0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views8 pagesInverted Pendulum Control Techniques
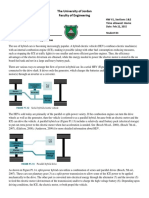
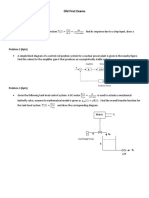
This document discusses control theory applications for balancing scooters. It presents an inverted pendulum model of a balancing scooter as a rod attached to a cart that can move back and forth. The document derives the system transfer function and shows that the inverted pendulum is unstable. It then describes how adding a P-controller can stabilize the system by closing the loop transfer function.
Uploaded by
Atikah AbdallaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views8 pagesInverted Pendulum Control Techniques
This document discusses control theory applications for balancing scooters. It presents an inverted pendulum model of a balancing scooter as a rod attached to a cart that can move back and forth. The document derives the system transfer function and shows that the inverted pendulum is unstable. It then describes how adding a P-controller can stabilize the system by closing the loop transfer function.
Uploaded by
Atikah AbdallaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd