Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Word List Urinalysis
Uploaded by
cherry100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
49 views2 pagesMLA word list for urinalysis definitions
Original Title
Word list urinalysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMLA word list for urinalysis definitions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
49 views2 pagesWord List Urinalysis
Uploaded by
cherryMLA word list for urinalysis definitions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
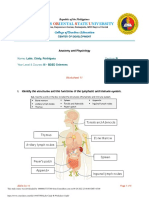
ADH; antidiuretic hormone also called vasopressin is produced in the hypothalamus and is then
transported to and released by the pituitary gland
Albuminuria; the presence of the protein albumin in the urine
Aldosterone; a corticosteroid that regulates the sodium and water levels in the body by
increasing sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion by the kidneys
Angiotensin; a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstrictive action, a synthetic amide
derivative of the physiologically active form used to treat some forms of hypotension
Anuria; the absence of urine formation by the kidneys
Bowman’s Capsule; a cupped shaped membrane that surrounds the glomerulus
Cystitis; inflammation of the bladder
Cystogram; the resulting film from a cystography
Dialysis; procedure to remove waste products such as urea, creatinine and excess water from
the blood of a patient whose kidneys no longer function
Diuretic; stimulates the kidneys to increase the secretion of urine to rid the body of excess
sodium and water, treats hypertension and heart failure by reducing the amount of fluid
circulating in the blood
Dysuria; difficult or painful urination frequently associated with UTIs
Epispadias; congenital abnormality of the urethral opening, in males the urethral opening is
located on the upper surface, in female the urethral opening is in in the region of the clitoris
Erythropoietin; stimulates red blood cell synthesis in the bone marrow
Glomerulus; a cluster of capillaries surrounded on a nephron
Glycosuria; presence of glucose in the urine, most commonly caused by untreated diabetes
mellitus
Hematuria; presence of blood in the urine, condition can be caused by kidney stones, infection,
kidney damage or bladder cancer
Hypospadias; congenital abnormality of the urethral opening, in male the urethral opening in
on the underside, in female the urethra opens into the vagina
IVP; a radiographic study of the kidneys and ureters, intravenous pyelography
Incontinence; the inability to control the excretion of urine and or feces
KUB; a radiographic study without the use of a contrast medium, also referred to as a flate-
plate of the abdomen
Nephrectomy; surgical removal of the kidney
Nephron; the microscopic functional units of each kidney, urine is produced through the
process of filtration, reabsorption and secretion
Nephrosis; group of conditions in which excessive amounts of protein are lost through the
urine, usually cause by damage to the glomeruli, results in abnormally low levels of protein in
the blood
Nitrites; consist of one nitrogen atom and two oxygen atoms, a salt or ester of nitrous acid
Nocturia; frequent and excessive urination during the night
Nocturnal Enuresis; also known as bed wetting, urinary incontinence during sleep
Oliguria; scanty urination, caused by dehydration, renal failure or UT obstruction
Polyuria; excessive urination common symptom of diabetes
Proteinuria; presence of an abnormal amount of protein in the urine, usually a sign of kidney
disease
Pyuria; presence of pus in the urine, urine is turbid in appearance
Renal Calculi; kidney stones can vary in size
Renal Cortex; outer region of the kidney, contains more than 1 mill microscopic units called
nephrons
Renal Medulla; inner region of the kidney, contains most of the urine collecting tubules
Renin; a proteolytic enzyme of the kidney that plays a major role in the release of angiotensin
Uremia; toxic condition in which urea and other waste products normally excreted in the urine
are retained in the blood
You might also like
- Analysis of UrineDocument22 pagesAnalysis of UrineFaith Domingo100% (1)
- The yellow color of urine is caused by urochromeDocument3 pagesThe yellow color of urine is caused by urochromeIYA LABAO100% (1)
- Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid BalanceDocument20 pagesSeeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid BalanceAce Khiel Peralta100% (1)
- Republic of the Philippines State University Anatomy and Physiology WorksheetDocument6 pagesRepublic of the Philippines State University Anatomy and Physiology WorksheetChristine ElnasNo ratings yet
- 3 4Document2 pages3 4cherryNo ratings yet
- MLT Content Guidelin9Document13 pagesMLT Content Guidelin9Mutaz Baniamer100% (1)
