Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COSMOS solution manual chapter 11 problem 42
Uploaded by
LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COSMOS solution manual chapter 11 problem 42
Uploaded by
LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATACopyright:
Available Formats
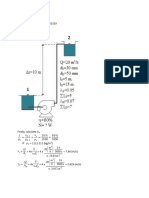
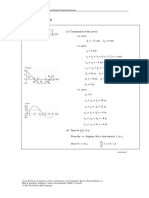
COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization System
Chapter 11, Solution 42.
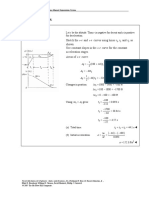
Place the origin at A when t = 0.
Motion of A: ( x A )0 = 0, ( v A )0 = 15 km/h = 4.1667 m/s, a A = 0.6 m/s 2
v A = ( v A )0 + a At = 4.1667 + 0.6t
1
x A = ( x A )0 + ( v A )0 t + a At 2 = 4.1667 t + 0.3t 2
2
Motion of B: ( xB )0 = 25 m, ( vB )0 = 23 km/h = 6.3889 m/s, aB = − 0.4 m/s 2
vB = ( vB )0 + aBt = 6.3889 − 0.4t
1
xB = ( xB )0 + ( vB )0 t + aBt 2 = 25 + 6.3889t − 0.2 t 2
2
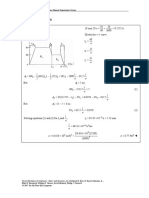
(a) When and where A overtakes B. x A = xB
4.1667 t + 0.3 t 2 = 25 + 6.3889 t − 0.2 t 2
0.5t 2 − 2.2222t − 25 = 0
2.2222 ± 2.22222 − ( 4 )( 0.5 )( − 25 )
t=
( 2 )( 0.5)
t = 2.2222 ± 7.4120 = 9.6343 s and − 5.19 s
Reject the negative root. . t = 9.63 s W
2
x A = ( 4.1667 )( 9.6343) + ( 0.3)( 9.6343) = 68.0 m
2
xB = 25 + ( 6.3889 )( 9.6343) − ( 0.2 )( 9.6343) = 68.0 m
A moves 68.0 m W
B moves 43.0 m W
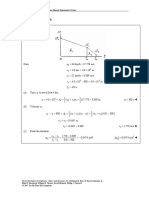
(b) Corresponding speeds.
v A = 4.1667 + ( 0.6 )( 9.6343) = 9.947 m/s v A = 35.8 km/h W
vB = 6.3889 − ( 0.4 )( 9.6343) = 2.535 m/s vB = 9.13 km/h W
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics, 8/e, Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston, Jr.,
Elliot R. Eisenberg, William E. Clausen, David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies.
You might also like
- Maxxecu Plugin - Engine Specifics Audi 1.8T Me 7.5: Vehicle Enginecode Year Lsu Sensor NoteDocument4 pagesMaxxecu Plugin - Engine Specifics Audi 1.8T Me 7.5: Vehicle Enginecode Year Lsu Sensor NoteMaxuel Antunes100% (1)
- Design of Retaining Wall ReinforcementDocument7 pagesDesign of Retaining Wall ReinforcementMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Flight Mechanics - Part 1Document44 pagesFlight Mechanics - Part 1Muhamad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall (L-Type) 6.0mDocument22 pagesRetaining Wall (L-Type) 6.0mPrabha KaranNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Construction JointsDocument18 pagesHorizontal Construction JointsPremasiri KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Design and analysis of concrete roof beamsDocument30 pagesDesign and analysis of concrete roof beamsLee Yu Chan88% (8)
- (Hoccokhi - VN) Bai Tap Lap Rap Solidworks 2dongco NgangDocument4 pages(Hoccokhi - VN) Bai Tap Lap Rap Solidworks 2dongco NgangChien Dang VanNo ratings yet
- Louver CalculationDocument9 pagesLouver Calculationkumar12121984No ratings yet
- Physics Answers PDFDocument82 pagesPhysics Answers PDFJoanne ChitoroNo ratings yet
- Panda PMS 8mini E-TEC Operation Manual (V02)Document56 pagesPanda PMS 8mini E-TEC Operation Manual (V02)Dình Trần100% (1)
- Types of Stoppers Used in Press Working ToolsDocument44 pagesTypes of Stoppers Used in Press Working ToolsSubodh KumarNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing Unit for Well Servicing and Sand RemovalDocument40 pagesCoiled Tubing Unit for Well Servicing and Sand RemovalPratimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 48.: X X V VDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 48.: X X V VLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- (Estimation of Dead Load) in A 2-Storey Residential House: Ce 115 - Structural Theory IiDocument31 pages(Estimation of Dead Load) in A 2-Storey Residential House: Ce 115 - Structural Theory Iishinichi falcoNo ratings yet
- Insta Laci Ones Electrostatic As I IDocument12 pagesInsta Laci Ones Electrostatic As I IEnrique ArturoNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Beam 1Document18 pagesDesign of Cantilever Beam 1Rogen Graciano DelgadoNo ratings yet
- CALCULATIONDocument31 pagesCALCULATIONketut feliksNo ratings yet
