Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Behavior / Territoriality
Uploaded by
Istikharoh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesTerritoriality provides reproductive and nutritional benefits to animals by allowing them to defend important resources like food, nesting sites, and mating areas. However, defending a territory requires a lot of time and energy. Whether territoriality is advantageous depends on how abundant and predictable resources are - if resources are plentiful, defending a territory is not necessary, but if resources are scarce, territoriality helps animals survive. The size and quality of the territory also impact an animal's habitat - larger territories require more energy to defend but provide access to more resources, while higher quality territories with more food and shelter lead to greater reproductive success. Animals vigorously defend their territories through evolution because this behavior increases their fitness by securing habitat and food needed to reproduce
Original Description:
Original Title
Animal Behavior
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTerritoriality provides reproductive and nutritional benefits to animals by allowing them to defend important resources like food, nesting sites, and mating areas. However, defending a territory requires a lot of time and energy. Whether territoriality is advantageous depends on how abundant and predictable resources are - if resources are plentiful, defending a territory is not necessary, but if resources are scarce, territoriality helps animals survive. The size and quality of the territory also impact an animal's habitat - larger territories require more energy to defend but provide access to more resources, while higher quality territories with more food and shelter lead to greater reproductive success. Animals vigorously defend their territories through evolution because this behavior increases their fitness by securing habitat and food needed to reproduce
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesAnimal Behavior / Territoriality
Uploaded by
IstikharohTerritoriality provides reproductive and nutritional benefits to animals by allowing them to defend important resources like food, nesting sites, and mating areas. However, defending a territory requires a lot of time and energy. Whether territoriality is advantageous depends on how abundant and predictable resources are - if resources are plentiful, defending a territory is not necessary, but if resources are scarce, territoriality helps animals survive. The size and quality of the territory also impact an animal's habitat - larger territories require more energy to defend but provide access to more resources, while higher quality territories with more food and shelter lead to greater reproductive success. Animals vigorously defend their territories through evolution because this behavior increases their fitness by securing habitat and food needed to reproduce
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
increases; in times of depleted resources the
presence of territoriality increases. The
presence of territoriality often forces less fit
animals to live in sub optimal habitats, thus
reducing their reproductive success.
Though territoriality offers immense
reproductive and nutritional benefits, it also
comes at a cost. Defending territory is not
Animal Behavior / easy. Territoriality cost time and energy and
Territoriality can often interfere with other fundamental
activities as parenting, feeding, courting, and
mating. For these reasons territoriality may
not be seen as a benefit in all animals.
Animals must be able to reap the fruits of
territoriality, while expending the least
amount of energy. For these reasons if
resources are abundant and predictable it
would be disadvantageous to defend the
territory. On the other hand, if resources are
scarce and undependable it would be
advantageous to exhibit territoriality.
In selecting a territory the size and
the quality play a crucial role in determining
an animals habitat. Territory size generally
tends to be no larger than the organism than
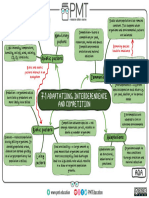
Territoriality is a type of
requires to survive, because with an increase
intraspecific or interspecific competition that
in territory comes an increased in energy
results from the behavioral exclusion of
expenditure. For some animals the territory
others from a specific space that is defended
size is not the most important aspect of
as territory. This well-defined behavior is
territoriality, but rather the quality of
exhibited through songs and calls,
defended territory. The quality is considered
intimidation behavior, attack and chase, and
to be fundamentally important due to
marking with scents. This form of defense
amount of food availability and superior
proves to be very costly for animals. So one
nesting sights. Animals depend on these
is forced to ask, Why do animals take part in
features to ensure their superior fitness.
such interspecific competition?
Animals invest a lot of time and
In order to understand this question
energy in defending their territories, and for
one must take a cost-benefit approach to
this reason they fight vigorously to defend
territoriality. The proximate reasons for such
their territory at all cost. Researchers suggest
defense vary. For some animals the reason
for this reason that when a rival challenges a
for participating in such elaborate protective
territory holder, the owner almost always
behavior is to acquire and protect food
wins the contest. This phenomenon could be
sources, nesting sites, mating areas, or to
attributed to an evolutionary stable strategy
simply attract a mate. The ultimate cause of
which assets that rules for behavior is
this behavior may be attributed to the
controlled by an inherited proximate
increased probability of survival and
mechanism such that the differences
reproductive successes. In defending a
between individuals in their strategies are
territory an animal is ultimately securing that
liked to differences in their genes. Territory
it will have an habitat in which to forage for
plays an important role as a mechanism of
food and to successfully reproduce, thus
population regulation, insuring the success
increasing the animal's overall fitness. This
of fit animals, and aiding in the eradication
ultimate theory is strengthened when one
of less fit animals. Territorially also plays a
considers the instances in which territoriality
fundamental role as an indicator of carrying
capacity; it also serves as an indicator of
how much habitat is necessary to support
viable populations. For these reasons
researchers continue to examine the well-
developed behavior of territoriality.
