Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revised Bloom's Taxonomy Action Verbs
Uploaded by
OvaisAkhterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revised Bloom's Taxonomy Action Verbs
Uploaded by
OvaisAkhterCopyright:
Available Formats
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs: Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor*
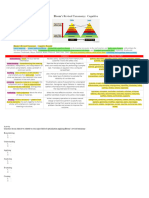
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy—Cognitive Domain
The cognitive domain involves knowledge and the development of intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns,
and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills. Lorin Anderson, a former student of Bloom, revisited the cognitive domain in the
learning taxonomy in the mid-nineties and made some changes, with perhaps the two most prominent ones being, 1) changing the names in the six categories
from noun to verb forms, and 2) slightly rearranging them. This new taxonomy reflects a more active form of thinking and is perhaps more accurate.
*appropriate synonyms and illustrated verbs can be preferred with level of ability.
Category Examples Keywords [Verbs]
Remembering (C1): Recall previous learned Exhibit memory of previously Learned material by Define, describe, identify, know, list, match, name,
information. recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. outline, recall, recognize, reproduce, state, choose,
Recite a policy. Quote prices from memory to a find, how, label, omit, show, spell, tell, what, when,
customer. Knows the safety rules.
where, which, who, why, cite, give an example,
listen, locate, memorize, quote, recite, record,
repeat, underline.
Understanding (C2): Comprehending the Rewrites the principles of test writing. Explain in Comprehend, convert, distinguish, demonstrate,
meaning, translation, interpolation, and one's own words the steps for performing a estimate, guess, explain, extend, generalize, give
interpretation of instructions and problems. State a complex task. Translates an equation into a multiple examples, infer, interpret, paraphrase,
computer spreadsheet. Demonstrate understanding
problem in one's own words. of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, rewrite, translate, classify, rephrase, ask, calculate,
translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and discuss, observe, report, re-tell, review, summarize.
stating main ideas.
Applying (C3): Use a concept in a new situation or
unprompted use of an abstraction. Applies what was Use a manual to calculate an employee's vacation Apply, change, compute, construct, demonstrate
learned in the classroom into novel situations in the time. Apply laws of statistics to evaluate the new concept, discover, manipulate, modify, operate,
reliability of a written test. prepare, produce, solve, develop, experiment,
work place.
interview, make, use, make use of, model, plan,
utilize, dramatize, draw, illustrate, practice,
sequence, teach, execute.
Analyzing (C4): Separates material or concepts Troubleshoot a piece of equipment by using logical Analyze, breakdown, compare, contrast, diagram,
into component parts so that its organizational deduction. Recognize logical fallacies in deconstruct, differentiate, discriminate, identify,
structure may be understood. Distinguishes reasoning. Gathers information from a department relate, group, order, investigate, separate, assume,
between facts and inferences. and selects the required tasks for training. Examine categorize, conclusion, dissect, divide, examine,
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 1 of 7
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
and break information into parts by identifying research, function, inference, inspect, motive,
motives or causes. Make inferences and find relationship, simplify, survey, take, part in,
evidence to support generalizations. question, test, test for, theme, distinguish the fact,
classify the materials, graph, plot.
Evaluating (C5): Make judgments about the value Select the most effective solution. Hire the most Appraise, contrast, criticize, critique, defend,
of ideas or materials. qualified candidate. Justify a new budget. discriminate, evaluate, agree, asses, award,
Present and defend opinions by making judgments conclude, criteria, decide, deduct, determine, prove,
about information, validity of ideas, or quality of disprove, importance, influence, judge, justify,
work based on a set of criteria. mark, measure, opinion, perceive, itize, rate,
recommend, rule on, select, support, argue, debate,
tell why, value.
Creating (C6): Builds a structure or pattern from Write a company operations or process manual. Categorize, combine, compile, compose, create,
diverse elements. Put parts together to form a Design a machine to perform a specific task. devise, design, generate, modify, organize, arrange,
whole, with emphasis on creating a new meaning or Integrates training from several sources to solve a predict, rearrange, reconstruct, reorganize, revise,
structure. problem. Revises and process to improve the summarize elements, tell, write, adapt, build,
outcome. delete, grow, evolve, enlarge, spread, elaborate,
Compile information together in a different way by approximate, formulate, happen, imagine, forecast,
combining elements in a new pattern or proposing divine, formulate, happen, imagine, improve,
alternative solutions. invent, make up, maximize, minimize, original,
originate, propose, solution, resolve, suppose,
theory.
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 2 of 7
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy—Affective Domain
The affective domain includes the manner in which we deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms, motivations, and
attitudes. This domain includes the manner in which we deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms, motivations, and
attitudes. The five major categories are listed from the simplest behavior to the most complex:
Category Examples Keywords [Verbs]
Receiving Phenomena (A1): Awareness, Listen to others with respect. Listen for and Ask, choose, describe, give, hold, identify, locate,
willingness to hear, selected attention. remember the name of newly introduced people. name, point to, select, sit, erect, reply, use, accept,
acknowledge, be aware, listen, notice, pay
attention, tolerate.
Responding to Phenomena (A2): Active Participates in class discussions. Gives a Answer, respond, answer freely, assist, aid, comply,
participation on the part of the learners. Attends and presentation. Questions new ideals, concepts, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, perform,
reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning models, etc. in order to fully understand them. practice, present, read, read voluntarily, recite,
outcomes may emphasize compliance in Know the safety rules and practices them. report, select, tell, write, agree to, care for,
responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction communicate, comply, confirm, consent,
in responding (motivation). contribute, cooperate, participate, participate
willingly, follow, obey, visit.
Valuing (A3): The worth or value a person attaches Demonstrates belief in the democratic process. Is Complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain,
to a particular object, phenomenon, or behaviour. sensitive towards individual and cultural form, initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, report,
This ranges from simple acceptance to the more differences (value diversity). Shows the ability to select, share, study, work, adopt, assume, assume
complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on solve problems. Proposes a plan to social responsibility, behave, behave according to,
the internalization of a set of specified values, while improvement and follows through with commit, desire, exhibit loyalty, express, prefer,
clues to these values are expressed in the learner's commitment. Informs management on matters that seek, show, show continual desire to, show concern,
overt behavior and are often identifiable. one feels strongly about. use resources to
Organization (A4): Organizes values into Recognizes the need for balance between freedom Adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare,
priorities by contrasting different values, resolving and responsible behaviour. Accepts responsibility complete, defend, explain, formulate, generalize,
conflicts between them, and creating a unique value for one's behaviour. Explains the role of systematic integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate,
system. The emphasis is on comparing, relating, planning in solving problems. Accepts professional synthesize, adapt, adjust, balance, classify,
and synthesizing values. ethical standards. Creates a life plan in harmony conceptualize, group, theorize.
with abilities, interests, and beliefs. Prioritizes time
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 3 of 7
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
effectively to meet the needs of the organization,
family, and self.
Internalizing values/characterization (A5): Has a Shows self-reliance king independently. Act, act upon, discriminate, display, influence,
value system that controls their behavior. The Cooperates in group activities (displays teamwork). modify, perform, practice, propose, qualify,
behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and Uses an objective approach in problem solving. question, revise, serve, solve, verify, advocate,
most importantly, characteristic of the learner. Displays a professional commitment to ethical exemplify, justify behavior, maintain, support.
Instructional objectives are concerned with the practice on a daily basis. Revises judgments and
student's general patterns of adjustment (personal, changes behavior in light of new evidence. Values
social, emotional). people for what they are, not how they look.
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 4 of 7
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
Bloom’s Taxonomy—Psychomotor Domain
The psychomotor domain includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. Development of these skills requires practice and is
measured in terms of speed, precision, distance, procedures, or techniques in execution. The seven major categories are listed from the simplest behavior to the
most complex.
Category Examples Keywords [Verbs]
Perception (P1): The ability to use sensory cues to Senses cues that guide more activity. Detects non- Choose, describe, detect, differentiate, distinguish,
guide motor activity. This ranges from sensory verbal communication cues. Estimate where a ball identify, isolate, relate, select, hear, listen, observe,
stimulation, through cue selection, to translation. will land after it is thrown and then moving to the perceive, recognize, see, sense, smell, taste, view,
correct location to catch the ball. Adjusts heat of watch.
stove to correct temperature by smell and taste of
food. Adjusts the height of the forks on a forklift by
comparing where the forks are in relation to the
pallet.
