Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome NCP
Uploaded by
JM RomiasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome NCP
Uploaded by
JM RomiasCopyright:
Available Formats
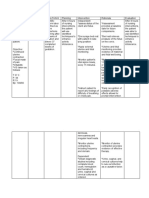
MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME
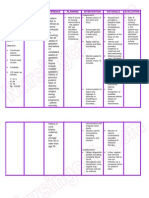
ASSESMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
After 8 hours INDEPENDENT After 8 hours of
OBJECTIVE: Ineffective of nursing Assess for signs of nursing
Altered skin tissue intervention decreased tissue Particular clusters of intervention the
characteristics. perfusion the patient perfusion. signs and symptoms patient was
(poor skin related to will be able occur with differing able to maintain
turgor) impaired to maintain causes. Evaluation of maximum
Skin color: transport of maximum Ineffective Tissue tissue perfusion
pale oxygen tissue Perfusion defining to vital organs,
Weak pulse perfusion to characteristics provides as evidenced by
Presence of vital organs, a baseline for future warm and dry
bruits as evidenced comparison. skin, present
Presence of by warm and and strong
edema dry skin, Assess for probable early detection of the peripheral
Capilliary refill present and contributing factors source facilitates quick, pulses, vitals
test >3 strong related to temporarily effective management within patient’s
seconds peripheral impaired arterial normal range,
pulses, vitals blood flow. Some balanced I&O,
within examples include absence edema.
patient’s compartment
normal syndrome,
range, constricting cast,
balanced embolism, indwelling
I&O, absence arterial catheters,
edema. positioning,
thrombus, and
vasospasm.
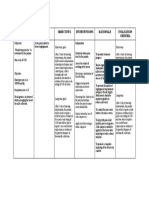
Check respirations and Cardiac pump malfunction
absence of work of and/or ischemic pain may
breathing. result in respiratory
distress. Nevertheless,
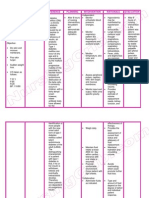
MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME
abrupt or continuous
dyspnea may signify
thromboembolic pulmonary
complications.
Examine GI function,
noting anorexia, Decreased blood flow to
decreased or absent mesentery can turn out to
bowel sounds, nausea GI dysfunction, loss of
or vomiting peristalsis
use pulse oximetry to pulse oximetry is a useful
monitor oxygen tool to detect changes in
saturation and pulse oxygenation.
rate.
Check Hgb levels Low levels reduce the
uptake of oxygen at the
alveolar-capillary
membrane and
oxygen delivery to the
tissues.
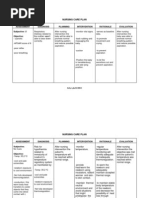
Check for pallor, Nonexistence of peripheral
cyanosis, mottling, cool pulses must be reported or
or clammy skin. Assess managed immediately.
quality of every pulse. Systemic vasoconstriction
resulting from reduced
cardiac output may be
manifested by diminished
skin perfusion and loss of
pulses. Therefore,
assessment is required for
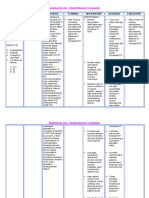
MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME
constant comparisons
Note skin texture and Thin, shiny, dry skin with
the presence of hair, hair loss; brittle nails; and
ulcers, or gangrenous gangrene or ulcerations on
areas on the legs or toes and anterior surfaces
feet. of feet are seen in patients
with arterial insufficiency. If
ulcerations are on the side
of the leg, they are usually
venous
Reduced intake or
Monitor intake, observe unrelenting nausea may
changes in urine output. consequence in lowered
Record urine specific circulating volume, which
gravity as necessary. negatively affects perfusion
and organ function.
Hydration status and renal
function are revealed by
specific gravity
measurements.
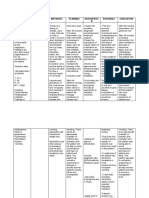
DEPENDENT
Check for optimal Sufficient fluid intake
fluid balance. maintains adequate
Administer IV fluids as filling pressures and
ordered. optimizes cardiac output
needed for tissue
perfusion.
Administer phenytoin a These reduce risk
s needed. of seizure.
MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan of The NewbornDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan of The Newbornappleliciouz0860% (10)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- NCP PrematureinfantDocument19 pagesNCP Prematureinfantysamariano100% (1)
- NCP NicuDocument3 pagesNCP NicuNoel Telosa100% (1)
- Hydrocephalus N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageHydrocephalus N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Altered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalDocument4 pagesAltered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalAlyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument20 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Intervention S Rational E EvaluationDocument21 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Intervention S Rational E EvaluationJoanne Bernadette Aguilar100% (1)
- NCP - Hyperbilirubinemia - Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP - Hyperbilirubinemia - Staff NursingnurseM67% (3)
- NCP Preterm NeonateDocument3 pagesNCP Preterm NeonateLilia Priscilla Tuibuen Aureus100% (2)
- NCP On Preterm LaborDocument2 pagesNCP On Preterm Laborinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Delayed Growth NCPDocument3 pagesDelayed Growth NCPPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Fetal Death in Utero NCP'sDocument4 pagesFetal Death in Utero NCP'sshadow gonzalez100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted To: Submitted By: Ms Kamini Manisha Joshi Asst. Prof. Acn Msc. Nursing 1 SemesterDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted To: Submitted By: Ms Kamini Manisha Joshi Asst. Prof. Acn Msc. Nursing 1 SemesterDIMPYNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- NCP For RDSDocument3 pagesNCP For RDSKevin P. Feliciano74% (23)
- College of Nursing NURSING Care PlanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing NURSING Care PlanToyour EternityNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breastfeeding RT To Inadequate Milk Supply Secondary To Inverted NippleDocument3 pagesIneffective Breastfeeding RT To Inadequate Milk Supply Secondary To Inverted NippleKerny BasilioNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionJulia Shane Barrios100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Breast EngorgementDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Breast EngorgementMarceline VueenNo ratings yet
- NCP BreastfeedingDocument3 pagesNCP BreastfeedingLeo FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- NCP (Hyperbilirubinemia) IIDocument4 pagesNCP (Hyperbilirubinemia) IIbluewipes67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan. LyksDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan. LyksKiyla92No ratings yet
- NCP On LBWDocument22 pagesNCP On LBWMeena Koushal100% (3)
- NCP Gestational HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Gestational Hypertensionshila_glangNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breast Feeding R/T Flat NippleDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breast Feeding R/T Flat NippleLafayette Kirsi Noel100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDianne100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Knowledge DeficitDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan: Knowledge DeficitMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- NCP Case 3Document3 pagesNCP Case 3boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Drug Ang NCPDocument9 pagesDrug Ang NCPMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan Scabies 11Document4 pagesTeaching Plan Scabies 11umar khan0% (1)
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanDickson,Emilia Jade100% (1)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breastfeeding PDFDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Breastfeeding PDFJACOB AQUINTEYNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care With EclampsiaDocument40 pagesNursing Care With EclampsiaNadia DesyerianNo ratings yet
- NCP NewbornDocument2 pagesNCP Newbornsonylynne94% (17)
- NCP SepsisDocument6 pagesNCP SepsisgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPGerna Anne Salenga CabilingNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breast FeedingDocument3 pagesIneffective Breast FeedingNikka JunioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJan DeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Preterm LaborDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Preterm Laborderic87% (23)
- Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesDischarge PlanningCassey CamamaNo ratings yet
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Altered Uteroplacental Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesAltered Uteroplacental Tissue PerfusionArielle BajalaNo ratings yet
- TPR Sheet - Bito-OnDocument2 pagesTPR Sheet - Bito-OnBryle James Bito-on100% (1)
- NCP For NewbornDocument2 pagesNCP For NewbornErica Veluz LuyunNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual EvaluationPabhat Kumar50% (2)
- N E E D S C O G N I T I V E P E R P E T U A L RationaleDocument14 pagesN E E D S C O G N I T I V E P E R P E T U A L RationaleArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNcp-Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDayanaj OngNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1deric85% (46)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explaination Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explaination Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDiana MuañaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Ysun Espino100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanIan GabrielouNo ratings yet
