphosate.
Explain why the scientists add glyphosate to the agar.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
Rossett School Page 9 of 18
(c) Some people disagree with the use of GM herbicide-resistant crop plants.
Figure 2 shows data published on a website in 2013.
Rossett School Page 10 of 18
A journalist used the data to claim: ‘Scientists show that GM crops cause kidney disease in
humans.’
Use information from Figure 2 to evaluate the evidence for this claim.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(Total 11 marks)
Rossett School Page 11 of 18
DNA is the genetic material of human cells.
5
Figure 1 shows the structure of part of a DNA molecule.
(a) (i) Describe where DNA is found in a human cell.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(ii) When a cell divides by mitosis the new cells are genetically identical.
What causes the cells to be genetically identical?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(b) Many genes have different forms called alleles.
(i) A person has polydactyly (extra fingers or toes). Polydactyly is caused by a dominant
allele.
What is the smallest number of copies of the dominant allele for polydactyly that
could be found in a body cell of this person?
______________
(1)
(ii) Another person has cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by a recessive
allele.
How many copies of the recessive CF allele are there in a body cell of this person?
______________
(1)
Rossett School Page 12 of 18
(c) A burglar broke into a house. The burglar cut his hand on some broken glass. Scientists
extracted DNA from the blood on the broken glass.
The scientists analysed the DNA from the glass and DNA from three suspects, A, B and C.
The scientists used a method called DNA fingerprinting.
Figure 2 shows the scientists’ results.
Which suspect, A, B or C, is most likely to have been the burglar?
Tick ( ) one box.
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
Rossett School Page 13 of 18
Mark schemes
(a) any three from:
1
• (gene) cut out
• (gene / cut out) from (bacterial) chromosome / DNA
accept (gene / cut out) from (bacterial) plasmid
• ref to enzymes (at any point)
• (gene spliced) into maize chromosome / DNA
• (gene added) at an early stage of development
3
(b) any four from:
• justification based on comparison of the relative merits of at least one
advantage and one disadvantage
max 3 marks if only advantages or disadvantages given
Advantages:
• less effort for farmer or less likely to harm farmer
ignore ref to cost
• (pesticide) always there or doesn’t wash away
allow examples eg no need to spray
• less insects to eat crop / maize or carry disease
allow pesticide doesn’t contaminate water courses
• so greater crop production / yield
Disadvantages:
• (toxin) kills other insects
ignore ref to cost
• so (some) crops don’t get pollinated / (sexually) reproduce
allow maize not pollinated
• possible harm when eaten by humans / animals
allow may have unpleasant taste
• damage to food chains
allow reduced biodiversity
• gene may spread to other species
4
[7]
(a) lack of fossils / fossils destroyed
2
allow lack of evidence
1
(due to soft parts) decaying / geological activity
allow an example – eg vulcanism or earth movements or erosion
allow converse points re skeletons, shells, hard parts
1
Rossett School Page 14 of 18
(b) (i) A and B did not mate successfully
‘ A and B did not mate’ insufficient
allow did not produce fertile offspring
1
(ii) any two from:
• may not be mating season
• A and B may not find each other attractive
• this is just a one-off attempt / an anomaly / need repeats
• may be juvenile / immature
• may be the same sex
allow other sensible suggestion eg were put in unfavourable
environment or one / both could be infertile
2
(c) 1. (two ancestral populations) separated (by geographical barrier / by land) / were
isolated
1
2. genetic variation (in each population) or different / new alleles or mutations
occur
1
3. different environment / conditions
allow abiotic or biotic example
1
4. natural selection occurs or some phenotypes survived or some genotypes
survived
1
5. (favourable) alleles / genes / mutations passed on (in each population)
1
6. eventually two types cannot interbreed successfully
allow eventually cannot produce fertile offspring
1
[11]
(a) (i) 3.15 : 1
3
accept 3.147:1 or 3.1 : 1 or 3 : 1
do not accept 3.14 : 1
Ignore 705:224
1
Rossett School Page 15 of 18
(ii) any two from:
• fertilisation is random or ref. to chance combinations (of alleles / genes /
chromosomes)
• more likely to get theoretical ratios or see (correct) pattern or get valid
results if large number
allow ref. to more representative / reliable
do not allow more accurate or precise
ignore fair / repeatable
• anomalies have limited effect / anomalies can be identified
accept example of an anomaly