- Microbiology - Overview Reports and IntepretationDocument9 pagesMicrobiology - Overview Reports and IntepretationRo RyNo ratings yet
- Answerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Document4 pagesAnswerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Omar H100% (1)
- 200L Histology NotesDocument21 pages200L Histology Notesidokofavour2015100% (1)
- Anaphy Midterm Notes (The Blood Summary)Document4 pagesAnaphy Midterm Notes (The Blood Summary)Zosia Sage100% (1)
- Unit 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Reviewduonghi3lpsNo ratings yet
- Exam AMG2BDocument7 pagesExam AMG2BGhiveciu Alexandru100% (1)
- Micropara (Lec)Document10 pagesMicropara (Lec)Jhon VincentNo ratings yet
- Growth media biochemical methods identification bacteriaDocument2 pagesGrowth media biochemical methods identification bacteriamehek100% (1)
- Medical Laboratory Science Program CoursesDocument3 pagesMedical Laboratory Science Program CoursesMae Manaloto100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerNaka Limut100% (1)
- Pipettes and Their Safely UseDocument14 pagesPipettes and Their Safely UseTapeshwar Yadav100% (1)
- Anh 2Document3 pagesAnh 2Hiếu Trung100% (1)
- Hazard Symbol in LaboratoryDocument3 pagesHazard Symbol in LaboratoryWindy WayneNo ratings yet
- BT102-Microbiology Current Paper Solved Question Final Term February 2020Document11 pagesBT102-Microbiology Current Paper Solved Question Final Term February 2020Awais Bhutta100% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry Review 1 110Document6 pagesClinical Chemistry Review 1 110DELLNo ratings yet
- MLAExamHandbook 2014b EGDocument32 pagesMLAExamHandbook 2014b EGArif Shaikh50% (2)
- SAS CC1 Session 1 Scope of Clinical ChemistryDocument9 pagesSAS CC1 Session 1 Scope of Clinical ChemistryRuchieNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids2020Document47 pagesUrinalysis and Body Fluids2020MONFOLA100% (1)
- Hematology summary guideDocument91 pagesHematology summary guidePeter Shirima100% (1)
- Biological Safety CabinetDocument15 pagesBiological Safety CabinetTapeshwar Yadav100% (1)
- Preparation of Microbial Media: Grow and Isolate BacteriaDocument7 pagesPreparation of Microbial Media: Grow and Isolate BacteriasurabhiNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument6 pagesCulture MediaTryfingNo ratings yet
- Intro To HematologyDocument9 pagesIntro To HematologyDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Word Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Word Circulatory SystemChandan Shah100% (2)
- MLT. 1st stage tissue types & functionsDocument8 pagesMLT. 1st stage tissue types & functionskawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Cells and TissuesHenri Tirich100% (1)
- BIO2134 Final Exam 2011: This Part of The Exam Includes 40 Multiple Choice Questions (1 Pts/each)Document11 pagesBIO2134 Final Exam 2011: This Part of The Exam Includes 40 Multiple Choice Questions (1 Pts/each)angela100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Lab Sciences - QuDocument66 pagesFundamentals of Lab Sciences - QueebookachipNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument20 pagesHematologyJunaid SabirNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Equip: Pipet. It Has Only OneDocument3 pagesLaboratory Equip: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Blood Tests ExplainedDocument3 pagesKidney Function Blood Tests ExplainedJohn ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Culture .: Ahmed GomaaDocument42 pagesAnaerobic Culture .: Ahmed Gomaaah7510No ratings yet
- CH 15 BloodDocument6 pagesCH 15 Bloodsann1992No ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory TechnologyDocument3 pagesMedical Laboratory TechnologyAHMEDNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesReview Questionsmiguel gaquit100% (1)
- HOLTERDocument149 pagesHOLTERSam PravashNo ratings yet
- Medical Ethics and ProfessionalismDocument71 pagesMedical Ethics and ProfessionalismHaymanot GirmaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Key Parameters, Units, and InstrumentationDocument7 pagesClinical Chemistry Key Parameters, Units, and InstrumentationAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab Technologists:: The Hidden Profession' That Saves LivesDocument15 pagesMedical Lab Technologists:: The Hidden Profession' That Saves LivesFaiza Rashid100% (1)
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesemms meNo ratings yet
- Medical Abbreviation GuideDocument2 pagesMedical Abbreviation GuideNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument85 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture Seriesandina rosmalianti100% (1)
- Collection of SamplesDocument6 pagesCollection of SamplesAlexandru AndreiNo ratings yet
