Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACFrOgDsMSP8 eIdCeXPnq3r VZH7oPTj5ZZ3euDLAc gwYlvtAM - EmJ0ui19vi72PBOhkknNfwgAO2U75m5JNYJ91ByYUCkmVM4De9DFO4wqhzRIEbFjaKgQQRSTS4
ACFrOgDsMSP8 eIdCeXPnq3r VZH7oPTj5ZZ3euDLAc gwYlvtAM - EmJ0ui19vi72PBOhkknNfwgAO2U75m5JNYJ91ByYUCkmVM4De9DFO4wqhzRIEbFjaKgQQRSTS4
Uploaded by
Comet Astro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesOriginal Title
ACFrOgDsMSP8-eIdCeXPnq3r-VZH7oPTj5ZZ3euDLAc-gwYlvtAM_EmJ0ui19vi72PBOhkknNfwgAO2U75m5JNYJ91ByYUCkmVM4De9DFO4wqhzRIEbFjaKgQQRSTS4=
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesACFrOgDsMSP8 eIdCeXPnq3r VZH7oPTj5ZZ3euDLAc gwYlvtAM - EmJ0ui19vi72PBOhkknNfwgAO2U75m5JNYJ91ByYUCkmVM4De9DFO4wqhzRIEbFjaKgQQRSTS4
ACFrOgDsMSP8 eIdCeXPnq3r VZH7oPTj5ZZ3euDLAc gwYlvtAM - EmJ0ui19vi72PBOhkknNfwgAO2U75m5JNYJ91ByYUCkmVM4De9DFO4wqhzRIEbFjaKgQQRSTS4
Uploaded by
Comet AstroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Cane
Reform BOW 102
arewareare—itfte aw orgeone dear, af Reet CSIR-CRRL, New Delhi
eats arcind eetraar seat artes Fre sr Pina for Approval o-oo RAD Poet Propo
Treat wey Teo
‘xperimental Investigations of “HYBRID COMPOSITE BEAM System™ [Wuvre, fr *. OLP~ 06/0
ts yy Rus 2 Be Sita Lilt weet Compost Girder
{rade mye tae nem Sanat Popelasr ep -Dungaprased Gola - Sele
2, thee aver #8 w afbern 50 a) (aera Gee
‘RECINER omen Doar a {FF ante + 18a
‘The ultimate objective Isto develop and Investigate an Innovative light weight composite beam system, whether
‘tcould be implemented in a commercial application, asa viable alternate tothe conventional girders, whether
‘the proposed beam is competitive with prestressed concrete beams with respect to structural performance and
cost performance
a, extyarace [Byes] stn
4 fre eit are San en Re 0 PRES CE WORK WTH GARTELY TARGETS a ae:
Tre [Literature review, State ofA preparation, Concrete mix propetion fr sel-consolidated concrete
or | Design ofthe Hybrid composite beam along with reinforcement dealing, Material procurement
TTT GE | Experimental study of Load Deflection behavior, Strese-Strain profiles, crack patterns
TTT GF | Experimental study of Behavior of Prestessng strands, Behavior of Fiber reinforced polynee
m (Cores fae] vem [ov 6 fo]
TG | Correborative Analytical study
35 | Compilation of data, Interpretation of Rests, Report Preparation,
5, eater gf oer. RB / WHS OUTPUT EHYEAGED. Pre rat se)
Taran Pom | ost Pak | TO SPH Toone | eon Serer Contam [Wa Ta
Ces as aii, is
eT Sen aE | fer eA ae Coin | WE wT eye
Sewer fen in 7 *
Sumnpe:
6. D/al Ree BRR BF aoe Sa (ove 500 wa E ww Fh ear D7
STATE OF ART fase ocr gh bom si
Hillman introduced this hybrid composite beam (HCB n 1996 that was used forthe fist time commercially in 2008
(Corley et a, 2013), The HCB fe comprised of three min sub-componens: @ composite shel, compression
reinforcement, and tension reinforcement. The shell i comprised of 9 glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) box
beam, The compresson relaforcemunt unable uf sel-unsuldting concrete (SC) that is poured in a asia arch
shape. The tension reinforcement consists of galvanized high strength (HS) steel tendons anchored at each end
‘within the end blocks. The concrete and steel are tucked inside the durable fibers shel and the voids are fled
with 2 polysocyanurate (pose) foam, The profile of the compression reinforcement is designed to rest the
compression and shear forces resuitng from vertical loads applied to the beam In much te same manner asan arch
structure. Due to this unique configurstion, the fiberglass box protects the steel and concrete from the
environmental effects and serves asthe formu forthe concrete arch, while the strength and stifness are
provided by an efficient use ofthe stein purely ail tension, andthe concrete in purely axial compression In
addition to the optimization of load carrying behavior offered by this configuration, It resuits In a lightweight
"member tat can be trensported easy and erected rapidly making ths technology well sulted to Accelerated Bridge
Construction (A).
