Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Physiology Reviewer
Uploaded by
Naka Limut100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
18 views2 pagesThis document provides an overview of anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of body structures and physiology as the study of functions. It discusses the different levels of anatomical study from gross to microscopic. It also describes regional and systemic anatomy. Key concepts covered include cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Homeostasis and the relationship between form and function are also mentioned.
Original Description:
Vhhh
Original Title
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of body structures and physiology as the study of functions. It discusses the different levels of anatomical study from gross to microscopic. It also describes regional and systemic anatomy. Key concepts covered include cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Homeostasis and the relationship between form and function are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
18 views2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reviewer
Uploaded by
Naka LimutThis document provides an overview of anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of body structures and physiology as the study of functions. It discusses the different levels of anatomical study from gross to microscopic. It also describes regional and systemic anatomy. Key concepts covered include cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Homeostasis and the relationship between form and function are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
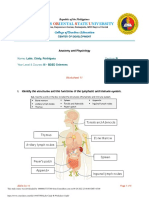
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEWER
ANATOMY a field in the biological sciences concerned with the identification and description of the
body structures of living things.
GROSS ANATOMY involves the study of major body structures by dissection and observation and in
its narrowest sense is concerned only with the human body.
HUMAN ANATOMY is the scientific study of the body’s structures
Some of these structures are very small and can only be observed and analyzed with the assistance
of a MICROSCOPE
DISSECTION is still used in medical schools, anatomy courses, and in pathology labs.
GROSS ANATOMY is the study of the larger structures of the body, those visible without the aid of
magnification
MACRO means “large,”
GROSS ANATOMY is also referred to as macroscopic anatomy.
MICRO means “small,”
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY is the study of structures that can be observed only with the use of a
microscope or other magnification devices
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY the study of cells and histology, the study of tissues.
The 2 general approaches of anatomist to study the body structures: REGIONAL ANATOMY AND
SYSTEMIC ANATOMY
REGIONAL ANATOMY is the study of the interrelationships of all of the structures in a specific body
region, such as the abdomen.
REGIONAL ANATOMY helps us appreciate the interrelationships of body structures, such as how
muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and other structures work together to serve a particular body region.
SYSTEMIC ANATOMY is the study of the structures that make up a discrete body system—that is, a
group of structures that work together to perform a unique body function.
ANATOMY is about structure.
PHYSIOLOGY is about function.
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY is the scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the
body and the ways in which they work together to support the functions of life.
HOMEOSTASIS is the state of steady internal conditions maintained by living things.
FORM is closely related to function in all living things.
The smallest unit of any of these pure substances (elements) is called an ATOM
Two or more atoms combine to form a MOLECULE
MOLECULES are the chemical building blocks of all body structures.
CELL is the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism.
A human cell typically consists of flexible membranes that enclose cytoplasm, a water-based cellular
fluid together with a variety of tiny functioning units called ORGANELLES
CELLS perform all functions of life.
TISSUE is a group of many similar cells (though sometimes composed of a few related types) that
work together to perform a specific function.
ORGAN is an anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types. Each
organ performs one or more specific physiological functions.
ORGAN SYSTEM is a group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet
physiological needs of the body.
PLASMA MEMBRANE keeps the intracellular environment—the fluids and organelles—separate
from the extracellular environment. Blood vessels keep blood inside a closed circulatory system, and
nerves and muscles are wrapped in connective tissue sheaths that separate them from surrounding
structures.
The body’s largest organ system is the SKIN OR THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
There are two types of reactions that accomplish this: ANABOLISM AND CATABOLISM
ANABOLISM is the process whereby smaller, simpler molecules are combined into larger, more
complex substances. Your body can assemble, by utilizing energy, the complex chemicals it needs by
combining small molecules derived from the foods you eat
CATABOLISM is the process by which larger more complex substances are broken down into smaller
simpler molecules.
METABOLISM is the sum of all anabolic and catabolic reactions that take place in the body
Every cell in your body makes use of a chemical compound called ATP OR ADENOSINE
TRIPHOSPHATE
RESPONSIVENESS is the ability of an organism to adjust to changes in its internal and external
environments.
HUMAN MOVEMENT includes not only actions at the joints of the body, but also the motion of
individual organs and even individual cells.
