Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Building Blocks of Geometry
Uploaded by
AmyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1 Building Blocks of Geometry
Uploaded by
AmyCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
1 Building Blocks of Geometry
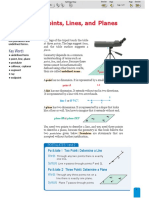
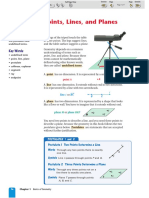
Definitions
- The most basic building block of Geometry. It has no size, only location. It is
represented with a dot and named using a capital letter.
•A (read as the A)
- A straight, continuous arrangement of infinitely many points. It has infinite
length but no thickness and is named using any two points on the line.
A B
AB or BA
- A flat surface that extends infinitely along its length and width. It is
represented as a four-sided figure and named using a script capital letter.
P read as the
P P
- On the same line
- On the same plane
__ – two points (the endpoints of the ) and all the
points between them that are on the line containing them.
C D
CD or DC
Geometry Lesson 1.1: Building Blocks of Geometry Page 1
– Two or more segments with the same measure or
length.
C
2 cm 2 cm
A D
AC = DC means that the lengths are equal. AC ≅ DC means that the segment AC is
congruent to the segment DC.
– The point on a segment that is the same distance from both endpoints.
– divide into two congruent pieces.
– All of the points on a line that lie on one side of a specified point, the ray’s
endpoint. A ray is referred to by giving the names of two points, first the endpoint and then
any point on the ray.
O P
OP read as the ray OP
– The set of all points, usually taken to be three-dimensional.
Geometry Lesson 1.1: Building Blocks of Geometry Page 2
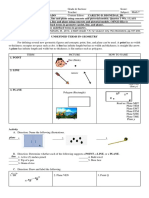
Example1: Study the following diagrams. Name each midpoint and the segment it bisects.
Name all the congruent segments.
C F
3m
A E 3m
B
D G H
I
J L K
Geometry Lesson 1.1: Building Blocks of Geometry Page 3
Example 2: Name each line, ray, or segment using proper geometric notation.
A B
C D
J
F G
E
I
K L M
Example 3: Measure each segment to the nearest tenth of a centimeter.
E F
A
C
Homework: pp. 33 – 34 => 2 – 6; 8 – 11; 13 – 18; 21 – 23
Geometry Lesson 1.1: Building Blocks of Geometry Page 4
You might also like
- Phys 1Document5 pagesPhys 1Sandra Phan50% (2)
- Math7 Le Q3W1Document2 pagesMath7 Le Q3W1Anna Lizette Clapis DeGuzman100% (2)
- Math-8 Q3 LAS Week1Document16 pagesMath-8 Q3 LAS Week1Aryan Francis LampitocNo ratings yet
- Points, Lines, and Planes: Po T Late 1 Two Point Determine A LineDocument12 pagesPoints, Lines, and Planes: Po T Late 1 Two Point Determine A LineKerwin SoriaoNo ratings yet
- ML Geometry 1-2 Points Lines and PlanesDocument7 pagesML Geometry 1-2 Points Lines and Planesmadhuraju778797No ratings yet
- A Course of Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists: Volume 1From EverandA Course of Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists: Volume 1No ratings yet
- 1.1 Law of Demand Practice ActivityDocument4 pages1.1 Law of Demand Practice ActivityHassan Khan0% (1)
- Building Blocks of GeometryDocument18 pagesBuilding Blocks of GeometryElektro LitosNo ratings yet
- 1-2: Points, Lines, and Planes: Basic Geometry TermsDocument12 pages1-2: Points, Lines, and Planes: Basic Geometry TermsMark Jomil ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Full Student PacketDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Full Student PacketJillian MarceloNo ratings yet
- 1-2 PowerPoint PRESENTATIONDocument12 pages1-2 PowerPoint PRESENTATIONRS DulayNo ratings yet
- XI N.M. CODE - A Paper - I (Minor Test-3) 29-01-2023Document11 pagesXI N.M. CODE - A Paper - I (Minor Test-3) 29-01-2023Luv KaushikNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Defined and Undefined TermsDocument6 pagesLesson Plan On Defined and Undefined TermsKith PlumoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 q3 Week 1-4Document12 pagesMath 7 q3 Week 1-4Michelle Jane JapsonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Guided Learning Activity KitDocument16 pagesMathematics: Guided Learning Activity KitJaeda BaltazarNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET NO2 NFDocument3 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET NO2 NFMariel PastoleroNo ratings yet
- Points, Lines, and Planes: Point, Line, and Plane. Because TheseDocument7 pagesPoints, Lines, and Planes: Point, Line, and Plane. Because TheseJamiraNo ratings yet