You might also like
- MH5-C Prospekt PDFDocument16 pagesMH5-C Prospekt PDFvatasaNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Online Toefl Pertemuan 6 - TeritorialityDocument2 pagesJawaban Online Toefl Pertemuan 6 - TeritorialityIstikharohNo ratings yet
- KPI AssignmentDocument7 pagesKPI AssignmentErfan Ahmed100% (1)
- Yetta Company ProfileDocument6 pagesYetta Company ProfileAfizi GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Tese Beatbox - Florida PDFDocument110 pagesTese Beatbox - Florida PDFSaraSilvaNo ratings yet
- Borges, The SouthDocument4 pagesBorges, The Southdanielg233100% (1)
- 25 Middlegame Concepts Every Chess Player Must KnowDocument2 pages25 Middlegame Concepts Every Chess Player Must KnowKasparicoNo ratings yet
- Story Tugas Sebelum UTSDocument1 pageStory Tugas Sebelum UTSIstikharohNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledmodehvaNo ratings yet
- Impact Analysis Model: Conversion of Natural Habitat Into Agricultural LandDocument1 pageImpact Analysis Model: Conversion of Natural Habitat Into Agricultural LandDia RoseNo ratings yet
- Aeap-65-Ex.-2-Rollon-Jim Aldrix, C.Document9 pagesAeap-65-Ex.-2-Rollon-Jim Aldrix, C.JIM ALDRIX ROLLONNo ratings yet
- Competition Evolution ReadingDocument2 pagesCompetition Evolution Readingapi-242868690No ratings yet
- CH 5Document18 pagesCH 5Boţu AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Part I - Define & Note: 5.3 - What Limits The Growth of Populations?Document3 pagesPart I - Define & Note: 5.3 - What Limits The Growth of Populations?Aaren MitchellNo ratings yet
- Bio105-L11 - Adaptation and Survival - F20Document11 pagesBio105-L11 - Adaptation and Survival - F20Maksim PetrushinNo ratings yet
- ESS - Chapter 3 RevisionDocument7 pagesESS - Chapter 3 RevisionSachitNo ratings yet
- Wasko 2012Document9 pagesWasko 2012NacorNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document65 pagesGroup 1025wilmelNo ratings yet
- Green Olive Minimalis Modern Trip Promotion Trifold Brochure (Trifolds)Document2 pagesGreen Olive Minimalis Modern Trip Promotion Trifold Brochure (Trifolds)jovanie baliliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Module 4Document1 pageUnit 3 Module 4heideNo ratings yet
- Silvopasture - The Main Components of SilvopastureDocument6 pagesSilvopasture - The Main Components of SilvopastureChelsea Green Publishing100% (1)
- The Role of Zoos: June 2013Document11 pagesThe Role of Zoos: June 2013Azucena López GómezNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human SocietyDocument4 pagesScience, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human Societyjennylyn karunungan100% (1)
- Behavioural EcologyDocument20 pagesBehavioural EcologyKargboNo ratings yet
- Instructional Project 6 Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesInstructional Project 6 Lesson Planapi-322596215No ratings yet
- Smallholder Dairy HousingDocument74 pagesSmallholder Dairy HousinglukamasiaNo ratings yet
- StudyGuide Exam2Document15 pagesStudyGuide Exam2Gugan RaghuramanNo ratings yet
- Zarco Et Al 2019 Flocks GrazingDocument6 pagesZarco Et Al 2019 Flocks GrazingagustinzarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 MAGCAMIT Reina Chiara G.Document5 pagesWorksheet 6 MAGCAMIT Reina Chiara G.Carlo MagcamitNo ratings yet
- A. Human Activities & Stability of EcosystemsDocument7 pagesA. Human Activities & Stability of EcosystemsJames Philip RelleveNo ratings yet
- K and R Reproductive Strategies PDFDocument2 pagesK and R Reproductive Strategies PDFElyse GarciaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Intro To Livestock and PoultryDocument8 pagesMODULE 4 Intro To Livestock and PoultryJessa Pabillore100% (1)
- Behavioural Ecology LecturesDocument10 pagesBehavioural Ecology LecturesHamzullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Conditioning and Behavioral Training in ReptilesDocument5 pagesConditioning and Behavioral Training in ReptilesChecko LatteNo ratings yet
- GE 10 Assign. 8Document2 pagesGE 10 Assign. 8Cyrelle Rose JumentoNo ratings yet
- Ecology Study GuideDocument18 pagesEcology Study Guidescienceguy10No ratings yet