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Anatomy Physiology Week 2 3 For LmsDocument88 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy Physiology Week 2 3 For LmsClaire Jasmine Ilao100% (1)
- 200L Histology NotesDocument21 pages200L Histology Notesidokofavour2015100% (1)
- Republic of the Philippines State University Anatomy and Physiology WorksheetDocument6 pagesRepublic of the Philippines State University Anatomy and Physiology WorksheetChristine ElnasNo ratings yet
- Answerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Document4 pagesAnswerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Omar H100% (1)
- Micropara (Lec)Document10 pagesMicropara (Lec)Jhon VincentNo ratings yet
- MLT Content Guidelin9Document13 pagesMLT Content Guidelin9Mutaz Baniamer100% (1)
- Analysis of UrineDocument22 pagesAnalysis of UrineFaith Domingo100% (1)
- Growth media biochemical methods identification bacteriaDocument2 pagesGrowth media biochemical methods identification bacteriamehek100% (1)
- Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid BalanceDocument20 pagesSeeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid BalanceAce Khiel Peralta100% (1)
- Medical Laboratory Science Program CoursesDocument3 pagesMedical Laboratory Science Program CoursesMae Manaloto100% (1)
- 3 4Document2 pages3 4cherryNo ratings yet
- Exam AMG2BDocument7 pagesExam AMG2BGhiveciu Alexandru100% (1)
- The yellow color of urine is caused by urochromeDocument3 pagesThe yellow color of urine is caused by urochromeIYA LABAO100% (1)
- Unit 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Reviewduonghi3lpsNo ratings yet
- BT102-Microbiology Current Paper Solved Question Final Term February 2020Document11 pagesBT102-Microbiology Current Paper Solved Question Final Term February 2020Awais Bhutta100% (1)
- Microbiology - Overview Reports and IntepretationDocument9 pagesMicrobiology - Overview Reports and IntepretationRo RyNo ratings yet
- Pipettes and Their Safely UseDocument14 pagesPipettes and Their Safely UseTapeshwar Yadav100% (1)
- Anaphy Midterm Notes (The Blood Summary)Document4 pagesAnaphy Midterm Notes (The Blood Summary)Zosia Sage100% (1)
- Word List UrinalysisDocument2 pagesWord List Urinalysischerry100% (1)
- SAS CC1 Session 1 Scope of Clinical ChemistryDocument9 pagesSAS CC1 Session 1 Scope of Clinical ChemistryRuchieNo ratings yet
- Anh 2Document3 pagesAnh 2Hiếu Trung100% (1)
- Hazard Symbol in LaboratoryDocument3 pagesHazard Symbol in LaboratoryWindy WayneNo ratings yet
- Biological Safety CabinetDocument15 pagesBiological Safety CabinetTapeshwar Yadav100% (1)
- MLT. 1st stage tissue types & functionsDocument8 pagesMLT. 1st stage tissue types & functionskawiNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument6 pagesCulture MediaTryfingNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Lab Sciences - QuDocument66 pagesFundamentals of Lab Sciences - QueebookachipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Cells and TissuesHenri Tirich100% (1)
- MLAExamHandbook 2014b EGDocument32 pagesMLAExamHandbook 2014b EGArif Shaikh50% (2)
- BIO2134 Final Exam 2011: This Part of The Exam Includes 40 Multiple Choice Questions (1 Pts/each)Document11 pagesBIO2134 Final Exam 2011: This Part of The Exam Includes 40 Multiple Choice Questions (1 Pts/each)angela100% (1)
- Medical Ethics and ProfessionalismDocument71 pagesMedical Ethics and ProfessionalismHaymanot GirmaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesemms meNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Word Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Word Circulatory SystemChandan Shah100% (2)
- Laboratory Equip: Pipet. It Has Only OneDocument3 pagesLaboratory Equip: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Review 1 110Document6 pagesClinical Chemistry Review 1 110DELLNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Microbial Media: Grow and Isolate BacteriaDocument7 pagesPreparation of Microbial Media: Grow and Isolate BacteriasurabhiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesClinical Chemistry 1: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceEidriel Paras100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concept of MeasurementsDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concept of MeasurementsSarweash RaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab Technologists:: The Hidden Profession' That Saves LivesDocument15 pagesMedical Lab Technologists:: The Hidden Profession' That Saves LivesFaiza Rashid100% (1)
- Intro To HematologyDocument9 pagesIntro To HematologyDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary SystemJeoffrey GabongNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Culture .: Ahmed GomaaDocument42 pagesAnaerobic Culture .: Ahmed Gomaaah7510No ratings yet
- Types of Media For MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesTypes of Media For MicrobiologyThulasi Devadoss100% (1)
- CH 15 BloodDocument6 pagesCH 15 Bloodsann1992No ratings yet
- Collection of SamplesDocument6 pagesCollection of SamplesAlexandru AndreiNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology PDFDocument226 pagesBacteriology PDFWaseem Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Pathology - WikipediaDocument15 pagesPathology - WikipediaTejasNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Blood Tests ExplainedDocument3 pagesKidney Function Blood Tests ExplainedJohn ReyesNo ratings yet
- Microbiology I 2nd MidtermDocument12 pagesMicrobiology I 2nd Midtermangel mints100% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry Key Parameters, Units, and InstrumentationDocument7 pagesClinical Chemistry Key Parameters, Units, and InstrumentationAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids2020Document47 pagesUrinalysis and Body Fluids2020MONFOLA100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Laboratory Safety and RegulationDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Laboratory Safety and RegulationClaire Nicole100% (1)
