Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review of Bonds
Uploaded by
Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review of Bonds
Uploaded by
Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaCopyright:
Available Formats
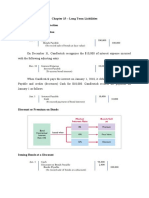
Summary :
BONDS is a contract between the issuer and the investor
Pay specified sum of money at a determinable future date:
The different terms of bonds.
Measurement
Bond not designated of FVPL shall be measured initially at FV minus transaction cost that are
directly attributable to the issue of the bonds payable.
Bond shall be deducted from the fair value or issue price of the bonds payable in measuring
initially the bonds payable.
However if the bonds are designated and accounted for if FV PL “ bond issue costs are treated
as expense immediately.
PFRS 9 provides that after initial recognition ,bonds payable shall be measured either
Amortized cost using effective interest method.
At FVPL .
EFFECTIVE INTEREST METHOD
Nominal rate or stated rate appearing on the face of the bonds
Effective rate – actual interest incurred on the bond issue
The rate that exactly discounts estimated cash future payments through the expected life of the
bonds payable or when approximate, a shorter period to the net carrying amount of the bonds
payable.
The effective rate is also known as yield or market rate.
If the bonds are sold at face amount, the nominal rate and effective rate the same.
If the bonds are sold at a discount the effective is higher than nominal rate.
If the bonds are sold at a premium the effective is lower than nominal rate.
Effective interest method of amortizing discount and premium on bonds payable.
Effective interest method or simply interest method or scientific method recognizes two kinds of
interest rate nominal rate and effective rate.
The annual amortization of premium or discount is the difference between effective interest
expense and nominal interest expense.
How will you compute:
The interest expense is computed by multiplying the CA of the bonds payable at the beginning
of the year by the effective rate.
The nominal interest expense is computed by multiplying the Face Amount of the bonds
payable by the nominal rate.
The effective interest method provides for an increasing of discount amortization and increasing
amount of interest expense.
The effective interest method provides for an increasing amount premium amortization but a
decreasing amount of interest expense.
You might also like
- Gialogo, Jessie LynDocument2 pagesGialogo, Jessie LynMeidrick Rheeyonie Gialogo AlbaNo ratings yet
- Bonds PayableDocument3 pagesBonds PayableRussel CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Act. 9 IntaccDocument6 pagesAct. 9 IntaccedrianclydeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Cost of Debt: The Issue of Premium or Discount BondsDocument6 pagesCorporate Cost of Debt: The Issue of Premium or Discount BondsDipal KotakNo ratings yet
- IA Chap. 19, 20, and 22Document31 pagesIA Chap. 19, 20, and 22Pitel O'shoppeNo ratings yet
- A4 Chapter 5 - Bonds PayableDocument8 pagesA4 Chapter 5 - Bonds PayableMa Jhenelle De Leon100% (1)
- ReportDocument105 pagesReportGanesh JounjalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Long Term Liabilities Journalizing Bond Transaction Issuing Bonds at Face ValueDocument11 pagesChapter 15 - Long Term Liabilities Journalizing Bond Transaction Issuing Bonds at Face Valueowais khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Financing Liabilities: Bonds and Long-Term Notes PayableDocument4 pagesChapter 14: Financing Liabilities: Bonds and Long-Term Notes PayableJason BrightNo ratings yet
- Libby 4ce Solutions Manual - Ch11Document59 pagesLibby 4ce Solutions Manual - Ch117595522No ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Long Term LiabilitiesDocument29 pagesChapter 14: Long Term LiabilitiesVirginia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bonds Payable Multiple Choice ReviewerDocument3 pagesBonds Payable Multiple Choice ReviewerLouise100% (1)
- BondsDocument16 pagesBondsReignNo ratings yet