- Date Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoselyn Velasco100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- FinalDrugStudy ObwardDocument9 pagesFinalDrugStudy ObwardJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1043Document1 pageReviewer 1043CiarraMaeMabbayadAtienzaNo ratings yet
- CFED ReqsDocument2 pagesCFED ReqsJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Reflection On The Practice of Psychiatric Nursing During The Early Periods?Document2 pagesWhat Is Your Reflection On The Practice of Psychiatric Nursing During The Early Periods?JM RomiasNo ratings yet
- My Goal in LifeDocument1 pageMy Goal in LifeJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- My Mission in Life: By: Kyla Fae BitalesDocument1 pageMy Mission in Life: By: Kyla Fae BitalesJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Family History: Healthy or Medical Issues?Document8 pagesFamily History: Healthy or Medical Issues?JM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Health Assessment Form: Instructions For CompletionDocument6 pagesNursing Care Health Assessment Form: Instructions For CompletionJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- System Normal Abnormal Remarks Vital SignsDocument3 pagesSystem Normal Abnormal Remarks Vital SignsJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- System Normal Abnormal Remarks Vital SignsDocument8 pagesSystem Normal Abnormal Remarks Vital SignsJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Learning Feedback DiaryDocument1 pageLearning Feedback DiaryVhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- CFED ReqsDocument2 pagesCFED ReqsJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- CHN Reviewer JongDocument2 pagesCHN Reviewer JongJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesFamily Nursing ProcessJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- FamilyDocument4 pagesFamilyJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- The Epidemiological Approach To CausationDocument37 pagesThe Epidemiological Approach To CausationFYMNo ratings yet
- VPE 321veterinary Epidemiology and ZoonosisDocument240 pagesVPE 321veterinary Epidemiology and ZoonosisshivaNo ratings yet
- Literatura 6Document4 pagesLiteratura 6Анастасія КарпенкоNo ratings yet
- Bray 2021Document2 pagesBray 2021alyssa azzahraNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics-Case Presentation: - Sumanga, Juan Cheska Eunice ADocument62 pagesPediatrics-Case Presentation: - Sumanga, Juan Cheska Eunice ALhio Tuguegarao PcbNo ratings yet
- Drama PTB ScriptDocument6 pagesDrama PTB ScriptJevialoomsNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument5 pagesMyasthenia GravisPJHGNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection Print PDFDocument8 pagesSpecimen Collection Print PDFgeehan Ahmed100% (1)
- EpidemiologyDocument24 pagesEpidemiologyasdfsNo ratings yet
- N O Diagnosa Kode Terminologi Icd.10Document13 pagesN O Diagnosa Kode Terminologi Icd.10anonimusingkeunNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets Biotechnology 8 (Q4-Lesson 1 & 2) Application of Biotechnology in HealthDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Biotechnology 8 (Q4-Lesson 1 & 2) Application of Biotechnology in Healthms. dlcrzNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)Document41 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)ririNo ratings yet
- Frequency and Risk Factors of Symptomatic Dry Eye Disease at Tertiary Care Eye Hospital, KarachiDocument4 pagesFrequency and Risk Factors of Symptomatic Dry Eye Disease at Tertiary Care Eye Hospital, KarachiekalapaleloNo ratings yet
- PBL4 ScenarioDocument2 pagesPBL4 ScenarioNatalia RomanNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus EpidermidisDocument4 pagesStaphylococcus Epidermidisemanuel santiago triana rujanaNo ratings yet
- N Hemanth Reddy PDFDocument16 pagesN Hemanth Reddy PDFdiksha singhNo ratings yet
- Intrahepatic CholangiocarcinomaDocument2 pagesIntrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomaabdullatif şirinNo ratings yet
- ID For ABIM - Parham 2014Document140 pagesID For ABIM - Parham 2014Jeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- Eapp EssayDocument3 pagesEapp EssayPatricia PabresNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Unit 5 Health Practice Makes Perfect! 1 Worksheet 1 PDFDocument2 pages5th Grade Unit 5 Health Practice Makes Perfect! 1 Worksheet 1 PDFAmin ZakiNo ratings yet
- Certificate PDFDocument1 pageCertificate PDFKrupasham S JadhavNo ratings yet
- Lip CancerDocument4 pagesLip CancerSaman SadeghiNo ratings yet
- Guadalupe Sabio - ENDocument2 pagesGuadalupe Sabio - ENIlaria iudiceNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument1 pageImmunizationMicah Lou CalambaNo ratings yet
- McDonald Criteria 2005Document2 pagesMcDonald Criteria 2005api-3828181100% (1)
- Leflet Asmpid New-3Document1 pageLeflet Asmpid New-3TheAru21No ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Fever?: 1 DR - Shamol /inter/feverDocument28 pagesApproach To A Patient With Fever?: 1 DR - Shamol /inter/feverkiloNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Cheat Sheet Copyright BNDocument2 pagesDiabetes Cheat Sheet Copyright BNJeshan Yanong BeltranNo ratings yet
- Gapan City Mayor Donates Sacks of Rice To 34,000 HouseholdDocument3 pagesGapan City Mayor Donates Sacks of Rice To 34,000 HouseholdDragon SlayerNo ratings yet
- Bed Side Teaching: By: Elda AriyaniDocument13 pagesBed Side Teaching: By: Elda Ariyanielda ariyaniNo ratings yet