Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Copd Flowchart PDF
Copd Flowchart PDF
Uploaded by
silkofosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Copd Flowchart PDF
Copd Flowchart PDF
Uploaded by
silkofosCopyright:
Available Formats
V-03/2008
KNGF-Guideline for physical therapy in patients with
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
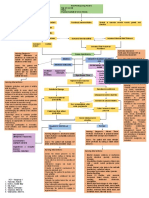
Problem solving
• Dysnea
• Impaired mucus clearance
• Impaired exercise performance
• Infections
• PA
Screening Referral
• Pulmonary function tests
• Pulmonary function tests
• and exercise test
• Exertional dyspnea
• Recurrent respiratory infections • Poor physical activity in daily
Case
• exacerbations with hypersecretion life (MRC ≥ 2), < 30 min/day
history
• Adherence to treatment • Comorbid conditions
(cardiovascular disease)
• Exercise performance and
• Mucus quality and quantity
physical activity
Physical • Impaired cough:
• Respiratory and peripheral
assessment - airway collapse,
muscle function
- muscleweakness
• Quality of life
• Causes of exercise limitation / inactivity
• Causes of impaired cough
• Motivation / self-management
Analysis
• Optimal medical treatment no
• Referral physician
• Sufficient referral data
• Health education
• Self-management
Treatment
• Forced expiration • Excercise training
• Cough • Muscle training
• Adjuncts (PEP, PD) • Breathing exercises
• Exercise performance, physi-
• Number of respiratory infections
Outcome cal activity, Muscle strength,
with mucus retention - Symptoms
Quality of life
PA = physical activity; PEP = positive expiratory pressure; PD = postural drainage.
Royal Dutch Society for Physical Therapy
V-03/2008
KNGF-Guideline for physical therapy in patients with
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Dyspnea, impaired physical activity and physical fitness
Spirometry / MRC-score / Physical activity (< 30 min./day)
FEV1 ≥ 50% pred. FEV1 ≥ 50% pred. FEV1 < 50% pred.
MRC-score <2 MRC-score ≥2 MRC-score ≥2
• Multidisciplinary
No physical therapy • Cycly ergometry*
Assessment
Advice:
• Increase physical activity
• Adapted sports activity
Wmax ≥ 70% pred. Wmax < 70% pred.
• Regular sports activity
VO2max ≥ 80% pred. VO2max < 80% pred.
Advice: • Multidisciplinary
• Increase physical activity Rehabilitation
• PT intake physical activity programme
• Physical activity programme
• Adapted sports activities
* The ‘Primary care physicians guideline’ and ‘Transmural guideline for COPD’ only recommend exercise testing in patients
with increased cardiovascular risk. The ‘ACSM guideline’ recommends exercise testing in any elderly subject, while the ‘Physical
therapy in COPD guideline’ recommends exercise testing in any COPD patient.
MRC = Medical Research Council dyspnea score
FEV = positive expiratory pressure
no physical therapy / advice to increase physical activity
treatment in primary care (physical activity program)
treatment in secondary/tertiary care (rehabilitation)
Royal Dutch Society for Physical Therapy
V-03/2008
KNGF-Guideline for physical therapy in patients with
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Impaired exercise performance/dyspnea
• Peripheral • Anxiety
• Cardio- • Oxygen transport
• Ventilatory muscle • Motivation
circulatory in the lungs
strength • Self-esteem
• Respiratory
muscle weakness
• Hyperinflation
• Hypoxemia/Hypercapnia
during exercise?
• IMT
• Body positioning
• Rollator • Muscle training • Counseling
• Endurance • Interval training • NIV • EMS • Relaxation
training • ev. suppl. O2 • Active expiration • Nutrition • Education
• PLB
IMT = inspiratory muscle training; NIV = non-invasive ventilation; EMS = electrical muscle stimulation;
PLB = pursed lips breathing; ev. = eventually.
Royal Dutch Society for Physical Therapy
V-03/2008
KNGF-Guideline for physical therapy in patients with
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Impaired Mucus Clearance
Yes • Hypersecretion? No
Yes
• Cough/Huff effective?
• Physically active?
• Treatment compliance?
No Yes
No
• See Flow Chart • No indication for physical
‘Impaired Exercise Performance’ therapy
(see figure 3)
• Inadequate technique?
• Airway collapse?
• Non-compliance?
Yes Yes
• Teach coughing/huffing/breathing exercise dependent on severity and
causes of obstruction
• Education - improve compliance
• Re-assessment • Evaluation: treatment effective?
• Confirm indication with
referring physician Yes
No
• ‘Stop’ treatment
• Other treatments:
• Postural drainage, PEP
• Flutter
• Report to referring physician
• Percussion/Vibration
PEP = positive expiratory pressure.