- Valuation Method FinalDocument17 pagesValuation Method FinalJESSICA ONGNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four FMDocument7 pagesChapter Four FMHope GoNo ratings yet
- Term Structure of Interest RatesDocument12 pagesTerm Structure of Interest RatesNikunj ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 FA - IIDocument22 pagesUnit 5 FA - IIBlack boxNo ratings yet
- Yield To CallDocument16 pagesYield To CallSushma MallapurNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Liabilities AnswersDocument15 pagesLong-Term Liabilities AnswersNicoleNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document31 pagesCH 14mohamedhusseindableNo ratings yet
- Advanced Bond ConceptsDocument8 pagesAdvanced Bond ConceptsEllaine OlimberioNo ratings yet
- Bonds Payable: Acc 102-Intermediate AccountingDocument22 pagesBonds Payable: Acc 102-Intermediate AccountingCrisangel de LeonNo ratings yet
- TOA Bond Payable and Notes PayableDocument3 pagesTOA Bond Payable and Notes PayablePatrick BacongalloNo ratings yet
- CMA Part 2 - Section E - BondsDocument4 pagesCMA Part 2 - Section E - Bondsasafoabe4065No ratings yet
- Week 2 Chapter 9Document8 pagesWeek 2 Chapter 9Sahaja SarvaNo ratings yet
- Long Term Debt EditedDocument16 pagesLong Term Debt EditedAdugnaNo ratings yet
- What Is Bond Yield?Document5 pagesWhat Is Bond Yield?JNo ratings yet
- BondDocument44 pagesBondSumit VaishNo ratings yet
- Project in Acctg4 For Pre-FinalsDocument12 pagesProject in Acctg4 For Pre-FinalsJohn Kenneth Escober BentirNo ratings yet
- Project in Acctg4 For Pre-FinalsDocument12 pagesProject in Acctg4 For Pre-FinalsJohn Kenneth Escober BentirNo ratings yet
- Reporting and Interpreting Bonds: Answers To QuestionsDocument43 pagesReporting and Interpreting Bonds: Answers To QuestionsceojiNo ratings yet
- Effective Interest Method A. Method Required in AmortizingDocument1 pageEffective Interest Method A. Method Required in AmortizingJanna rae BionganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 OutlineDocument6 pagesChapter 13 OutlineShella FrankeraNo ratings yet
- Non-Current Liabilities - : Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesNon-Current Liabilities - : Learning ObjectivesJiddah0% (1)
- What Do Interest Rates Mean and What Is Their Role in Valuation?Document3 pagesWhat Do Interest Rates Mean and What Is Their Role in Valuation?Alessandra PilatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Solutions Excluding HomeworkDocument31 pagesChapter 10 Solutions Excluding HomeworkMissing PersonNo ratings yet
- Bonds Payable SummaryDocument16 pagesBonds Payable SummaryJovel DiazNo ratings yet
- Bond Pricing, Yield Measures and Total Return (2) .Document42 pagesBond Pricing, Yield Measures and Total Return (2) .Josua PranataNo ratings yet
- Fin Acc - Chapter 9 NotesDocument2 pagesFin Acc - Chapter 9 NotesmakaylaxbooksNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Bonds PayableDocument18 pagesLesson - Bonds PayableDesiree GalletoNo ratings yet
- Coupon RateDocument2 pagesCoupon RateVirajRautNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Long Term LiabilitiesDocument30 pagesChapter 14: Long Term LiabilitiesMohammed Akhtab Ul HudaNo ratings yet
- 015 - Quick-Notes - Financial Liabilities From Borrowings Part 2Document3 pages015 - Quick-Notes - Financial Liabilities From Borrowings Part 2Zatsumono YamamotoNo ratings yet
- Bond DurationDocument2 pagesBond DurationBalasingam PrahalathanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management AssignmentDocument8 pagesFinancial Management AssignmentLovely KhanNo ratings yet
- ValixDocument17 pagesValixAnne Hawkins100% (7)
- Corporate Finance 5Document3 pagesCorporate Finance 5Mujtaba AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bonds PayableDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Bonds PayableMarko Zero FourNo ratings yet
- BF330 FPD 8 2020 1Document49 pagesBF330 FPD 8 2020 1richard kapimpaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Effective Interest MethodDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 5 Effective Interest MethodbluemajaNo ratings yet
- I-Bond Rate: TreasurydirectDocument19 pagesI-Bond Rate: TreasurydirectkoggleNo ratings yet