- Chapter Three: 3.principles of Wildlife Ecology 3.1 - Wildlife Habitat, Cover and Territory 3.1.1. Wildlife HabitatDocument86 pagesChapter Three: 3.principles of Wildlife Ecology 3.1 - Wildlife Habitat, Cover and Territory 3.1.1. Wildlife HabitatnasimalshoqNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 14.4.1 Competitive BehaviorDocument2 pagesBio Notes 14.4.1 Competitive BehaviorKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- Nickley and Bulluck - 2019 - Spanning The Habitat GradientDocument12 pagesNickley and Bulluck - 2019 - Spanning The Habitat GradientBen NickleyNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsDocument56 pagesGenetics and Evolution GZ 2018 ChsSayali PatilNo ratings yet
- Animal Domestication and Behavior - F Ch4Document9 pagesAnimal Domestication and Behavior - F Ch4FuligemzNo ratings yet
- Examples of Natural SelectionDocument26 pagesExamples of Natural SelectionMuneer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Geographic Variation in The Sensitivity of An Herbivore-Induced Seaweed DefenseDocument11 pagesGeographic Variation in The Sensitivity of An Herbivore-Induced Seaweed DefenseHarry MeyasNo ratings yet
- Conservation Biology CIE IGCSE PresentationDocument13 pagesConservation Biology CIE IGCSE Presentationuwizewe.kezaNo ratings yet
- Minggu II: Wildlife MovementDocument32 pagesMinggu II: Wildlife MovementRenata MonicaNo ratings yet
- In Situ Ex Situ Policy BriefDocument4 pagesIn Situ Ex Situ Policy BriefDevil AbiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Insight From Distribution Dynamics Strategies To Conserve A Dhole Metapopulation in IndiaDocument12 pages2019 Insight From Distribution Dynamics Strategies To Conserve A Dhole Metapopulation in IndiaPatrick RouxNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes Sa1 Kim Chia 2012Document23 pagesBio Notes Sa1 Kim Chia 2012joleneNo ratings yet
- Digitalcommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Digitalcommons@University of Nebraska - LincolnDocument4 pagesDigitalcommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Digitalcommons@University of Nebraska - LincolnBoyet FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Def WildDocument9 pagesDef WildFrancis Ben BerjaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map ch7Document1 pageMind Map ch7hazel loyNo ratings yet
- Zeder Melinda - 2012 - Pathways To Animal DomesticationDocument34 pagesZeder Melinda - 2012 - Pathways To Animal DomesticationmascaradeNo ratings yet
- K and R Reproductive StrategiesDocument2 pagesK and R Reproductive StrategiesjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Zoo Biology, 16, 1-2.Document2 pagesZoo Biology, 16, 1-2.Sebas CirignoliNo ratings yet
- Theacher GuideDocument4 pagesTheacher GuideAlejandro Lavid SaizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Environmental Science. Miller & Spoolman 17th EdDocument54 pagesChapter 5. Environmental Science. Miller & Spoolman 17th EdEzra Je Lombiso AballeNo ratings yet
- 2015.14 Veld Management PrinciplesDocument3 pages2015.14 Veld Management PrinciplesTrevor ChadNo ratings yet
- Mcintyre - Habitat Variegation, An Alternative To Fragmentation PDFDocument3 pagesMcintyre - Habitat Variegation, An Alternative To Fragmentation PDFivanNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument13 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationDHANUSHNo ratings yet
- PredatorimportanceDocument2 pagesPredatorimportanceCafezinho NoturnoNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Distributions - 2011 - Pe Er - Butterfly Diversity at The Ecotone Between Agricultural and Semi NaturalDocument12 pagesDiversity and Distributions - 2011 - Pe Er - Butterfly Diversity at The Ecotone Between Agricultural and Semi NaturalAlessio VovlasNo ratings yet
- Albright - 1993Document14 pagesAlbright - 1993Alberto ChambelaNo ratings yet
- Conservation Genetics: Robin AllabyDocument43 pagesConservation Genetics: Robin AllabyHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- BIOL Final Exam Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesBIOL Final Exam Cheat Sheetrishabhvasisht03No ratings yet
- Diversity Assessment Methods Biodiversity Values: Centre of Advanced Study in Marine Biology Annamalai UniversityDocument8 pagesDiversity Assessment Methods Biodiversity Values: Centre of Advanced Study in Marine Biology Annamalai UniversityDhoni CskNo ratings yet