‘Three recently constructed bridges in Missour incorporated HCBs in conjunction with traditional reinforced concrete
eck systems, HCB is, however, quite novel. Because ofthe novelty ofthe HCB and its vague structural behavior, an
‘exploratory program tothe Missouri University of Science and Technology MSE.) in cooperation wit University of
Missouri Columbia (UMC) was undertaken to evaluate the in-service beam behavior in 2014,
‘Thus, its structural behavior needs comprehensive experimental Investigation, along wth thorough, theoretical and
numerical analyses.
compassion Reitremane
‘nce Wh xddioa
Payor
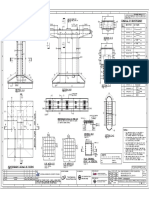
Fragmentary Perspective of Hybrid-Composite Beam
‘w/a et Seo BOAR pe 200 at Hy
TWN ETHCDSLOG a oe
WORK PLAN
+ iteatue survey, Preparation of state of the Art.
+ Concrete Mik Design, Design of 1c.
+ Procurement of materials and Development of Experimental Pian,
+ Casting of Specimens (Cubes/Cylinders/HC8 Beams
‘+ Experimental studies on HCB with Tensioned stands
‘+ Corroboratve analytical studs
+ Compilation of Experimental dato, interpretation of test results
‘+ Report Preparation,
Methodology
‘The fst step inthe HCB casting isthe fabriction ofthe FAP box and steel strands. The bottom shell of the beam
{RP bottom flange and wet), ramplete with tension reinforcing are fabricated In one mold. The top flange is
fabricated in separate mold. A three-sided box is fabricated tothe dimensions ofthe beam. Along the centerlnes
‘ofthe flange, slots are made to install channels. These channels 2et 28a line source forthe resin infusion and
‘vacuum, The layup ofthe shell consists of placing one layer of a surface vel over the entire mold surface, followed
by one layer ofa distribution meta, and finaly the glass fiber layers Sevenswire high strength tendons are then
laced on the top ofthe hottam flange fher layers with ends running up vertically to anchor the compresion
‘elnfurvement, Once the posc-rensloning bars are positioned, polysocyanurate foam blocks are placed within the
‘mold forming arch shape. A bag is placed on the foam blocks and inflated to keep a cavity forthe compression
reinforcement. Spacers and clamps ae used tote the shell webs and ensure the dimensions ofthe eavty. Upper
layer of foam blocs is placed on the top ofthe bag while sil leaving a cavity to accommodate the conerete web.
‘The entire meld is completely enclosed in layers of varnim aging fm sent with tarky tape, Vacuum i thon
applied through the vacuum ports, After evacuating al ofthe a, the vinylester resin i pulled into the form by the
‘vacuum pressure and the mold is kept under vacuum. FRP bottom flange and webs ae fabricated as one mold
Wile the top flange of FRM shell is fabricated seperately The FRP top flange is glued to the bottom shell using
methyl methacvate adhesives. These adhesives provide strong bond that ensure thatthe lid acts compostly with
the bottom shell during the arch pour and the erection ofthe Hybrid Composite Beam, Sel tapping stainless stel
screws are used to futher connect the two elements. The serews are important to arrest any crack that might
propagate through the adhesive bond. Finally, holes are dll Into the ld andthe bottom legs of the shear
‘orector ee then developed below the loose sands. The FAP ld top flange) fbrieated In a separate mold with
‘the same procedure Before attaching the top flange tothe bottom shel, seven-wire strands (generally two strands)
are installed in the bottom ofthe arch and run the full length ofthe beam. Te wires are atached tothe strands to
it them up during installation ofthe shear connectors, After Casting ofthe 3.5m-Sm beam, the load vs deflection
behavior, failure patterns along with Sending, shear force, stresses, and relaxation losses wil be studied Finally,
based on the experimental resuts and Corroborative analytical studies detailed technical reports wil be prepared
and publications will be made.
co)
©
(4) Layup ofthe GRP shel (b) Placement and positioning ofthe strands
2 fer ety aces re PROC
15 we tbe ar whoha perm)
ats tatioas
1 PP,
0) et ee rap)
1 ef amt:
12) ee Paee
Ta ea = or
WAT | Ria Gana | F500 —] AsaanG | Bases
S| RTT OT RT
Se Ea ae Feat] TO | aS a
[ae TT Bom [5 io
‘ove [ROAR RT
TE (6 0 5000 10,000
ie 57D 25000 [5000 50
TR oO a ORT
RET CS SRT (Pov | TORT aoe
Ter Ww Re Tender | aa 200 an
Eemer Ege ie FA 6 021
Te [ee See RR GoTo
Sania
Ea FO 8) os ene E
TELIR Gy ore? Reem opm | asapm | Smaee — | aapa
Shon
ee 2 TT
SB ma TT
Fi et TT aes a Bo
FR Tae Sn ealoatp 7359000
9% SLLgeren ah wt wk ete wth ir fer Eo at Pe lr Far 37 wen f/EQUPENT TO
{SE PRcuRED nea aye peso eae a haa
w a a7 TEE Rane aT
os mtn Cons)
Hee Tao
a) stg swe oy zo UE oF EHETNOAUEMENT
a |e at 9 TT 7 [a A a ae
m ‘pet {or Eee Cnt ae
i
0. ae fr wawonea cer onesT
me C/K a RT Don | eR
Denton weap San
7 | tarpesae come FT cs ca
2 [ete cae = i 2
3 radep ne eer is 0
‘estes anion a6 es =.