- General QuestionDocument70 pagesGeneral QuestionMONFOLA100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesClinical Chemistry 1: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceEidriel Paras100% (1)
- 33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileDocument40 pages33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Pathology - WikipediaDocument15 pagesPathology - WikipediaTejasNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Viruses Fungi and Prions Protozoa, Worms, Flukes and ExoparasitesDocument2 pagesBacteria Viruses Fungi and Prions Protozoa, Worms, Flukes and ExoparasitesJohn PrineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concept of MeasurementsDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concept of MeasurementsSarweash RaoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology I 2nd MidtermDocument12 pagesMicrobiology I 2nd Midtermangel mints100% (1)
- URINALYSIS & BODY FLUIds Pericardial Analysis.Document48 pagesURINALYSIS & BODY FLUIds Pericardial Analysis.Syazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Basic Clinical Chemistry TestsDocument49 pagesBasic Clinical Chemistry TestsMegbaru100% (1)
- 4 7Document1 page4 7cherry100% (1)
- 7 2Document1 page7 2cherry100% (1)
- 4 6Document2 pages4 6cherry100% (1)
- 4 5Document1 page4 5cherryNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument4 pagesCase Studiescherry100% (10)
- Word List MicroDocument1 pageWord List Microcherry100% (1)
- JO1 Plar GIE and MIEDocument2 pagesJO1 Plar GIE and MIEKaloy PlarNo ratings yet
- GSDocument26 pagesGSkarinadegomaNo ratings yet
- Work Education (Pass)Document5 pagesWork Education (Pass)sanbarunNo ratings yet
- Extended Paper 2 May 00Document12 pagesExtended Paper 2 May 00Mari Carmen Pérez GómezNo ratings yet
- Roman Epicurean'ism - Natural Law and HomosexualityDocument21 pagesRoman Epicurean'ism - Natural Law and HomosexualityPapa Giorgio100% (1)
- Clinical Application of Neuromuscular .Techniques Upper 2nd 2008Document608 pagesClinical Application of Neuromuscular .Techniques Upper 2nd 2008Vishwanath Tejaswi97% (39)
- Conversation LaundryDocument2 pagesConversation Laundryvanni octavania88% (8)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IIIApril Ann Lopez Custodio94% (18)
- Brain-Ring "What? Where? When?"Document4 pagesBrain-Ring "What? Where? When?"Оксана ГорькаяNo ratings yet
- l2 Unit 8 Statement of Aims Blank 2023 Templa 1Document8 pagesl2 Unit 8 Statement of Aims Blank 2023 Templa 1api-631701024No ratings yet
- Carnatic Music of South IndiaDocument14 pagesCarnatic Music of South IndiaMiriana FaietaNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning GodrejDocument199 pagesFinancial Planning GodrejriteshnaikNo ratings yet
- Convertible Note Bridge Financing Term SheetDocument2 pagesConvertible Note Bridge Financing Term Sheetwchiang1226No ratings yet
- Un Ejercicio para 2º BACHILLERATO. (An Exercise For Advanced Students.)Document4 pagesUn Ejercicio para 2º BACHILLERATO. (An Exercise For Advanced Students.)Herber HerberNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Exam Math 9Document1 page3rd Periodical Exam Math 9DhangManongas-LlaboreVete100% (2)
- IN Contemporary World: Student's NameDocument9 pagesIN Contemporary World: Student's NameJessan Ybañez JoreNo ratings yet
- Gods Revelation in Jesus and in His ChurchDocument13 pagesGods Revelation in Jesus and in His ChurchMerry DaceraNo ratings yet
- 16-31 Maret 2021Document23 pages16-31 Maret 2021Medika AntapaniNo ratings yet
- The Law of AttractionDocument26 pagesThe Law of Attractionradharani131259No ratings yet
- HRM Issues and Challenges in Cooperative Banks in IndiaDocument6 pagesHRM Issues and Challenges in Cooperative Banks in Indiaghanshamdas67% (3)
- Interzone 5140: Epoxy PrimerDocument4 pagesInterzone 5140: Epoxy PrimerTrịnh Minh KhoaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan and ProductDocument4 pagesLesson Plan and Productapi-435897192No ratings yet
- M.2 - R-Value References - Learn C++Document18 pagesM.2 - R-Value References - Learn C++njb25bcnqfNo ratings yet
- Rule MiningDocument2 pagesRule Miningravi ramaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ScreenplayDocument115 pagesAnimal Kingdom ScreenplayAnonymous 9oQhdeNo ratings yet
- 2012 09 16 Our Anchor in Times of StormDocument3 pages2012 09 16 Our Anchor in Times of StormJohn S. KodiyilNo ratings yet
- UED102Document24 pagesUED102Nik Noor Aisyah Mohd DaudNo ratings yet
- SCA No. 8220-R - Petitioner's MemorandumDocument9 pagesSCA No. 8220-R - Petitioner's MemorandumElizerNo ratings yet
- Understanding Balance of PaymentsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Balance of PaymentsMurtaza JamaliNo ratings yet
- Paul's View of Justification and Last JudgmentDocument13 pagesPaul's View of Justification and Last JudgmentMik3reyesNo ratings yet