Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sepsis and SIRS
Uploaded by
Fortune Rubengo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
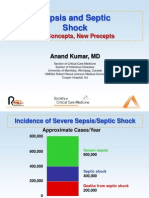
18 views2 pagesSevere sepsis affects 500,000 people annually in the United States and has a high mortality rate of 20-50% despite improvements in critical care. Sepsis is defined as a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) due to an infection, while severe sepsis is SIRS with organ dysfunction. Common causes of SIRS include infection, trauma, burns, and ischemia. Bacterial infection is the most common cause, with gram-negative and gram-positive organisms each accounting for around half of cases.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSevere sepsis affects 500,000 people annually in the United States and has a high mortality rate of 20-50% despite improvements in critical care. Sepsis is defined as a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) due to an infection, while severe sepsis is SIRS with organ dysfunction. Common causes of SIRS include infection, trauma, burns, and ischemia. Bacterial infection is the most common cause, with gram-negative and gram-positive organisms each accounting for around half of cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesSepsis and SIRS
Uploaded by
Fortune RubengoSevere sepsis affects 500,000 people annually in the United States and has a high mortality rate of 20-50% despite improvements in critical care. Sepsis is defined as a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) due to an infection, while severe sepsis is SIRS with organ dysfunction. Common causes of SIRS include infection, trauma, burns, and ischemia. Bacterial infection is the most common cause, with gram-negative and gram-positive organisms each accounting for around half of cases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Sepsis and SIRS
Severe sepsis affects 500,000 annually in the United States
Despite improvements in critical care mortality of 20-50% remains
unchanged
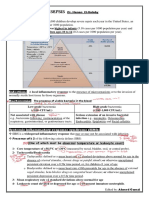
Definitions
Condition Definition
Bacteraemia The presence of viable bacteria in the bloodstream
SIRS The systemic inflammatory response to a variety of
clinical insults manifest by two or more of the following:
Temperature >38C or <36
Heart Rate > 90 bpm
Respiratory Rate > 20 breaths per minute or
PaCO2 > 4.3 kPa White Cell Count > 12,000 or
<4,000 per mm3
Sepsis SIRS with documented infection
Severe SIRS with documented infection and hypoperfusion,
SIRS hypotension and organ dysfunction
Septic Sepsis with hypotension despite adequate fluid
Shock resuscitation
Clinical features of sepsis and SIRS
Cardiorespiratory effects
o Increased cardiac output
o Decreased vascular resistance
o Increased oxygen consumption
o Fever or hypothermia
o Tachycardia
o Tachypnoea
Metabolic or haematological effects
o Respiratory alkalosis
o Deranged liver function
o Deranged renal function
o Altered whit cell count and platelets
o Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Aetiology of SIRS
SIRS can arise from a number of aetiological triggers
Infection – bacterial, viral, fungal
Hypovolaemic shock
Trauma
Burns
Tissue ischaemia
Pancreatitis
Bacterial Infection is commonest cause
50% due to gram-negative organisms
40% due to gram-positive organisms
Mechanisms in the pathology of SIRS
Over-production of inflammatory mediators
Under-production of anti-inflammatory mediators
Receptor abnormalities
Decreased destruction of inflammatory mediators
Abnormal leukocytes
Major inflammatory mediators involved in SIRS
Platelet activating factor
Tumour necrosis factor -alpha
Interleukin-1
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukin-10
Bibliography
Boontham P, Chandran P, Rowlands B, Eremin O. Surgical sepsis:
dysregulation of immune function and therapeutic implications. Surg J R Coll
Surg Edinb Irel 2003; 1: 187-206.
Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002; 420: 885-891.
Parker S J, Watkins P E. Immunomodulatory therapies of sepsis and SIRS.
In: Johnson C D, Taylor I eds. Recent advances in surgery 23. Edinburgh,
Churchill Livingston 2000: 55-68.
Paterson R L, Webster N R. Sepsis and the systemic inflammatory response
syndrome. J R Coll Surg Ed 2000; 45: 178-182.
Vincent J L, de Carvalho F B, de Backer D. Management of septic shock. Ann
Med 2002; 34: 606-613.
Wheeler A P, Bernard G R. Treating patients with severe sepsis. N Eng J Med
1999; 340: 207-214.
You might also like
- SEPSIS - 2016 - 18 (Dr. Erwin)Document68 pagesSEPSIS - 2016 - 18 (Dr. Erwin)Falayna Ithu DheisyaNo ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument26 pagesSirs & Modsnerlyn silao50% (2)
- W2D3 DR - Yasa-Bacteremia Dan SepsisDocument54 pagesW2D3 DR - Yasa-Bacteremia Dan SepsisJaka BawaviNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and Septic Shock 2020Document53 pagesSepsis and Septic Shock 2020bigbrain97100% (1)
- Sepsis 2022 Final2Document70 pagesSepsis 2022 Final2marinaNo ratings yet
- SHOCK KMTCDocument28 pagesSHOCK KMTCJohn Wesley OmbogoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial "Sepsis": Rossy Efridanis Ballona Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono, SP - PDDocument12 pagesTutorial "Sepsis": Rossy Efridanis Ballona Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono, SP - PDYudhistira AdiNo ratings yet
- Martin 2016Document12 pagesMartin 2016rositha prabandariNo ratings yet
- SEPSIS Recognition, Treatment and ReferralDocument23 pagesSEPSIS Recognition, Treatment and Referralariandy123No ratings yet
- Sepsis Septic Shock The LectDocument95 pagesSepsis Septic Shock The LecthrmosalamNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pasien Dengan Sepsis: Ns. Anastasia Hardyati., M.Kep., Sp. KMBDocument17 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pasien Dengan Sepsis: Ns. Anastasia Hardyati., M.Kep., Sp. KMBchika wahyu sasqiautamiNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and SIRSDocument24 pagesSepsis and SIRSFryda 'buona' YantiNo ratings yet
- SEPSIS Kuliah Prof Herdiman (S1) RevDocument41 pagesSEPSIS Kuliah Prof Herdiman (S1) RevSianipar Mangara Wahyu CharrosNo ratings yet
- Causes of Drowsiness in This PatientDocument12 pagesCauses of Drowsiness in This PatientNu JoeNo ratings yet
- Amjad Bani Hani: Sir S, Sep S Is, A N D ModsDocument67 pagesAmjad Bani Hani: Sir S, Sep S Is, A N D ModsRuffaeelJabrNo ratings yet
- NCM118 ReportDocument35 pagesNCM118 ReportJoy Ce VeralloNo ratings yet
- Sepsis 2016: The Protocol Watch: B. Mclean Clinical Specialist Critical Care Grady Hospital, Atl, GaDocument94 pagesSepsis 2016: The Protocol Watch: B. Mclean Clinical Specialist Critical Care Grady Hospital, Atl, GaHimawan WidyatmikoNo ratings yet
- Bacteremia - Dan - Sepsis and ShockDocument232 pagesBacteremia - Dan - Sepsis and ShockKiki Luhita SariNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Cap 44 Cirugía GeneralDocument14 pagesSepsis Cap 44 Cirugía GeneralKarla Montserrat González MuroNo ratings yet
- Sepsis ShockDocument11 pagesSepsis ShockDr. LNo ratings yet
- Materi Presentasi Immune Response To Trauma & SIRS - SepsisDocument27 pagesMateri Presentasi Immune Response To Trauma & SIRS - SepsisYASMINDPNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument9 pagesSepsisWawan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: Pathophysiology and Management: Rajani AnnamaneniDocument67 pagesSepsis: Pathophysiology and Management: Rajani AnnamaneniLemari KunoNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument16 pagesSeptic ShockGelo JvrNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and Septic Shock: Old Concepts, New PreceptsDocument44 pagesSepsis and Septic Shock: Old Concepts, New PreceptsEllagEszNo ratings yet
- Risk and Setting For Multiple Organ Failure in Medical PatientsDocument2 pagesRisk and Setting For Multiple Organ Failure in Medical PatientsabdullahNo ratings yet
- SirsDocument31 pagesSirsSolomon ElenaNo ratings yet
- Uro SepsisDocument23 pagesUro SepsisJihad Anad100% (1)
- Sepsis and Septic ShockDocument70 pagesSepsis and Septic ShockLily SolNo ratings yet
- EDITED SEPSIS (Dr. Hanan El-Halaby)Document4 pagesEDITED SEPSIS (Dr. Hanan El-Halaby)AmiNo ratings yet
- Sepsis (from Gr. Σ: Systemic inflammatory response syndromeDocument5 pagesSepsis (from Gr. Σ: Systemic inflammatory response syndromeReyes PaulNo ratings yet
- Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) : Pranee Sitaposa, MDDocument43 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) : Pranee Sitaposa, MDAli TawbeNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and Septic Shock: Elise Mittleman Boller, - Cynthia M. OttoDocument9 pagesSepsis and Septic Shock: Elise Mittleman Boller, - Cynthia M. OttoIan SabogalNo ratings yet
- Superficial Infection and SepisDocument35 pagesSuperficial Infection and Sepissanjivdas100% (1)
- Anestesi SepsisDocument10 pagesAnestesi SepsisFemiko Panji AprilioNo ratings yet
- Sepsis & SIRS: Wade Woelfle, MD, FAAEM UW ECC 2016 June 21,2016Document44 pagesSepsis & SIRS: Wade Woelfle, MD, FAAEM UW ECC 2016 June 21,2016Elavarasi GanesanNo ratings yet
- Sepsis & SIRS: Wade Woelfle, MD, FAAEM UW ECC 2016 June 21,2016Document44 pagesSepsis & SIRS: Wade Woelfle, MD, FAAEM UW ECC 2016 June 21,2016DaintyGarciaNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Management of Septic ShockDocument38 pagesDiscuss The Management of Septic ShockKelvin Obiano100% (1)
- Septic Shock: Ask The ExpertDocument4 pagesSeptic Shock: Ask The ExpertIvy Dianne PascualNo ratings yet
- Immunopatologi Sepsis - DR Nur Farhanah SPPD K-PTIDocument29 pagesImmunopatologi Sepsis - DR Nur Farhanah SPPD K-PTIanita tri hastutiNo ratings yet
- Sepsis 2013Document42 pagesSepsis 2013RatnaNo ratings yet
- Management of Septic ShockDocument33 pagesManagement of Septic ShockswatisinghnigeriaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeDocument33 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 176Document13 pagesChapter 176Intan Sanditiya AlifNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: L Nursing2010 L AprilDocument5 pagesSepsis: L Nursing2010 L ApriljunelgoodNo ratings yet
- Define and Classify Shock. Discuss The Current Concepts in The Pathophysiology and Management of Endotoxic ShockDocument61 pagesDefine and Classify Shock. Discuss The Current Concepts in The Pathophysiology and Management of Endotoxic ShockEretare OdjugoNo ratings yet
- SIRSDocument8 pagesSIRSʕ•ᴥ•ʔNo ratings yet
- Sepsis For Blok 26 Selasa 12 AgustusDocument32 pagesSepsis For Blok 26 Selasa 12 AgustusUtari Mudhia Arisa PutriNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and Septic Shock - Critical Care MedicineDocument2 pagesSepsis and Septic Shock - Critical Care MedicineMihaela MoraruNo ratings yet
- SEPSİS ARDS Eng 2020Document70 pagesSEPSİS ARDS Eng 2020Sarper Hikmet TAZENo ratings yet
- Dr. Limdawati FK Ukm / Rsi 2012Document45 pagesDr. Limdawati FK Ukm / Rsi 2012Limdawati KweeNo ratings yet
- The Human Race Is A Transient Episode in The History of BacteriaDocument60 pagesThe Human Race Is A Transient Episode in The History of BacteriaAfiqah So Jasmi100% (2)
- Systemic Inflammatory Respon Syndrom: SyaharaDocument41 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Respon Syndrom: Syaharaprima suci angrainiNo ratings yet
- Plante-2016-Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock For The Obstetrician-Gynecologist PDFDocument20 pagesPlante-2016-Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock For The Obstetrician-Gynecologist PDFntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Medicine - Tropical Infectious Diseases Leptospirosis 2014ADocument7 pages8.3 Medicine - Tropical Infectious Diseases Leptospirosis 2014ABhi-An BatobalonosNo ratings yet
- Penanganan Sepsis PitDocument43 pagesPenanganan Sepsis PitElfa RiniNo ratings yet
- Sepsis and SIRSDocument22 pagesSepsis and SIRSDr.Deb Sanjay Nag100% (1)
- SepsisDocument63 pagesSepsisIssela MilagrosNo ratings yet
- Sirs, Sepsis, and Mods: Claudio Martin, MSC, MDDocument32 pagesSirs, Sepsis, and Mods: Claudio Martin, MSC, MDMohamad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Bronchogenic CaDocument4 pagesBronchogenic CaFortune RubengoNo ratings yet
- Blunt Chest TraumaDocument10 pagesBlunt Chest TraumaFortune RubengoNo ratings yet
- Toastmaster New Member Induction ProcessDocument1 pageToastmaster New Member Induction ProcessFortune RubengoNo ratings yet
- Surviving Part V PDFDocument12 pagesSurviving Part V PDFFortune RubengoNo ratings yet
- .Trashed 1703825822 AIIMS NORCET Memory Based Paper Delhi 15 Sept 2019 EnglishDocument161 pages.Trashed 1703825822 AIIMS NORCET Memory Based Paper Delhi 15 Sept 2019 EnglishNanda NandaNo ratings yet
- Garcia, Poligrates: Sinus & FistulaDocument2 pagesGarcia, Poligrates: Sinus & FistulaPaulo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Freud Abstracts-Volume XX - An Autobiographical Study, Inhibitions, Symptoms and Anxiety, Lay Analysis and Other Works (1925-1926)Document19 pagesFreud Abstracts-Volume XX - An Autobiographical Study, Inhibitions, Symptoms and Anxiety, Lay Analysis and Other Works (1925-1926)mrpoetryNo ratings yet
- F. Physical Assessment: 5. EyesDocument47 pagesF. Physical Assessment: 5. EyesJuliane100% (1)
- Novartis Clinical PipelineDocument5 pagesNovartis Clinical PipelinemedtechyNo ratings yet
- Toij 2020 03 25 PDFDocument18 pagesToij 2020 03 25 PDFHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Medical Evaluation of Adverse Events in Pharmacovigilance Global Perspective of PharmacovigilanceDocument6 pagesMedical Evaluation of Adverse Events in Pharmacovigilance Global Perspective of PharmacovigilanceAdalbert P ShaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 FOODFISH TVL Q3WK7-8Document24 pagesGrade 11 FOODFISH TVL Q3WK7-8janeNo ratings yet
- Find Out The Lack of Healthcare Concerns of Mass Populations and The Local Government During The Epidemic in Rural Area: A Study On Basail Upazila, Tangail, BangladeshDocument6 pagesFind Out The Lack of Healthcare Concerns of Mass Populations and The Local Government During The Epidemic in Rural Area: A Study On Basail Upazila, Tangail, BangladeshMuhammad Al AminNo ratings yet
- Patient Profile: 1 - PageDocument6 pagesPatient Profile: 1 - PageRoane RoblesNo ratings yet
- Surgical Amputations: John C. AngelDocument30 pagesSurgical Amputations: John C. AngelAsma SaleemNo ratings yet
- SBI Youth For India Application No: 202107126: Personal InformationDocument10 pagesSBI Youth For India Application No: 202107126: Personal InformationSAMAYANTAR The theatre society of MACNo ratings yet
- AMG Curs 3Document2 pagesAMG Curs 3Maria PalNo ratings yet
- Malaria Infection in Children Below 10 Years Attending Doka Rural HospitalDocument9 pagesMalaria Infection in Children Below 10 Years Attending Doka Rural HospitalKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- QN BNK Og PeadDocument39 pagesQN BNK Og PeadZemen addiss100% (3)
- Đề Số 22 Có Giải Chi TiếtDocument17 pagesĐề Số 22 Có Giải Chi TiếtHuong Giang PhungNo ratings yet
- School Health ServicesDocument23 pagesSchool Health ServicesNeethu Vincent50% (2)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument44 pagesFundamentals of Nursingtheglobalnursing100% (2)
- Program PrezentariDocument14 pagesProgram PrezentariRoxana Alexandra BogosNo ratings yet
- SURGERY MockDocument15 pagesSURGERY MockFan Eli100% (1)
- BZYET 143 EnglishDocument4 pagesBZYET 143 EnglishSangita PaulNo ratings yet
- Sem2 2018 Epiforhealth SampleexamDocument5 pagesSem2 2018 Epiforhealth SampleexamAddis YeshitlaNo ratings yet
- Diff Betw Cohort N Case ControlDocument1 pageDiff Betw Cohort N Case ControlFirzuan WanNo ratings yet
- English Iii For Nursing Student: Unit 3 AdmissionDocument4 pagesEnglish Iii For Nursing Student: Unit 3 Admissiongriesna wheniNo ratings yet
- Suma Eden D4.5 Antimicrobial Fruit and Vegetable Wash: Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesSuma Eden D4.5 Antimicrobial Fruit and Vegetable Wash: Safety Data SheetekiyasekiNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument101 pagesCase Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseZNEROL100% (6)
- Plant Parts and Its Medicinal Uses in The Modern MedicineDocument3 pagesPlant Parts and Its Medicinal Uses in The Modern MedicineEmar Vince OliverosNo ratings yet
- Journal Benjolan Di LeherDocument9 pagesJournal Benjolan Di LeherStase IPD SoedarsoNo ratings yet
- Word List UrinalysisDocument2 pagesWord List Urinalysischerry100% (1)
- Stress and Its Coping Strategies Among The CaregiverDocument28 pagesStress and Its Coping Strategies Among The CaregiverSandesh BaralNo ratings yet