- 5 - Lab Math Molarity PDFDocument25 pages5 - Lab Math Molarity PDFkrizelNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Viruses Fungi and Prions Protozoa, Worms, Flukes and ExoparasitesDocument2 pagesBacteria Viruses Fungi and Prions Protozoa, Worms, Flukes and ExoparasitesJohn PrineNo ratings yet
- (Important!) Microbiology Vocabulary ListDocument6 pages(Important!) Microbiology Vocabulary ListKelly LeeNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesReview Questionsmiguel gaquit100% (1)
- Study Skills: by Vijay KhotDocument23 pagesStudy Skills: by Vijay KhotVijay KhotNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGY Flash PointsDocument3 pagesIMMUNOLOGY Flash PointsHassan AhmadNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1: INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGYDocument12 pagesLECTURE 1: INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGYEinah EinahNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cloud Computing Basics PDFDocument5 pages12 - Cloud Computing Basics PDFpooja0100No ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer in RizalDocument3 pagesFinals Reviewer in RizalNaka LimutNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY RevDocument3 pagesANATOMY RevNaka LimutNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document23 pagesLesson 10Naka LimutNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer in RizalDocument3 pagesFinals Reviewer in RizalNaka LimutNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument2 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyNaka LimutNo ratings yet
- Living in It Era Prelim ModuleDocument28 pagesLiving in It Era Prelim ModuleNaka LimutNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of TranspositionDocument16 pagesMechanism of TranspositionBandook Gamers100% (2)
- Appn H Column Cleaning RegenerationDocument3 pagesAppn H Column Cleaning RegenerationducngoctrinhNo ratings yet
- Anexo 1 - Natural History of DiseaseDocument16 pagesAnexo 1 - Natural History of DiseaseStefanyGomezNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology GCSE - Homeostasis MechanismsDocument4 pagesAQA Biology GCSE - Homeostasis MechanismsMareeb ShahNo ratings yet
- How Representations Are Transmitted Between GenerationsDocument26 pagesHow Representations Are Transmitted Between Generationstomasfeza5210100% (1)
- Ch11 Lecture PPT ADocument66 pagesCh11 Lecture PPT AMiky rose De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Malina 2020Document10 pagesMalina 2020Jaime VZNo ratings yet
- AsaphusDocument4 pagesAsaphusenzo abrahamNo ratings yet
- Aspek Laboratorium Untuk Menunjang Perencanaan Water Flooding Dan Water Flooding ImprovementDocument38 pagesAspek Laboratorium Untuk Menunjang Perencanaan Water Flooding Dan Water Flooding ImprovementInggit Yulias SaputriNo ratings yet
- Worksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1Document4 pagesWorksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1AreebNo ratings yet
- The Characteristic Morphological of Mimosa PudicaDocument3 pagesThe Characteristic Morphological of Mimosa PudicaTristanti RakhmaningrumNo ratings yet
- Uses and Abuses of Mathematics in BiologyDocument4 pagesUses and Abuses of Mathematics in Biologymuhammad sami ullah khanNo ratings yet
- The Spectator Alexander in Afghanistan Project - Matthew LeemingDocument9 pagesThe Spectator Alexander in Afghanistan Project - Matthew LeemingMarsyas PeriandrouNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Worksheets-Practice Blood-LymphDocument12 pagesCH 6 Worksheets-Practice Blood-LymphKatie ByarsNo ratings yet
- Practice Test: B C D B C Caused Cancer in Laboratory Rats. DDocument5 pagesPractice Test: B C D B C Caused Cancer in Laboratory Rats. DNguyen CuongNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems: 7 Grade ScienceDocument17 pagesHuman Body Systems: 7 Grade Sciencenona wayne dela peñaNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Staining Methods and MechanismsDocument9 pagesHistopathology Staining Methods and MechanismsJanneth MendozaNo ratings yet
- Protein Data BankDocument5 pagesProtein Data Bankwilliam919No ratings yet
- Banasthali Vidyapith: Internal Research SupervisorsDocument10 pagesBanasthali Vidyapith: Internal Research SupervisorsasanyogNo ratings yet
- Skema-Amali - Peperiksaan Akhir Semester 1 Tingkatan 4Document4 pagesSkema-Amali - Peperiksaan Akhir Semester 1 Tingkatan 4Khaw Poh HwaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering NotesDocument52 pagesGenetic Engineering NotesBulan PutriNo ratings yet
- 17.IFU G11 Var ReagentsDocument68 pages17.IFU G11 Var ReagentsAufar SyahrulianNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 OogenesisDocument7 pagesActivity 2 OogenesisHILARY PARAGAS. CORUÑANo ratings yet
- Indian Institutions Research AreasDocument40 pagesIndian Institutions Research AreasAbhilashRayaguruNo ratings yet
- CSIR NET Dec 2015 Ls Answer KeyDocument32 pagesCSIR NET Dec 2015 Ls Answer KeyAbhay Kumar50% (2)
- Crush Step 1 ErrataDocument2 pagesCrush Step 1 ErrataAbd SamadNo ratings yet
- The Hunt For A Healthy Microbiome: OutlookDocument3 pagesThe Hunt For A Healthy Microbiome: OutlookLindo PulgosoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication PDFDocument7 pagesDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNo ratings yet
- VO2 MaxDocument30 pagesVO2 MaxDeva JCNo ratings yet
- Anuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)Document1 pageAnuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)khushi kumariNo ratings yet