Royal Dutch Society for Physical Therapy
You might also like
- Basic Veterinary Immunology - CallahanDocument350 pagesBasic Veterinary Immunology - CallahanNana0% (1)
- 02b IGCSE Maths 4MB1 02 - January 2021 Mark Scheme PDFDocument20 pages02b IGCSE Maths 4MB1 02 - January 2021 Mark Scheme PDFSaiful Islam100% (2)
- AACVPR Guidelines For AACVPR Guidelines For Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs (4 Edition)Document37 pagesAACVPR Guidelines For AACVPR Guidelines For Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs (4 Edition)Jeffery SamuelNo ratings yet
- PNF Respiration PDFDocument7 pagesPNF Respiration PDFBlake d souzaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonaryrehabilitation 180412172759Document44 pagesPulmonaryrehabilitation 180412172759IvanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary RehabilitationDocument41 pagesPulmonary RehabilitationAnandhu G100% (1)
- Intermittant Claudication FlowchartDocument2 pagesIntermittant Claudication FlowchartsilkofosNo ratings yet
- The Proprioceptive Lumbar Spine and The Role of Manual Therapy NLDocument41 pagesThe Proprioceptive Lumbar Spine and The Role of Manual Therapy NLVizaNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons Disease.... 4Document13 pagesParkinsons Disease.... 4bibi bennyNo ratings yet
- 1 LBP - Guide - Line - CongresDocument53 pages1 LBP - Guide - Line - Congresyayu latifahNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Prof. V.P.SharmaDocument34 pagesCerebral Palsy: Prof. V.P.Sharmaخالد القرشيNo ratings yet
- Symptom Management Guidelines: Dyspnea: Dyspnea: A Disorder Characterized by Difficulty BreathingDocument8 pagesSymptom Management Guidelines: Dyspnea: Dyspnea: A Disorder Characterized by Difficulty Breathingmia fitryniNo ratings yet
- PostCovidConditionsClinicalGuidance ENDocument3 pagesPostCovidConditionsClinicalGuidance ENPaula VidicaNo ratings yet
- Physical Medicine and Therapy. Means of PT. Therapeutic Exercise. Electrotherapy. Balneology and Climate MedicineDocument64 pagesPhysical Medicine and Therapy. Means of PT. Therapeutic Exercise. Electrotherapy. Balneology and Climate MedicineEcaterina GorganNo ratings yet
- Physical Medicine and Therapy. Means of PT. Therapeutic Exercise. Electrotherapy. Balneology and Climate MedicineDocument64 pagesPhysical Medicine and Therapy. Means of PT. Therapeutic Exercise. Electrotherapy. Balneology and Climate MedicineEcaterina GorganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 4 Gas Exchange, ImpairedDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan 4 Gas Exchange, Impaireddbryant0101100% (6)
- Principles of Therapeutic Exercise StudynetDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Therapeutic Exercise StudynetProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- JR 3 Aulia-High-intensity Inspiratory Muscle Training in Bronchiectasis EditDocument26 pagesJR 3 Aulia-High-intensity Inspiratory Muscle Training in Bronchiectasis EditauliaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 - Kelas B - Nursing English IIDocument7 pagesKelompok 1 - Kelas B - Nursing English IINazimatul FitriyahNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Colorectal Cancer Case StudyDocument9 pagesGroup 5 Colorectal Cancer Case Studyapi-551496110No ratings yet
- Telus Health - Care Centres Elite Preventative Health Assessment 2021Document2 pagesTelus Health - Care Centres Elite Preventative Health Assessment 2021sergii volodarskiNo ratings yet
- Day 13 - KIN 4200 - 2024 - Exercise Prescription For Select Conditions (Cerebral Palsy)Document32 pagesDay 13 - KIN 4200 - 2024 - Exercise Prescription For Select Conditions (Cerebral Palsy)avocado 677No ratings yet
- Disabilitas Pada Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Dan Restriktif - WillDocument50 pagesDisabilitas Pada Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Dan Restriktif - WillMartina SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Measuring Physical Activity: Tools and Indicators: Bill KohlDocument53 pagesMeasuring Physical Activity: Tools and Indicators: Bill KohlhanikyuniwiyatiNo ratings yet
- Preventing Exercise Related Cardiovascular EventsDocument23 pagesPreventing Exercise Related Cardiovascular EventsYustinus TeddyNo ratings yet
- Definition / UnderstandingDocument11 pagesDefinition / UnderstandingRos ArruanNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Physio Clinical Reasoning (Heywood 2009)Document39 pagesAquatic Physio Clinical Reasoning (Heywood 2009)oana.ostafiNo ratings yet
- Therapy LIVE Ben CormackDocument23 pagesTherapy LIVE Ben Cormackgemichan26No ratings yet
- Exercise PrescriptionDocument9 pagesExercise PrescriptionJoshua Arceo100% (2)
