Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PDF Display Board 2
Uploaded by
api-502885271Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PDF Display Board 2
Uploaded by
api-502885271Copyright:
Available Formats
Age in Style with a Healthy Smile: How to Fight the Oral Changes That
Come with Aging
Jennifer Anderson, Kristin Brenkus, & Madelyne Smith
Public Heath Dental Hygiene
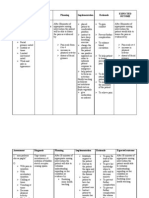
Abstract Purpose Literature Review Conclusion
The purpose of this research is to evaluate the oral hygiene of The purpose of this research is to evaluate the • As the population of elderly individuals continues to
the elderly population with diabetes and the effects of increase, combined with the increase in levels of
periodontal disease on their dentition. The elderly population
oral hygiene of the diabetic elderly population
diabetes due to poor health and diet, healthcare
is growing, and due to the oral health changes that come along and the effects of periodontal disease on their
professionals must be educated and equipped to
with this age group, the connection between periodontal and dentition. The elderly population is growing, and handle this population of patients with specific health
diabetes is critical for the best methods of patient care. A due to the oral health changes that come along
literature review of twelve peer reviewed articles was needs.
conducted to compare relevant data on this topic. Research with this age group, it is important to understand • The dental team plays an important role in educating
found that there is a link between periodontal disease and the connection between periodontal disease and • Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition that patients on the harmful effects of diabetes in relation
diabetes due to the inflammatory process being reduced in diabetes. causes blood glucose levels to rise, which can lead to to oral health (Figure 2).
patients with the disease. The control of periodontal disease other serious and life-threatening problems (4). • Specifically, dental hygienists can inform
can have a positive influence on those with diabetes by patients on the link between oral health and
decreasing the levels of insulin needed by the body and • There are two types of diabetes, type 1 and type 2, with overall systemic health.
reducing hemoglobin A1C levels. Current research shows that type 2 being the most common. • Patients with diabetes have a decreased immune
nutrition counseling can provide beneficial effects towards system that negatively impacts their immune system
preventing and maintaining diabetes therefore benefiting the Significance of Study • Type 1 diabetes is when the pancreas does not produce and the ability to maintain a high level of oral health.
oral cavity from the harmful effects of diabetes. Further enough insulin, a hormone that produces glucose. It is crucial that elderly patients are aware of their
research is needed to provide the best methods of prevention
and care regarding the connections of elderly patients with This study is important because the elderly • Type 2 diabetes is when there is a resistance to insulin, health conditions, receive proper education and
diabetes and periodontal disease. population is living longer, and as the body produces insulin but is unable to process treatment in order to best care for their health.
glucose appropriately (4).
healthcare professionals, it is crucial to
understand the changing needs of this
population and the connection with
Introduction periodontal disease. There is a lack of
“Aging, an inevitable process, is commonly knowledge on how to provide care in the
measured by chronological age and, as a elderly population and how to best meet
convention, a person aged 65 years or more is their specific oral health needs. This paper Periodontitis & Diabetes
often referred to as ‘elderly’” –Shamsher Singh. provides evidence on the importance of oral • Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are predictors of
The aging population will be affected by health in the elderly population with periodontal disease (6). References
noncommunicable chronic diseases, including diabetes and how to best meet their needs • It is the sixth complication of diabetes (6). 1. Lamster, I. B. (2016). Geriatric periodontology: How the need to care for the aging population can
influence the future of the dental profession. Periodontology 2000, 72(1), 7–12.
diabetes mellitus (1). These individuals may by preventing and treating periodontal 2. Singh S, & Bajorek B. (2014). Defining ‘elderly’ in clinical practice guidelines for
• People with diabetes are 3x more likely to develop pharmacotherapy. Pharmacy Practice, 12(4), 489.
suffer from oral disease as they have a greater disease. Examining the connection to periodontitis (8). 3. Huang, D., Chan, K., & Young, B. (2013). Poor oral health and quality of life in older U.S. adults
risk of periodontal disease and subsequent tooth diabetes, resources available, best methods with diabetes mellitus. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 61(10), 1782-1788.
• It has been proven that treating periodontal disease 4. Torpy, J., & Golub, Robert. (2011). Diabetes. JAMA, 305(24), 2592-2592.
loss (3). The connection between systemic and of care, and ways to empower the elderly 5. Chiniwala, N., & Jabbour, S. (2011). Management of diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Current
can result in reductions of individual’s A1C levels Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity,18(2), 148-152.
oral health embodies the need to explore the will aid their dental health.
(8,9). 6. Saini, R., Saini, S., & Sugandha, R. (2011). Periodontal disease: The sixth complication of diabetes.
role of diabetes and its effect on the oral health What can we do for our patients with Diabetes?
Journal of Family & Community medicine, 18(1), 31.
7. Bissett, S., Preshaw, P., & Pumerantz, A. (2015). Periodontal disease and diabetes. Journal of
of the growing elderly population (Figure 1). Diabetes Nursing,19(4), 134-140.
• Therapeutic scaling & root planing 8. Preshaw, P.A., Alba, A.L., Herrera, D., Jepsen, S. Konstantinidis, A., Makrilakis, K., & Taylor, R.
(2012). Periodontitis and diabetes: A two-way relationship. Diabetologia, 55(1), 21-31.
• Nutrition Counseling 9. Croitoru, G. A., Tilişcan, C., Carmen Marina, M., Victoria, A., Daniela, I., & Aramă, S. (2012). The
• Oral Hygiene Instructions role of diabetes mellitus in periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis: The dentist’s point
of view. Therapeutics, Pharmacology & Clinical Toxicology, 16(3), 177–180.