Set (P2): Readiness to act. It includes mental, Mentally, physical and/or emotionally ready to act. Begin, display, explain, move, proceed, react,
physical, and emotional sets. These three sets are Knows and acts upon a sequence of steps in a show, state, volunteer, sit, stand, station, achieve a
dispositions that predetermine a person's response manufacturing process. Recognize one's posture, assume a body stance, establish a body
to different situations (sometimes called mindsets). abilities and limitations. Shows desire to learn a position, place hands, place arms, position the
new process (motivation). NOTE: This subdivision body.
of Psychomotor is closely related with the
“Responding to phenomena” subdivision of the
Affective domain.
Guided Response (P3): The early stages in Imitates and practices skills, often in discrete steps. Copy, trace, follow, react, reproduce, respond,
learning a complex skill that includes imitation and Performs a mathematical equation as demonstrated. duplicate, imitate, manipulate with guidance,
trial and error. Adequacy of performance is Follows instructions to build a model. Responds operate under supervision, practice, repeat, try.
achieved by practicing. hand-signals of instructor while learning to operate
a forklift.
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 5 of 7
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
Mechanism (P4): This is the intermediate stage in Performs act with increasing efficiency, confidence Assemble, calibrate, construct, dismantle, display,
learning a complex skill. Learned responses have and proficiency. Use a personal computer. Repair a fasten, fix, grind, heat, manipulate with, measure,
become habitual and the movements can be leaking faucet. Drive a car. mend, mix, organize, sketch, conduct, demonstrate,
performed with some confidence and proficiency. execute, make, pace, produce, complete with
confidence, improve efficiency, increase speed.
Complex Overt Response/Expert (P5): The Performs automatically. Manoeuvres a car into a Control, direct, excel, build, guide, dismantle,
skilful performance of motor acts that involve tight parallel parking spot. Operates a computer perfect, manage, master, act habitually, advance
complex movement patterns. Proficiency is quickly and accurately. Displays competence while with assurance, maintain efficiency, perform
indicated by a quick, accurate, and highly playing the piano. automatically, proceed automatically..
coordinated performance, requiring a minimum of
energy. This category includes performing without
hesitation, and automatic performance. For
example, players are often utter sounds of
satisfaction or expletives as soon as they hit a tennis
ball or throw a football, because they can tell by the
feel of the act what the result will produce.
Adaptation (P6): Skills are well developed and the Adapts skill test to meet a problem solution. Adapt, alter, change, rearrange, reorganize, revise,
individual can modify movement patterns to fit Responds effectively to unexpected experiences. vary.
special requirements. Modifies instruction to meet the needs of the
learners. Perform a task with a machine that it was
not originally intended to do (machine is not
damaged and there is no danger in performing the
new task).
Origination (P7): Creating new movement Creates new patterns for specific solutions. Arrange, build, combine, compose, create, design,
patterns to fit a particular situation or specific Constructs a new theory. Develops a new and initiate, originate.
problem. Learning outcomes emphasize creativity comprehensive training programming.
based upon highly developed skills. Creates a new gymnastic routine.
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 6 of 7
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Action Verbs Electronic Engineering Department
References
• Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, Abridged Edition. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
• Anderson, Krathwohl, Airasian, Cruikshank, Mayer, Pintrich, Raths, Wittrock, 2000; Pohl, 2000.
• Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Chart; https://www.cloud.edu/Assets/PDFs/assessment/revised-blooms-chart.pdf
Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Revised Blooms Taxonomy All DomainsDocument4 pagesRevised Blooms Taxonomy All DomainsRelampago CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorDocument4 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotordeeeeeeeeedeeeeeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's TaxonomyDocument2 pagesRevised Bloom's TaxonomyLeila Ricci Llanillo0% (1)
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorDocument4 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorsumonNo ratings yet
- Categorization For The Thinking ProcessDocument2 pagesCategorization For The Thinking ProcessNavaneetha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of Learning DomainsDocument17 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of Learning DomainsVincentAlejandroNo ratings yet
- 3 Domains of ObjectiveDocument7 pages3 Domains of Objectiveromeo mirandaNo ratings yet
- Cooperative LearningDocument5 pagesCooperative LearningS ArunmethaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument8 pagesBloom's TaxonomyMarissaM.PerezNo ratings yet
- 38 SchtheeesyllDocument149 pages38 SchtheeesyllbharathgkNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsNuruel HassanNo ratings yet
- 38 SchtheeesyllDocument149 pages38 SchtheeesyllShantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A Framework for LearningDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: A Framework for LearningjenaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument6 pagesBloom's TaxonomyJisiamar GeromoNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBloom's TaxonomyRic PerezNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains ExplainedDocument11 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains ExplainedChai Ming Kuang100% (1)
- Lesson II Instructional DecissionsDocument14 pagesLesson II Instructional DecissionsGreta SuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Instructional Objectives and Learning Outcomes Handsout 1Document8 pagesLesson 3 Instructional Objectives and Learning Outcomes Handsout 1barcekylaNo ratings yet
- BloomDocument11 pagesBloomTalab_DeepakNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningDocument6 pagesCognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- Handout L5 The Bloom TaxonomiesDocument6 pagesHandout L5 The Bloom TaxonomiesNgọc Anh LưuNo ratings yet
- Table of The Revised Cognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningDocument11 pagesTable of The Revised Cognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningArjane LoquianoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningDocument4 pagesCognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningjanineNo ratings yet
- Table of The Cognitive Domain (Original)Document8 pagesTable of The Cognitive Domain (Original)Amiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionDocument17 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionNur ZaraNo ratings yet
- Bloom'S Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument27 pagesBloom'S Taxonomy of Learning DomainsnNo ratings yet
- Ecb 2306 - 1Document22 pagesEcb 2306 - 1peterambrose009No ratings yet
- 3 Domains of LearningDocument5 pages3 Domains of LearningFeinrirNo ratings yet
- Category Examples Key Words (Verbs)Document5 pagesCategory Examples Key Words (Verbs)Christine Sheena Batican-BulalaNo ratings yet
- Learning Domains: Bloom's Taxonomy ExplainedDocument16 pagesLearning Domains: Bloom's Taxonomy ExplainedummerbilalNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument9 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsmalexsastryNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument15 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsElma AisyahNo ratings yet
- Category Example and Key WordsDocument3 pagesCategory Example and Key WordsJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument25 pagesTaxonomy of Educational ObjectivesAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TexanomyDocument3 pagesBloom's TexanomyMuhammad Wajahat Ali KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint in Reading and Writing SkillsDocument79 pagesPowerpoint in Reading and Writing Skillssharmaine tamayo100% (9)
- Topic 1 - TEACHING and The TEACHING PROCESSDocument88 pagesTopic 1 - TEACHING and The TEACHING PROCESSmanrhe pilanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's T Axonomy of Learning DomainsDocument11 pagesBloom's T Axonomy of Learning DomainsEzra NolanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of LearningDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of LearningXiena Rose BaniquedNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of LearningDocument10 pagesThe Three Types of Learningmary heart baldemoroNo ratings yet
- Summary Assessment Long Quiz CPDDocument2 pagesSummary Assessment Long Quiz CPDMr.Regienald PuraNo ratings yet