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3Samantha PargadNo ratings yet
- Terapi Nutrisi Paoa Penyakit Kardiovaskuler: OutlineDocument11 pagesTerapi Nutrisi Paoa Penyakit Kardiovaskuler: OutlineJerNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons DiseaseDocument28 pagesParkinsons DiseaseShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Webinar 3 Exercise in PAD SlidesDocument46 pagesWebinar 3 Exercise in PAD SlidesRekha SatheesanNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy Treatment of Pudendal Neuralgia: Elizabeth Rummer, MSPT Stephanie Prendergast, MPTDocument30 pagesPhysical Therapy Treatment of Pudendal Neuralgia: Elizabeth Rummer, MSPT Stephanie Prendergast, MPTRamya Vasan100% (1)
- Kelompok 1 - Kelas B - Nursing English II-1Document6 pagesKelompok 1 - Kelas B - Nursing English II-1Nazimatul FitriyahNo ratings yet
- Back Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesBack Pain ManagementAbdul Quddus Mat IsaNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Heart FailuerDocument19 pagesSeminar - Heart Failuermustafalotfy01No ratings yet
- Assessment Backgrou ND Knowledg E Nursing Diagnosi S Plannin G Intervention S Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Backgrou ND Knowledg E Nursing Diagnosi S Plannin G Intervention S Rationale EvaluationJenny Juniora AjocNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Diseases and Long Term NIV: When?Document40 pagesNeuromuscular Diseases and Long Term NIV: When?Lavinia DavidescuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapy Brochure WebsiteDocument2 pagesRespiratory Therapy Brochure WebsiteAndroentNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sosm Stress Fracture Rehab Guideline 8 - 5x11Document5 pagesFlyer Sosm Stress Fracture Rehab Guideline 8 - 5x11toaldoNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic DrugsDocument7 pagesAnesthetic DrugsSpahneNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitacion CardiacaDocument25 pagesRehabilitacion CardiacaRenato Vilas BoasNo ratings yet
- Osa TerbaruDocument71 pagesOsa TerbaruAnastasia WibiantoNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi SenamDocument4 pagesFisiologi SenamFatin FatinNo ratings yet
- Core Strengthening From TheDocument35 pagesCore Strengthening From TheMartijn JohanNo ratings yet
- Work Related Poor and LBPDocument23 pagesWork Related Poor and LBPWikha AprianNo ratings yet
- SCSCSCDocument44 pagesSCSCSCHONGJYNo ratings yet
- Lumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsDocument4 pagesLumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsPatricia Ortega100% (1)
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Anemia NCP - NCM 112 LecDocument5 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Anemia NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document58 pagesExercise 2rahmisesariaNo ratings yet
- Management of Hypertention3Document14 pagesManagement of Hypertention3Nadeem AlviNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonismDocument33 pagesParkinsonismAbuzarNo ratings yet
- Home Care RN Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesHome Care RN Skills ChecklistGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- ShitDocument1 pageShitENKELI VALDECANTOSNo ratings yet
- Neurological Stressors III Chronic Neurological Disorders: Joy Borrero, RN, MSN and NUR240 Nursing StudentsDocument38 pagesNeurological Stressors III Chronic Neurological Disorders: Joy Borrero, RN, MSN and NUR240 Nursing StudentsCristina CenturionNo ratings yet
- Task 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesTask 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTine SabaulanNo ratings yet
- Establish A Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programme: Done By: Amina Issa Sarah Yaqoob Norhan Howary Shahad Al - HammadDocument18 pagesEstablish A Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programme: Done By: Amina Issa Sarah Yaqoob Norhan Howary Shahad Al - HammadAmina SawalmehNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Scqp21Document6 pagesPhysiotherapy Scqp21SAMARESH DASNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Workbook for use with Group ProgrammesFrom EverandCardiac Rehabilitation: A Workbook for use with Group ProgrammesNo ratings yet
- The Art of Healing Movement: Exploring Therapeutic Wu Shu Gymnastics.From EverandThe Art of Healing Movement: Exploring Therapeutic Wu Shu Gymnastics.No ratings yet
- Indications For Conservative Management of Scoliosis (Guidelines)Document6 pagesIndications For Conservative Management of Scoliosis (Guidelines)yohanNo ratings yet