- Chem Mock-Test-1 Solved Answer PDFDocument5 pagesChem Mock-Test-1 Solved Answer PDFParomitaMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Design A Small Mat For An Office Building.Document6 pagesDesign A Small Mat For An Office Building.Jajun IchromNo ratings yet
- FRAMEDocument31 pagesFRAMEยูมาเล้ งเฟิงNo ratings yet
- Vmax 0.9 M/s Z 1 (Suelo Cohesivo) 45 N 0.025 (Canal de Tierra)Document3 pagesVmax 0.9 M/s Z 1 (Suelo Cohesivo) 45 N 0.025 (Canal de Tierra)Estefani RuedaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Assignment 7Document8 pagesSolution of Assignment 7Hasan AraabiNo ratings yet
- Appendix For Detention TankDocument7 pagesAppendix For Detention TankCaroline LangitNo ratings yet
- ACTIVIDAD 7 - DinámicaDocument6 pagesACTIVIDAD 7 - DinámicaDiego PachecoNo ratings yet
- K P H K: Sin Sin31Document6 pagesK P H K: Sin Sin31John Pierce GumapacNo ratings yet
- يا رب فك الضيقهDocument80 pagesيا رب فك الضيقهAndrew KuwaitNo ratings yet
- AS 2E (JOINT 119 & 143 - UNDCON5 & UDCON 6) TanggaDocument16 pagesAS 2E (JOINT 119 & 143 - UNDCON5 & UDCON 6) TanggaHajie OmenNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis For Third Floor BeamDocument83 pagesDesign and Analysis For Third Floor BeamVergel Pabunan NogadasNo ratings yet
- Actividad-David Sierra SalazarDocument10 pagesActividad-David Sierra Salazarfarid perez bustoNo ratings yet
- Design Bridge Analysis and ReinforcementDocument12 pagesDesign Bridge Analysis and ReinforcementHuda MahdiNo ratings yet
- PHYS Problem Set 1Document10 pagesPHYS Problem Set 1khaizanjohnNo ratings yet
- Module-3-Activity-No.-4 Duero, Aerol Cedric DDocument6 pagesModule-3-Activity-No.-4 Duero, Aerol Cedric DAEROLCEDRIC DUERONo ratings yet
- TOS LAB REPORTDocument15 pagesTOS LAB REPORTStephanieNo ratings yet
- Lgtrung - MO - HW#4Document6 pagesLgtrung - MO - HW#4Trung SnowboyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering AssignmentDocument6 pagesMechanical Engineering AssignmentMinister Peace ShalomNo ratings yet
- Solution of Q4Document5 pagesSolution of Q4Asim HassanNo ratings yet
- Bab Iii ISI: I. PerhitunganDocument9 pagesBab Iii ISI: I. PerhitunganRaevansya Arya KanigaraNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Department: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesCivil Engineering Department: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMel CoderesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-4 QuestionsDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 1-4 Questionsaliali78613hassanNo ratings yet
- Square Footing With MomentDocument7 pagesSquare Footing With MomentGhiovani DayananNo ratings yet
- Elaborati 2-Complete1Document28 pagesElaborati 2-Complete1arianit thaqiNo ratings yet
- Dayanma Yapilari-11 HaftaDocument1 pageDayanma Yapilari-11 HaftaIhsan ShaarNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan 1. Laju Perpindahan KalorDocument6 pagesPerhitungan 1. Laju Perpindahan KalorAnggoro RestuNo ratings yet
- Homework Solutions: Crystal Structures and DiffractionDocument6 pagesHomework Solutions: Crystal Structures and DiffractionNitinSrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Y GX 2V 2yvDocument6 pagesY GX 2V 2yvp_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- Algoritmo Labo Fenomenos P4 TCDocument1 pageAlgoritmo Labo Fenomenos P4 TCJosue David Valerio MorenoNo ratings yet
- vDocument6 pagesvOrland Son FactorNo ratings yet
- Design 4-Pile Cap (Or More)Document7 pagesDesign 4-Pile Cap (Or More)khamsone pengmanivongNo ratings yet
- Bab V Perhitungan Alinemen HorizontalDocument16 pagesBab V Perhitungan Alinemen Horizontalvw123No ratings yet
- Define Positions As Positive Downward From A Fixed Level. Constraint of CableDocument1 pageDefine Positions As Positive Downward From A Fixed Level. Constraint of CableLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- MIDAS Girt Section Design DetailsDocument5 pagesMIDAS Girt Section Design Detailsျမတ္ သူ ေအာင္No ratings yet
- Quiz 07int Trapcontinous SolutionDocument9 pagesQuiz 07int Trapcontinous SolutionMikmikJojiNo ratings yet
- Rencana Pondasi Tiang Baja BetonDocument9 pagesRencana Pondasi Tiang Baja BetonAmirah UlfahNo ratings yet