- LAS Q3math8 - Q3 - wk2 - Melano For SubmissionDocument12 pagesLAS Q3math8 - Q3 - wk2 - Melano For SubmissionFlorame Algarme MelanoNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q3 Module4Document22 pagesMath7 Q3 Module4Mark Loveen AngNo ratings yet
- W1Q1 GeometryDocument7 pagesW1Q1 Geometrymarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Q3 W1 Undefined TermsDocument15 pagesQ3 W1 Undefined Termstorresclerk6No ratings yet
- Q3 Math 7 Week 1 Module 1 Jeston SudiacalDocument19 pagesQ3 Math 7 Week 1 Module 1 Jeston SudiacalARIEL V. ABANESNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Math-G8-Weeks 1-2-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Math-G8-Weeks 1-2-Q3Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 3 Geometric RelationsDocument18 pagesEASE Module 3 Geometric RelationsYeye Lo CordovaNo ratings yet
- MATH 8 Compendium 8 3rd Quarter 1Document26 pagesMATH 8 Compendium 8 3rd Quarter 1Michelle MatiasNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 1 Geometry of Shape and SizeDocument27 pagesEASE Module 1 Geometry of Shape and Sizemonera mohammad0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanJESSA CANOPINNo ratings yet
- Subset of A LineDocument7 pagesSubset of A Linejd gomezNo ratings yet
- LM Geometry8 Q1 W1Document12 pagesLM Geometry8 Q1 W1Shaira Nicole ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Geometric RelationsDocument22 pagesModule 3 - Geometric RelationsJudith CuevaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial IDocument4 pagesTutorial IEbeda BenardNo ratings yet
- Lesson 30 (Geometry) - Basic Concepts and Terms - LGDocument10 pagesLesson 30 (Geometry) - Basic Concepts and Terms - LGSwag Mooshroom100% (1)
- 7 Geometry PDFDocument202 pages7 Geometry PDFFuad_Khafizov_5342100% (1)
- TG For Book 7-1 GDocument38 pagesTG For Book 7-1 GJenonymouslyNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee (Advance) 2015: Paper - 1Document34 pagesIit Jee (Advance) 2015: Paper - 1raj singhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3: Point, Line, PlaneDocument15 pagesLesson 1-3: Point, Line, PlaneJenniferNo ratings yet
- Geometry LessonDocument19 pagesGeometry LessonРоджер БарреттNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Points, Lines, and Planes: Section 1.1Document17 pagesActivity 1 Points, Lines, and Planes: Section 1.1muhammad junaid ammarNo ratings yet
- W1.Mathematical SystemDocument34 pagesW1.Mathematical SystemMaria Louisa EfrenNo ratings yet
- LAS 3rd Q Math 7Document59 pagesLAS 3rd Q Math 7Maryfrance FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 1 PDFJoe0% (1)
- LP Geometry 2.1 (Art)Document10 pagesLP Geometry 2.1 (Art)Ivan MolinaNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Quarter3 Week1Document12 pagesGrade7 Quarter3 Week1midnight skyNo ratings yet
- A SemiDocument2 pagesA SemiJessie OlantigueNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Week 1 GEOMETRYDocument8 pagesQuarter 3 Week 1 GEOMETRYsineNo ratings yet
- Week1 LasDocument1 pageWeek1 LasSteward john Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- M8Ge-Iiia-1 M8Ge-Iiia-C-1Document5 pagesM8Ge-Iiia-1 M8Ge-Iiia-C-1astronNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument10 pagesGeometryPatrick Erwin Teñido AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument17 pagesChap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesAlrianne Batonghinog100% (1)
- Sem-LP - Apply Triangle Congruence (G8) - Day16Document5 pagesSem-LP - Apply Triangle Congruence (G8) - Day16merinalfred14No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Geometry and Kinds of Angles: Week 1Document7 pagesBasic Concepts in Geometry and Kinds of Angles: Week 1Jeremy CabilloNo ratings yet
- Math 7 3rd and 4RTH QuarterDocument53 pagesMath 7 3rd and 4RTH Quartercarlo angelo ydelNo ratings yet
- g8 3rd GP LCTG Lc41aDocument6 pagesg8 3rd GP LCTG Lc41aIan MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Geometry 1 - 1 Intro To Geometry HandoutDocument40 pagesGeometry 1 - 1 Intro To Geometry HandoutAlma ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Q3 Week 1Document10 pagesMath 7 Q3 Week 1Trisha ArizalaNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument60 pagesGeometryAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Math 7 (Week 1)Document40 pagesMath 7 (Week 1)John Raygie Ordoñez CinetaNo ratings yet
- Guided Noteboo Kin GED10 2 (Mathe Matics in The Modern World)Document6 pagesGuided Noteboo Kin GED10 2 (Mathe Matics in The Modern World)Aaronie DeguNo ratings yet