- Safari - 23 Oct 2018 at 7:07 AM PDFDocument1 pageSafari - 23 Oct 2018 at 7:07 AM PDFhr187No ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy - Lower and Higher Level Cognitive SkillsDocument1 pageBloom's Taxonomy - Lower and Higher Level Cognitive SkillsLeidyDanielaBenitezPantojaNo ratings yet
- Authentic and Alternative Assessment MethodsDocument3 pagesAuthentic and Alternative Assessment MethodsVino€ H€rmosoNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument12 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsRominaPaolaNo ratings yet
- The Three Learning Domains - Cognitive, Affective, PsychomotorDocument19 pagesThe Three Learning Domains - Cognitive, Affective, PsychomotorRicheal BrionesNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains: Cognitive DomainDocument4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains: Cognitive DomainChristian DadoNo ratings yet
- Blooms Domains 2Document9 pagesBlooms Domains 2Cherry-Ann C. OlajayNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet
- Learning - Types, Processes & Styles: Class 6Document9 pagesLearning - Types, Processes & Styles: Class 6rendboyNo ratings yet
- Verbs Used in Syllabus DesignDocument1 pageVerbs Used in Syllabus DesignMark Anthony MollejonNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy All Three DomainsDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy All Three DomainsIno JohannisNo ratings yet
- Learning domains and Bloom's taxonomyDocument11 pagesLearning domains and Bloom's taxonomymust dietNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains - VikaspediaDocument4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains - VikaspediaNAZIRA SANTIAGO ESCAMILLANo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A Framework for LearningDocument9 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: A Framework for LearningAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains: Concepts, Processes, Procedures, and PrinciplesDocument6 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains: Concepts, Processes, Procedures, and PrinciplesLen HebronNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy and Revised Version ExplainedDocument4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy and Revised Version Explainedjacqueline baeNo ratings yet
- Scenario Thinking: Preparing Your Organization for the Future in an Unpredictable WorldFrom EverandScenario Thinking: Preparing Your Organization for the Future in an Unpredictable WorldNo ratings yet
- Revised Invigilators Duties EED - Fall 2021 - EEDDocument2 pagesRevised Invigilators Duties EED - Fall 2021 - EEDOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- Revised Blooms TaxonomyDocument4 pagesRevised Blooms TaxonomyOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- Advance Topics in Wireless Networking & Communications ESC 716 Solution AssignmentDocument8 pagesAdvance Topics in Wireless Networking & Communications ESC 716 Solution AssignmentOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- CHI NI OTI Slami Apubli Cschool Syllabusformi Dtermexami Nati ON2021-22 Class:ViDocument3 pagesCHI NI OTI Slami Apubli Cschool Syllabusformi Dtermexami Nati ON2021-22 Class:ViOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems (EE-320) : Sir Syed University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument1 pageSignals and Systems (EE-320) : Sir Syed University of Engineering & TechnologyOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- FYP Project Report ChaptersDocument1 pageFYP Project Report ChaptersOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- NonEngineering CLO - S of TEDDocument4 pagesNonEngineering CLO - S of TEDOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 19042020 062850pm PDFDocument1 pageAssignment 01 19042020 062850pm PDFOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- FYP Hardware Issuance Notice for Remaining 2017 Batch StudentsDocument1 pageFYP Hardware Issuance Notice for Remaining 2017 Batch StudentsOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- ISSB Picture Story Writing SamplesDocument30 pagesISSB Picture Story Writing SamplesOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- DSP Practice Problem 1 PDFDocument2 pagesDSP Practice Problem 1 PDFOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- DSP Practice Problem 1 PDFDocument2 pagesDSP Practice Problem 1 PDFOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- SNS Practice Problem 1Document3 pagesSNS Practice Problem 1OvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- PC Setup For Workshop 6 April PDFDocument5 pagesPC Setup For Workshop 6 April PDFOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- PC Setup For Workshop 6 April PDFDocument5 pagesPC Setup For Workshop 6 April PDFOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- ISSB General Knowledge Islamic Questions 1Document12 pagesISSB General Knowledge Islamic Questions 1Qaisar RiazNo ratings yet