- Solution: Coordinate System. The Origin of The X@y Coordinate System Will Be Set To Coinside Horizontal Motion. Here (VDocument1 pageSolution: Coordinate System. The Origin of The X@y Coordinate System Will Be Set To Coinside Horizontal Motion. Here (VbasharNo ratings yet
- Taller ConcretosDocument21 pagesTaller ConcretoseduardoadiazNo ratings yet
- CLASE 4 Viga GerberDocument7 pagesCLASE 4 Viga GerberTrinidad Belen Carme HuascoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Assignment 2016Document8 pagesFluid Assignment 2016TlhologeloNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument7 pagesCover PageDale MikaellaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Tank DesignDocument10 pagesRectangular Tank DesignIssam TeladNo ratings yet
- 3.basin BlockDocument5 pages3.basin Blockp_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- P=γh P=9.81 (1.849) P=18.139 kn /m F= Ph: Structural Analysis Of Bench FlumeDocument16 pagesP=γh P=9.81 (1.849) P=18.139 kn /m F= Ph: Structural Analysis Of Bench FlumeAllyssa OpantoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Solution To Exccercise 3.2)Document4 pagesModule 3 (Solution To Exccercise 3.2)Muhammad FahimNo ratings yet
- 1.perhitungan Plat Lantai: Mu 22522 KG/CM 0,8 0,003 0,003 0,003 0,003+Document12 pages1.perhitungan Plat Lantai: Mu 22522 KG/CM 0,8 0,003 0,003 0,003 0,003+septian wiraputraNo ratings yet
- Check Punching For Edge ColumnsDocument5 pagesCheck Punching For Edge ColumnsAli AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - SI - Final SolutionsDocument12 pagesChapter 13 - SI - Final SolutionsDouglas FernandesNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 76.: A Is 24 Ft/s. Using A T T TDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 76.: A Is 24 Ft/s. Using A T T TLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 182.: R I J KDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 182.: R I J KLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 68Document1 pageChapter 11, Solution 68LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 77.: DX V DT DV A DTDocument2 pagesChapter 11, Solution 77.: DX V DT DV A DTLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 75.: Sketch The Curves. Slope of Curve For Car ADocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 75.: Sketch The Curves. Slope of Curve For Car ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 70.: VT T A T A T ADocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 70.: VT T A T A T ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 67.: T AA ADocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 67.: T AA ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Sketch Curve For First 660 FT.: Chapter 11, Solution 72Document2 pagesSketch Curve For First 660 FT.: Chapter 11, Solution 72LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Soln11069 PDFDocument1 pageSoln11069 PDFLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 57.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 57.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 74.: Sketch The CurvesDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 74.: Sketch The CurvesLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Soln11073 PDFDocument1 pageSoln11073 PDFLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Soln 11162Document2 pagesSoln 11162LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 65.: T A T ADocument2 pagesChapter 11, Solution 65.: T A T ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 63.: at A ADocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 63.: at A ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Soln 11060Document1 pageSoln 11060LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 64Document2 pagesChapter 11, Solution 64LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 56.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at Right AnchorDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 56.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at Right AnchorLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 54.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 54.