2
(b) (i) in sequence:
Homozygous
Homozygous
Heterozygous
All 3 correct = 2 marks
2 correct = 1 mark
1 or 0 correct = 0 marks
2
(ii) genetic diagram including:
Parental genotypes: Nn and Nn
allow other characters / symbols only if clearly defined
1
or
Gametes: N and n + N and n derivation of offspring genotypes: NN Nn Nn
nn
allow genotypes correctly derived from candidate’s P gametes
1
identification: NN and Nn as purple and nn as white
allow correct identification of candidate’s offspring genotypes but
only if some F2 are purple and some are white
1
Rossett School Page 16 of 18
(c) any two from:
• did not know about chromosomes / genes / DNA
or did not know chromosomes occurred in pairs
ignore genetics
• had pre-conceived theories
eg blending of inherited characters
ignore religious ideas unless qualified
• Mendel’s (mathematical) approach was novel concept
allow his work was not understood or no other scientist had similar
ideas
• Mendel was not part of academic establishment
allow he was not considered to be a scientist / not well known / he
was only a monk
• work published in obscure journal / work lost for many years
• peas gave unusual results cf other species
allow he only worked on pea plants
• Mendel’s results were not corroborated until later / 1900
2
[10]
(a) kills weeds among crops / does not kill crops
4 1
(kills weeds) so less competition for named factor eg light / water / ions
ignore space
1
crops grow better / higher yield
1
(b) (i) plasmid
1
(ii) use an enzyme
allow correct example
1
(iii) only some cells become GM / take up the plasmid / take up resistance gene
allow idea of transfer of gene / plasmid to some plant cells from
bacteria
1
GM cells survive / non-GM cells are killed
1
Rossett School Page 17 of 18
(c) Pro:
(positive) correlation between use of glyphosate and number of cases of kidney
disease
allow 1 mark for justified conclusion that the claim is not justified
1
+ any three from:
Con:
• lack of controls / control group
• correlation does not prove a causal link
• some other factor could be the cause
accept obesity / infection
• no evidence that kidney patients actually consumed GM crops / crops treated
with glyphosate / no evidence about amount consumed
or graph shows amount of herbicide not amount of GM crops grown
or graph shows data only for maize and soya / not for other (GM) crops
• data have been manipulated by carefully chosen scales to make it look like they
coincide
• data from some years is missing
• no data for the dosage of herbicide used
allow kidney disease has been around for much longer than GM
crops / better diagnosis of kidney disease.
3
[11]
(a) (i) in the chromosome(s)
5
ignore genes / alleles
1
in the nucleus
allow nuclei
allow mitochondria
1
(ii) the DNA / chromosomes / genes are replicated / copied / multiplied / doubled /
duplicated
allow DNA is cloned
ignore same DNA / chromosomes / genes if unqualified
1
(b) (i) 1 / one
1
(ii) 2 / two
1
(c) B
1
[6]
Rossett School Page 18 of 18
You might also like
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Organismal BiologyNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Extra QPDocument23 pagesInheritance Extra QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 7 9 6Document22 pagesInheritance 7 9 6Philip VuuNo ratings yet
- YEAR 13 Questions Speciation, Hardy WeinbergDocument5 pagesYEAR 13 Questions Speciation, Hardy WeinbergszyzypNo ratings yet
- 3 7 3-EvolutionDocument74 pages3 7 3-Evolutiontomtinoy2019No ratings yet
- 3.7.4 Populations in Ecosystems Pack 2Document79 pages3.7.4 Populations in Ecosystems Pack 2savinbusinesswomanNo ratings yet
- Recovery Lesson 3 QuestionsDocument11 pagesRecovery Lesson 3 QuestionsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 14.2Document6 pagesInheritance 14.2YashodhaNo ratings yet
- DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION - BIOLOGY FORM III ANNUAL EXAMINATION 2012Document12 pagesDIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION - BIOLOGY FORM III ANNUAL EXAMINATION 2012Ana RadisaNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument26 pagesInheritanceStefaniya Dmitrievna “Stef” DeminetsNo ratings yet
- 5 Living Things in Their Environment - 6 - People and Planet - QueDocument9 pages5 Living Things in Their Environment - 6 - People and Planet - Querashmi_harry100% (1)
- Inheritance QPDocument47 pagesInheritance QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- RAMP EQsDocument11 pagesRAMP EQsalma.khaleefaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 1 - QuestionsDocument58 pages3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 1 - QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- P5 CT T3 (Science) 2022-2023Document10 pagesP5 CT T3 (Science) 2022-2023Alva SevenNo ratings yet
- Maths Skills QuestionsDocument71 pagesMaths Skills Questionsyamaharider4996No ratings yet