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Theory: "The Ten Questions" Clinical Questioning in TCM Acupuncture Theory - TCM TheoryDocument7 pagesTraditional Chinese Medicine Theory: "The Ten Questions" Clinical Questioning in TCM Acupuncture Theory - TCM TheoryyohanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Traditional Chinese Medicinal HerbsDocument17 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Activity of Traditional Chinese Medicinal HerbsyohanNo ratings yet
- 49-Article Text-153-3-10-20200225Document12 pages49-Article Text-153-3-10-20200225yohanNo ratings yet
- Cultural Interpretation On Xiang Thinking of Traditional Chinese MedicineDocument4 pagesCultural Interpretation On Xiang Thinking of Traditional Chinese MedicineyohanNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture in Reproductive MedicineDocument13 pagesAcupuncture in Reproductive MedicineyohanNo ratings yet
- Cryotherapy-Induced Injury : NerveDocument3 pagesCryotherapy-Induced Injury : NerveyohanNo ratings yet
- PDF Post Stroke Scalp Acupuncture DLDocument64 pagesPDF Post Stroke Scalp Acupuncture DLyohan100% (3)
- Dyspnea On Exertion - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesDyspnea On Exertion - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfyohanNo ratings yet
- 导出页面自 0. FLEXCON HDPE Company Profile 2019Document5 pages导出页面自 0. FLEXCON HDPE Company Profile 2019Ge DanielNo ratings yet
- 2016 E450 Schematic-A PDFDocument25 pages2016 E450 Schematic-A PDFGerman torresNo ratings yet
- Research Writing Series 6 How To Write An AbstractDocument20 pagesResearch Writing Series 6 How To Write An AbstractMaria Leira Calubayan Laurel0% (1)
- ICT Project For Social ChangeDocument17 pagesICT Project For Social ChangeTeacher Anne ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Journalnx GreenDocument5 pagesJournalnx GreenJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Slides ForDocument26 pagesPowerPoint Slides Forchamylk75% (4)
- Failure Modes & Effects Analysis: Leverling Critical EquipmendDocument5 pagesFailure Modes & Effects Analysis: Leverling Critical Equipmendyohanes adi saputroNo ratings yet
- Department of Information Technology: Data Structure Semester IV (4IT01) Question Bank Prepared by Prof. Ankur S. MahalleDocument13 pagesDepartment of Information Technology: Data Structure Semester IV (4IT01) Question Bank Prepared by Prof. Ankur S. MahalleSingh ShishirNo ratings yet
- 06 Steve Clarke TEAM 3D Weaving UAMMI Slides 032018Document23 pages06 Steve Clarke TEAM 3D Weaving UAMMI Slides 032018Zheng XjNo ratings yet
- Docufold mk2Document28 pagesDocufold mk2januszNo ratings yet
- Guide To Install Mac Os XDocument5 pagesGuide To Install Mac Os XMdnor RahimNo ratings yet
- 1 SATIP-N-001-02 Hot InsulationDocument2 pages1 SATIP-N-001-02 Hot InsulationJithuJohnNo ratings yet
- BL InstructionDocument1 pageBL InstructionJerriel MisolesNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - Bateria - Everexceed - ST-12120Document2 pagesData Sheet - Bateria - Everexceed - ST-12120JAIRO LOPEZNo ratings yet
- 2749 8488 1 PBDocument10 pages2749 8488 1 PBIgor BaltaNo ratings yet
- ZED Partner Carriers: For 9W and S2 Employees Annexure A: List of Zed PartnersDocument4 pagesZED Partner Carriers: For 9W and S2 Employees Annexure A: List of Zed PartnersAakash SawaimoonNo ratings yet
- Tib Amx AdministrationDocument384 pagesTib Amx AdministrationTaher HarrouchiNo ratings yet
- Lecture#3 Kinematic AnalysisDocument8 pagesLecture#3 Kinematic AnalysisRenuga Subramaniam100% (1)
- Thread: Tanjina HelalyDocument38 pagesThread: Tanjina Helalytomar amiNo ratings yet
- Aashirvaad AttaDocument8 pagesAashirvaad AttaPulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- SUMP PumpsDocument44 pagesSUMP PumpsRaghavendra NK100% (1)
- 28 Societe Produits Nestle S.A. v. Dy Jr.Document2 pages28 Societe Produits Nestle S.A. v. Dy Jr.Rain HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Dec 22 Sunday Manila To Shanghai 8:15pm Dec 23 Monday Arrives 12:05amDocument7 pagesDec 22 Sunday Manila To Shanghai 8:15pm Dec 23 Monday Arrives 12:05amJan Kaeko BalmeoNo ratings yet
- CRU Primary Aluminium Smelting Cost Service Smelter List2Document5 pagesCRU Primary Aluminium Smelting Cost Service Smelter List2srkmNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 - Ray Adrian LanduayDocument9 pagesActivity Sheet 1 - Ray Adrian Landuayralanduay29652No ratings yet
- E PassbookDocument3 pagesE PassbookJASVINDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- Örnek - Elon Musk'in CV'SiDocument2 pagesÖrnek - Elon Musk'in CV'SiSümeyye GünayNo ratings yet
- Algor Mortis Describes The Postmortem Temperature Change After Someone Has DiedDocument4 pagesAlgor Mortis Describes The Postmortem Temperature Change After Someone Has DiedBelinda ViernesNo ratings yet