- LUMBAB Module 1 Lesson 1Document11 pagesLUMBAB Module 1 Lesson 1LONGAKIT ROANNo ratings yet
- No Tenses Active Voice Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesNo Tenses Active Voice Passive VoiceIstikharohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document34 pagesChapter 15IstikharohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document27 pagesChapter 14IstikharohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document26 pagesChapter 10IstikharohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document26 pagesChapter 2IstikharohNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 3Document2 pagesPertemuan 3IstikharohNo ratings yet
- ANALYSISDocument1 pageANALYSISIstikharohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document33 pagesChapter 12IstikharohNo ratings yet
- Magic Bullet Theory - PPTDocument5 pagesMagic Bullet Theory - PPTThe Bengal ChariotNo ratings yet
- Evidence Prove DiscriminationDocument5 pagesEvidence Prove DiscriminationRenzo JimenezNo ratings yet
- 0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andDocument20 pages0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andJuke LastNo ratings yet
- PlateNo 1Document7 pagesPlateNo 1Franz Anfernee Felipe GenerosoNo ratings yet
- State Space ModelsDocument19 pagesState Space Modelswat2013rahulNo ratings yet
- Inspección, Pruebas, Y Mantenimiento de Gabinetes de Ataque Rápido E HidrantesDocument3 pagesInspección, Pruebas, Y Mantenimiento de Gabinetes de Ataque Rápido E HidrantesVICTOR RALPH FLORES GUILLENNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Cement Concrete ElementsDocument14 pagesDesign of Reinforced Cement Concrete ElementsSudeesh M SNo ratings yet
- Engleza Referat-Pantilimonescu IonutDocument13 pagesEngleza Referat-Pantilimonescu IonutAilenei RazvanNo ratings yet
- Based On PSA 700 Revised - The Independent Auditor's Report On A Complete Set of General Purpose Financial StatementsDocument12 pagesBased On PSA 700 Revised - The Independent Auditor's Report On A Complete Set of General Purpose Financial Statementsbobo kaNo ratings yet
- Niveshdaily: From Research DeskDocument53 pagesNiveshdaily: From Research DeskADNo ratings yet
- ISA InTech Journal - April 2021Document50 pagesISA InTech Journal - April 2021Ike EdmondNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Project 4º Eso Beauty Canons 2015-16 DefinitivoDocument2 pages2nd Term Project 4º Eso Beauty Canons 2015-16 DefinitivopasferacosNo ratings yet
- Smart Door Lock System Using Face RecognitionDocument5 pagesSmart Door Lock System Using Face RecognitionIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Reference Paper Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesReference Paper Literature ReviewAani RashNo ratings yet
- 9400 Series - Catalogue - AccessoriesDocument86 pages9400 Series - Catalogue - AccessoriesSaulo Leonardo Fabelo FontesNo ratings yet
- ABARI-Volunteer Guide BookDocument10 pagesABARI-Volunteer Guide BookEla Mercado0% (1)
- Precursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationDocument7 pagesPrecursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationAlv R GraciaNo ratings yet
- Imabalacat DocuDocument114 pagesImabalacat DocuJänrëýMåmårìlSälängsàngNo ratings yet
- The Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsDocument58 pagesThe Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsWael HaidarNo ratings yet
- Educationusa 2022globalguide Final Reduced SizeDocument84 pagesEducationusa 2022globalguide Final Reduced SizeAnna ModebadzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Main Hydrological ConceptsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Main Hydrological ConceptsWhy Merah0% (1)
- Financial Market - Bsa 2A Dr. Ben E. Bunyi: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument3 pagesFinancial Market - Bsa 2A Dr. Ben E. Bunyi: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyAsh imoNo ratings yet
- Nizkor Project Fallacies - LabossierDocument77 pagesNizkor Project Fallacies - Labossierapi-3766098100% (1)
- Sample Learning Module As PatternDocument23 pagesSample Learning Module As PatternWilliam BulliganNo ratings yet