- ISSB Obstacles: Individual ChallengesDocument10 pagesISSB Obstacles: Individual ChallengesOvaisAkhter100% (1)
- S& S Course OutlineDocument2 pagesS& S Course OutlineOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- S Signal Lsands System Ms (Te - 220) : Lect Ture Pla AnDocument3 pagesS Signal Lsands System Ms (Te - 220) : Lect Ture Pla AnOvaisAkhterNo ratings yet
- Myth & Reality in YayatiDocument6 pagesMyth & Reality in YayatiDEEPALI SETHNo ratings yet
- Abolitionist Rhetoric Alyssa HendersonDocument6 pagesAbolitionist Rhetoric Alyssa Hendersonapi-438326329100% (1)
- Cunningham-Class and Class Consciousness E. P. Thompson-2024Document21 pagesCunningham-Class and Class Consciousness E. P. Thompson-2024Miguel Ángel Cabrera AcostaNo ratings yet
- ICT Form 5 Chapter 1Document34 pagesICT Form 5 Chapter 1Benammi Al-KhawarizmiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between TRAVEL, TRIP and JOURNEY (With Answers)Document3 pagesDifference Between TRAVEL, TRIP and JOURNEY (With Answers)Inglês e Espanhol Direto da EuropaNo ratings yet
- Dont Be Left BehindDocument66 pagesDont Be Left BehindkameronkellyNo ratings yet
- Leadership StudentsDocument11 pagesLeadership StudentsQuỳnh NameNo ratings yet
- Essential Practices: For Overcoming InsecurityDocument19 pagesEssential Practices: For Overcoming InsecurityFariza IchaNo ratings yet
- GerontionDocument4 pagesGerontionParam Kesare100% (1)
- Call Center StudyDocument189 pagesCall Center StudyAmit Rakshe100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - RULES AND MORAL STANDARDS-2Document10 pagesLecture 2 - RULES AND MORAL STANDARDS-2CIARA VICTORIA LLADONESNo ratings yet
- Pemetaan Sebaran Pedagang Kaki Lima (PKL) Di Kecamatan Palu TimurDocument17 pagesPemetaan Sebaran Pedagang Kaki Lima (PKL) Di Kecamatan Palu TimurAhmad BagendaNo ratings yet
- "Psychologie Des Foules" CommentaryDocument31 pages"Psychologie Des Foules" CommentaryaraceliNo ratings yet
- Mccrae and Costa Theories of PersonalityDocument7 pagesMccrae and Costa Theories of PersonalityKieya Jade GalerioNo ratings yet
- Colour StaffDocument19 pagesColour StaffGiulio PirondiniNo ratings yet
- Satanic SymbolsDocument123 pagesSatanic SymbolsPoorna Kalandhar67% (9)
- SHS Applied Economics Rubric For PapersDocument1 pageSHS Applied Economics Rubric For PapersRoly Jr PadernaNo ratings yet
- Desafio UHVDCDocument7 pagesDesafio UHVDCAlfonso Peralta DíazNo ratings yet
- Early 19th century architectural theoriesDocument8 pagesEarly 19th century architectural theoriesShivram VJNo ratings yet
- The Life of Frank Lloyd WrightDocument33 pagesThe Life of Frank Lloyd WrightAhmed100% (4)
- Double Integrals 1Document22 pagesDouble Integrals 1Aztec MayanNo ratings yet
- ESP Course and Syllabus Design Paper PDFDocument23 pagesESP Course and Syllabus Design Paper PDFputri novaNo ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument2 pagesConstructivismDece Jane Veriña EgeNo ratings yet
- C.L.R. James Mariners Renegades and Castaways The Story of Herman Melville and The World We Live inDocument178 pagesC.L.R. James Mariners Renegades and Castaways The Story of Herman Melville and The World We Live inBreixo Harguindey100% (1)
- CounselingDocument23 pagesCounselingrashmi patooNo ratings yet
- School Name My Family - Listening Comprehension NameDocument2 pagesSchool Name My Family - Listening Comprehension NameDelia ChiraNo ratings yet
- The Allure of Travel Writing - Travel - SmithsonianDocument2 pagesThe Allure of Travel Writing - Travel - SmithsonianJINSHAD ALI K P0% (1)
- AbsA divisor cordial labeling of a graph G with vertex set V is a bijection f from V to {1,2,...|V |} such that an edge uv is assigned the label 1 if f (u)| f (v) or f (v)| f (u) and the label 0 otherwise, then number of edges labeled with 0 and thenumber of edges labeled with 1 differ by at most 1. A graph with a divisor cordial labeling is called a divisor cordial graph. In this paper we prove that helm Hn , flower graph Fln and Gear graph Gn are divisor cordial graphs. Moreover we show that switching of a vertex in cycle Cn , switching of a rim vertex in wheel Wn and switching of the apex vertex in helm Hn admit divisor cordial labeling.tractDocument87 pagesAbsA divisor cordial labeling of a graph G with vertex set V is a bijection f from V to {1,2,...|V |} such that an edge uv is assigned the label 1 if f (u)| f (v) or f (v)| f (u) and the label 0 otherwise, then number of edges labeled with 0 and thenumber of edges labeled with 1 differ by at most 1. A graph with a divisor cordial labeling is called a divisor cordial graph. In this paper we prove that helm Hn , flower graph Fln and Gear graph Gn are divisor cordial graphs. Moreover we show that switching of a vertex in cycle Cn , switching of a rim vertex in wheel Wn and switching of the apex vertex in helm Hn admit divisor cordial labeling.tractkarthikroshan3No ratings yet
- Qazi Assignment Jun 20Document8 pagesQazi Assignment Jun 20kamal62747No ratings yet
- Word Cloud Activity RubricDocument1 pageWord Cloud Activity Rubricangelito alaras100% (1)