- 27032024_182135_Mock TestDocument6 pages27032024_182135_Mock TestHiral ShukalNo ratings yet
- Diversity Q and ADocument16 pagesDiversity Q and AGavan CookeNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Survival of Butterfly SpeciesDocument10 pagesEvolution and Survival of Butterfly SpeciesNovanolo Christovori Zebua100% (1)
- Plant Hormones QPDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Plants Test KS3 AVGDocument14 pagesPlants Test KS3 AVGArisa PatthawaroNo ratings yet
- B6 Speciation Biol OnlyDocument21 pagesB6 Speciation Biol OnlyFatma Taha MohamedNo ratings yet
- 4.3: Intruders in An Ecosystem: Page 1 of 2Document2 pages4.3: Intruders in An Ecosystem: Page 1 of 2Teng Xuen ChanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Variation-WorksheetDocument17 pagesYear 7 Variation-WorksheetCally ChewNo ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Resources and Population DensityDocument1 pageResources and Population DensityAryan Francis LampitocNo ratings yet
- Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesSexual vs Asexual Reproduction Exam QuestionsBenjamin Watson100% (1)
- Investigating Populations Exam Qs and MSDocument7 pagesInvestigating Populations Exam Qs and MSafivealeNo ratings yet
- 0610/42 Biology: DC (ST/CT) 166141/1Document32 pages0610/42 Biology: DC (ST/CT) 166141/1Thapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2010 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2010 P2Joy Boehmer100% (1)
- Quiz #2 (P4)Document7 pagesQuiz #2 (P4)Mega SukmadiNo ratings yet
- SC Paper 2 Yr 5 (2022)Document6 pagesSC Paper 2 Yr 5 (2022)SHEELA A/P ARUMUGAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Practical Skills QuestionsDocument62 pagesPractical Skills QuestionshftuuNo ratings yet
- 3 7 2-PopulationsDocument41 pages3 7 2-Populationstomtinoy2019No ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Evolution-WorkbookDocument9 pagesBiodiversity and Evolution-WorkbookJenny Rose BatalonNo ratings yet
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDocument8 pagesSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Comparing Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration in Plants and AnimalsDocument8 pagesComparing Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration in Plants and AnimalsJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 QuestionsDocument14 pagesLesson 4 QuestionsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Assessment Booklet: Marks 164 Time Allowed 207 MinutesDocument54 pagesTopic 4 Assessment Booklet: Marks 164 Time Allowed 207 MinutesHayley CamenzuliNo ratings yet
- Ecology QPDocument23 pagesEcology QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Aecs Class 5 Practice Test Term1evs17Document13 pagesAecs Class 5 Practice Test Term1evs17spanja_barcNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument35 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPZaynab Ameenah KhanNo ratings yet
- A DOSE OF LISTENING 02: How Earth’s Population ExplodedDocument6 pagesA DOSE OF LISTENING 02: How Earth’s Population ExplodedHub EnglishNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 - Selection and Speciation - QuestionDocument5 pagesTOPIC 3 - Selection and Speciation - QuestionSHASWIN RAJ A/L KARTTIKAN MoeNo ratings yet
- PopulationsinecosystemsDocument110 pagesPopulationsinecosystems/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Bio QuestionsDocument12 pagesBio QuestionsYasmine CaparNo ratings yet
- Mr. Thomas' Integrated Science Exam on Food Chains and Human ReproductionDocument6 pagesMr. Thomas' Integrated Science Exam on Food Chains and Human ReproductionScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 QuestionDocument25 pagesChapter 05 Questionapi-19650882No ratings yet
- Campylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaDocument5 pagesCampylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaBob yuNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2Document88 pagesGenetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2kafiazabit200No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 QuestionDocument22 pagesChapter 18 Questionapi-19650882No ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Exam QsDocument6 pagesHardy Weinberg Exam QsmoNo ratings yet
- AKUEB SSC-II Biology Paper II Composite '08Document12 pagesAKUEB SSC-II Biology Paper II Composite '08HussainRyzveeNo ratings yet
- L9-5-Exam-Qu-NTDocument9 pagesL9-5-Exam-Qu-NTw.lamNo ratings yet
- Ecology WorksheetDocument12 pagesEcology WorksheetManongdo Allan0% (1)
- Mitosis & MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis & MeiosisamaraadomaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE EXERCISE For 6 GradeDocument5 pagesSCIENCE EXERCISE For 6 Gradelenny dianaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science Set 2 Part 2 160559226Document30 pagesYear 10 Science Set 2 Part 2 160559226osasnelly2006No ratings yet
- Host and Environmental Factors Influencing Individual Human Cytokine Responses PDFDocument37 pagesHost and Environmental Factors Influencing Individual Human Cytokine Responses PDFLluis GomezNo ratings yet
- 2016 Medical Diagnosis With The Aid of Using Fuzzy LogicDocument19 pages2016 Medical Diagnosis With The Aid of Using Fuzzy LogicRay Dueñas JiménezNo ratings yet
- 10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateDocument2 pages10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateamitNo ratings yet
- 0737743387Document145 pages0737743387Andrej HodonjNo ratings yet
- Disease Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms2020 PDFDocument7 pagesDisease Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms2020 PDFSumati BaralNo ratings yet
- Colour Therapy GuideDocument7 pagesColour Therapy GuideTINTU JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 (SF 8)Document3 pagesSchool Form 8 (SF 8)yZNo ratings yet
- Feed Addditives NEW ANN 211Document44 pagesFeed Addditives NEW ANN 211Mohit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- PSCP Tables (MDRRMO Accomplished Table)Document11 pagesPSCP Tables (MDRRMO Accomplished Table)Chelsie Barbonio OnoyaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORY ACTIVITIES OF SOME ZINGIBERACEAE PLANTSDocument13 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORY ACTIVITIES OF SOME ZINGIBERACEAE PLANTSZalfa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus - : One Disease Two Lives at StakeDocument31 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus - : One Disease Two Lives at StakeSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Reflection About The Current ECQ? How Do People Behave and Communicate During This ECQ?Document3 pagesWhat Is Your Reflection About The Current ECQ? How Do People Behave and Communicate During This ECQ?Allijah Trish HernandezNo ratings yet
- Microteaching: MDR - TBDocument16 pagesMicroteaching: MDR - TBVikram Singh RanawatNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Mycoses: Presenter: DR Pranay Reddy Moderator: DR Tonita MNDocument81 pagesSubcutaneous Mycoses: Presenter: DR Pranay Reddy Moderator: DR Tonita MNSandipNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy: Summary of ConditionsDocument22 pagesMusculoskeletal Physiotherapy: Summary of ConditionsJess MarriottNo ratings yet
- TLE6 - Q1 - Mod8 - Conduct Survey On Animal and Fish Raising - Version3Document43 pagesTLE6 - Q1 - Mod8 - Conduct Survey On Animal and Fish Raising - Version3LYNN MADDAWATNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Dyslipidemia in Family PracticeDocument41 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Dyslipidemia in Family PracticeKai ChuaNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in Pregnancy FinalDocument24 pagesHeart Disease in Pregnancy FinalBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-584358270No ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurobehavioural Status and Motor Disorders With Malocclusion in ChildrenDocument18 pagesAssessment of Neurobehavioural Status and Motor Disorders With Malocclusion in ChildrenGaurav JainNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B OverviewDocument11 pagesHepatitis B OverviewJose RonquilloNo ratings yet
- WHO STAGE Advisory Group Discusses Mitigating COVID-19 Impacts on MNCAHNDocument33 pagesWHO STAGE Advisory Group Discusses Mitigating COVID-19 Impacts on MNCAHNAbebe TilahunNo ratings yet
- Logic Part 2Document21 pagesLogic Part 2JohnNo ratings yet
- Fournier'S Gangrene: Rajah Amina SuleimanDocument27 pagesFournier'S Gangrene: Rajah Amina SuleimanAmina RajahNo ratings yet
- Icmr Specimen Referral Form For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) : (These Fields To Be Filled For All Patients Including Foreigners)Document2 pagesIcmr Specimen Referral Form For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) : (These Fields To Be Filled For All Patients Including Foreigners)aishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument1 pageHealth Declaration FormZyreane FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lit Ing 060523Document6 pagesLit Ing 060523gloriussihombing18No ratings yet
- Biliary Tract Cancers: Epidemiology, Molecular Pathogenesis and Genetic Risk AssociationsDocument31 pagesBiliary Tract Cancers: Epidemiology, Molecular Pathogenesis and Genetic Risk AssociationsleartaNo ratings yet
- National Guideline On Integrated Vector Management 2020 NewDocument140 pagesNational Guideline On Integrated Vector Management 2020 NewNeha AmatyaNo ratings yet
- Frontal Lobe SyndromeDocument67 pagesFrontal Lobe SyndromeVIJAYKUMAR HIREMATH100% (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)