- Motp Junior Geometry Essentials Problem Set 3Document4 pagesMotp Junior Geometry Essentials Problem Set 3K. M. Junayed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Poolroom MathDocument4 pages1.2 Poolroom MathAmyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and Molecules of Life NotesDocument2 pagesBiochemistry and Molecules of Life NotesAmyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport TestDocument1 pageCellular Transport TestAmyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport NotesDocument3 pagesCellular Transport NotesAmyNo ratings yet
- Make To Order ScenariosDocument3 pagesMake To Order ScenariosEncyptNo ratings yet
- Gulrajani-1992-Review of Progress in Coloration and Related TopicsDocument12 pagesGulrajani-1992-Review of Progress in Coloration and Related TopicsPratik KaleNo ratings yet
- Manual HP700 2020Document11 pagesManual HP700 2020Jefril SiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter C15 Design Requirements For Structures With Supplemental Energy DissipationDocument6 pagesChapter C15 Design Requirements For Structures With Supplemental Energy DissipationEDWIN CHAUCA MEJÍANo ratings yet
- A New Continuous Contact Low-Noise Gear Pump: K. MitomeDocument6 pagesA New Continuous Contact Low-Noise Gear Pump: K. MitomeMorteza ShakerienNo ratings yet
- Laser HardeningDocument12 pagesLaser HardeningSebastián Andrés Rojas MontielNo ratings yet
- Exact Ising Model Simulation On A Quantum ComputerDocument11 pagesExact Ising Model Simulation On A Quantum Computerarsalanali2162No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Inexact Floating-Point AddersDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Inexact Floating-Point AddersshaliniNo ratings yet
- Alignmentcalculationv 107Document16 pagesAlignmentcalculationv 107Pavel MoratiNo ratings yet
- Eaton Char-Lynn Hydraulic 101 - Series - 8179574 - ManualDocument12 pagesEaton Char-Lynn Hydraulic 101 - Series - 8179574 - Manual2078oxfordNo ratings yet
- 8051 VariantsDocument10 pages8051 VariantsRomeu Corradi JúniorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-4 - Geometry of A Vertical Aerial PhotographDocument35 pagesLecture 3-4 - Geometry of A Vertical Aerial PhotographFaisel mohammedNo ratings yet
- DHP SlipSheets 2017 PDFDocument29 pagesDHP SlipSheets 2017 PDF11tkt11No ratings yet
- Bahir Dar University Ethiopian Institute of Textile and Fashion TechnologyDocument21 pagesBahir Dar University Ethiopian Institute of Textile and Fashion TechnologyAndebet KassawNo ratings yet
- Conector 7-16 Din Hembra 7/8" Cellflex.Document2 pagesConector 7-16 Din Hembra 7/8" Cellflex.SIMON S. FLORES G.No ratings yet
- IBS-Tool / Web Monitor Installation and Configuration Under Windows XP 1. Modem InstallationDocument15 pagesIBS-Tool / Web Monitor Installation and Configuration Under Windows XP 1. Modem InstallationlemsouguerNo ratings yet
- Nouns: ConcreteDocument15 pagesNouns: ConcreteAndreas Alvonso Y LNo ratings yet
- A 243 MT Exam 20202021 CDocument1 pageA 243 MT Exam 20202021 CIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Action Cameras For Photogrammetric Purposes: Sensors September 2014Document21 pagesCalibration of Action Cameras For Photogrammetric Purposes: Sensors September 2014Besim BnproNo ratings yet
- EO & EO-2 Metric Bite Type FittingsDocument66 pagesEO & EO-2 Metric Bite Type FittingsMiroslaw LabudaNo ratings yet
- Manual Remote Starter Compustar 2W901Document22 pagesManual Remote Starter Compustar 2W901cristianbachNo ratings yet
- Matrix Academy: MHT-CET-XII - New Syllabus (MH) 2022-23Document4 pagesMatrix Academy: MHT-CET-XII - New Syllabus (MH) 2022-23Light MayNo ratings yet
- Additional Requirements For Bus Construction: Automotive Industry StandardDocument59 pagesAdditional Requirements For Bus Construction: Automotive Industry StandardVishwas VaidyaNo ratings yet
- IT Skill-2Document58 pagesIT Skill-2Shashwat Chaudhary100% (1)
- Gate Leakage Mechanisms in AlGaN-GaN and AlInN-GaN HEMTs - Comparison and ModelingDocument9 pagesGate Leakage Mechanisms in AlGaN-GaN and AlInN-GaN HEMTs - Comparison and ModelingSreenidhi TuruvekereNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Week 9 - Day 1: Problem Solving Involving Sides and Angles of A PolygonDocument4 pagesQuarter 3 - Week 9 - Day 1: Problem Solving Involving Sides and Angles of A PolygonsineNo ratings yet
- Freebitco inDocument8 pagesFreebitco inGayan SankalpaNo ratings yet
- Operations On Fractions-Lesson 1Document18 pagesOperations On Fractions-Lesson 1Mye BeltranNo ratings yet