• Education on the link between diabetes and 10. Demmer, R. T., Holtfreter, B., Desvarieux, Moïse, M.D., Jacobs, David R, J.R., Kerner, Wolfgang,
Nauck, Matthias, Kocher, Thomas. (2012). The influence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes on periodontal
periodontitis disease progression: Prospective results from the study of health in pomerania (SHIP).Diabetes Care,
35(10), 2036-42.
11. Siddiqi, Zafar, Sharma, Quaranta, & Siddiqi, A. (2019). Diabetic patient's knowledge of the
bidirectional link: Are dental health care professionals effectively conveying the message. Australian
Dental Journal,doi: 10.1111/adj.12721
12. Evert, A. B., Dennison, M., Garder, C. D., Garvey, W. T., Lau, K. K., MacLeod, J., Mitri, J., Pereira,
R. F., Rawlings, K., Robinson, S., Saslow L., Uelmen, S., Urbanski, P. B., & Yancy Jr, W. S. (2019).
Nutrition therapy for adults with diabetes or prediabetes: A consensus report. Diabetes Care, 42,
731-754.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Healthy Running PlaybookDocument113 pagesThe Healthy Running PlaybookDay Traders DailyNo ratings yet
- Am Medicine - Com 210815 m77Document596 pagesAm Medicine - Com 210815 m77Cai Velasco Decena100% (16)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- Qigong - Master - Dr. - Yan - Xin - Secrets - and - Benefits - o PDFDocument193 pagesQigong - Master - Dr. - Yan - Xin - Secrets - and - Benefits - o PDFFranklin De Santa100% (2)
- EU Summit DR David Martin May 2023Document6 pagesEU Summit DR David Martin May 2023MA-DocNo ratings yet
- BLS Provider: Basic Life SupportDocument1 pageBLS Provider: Basic Life Supportapi-502885271No ratings yet
- The AAS Personal StatementDocument3 pagesThe AAS Personal StatementRetno Suminar100% (3)
- NCP Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocument20 pagesNCP Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisChristine Karen Ang Suarez100% (2)
- Certificate 2Document1 pageCertificate 2api-502885271No ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateapi-502885271No ratings yet
- Cecertificate JuulingrecordedDocument1 pageCecertificate Juulingrecordedapi-502885271No ratings yet
- 4 23 20resumeDocument1 page4 23 20resumeapi-502885271No ratings yet
- Cheyenne Scott Final ResumeDocument3 pagesCheyenne Scott Final Resumeapi-267328340No ratings yet
- Medi 99 E11005Document6 pagesMedi 99 E11005maninagaNo ratings yet
- Science Dept Ci TeamfinalDocument29 pagesScience Dept Ci TeamfinalEmely EstacioNo ratings yet
- Topics For Skills Laboratory N - 104 Community Health Nursing 1Document2 pagesTopics For Skills Laboratory N - 104 Community Health Nursing 1Bem PladeroNo ratings yet
- Deped Memo No. 165, S 2010: WastedDocument6 pagesDeped Memo No. 165, S 2010: WastedJayne InoferioNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument20 pagesAcute Rheumatic Feverfaizal samadNo ratings yet
- Hoffmann SignDocument5 pagesHoffmann SignClaudio Andrés Olmos de AguileraNo ratings yet
- The Policy Cycle PDFDocument11 pagesThe Policy Cycle PDFLauditta AchyaNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Go For Fitness GoalDocument35 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Go For Fitness GoalLeuweyne SerranoNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical Waste Authorization Certificate: Haryana State Pollution Control BoardDocument3 pagesBio Medical Waste Authorization Certificate: Haryana State Pollution Control BoardManishNo ratings yet
- 4-Hampshire Falls ProtocolDocument5 pages4-Hampshire Falls ProtocolsheenaNo ratings yet
- Stemi ChecklistDocument1 pageStemi ChecklistDanu SusantoNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Job Stress To The Work Performance On Employees of Plaridel AirportDocument19 pagesThe Relationship of Job Stress To The Work Performance On Employees of Plaridel AirportAmen MartzNo ratings yet
- Life After Stroke Guide - 7819Document36 pagesLife After Stroke Guide - 7819Dr. Victor A. RochaNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 in Kidney Transplant RecipientsDocument11 pagesCOVID 19 in Kidney Transplant RecipientsDouglas SantosNo ratings yet
- COPD AsthmaDocument16 pagesCOPD Asthma09172216507No ratings yet
- Barrientos Case Presentation Severe TetanusDocument10 pagesBarrientos Case Presentation Severe TetanusCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Coloproctology Brochure English 01 2019Document4 pagesColoproctology Brochure English 01 2019Gino PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Canmedaj01540 0049Document4 pagesCanmedaj01540 0049ImanNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Program To Prevent Violence Against Women (Vaw) in Selected Barangays of Batangas CityDocument44 pagesA Proposed Program To Prevent Violence Against Women (Vaw) in Selected Barangays of Batangas CityMarimarjnhioNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Booklet For Parents and CarersDocument40 pagesAutism Spectrum Disorders: A Booklet For Parents and CarersAndreea SanduNo ratings yet
- CEMONCDocument10 pagesCEMONCApril GuiangNo ratings yet
- Middle School Physical Education HomeworkDocument8 pagesMiddle School Physical Education Homeworkh41zdb84100% (1)