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization System Chapter 11 Solution 50Document1 pageCOSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization System Chapter 11 Solution 50LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 58.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 58.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Anchor, Positive To The RightLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 53.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 53.: Let X Be Position Relative To The Right Supports, Increasing To The LeftLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 62Document1 pageChapter 11, Solution 62LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 47.: T X X V T at T X TDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 47.: T X X V T at T X TLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 55.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at The Right AnchorDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 55.: Let X Be Position Relative To Left Anchor. at The Right AnchorLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 51.: Let XDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 51.: Let XLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Soln 11049Document1 pageSoln 11049LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 41.: A A A ADocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 41.: A A A ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Turbocharger Characteristics Analysis of 93 KW Marine Diesel EngineDocument6 pagesTurbocharger Characteristics Analysis of 93 KW Marine Diesel EngineFrank ChukwujiNo ratings yet
- Design of Truss Roof: University of Engineering & Technology, TaxilaDocument42 pagesDesign of Truss Roof: University of Engineering & Technology, TaxilaNicko Jay BajaoNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Tying Down Teh Machine D10RDocument4 pagesLifting and Tying Down Teh Machine D10Rpedro cNo ratings yet
- C24 BTTS-9 PhysicsDocument19 pagesC24 BTTS-9 Physicshello2006aditankNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool FL 5090aDocument14 pagesWhirlpool FL 5090aLiviu PetreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document24 pagesChapter 9Clement KipyegonNo ratings yet
- SSFPL Forgings Profile CurrentDocument16 pagesSSFPL Forgings Profile CurrentMahendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Checking The Geometrik AccuracyDocument6 pagesChecking The Geometrik AccuracyCatalyst IchsanNo ratings yet
- GBCPP PCV 2030Document1 pageGBCPP PCV 2030Firstyan Dhika AldaniNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - Separation EquipmentDocument9 pagesSection 7 - Separation Equipmentlulis171No ratings yet
- The 4-Stroke Cycle Engine: BackgroundDocument11 pagesThe 4-Stroke Cycle Engine: BackgroundAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Continuum MechanicsDocument4 pagesContinuum Mechanicsdwarika2006No ratings yet
- MR 10MSX 5400700 M2 GBDocument76 pagesMR 10MSX 5400700 M2 GBFarid RezigNo ratings yet
- BSC (Maths), Dmit (Aero. Engg,), Me (Aero. Engg., Iisc), PHD (Engg.) Hod-Aero@Dayanandasagar - EduDocument4 pagesBSC (Maths), Dmit (Aero. Engg,), Me (Aero. Engg., Iisc), PHD (Engg.) Hod-Aero@Dayanandasagar - EdumanojNo ratings yet
- Design, Codes and Guidelines: 10.1 OverviewDocument3 pagesDesign, Codes and Guidelines: 10.1 OverviewMiljan TrivicNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Residual StressDocument8 pagesHandbook of Residual StressDownNo ratings yet
- Tower 52M-20M2-4legDocument33 pagesTower 52M-20M2-4legBechir Ousseini GarbaNo ratings yet
- Route Sheet Lathe MachineDocument12 pagesRoute Sheet Lathe MachineOscar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DIN EN 809:2012-10 (E) : Pumps and Pump Units For Liquids - Common Safety RequirementsDocument2 pagesDIN EN 809:2012-10 (E) : Pumps and Pump Units For Liquids - Common Safety RequirementsBvitalizeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11-12Document44 pagesLecture 11-12Chauhdary Fazeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 32-2-Rigid Body Dynamics 2-2Document6 pagesLecture 32-2-Rigid Body Dynamics 2-2nhNo ratings yet
- AMSOIL DOMINATOR® Coolant BoostDocument2 pagesAMSOIL DOMINATOR® Coolant BoostamsoildealerNo ratings yet