- Chapter-05 Time Value of MoneyDocument20 pagesChapter-05 Time Value of MoneyZakaria SakibNo ratings yet
- 54556Document22 pages54556rellimnojNo ratings yet
- Are Securities That Promise To Make Fixed Payments According ToDocument26 pagesAre Securities That Promise To Make Fixed Payments According Toaddisyawkal18No ratings yet
- Notes PayableDocument35 pagesNotes PayableAllene MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Valuation of Bonds FM1Document25 pagesChapter 6 Valuation of Bonds FM1Alona Jane ObilloNo ratings yet
- Investment Module 4Document6 pagesInvestment Module 4miyanoharuka25No ratings yet
- Bond Value - YieldDocument40 pagesBond Value - YieldSheeza AshrafNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - AK. 2019I - Paper of 11th Meetings (1) - 2-11Document10 pagesGroup 3 - AK. 2019I - Paper of 11th Meetings (1) - 2-11Marsha CantikaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Achievement: Presented ToDocument1 pageCertificate of Achievement: Presented ToQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- AISPre10 Info SystemDocument7 pagesAISPre10 Info SystemQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Direct Costing and Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Multiple ChoiceDocument25 pagesDirect Costing and Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Multiple ChoiceQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Certificate Template Word 10Document1 pageCertificate Template Word 10Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- How To Assess Yourself in The 5 Key Areas of GrowthDocument3 pagesHow To Assess Yourself in The 5 Key Areas of GrowthQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- AE 25 Module 1 Lesson 1Document99 pagesAE 25 Module 1 Lesson 1Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 2 by Valix 2015Document247 pagesFinancial Accounting 2 by Valix 2015Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Development of Science in AfricaDocument18 pagesDevelopment of Science in AfricaQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- AE 24 Module 1 Lesson 6Document3 pagesAE 24 Module 1 Lesson 6Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- AE 24 Strategic Business Analysis Final Examination Instructions T FDocument6 pagesAE 24 Strategic Business Analysis Final Examination Instructions T FQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Accounting For Franchise Operations Franchisor Chapter 8 Accounting For Franchise Operations FranchisorDocument55 pagesChapter 8 Accounting For Franchise Operations Franchisor Chapter 8 Accounting For Franchise Operations FranchisorQueeny Mae Cantre Reuta100% (1)
- Prehistoric Art: Age of FaithDocument110 pagesPrehistoric Art: Age of FaithQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Noting DetailsDocument2 pagesNoting DetailsQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Dhis Special Transactions 2019 by Millan Solman PDFDocument158 pagesDhis Special Transactions 2019 by Millan Solman PDFQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Balance of PaymentDocument9 pagesBalance of PaymentQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Audit Reporting Presentation Deck 02.06.21Document60 pagesAudit Reporting Presentation Deck 02.06.21Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Ae3 Laws of Sale and PartnershipDocument2 pagesAe3 Laws of Sale and PartnershipQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Compound Financial Instrument?: Example 1: A Bond Convertible Into A Fixed Number of Issuer's SharesDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Compound Financial Instrument?: Example 1: A Bond Convertible Into A Fixed Number of Issuer's SharesQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Business Etiquette PunctualityDocument2 pagesBusiness Etiquette PunctualityQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Bsais 2c-Group 5Document17 pagesBsais 2c-Group 5Queeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Compound Financial InstrumentsDocument1 pageExercises Compound Financial InstrumentsQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet