0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views5 pagesDifference Between Census and Sampling
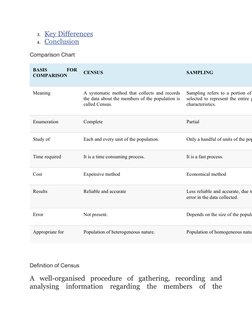
Census and sampling are two common methods for collecting survey data about a population. Census involves collecting data from all members of the population and aims for a complete enumeration. Sampling instead collects data from only a subset of the population and aims to draw conclusions about the whole. Key differences are that census takes more time and money but provides reliable results, while sampling is faster and cheaper but less accurate. Both have appropriate uses depending on whether the population is homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Uploaded by
SureshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views5 pagesDifference Between Census and Sampling
Census and sampling are two common methods for collecting survey data about a population. Census involves collecting data from all members of the population and aims for a complete enumeration. Sampling instead collects data from only a subset of the population and aims to draw conclusions about the whole. Key differences are that census takes more time and money but provides reliable results, while sampling is faster and cheaper but less accurate. Both have appropriate uses depending on whether the population is homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Uploaded by
SureshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Comparison Chart: Details a systematic comparison between census and sampling, outlining differences in meaning, cost, and appropriate scenarios for each.
- Definition: Provides definitions and detailed explanations for both census and sampling methodologies, including their processes and applications.
- Key Differences Between Census and Sampling: Lists and explains the key differences between census and sampling, focusing on methods, cost, time, results, and applicability.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the comparative insights and practical implications of census and sampling in different contexts.