5 | aes Sigh a 0.
Vise Eo
21, air wr fH AMTGPRED BEM APACE
aR aah tT (FT 100 a pn et Oe 1
* Technical Reports with a knowledge base onthe structural performance of imovatve and a light weight
Hybrid composite eam is expected
+ Pubications in Nationa international journals on the structural behavior ae envisaged
‘+ Probable atents/Licensing regarding the procedure and typeof materll to be used asthe filer.
(9 re ae ear ae COTE 100 ae Batya sn sted rt)
+ Extended service life of 100 years and bevond providing a longer sustainable solution In comparison to
‘conventional materials,
+ Utra-igne weight structure.
+ Notte cycle cost.
+ Cost competitive structure,
12, i ro @ Af REEMA ata moh tan
9 a arty ney ome FORTIN,
“pee ar. 32,
cabrio mea mpm
ee pach ah ede, Ta wT ABT wae 2]
as tr
4, tebe
ail
‘aaa pia A RR Few apa aa nara
[elie
8
sre st Ff/DECISONOFTHCOMPETENT AUTHOR
erme/sionatace
mace
1 ate Project Leads
2 Re et ter afr nvao
3. ig em Diviason
sae ee)
renee
Geet]
Pee)
Picture Showing Main Components of “HYBRID COMPOSITE BEAM/GIRDER SYSTEMS
Rafe TotW
eRe
Reviewer's comment on the proposal "Experimental Investigations of “HYBRID.
COMPOSITE BEAM SYSTEM”
| generally see some novelty in the work. This is worthwhile funding by you, but
the quantum & finance asked, you may iterate upon.
‘Ask him to address the following points:
1) How does the bond between outer FRP shell and conerete/ foam
concrete ensured.
2) What kind of spanidepth being envisaged.
3) Where are shear rainforcement/how shear torcee are taken by the eection.
4) Tension bar -pre-stressed or not.
65) Will the shear connectors protrude out of the top lid & the box.
Most importantly, let the team give the extra activities! novelties which are being
proposed to be carried out in the project, differentially this work from
the referred literature.
TAU ake the Carnet enna farm few -eerientey om He frat
pepe 1 thotd addnete all Hate points ond —refebwilh, te
sdemni elie
Preatheef
eet, Res | ee eee Nee
pls received oa
fork vase Sep ly a usal
aman douse oF 7 apt Aian:
GRetbe gue AO TS creel Me bem cue Rg
i be Paes Ei
Daan fo oe »
ott ee PL fe mins thine
wm
You might also like
- Section 9 Prestressed Concrete: LRFD Design Specifications. Bridge Designers Must Exercise Engineering Judgment inDocument14 pagesSection 9 Prestressed Concrete: LRFD Design Specifications. Bridge Designers Must Exercise Engineering Judgment inComet AstroNo ratings yet
- 23.1 Appearance in Design: Section 23 AestheticsDocument33 pages23.1 Appearance in Design: Section 23 AestheticsComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Drawing - 275+704 (1) - 11-EndDocument1 pageDrawing - 275+704 (1) - 11-EndComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Section 12 Bridge BearingsDocument38 pagesSection 12 Bridge BearingsComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Effect of Silica Fume On Recycled Aggregate ConcreteDocument7 pagesEffect of Silica Fume On Recycled Aggregate ConcreteComet AstroNo ratings yet
- MINOR BRIDGE at 289+370-SF-02-1Document1 pageMINOR BRIDGE at 289+370-SF-02-1Comet AstroNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregates ConcreteDocument32 pagesMechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregates ConcreteComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Restoration of Masonry Arch Bridges: Bridge Engineering September 2012Document23 pagesRestoration of Masonry Arch Bridges: Bridge Engineering September 2012Comet AstroNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Recycled AggregateDocument4 pagesExperimental Study On Recycled AggregateComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Repairing and Strengthening Techniques For Historic Masonry Arch BridgesDocument5 pagesRepairing and Strengthening Techniques For Historic Masonry Arch BridgesComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Repair of Stone Masonry Arch BridgesDocument9 pagesRepair of Stone Masonry Arch BridgesComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Accelerated Corrosion TestsDocument4 pagesTechniques For Accelerated Corrosion TestsComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study On Non Destructive Technique: Harish. G, Durga Prasad GollaDocument3 pagesComparative Study On Non Destructive Technique: Harish. G, Durga Prasad GollaComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Inventory and Condition Survey of Bridges (Road 2-Tac-03)Document109 pagesInventory and Condition Survey of Bridges (Road 2-Tac-03)Comet AstroNo ratings yet
- RCC Superstructure 21.5m (Rev.A)Document5 pagesRCC Superstructure 21.5m (Rev.A)Comet AstroNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)