Professional Documents
Culture Documents
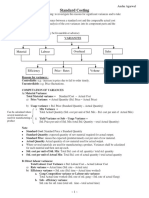
Standard Costing
Standard Costing
Uploaded by
ellaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Costing
Standard Costing
Uploaded by
ellaCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Costing
Wrap-up Exercises (Adapted from RESA Handouts)
Problem 1: Materials and Labor Variance Analysis
Kodak Company has established the following standards for a single unit of its main product, Selfie Camera Tripod
(Stainless Edition):
Inputs Standards
Direct materials 3 metal bars at P2 per bar
Direct labor ½ labor hour at P10 per hour
At the start of the month, the budget includes a planned production of 100 units of tripod based on
normal capacity.
At the end of the month, actual production was 120 units of tripod, which resulted to using 400 bars of
metal, purchased at a cost of P2.10 per bar.
Required:
1. Based on the BUDGETED production of 100 units:
A. How many bars must the company plan to use? (Budgeted quantity)
B. How much materials cost is included in the budget? (Budgeted cost)
2. Determine the actual cost of materials used (Actual cost)
3. Based on the ACTUAL production of 120 units:
A. How many bars should have been used? (Standard Quantity)
B. How much materials cost should have been incurred? (Standard material cost)
C. How many labor hours should have been spent? (Standard hours)
D. How much labor cost should have been incurred? (Standard labor cost)
4. Determine the following:
A. Materials budget variance
B. Materials standard cost variance
C. Materials Quantity Variance
D. Materials Price Variance
5. In the following month, Kodak purchased 500 bars at a total cost of P850 while only 400 bars out of these were
used; the standard quantity allowed for the actual production was 380 bars. Determine the following:
A. Total material variance
B. Materials quantity variance
C. Materials price usage variance
D. Materials purchase price variance
6. During the month, a total payroll of P540 was paid to laborers, working 45 labor hours, to produce the 120 units
of Tripod. Determine the following:
A. Total labor variance
B. Labor efficiency variance
C. Labor rate variance
Problem 2: Factory Overhead Budget:
RAFA Company shows the following data regarding its factory overhead:
Flexible budget formula: FOH = 20,000 + 1X
Where: X = number of labor hours.
Standard: 1 unit of product requires 4 labor hours.
Normal Capacity: 2,500 units.
Budgeted Hours: A)______ hours.
Fixed Overhead (FFOH) B)_________ Fixed Overhead Rate (FR) E)________
Variable Overhead (VFOH) C)_________ Variable Overhead Rate (VR) F)________
Total Budgeted Overhead D)_________ Standard Overhead Rate (SR) G)________
Required:
1. Compute for the missing amounts.
2. What is the budgeted FOH if adjusted based on 7,500 actual hours?
3. What is the budgeted FOH if adjusted based on 8,000 standard hours?
Problem 3: (Factory Overhead Variance Analysis – Two Variance Method)
The normal capacity of Nadal Company is 12,000 labor hours per month. At normal capacity, the standard factory
overhead rate is P13 per labor hour based on P96,000 of budgeted fixed cost per month and a variable cost rate of
P5 per labor hour. During January, the Company operated at 12,500 labor hours, with actual factory overhead cost
of P165,000. The number of standard labor hours allowed for the production actually attained is 11,000.
Required: 1. Overhead FOH Variance 2. FOH Controllable Variance 3. FOH Volume Variance
Problem 4: (Factory Overhead Variance Analysis – Two, Three, and Four Way Variance Method)
Spain Company provides the following production data:
Standard factory overhead cost per unit of product: 4 hours at P3.00 per hour
A) Budgeted fixed factory overhead P20,000
B) Normal Production 2,500 units
C) Actual Production 2,000 units
D) Actual Hours 7,500 hours
E) Actual/ Factory overhead incurred (75% fixed) P26,000
Required:
1. Budgeted factory overhead 6. Volume Variance
2. Standard factory overhead 7. Spending Variance
3. Budgeted FOH based on actual hours 8. Efficiency Variance
4. Budgeted FOH based on standard hours 9. Variable spending variance
5. Controllable variance 10. Fixed spending variance
You might also like
- Bonds CallableDocument52 pagesBonds CallablekalyanshreeNo ratings yet
- 16 Standard Costingx PDFDocument92 pages16 Standard Costingx PDFJessa Basarte40% (5)
- FM - Chapter 9Document5 pagesFM - Chapter 9sam989898No ratings yet
- Startup Valuation - Applying The Discoun... D in Six Easy Steps - EY - NetherlandsDocument14 pagesStartup Valuation - Applying The Discoun... D in Six Easy Steps - EY - NetherlandsRodrigo Langenhin Vásquez VarelaNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting Standards CouncilDocument6 pagesFinancial Reporting Standards CouncilFrancis Jerome Cuarteros0% (1)
- 09 Standard CostingDocument5 pages09 Standard CostingabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Cost2 - Finals SY 2020 21 PDFDocument10 pagesCost2 - Finals SY 2020 21 PDFshengNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument11 pagesStandard CostingJoydip Dasgupta100% (1)
- Module 2 Sub Mod 2 Standard Costing and Material Variance FinalDocument31 pagesModule 2 Sub Mod 2 Standard Costing and Material Variance Finalmaheshbendigeri5945No ratings yet
- Contoh Penelitian Akta Grosse Pengakuan HutangDocument26 pagesContoh Penelitian Akta Grosse Pengakuan Hutangjasa biro kitaNo ratings yet
- Acctng ProcessDocument4 pagesAcctng ProcessElaine YapNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cost Acctg. - HO#9Document5 pagesCost Acctg. - HO#9JOSE COTONER0% (1)
- 4th (Managerial Accounting)Document20 pages4th (Managerial Accounting)Amara ELprida SaniNo ratings yet
- Cost Acctg. ReportDocument9 pagesCost Acctg. ReportApril Joy ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Ma Lo5 NotesDocument2 pagesMa Lo5 NotesItumeleng RampatsiNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument43 pagesStandard Costing & Variance Analysis21-51749No ratings yet
- Chap 4 MNGT Acctng PDFDocument4 pagesChap 4 MNGT Acctng PDFRose Ann YaboraNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument3 pagesQuizAerin AenNo ratings yet
- VariancesDocument45 pagesVariancesanonNo ratings yet
- Synth 1 (STD COSTING)Document11 pagesSynth 1 (STD COSTING)Hassan AdamNo ratings yet
- Standart Costing PDFDocument3 pagesStandart Costing PDFVIHARI DNo ratings yet
- General Model For Variable Manufacturing Costs Variance AnalysisDocument2 pagesGeneral Model For Variable Manufacturing Costs Variance AnalysisEyuel SintayehuNo ratings yet
- 02.12.21 Variance AnalysisDocument25 pages02.12.21 Variance Analysisejazahmad5No ratings yet
- Standard Costs and Variance Analysis ERDocument19 pagesStandard Costs and Variance Analysis ERElyana SulayNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost Accounting Materials, Labor, and Factory OverheadDocument29 pagesStandard Cost Accounting Materials, Labor, and Factory OverheadKristine AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument24 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet STD CostingDocument3 pagesPractice Sheet STD CostingPrerna AroraNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument26 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisFidelina CastroNo ratings yet
- MAS 1 Standard CostingDocument1 pageMAS 1 Standard CostingFídely Pierré100% (1)
- Cost and Management AccountingDocument12 pagesCost and Management AccountingRohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7 - Standard CostingDocument3 pagesExercise 7 - Standard CostingSports savageNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument1 pageStandard CostingCristine ClarinNo ratings yet
- Sva - Student Copy P1Document101 pagesSva - Student Copy P1Joyce MamokoNo ratings yet
- ACC 223 SC Seatwork QDocument4 pagesACC 223 SC Seatwork Qmaica G.No ratings yet
- Variance AnalysisDocument31 pagesVariance AnalysisGift ChaliNo ratings yet
- STD CSTGDocument42 pagesSTD CSTGsanam20191No ratings yet
- Chapter Eleven: Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument43 pagesChapter Eleven: Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisnnonscribdNo ratings yet
- SCM Discussion 6Document10 pagesSCM Discussion 6M4ZONSK1E OfficialNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance Analysis!Document37 pagesStandard Costing & Variance Analysis!kunalNo ratings yet
- Questions - Chapter 9Document5 pagesQuestions - Chapter 9sajedulNo ratings yet
- COMA - 04 Variaance PDFDocument49 pagesCOMA - 04 Variaance PDFAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Variance AnalysisDocument15 pagesChapter 10 - Variance AnalysisNurryn QistinaNo ratings yet
- 26560standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument2 pages26560standard Costing and Variance AnalysisTalha HanifNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document46 pagesUnit 12aaravdhamija100No ratings yet
- Exercise STD CostingDocument1 pageExercise STD CostingMaria Callista LovinaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document16 pagesUnit 10Ziad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Standart Costing-ADocument39 pagesStandart Costing-ALamtiur LidiaqNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument7 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisNicko CrisoloNo ratings yet
- Acctg 10A Assignment - Standard CostingDocument2 pagesAcctg 10A Assignment - Standard CostingClaire diane Crave0% (1)
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Dishantely SamboNo ratings yet
- CMA II - Chapter 3, Flexible Budgets & StandardsDocument77 pagesCMA II - Chapter 3, Flexible Budgets & StandardsLakachew Getasew0% (1)
- 13 VariancesDocument7 pages13 VariancesJack PayneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 006 - Standard Costs VariancesDocument43 pagesChapter 006 - Standard Costs VariancesChi Nguyễn Thị KimNo ratings yet
- CostDocument2 pagesCostMarielle CuriosoNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost SystemDocument39 pagesStandard Cost SystemTricia Marie TumandaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Lecture and Sample ProblemDocument8 pagesStandard Costing Lecture and Sample ProblemAccounting FilesNo ratings yet
- Basic Questions Standard CostingDocument9 pagesBasic Questions Standard Costinganisasheikh83No ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument14 pagesStandard CostingRoselyn LumbaoNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: SISMIRA (1910531029) Rahimah Ramadhani P (1910536050)Document13 pagesStandard Costing: SISMIRA (1910531029) Rahimah Ramadhani P (1910536050)Rahimah ImNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: SISMIRA (1910531029) Rahimah Ramadhani P (1910536050)Document13 pagesStandard Costing: SISMIRA (1910531029) Rahimah Ramadhani P (1910536050)Rahimah ImNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost and VariancesDocument39 pagesStandard Cost and VariancesChristian AribasNo ratings yet
- Mod 2.2 Variance AnalysisDocument31 pagesMod 2.2 Variance AnalysisSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Acc 106 p3 Exam Set ADocument14 pagesAcc 106 p3 Exam Set ALexzy Chant LopezNo ratings yet
- ICAP JD - Senior Finance ManagerDocument4 pagesICAP JD - Senior Finance ManagerBin SaadunNo ratings yet
- Socio-Economic and Government Impact On BusinessDocument42 pagesSocio-Economic and Government Impact On BusinessaguNo ratings yet
- Trident Limited - CARE Upgrades Trident's Credit RatingDocument2 pagesTrident Limited - CARE Upgrades Trident's Credit RatingmanishkayalNo ratings yet
- Himanshu Lohia: Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesHimanshu Lohia: Curriculum Vitaehimanshulohia85No ratings yet
- Marketing-of-Financial-Services SAKSHIDocument9 pagesMarketing-of-Financial-Services SAKSHINageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON Ratio Analysis of TCS: Submitted to:SUBMITTED BY Prof. Anil TilakDocument32 pagesA Project Report ON Ratio Analysis of TCS: Submitted to:SUBMITTED BY Prof. Anil TilakSurbhi LodhaNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet ProblemsDocument10 pagesCost Sheet Problemsprapulla sureshNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Auditing The Art and Science of Assurance Engagements Fourteenth Canadian Edition Plus Mylab Accounting With Pearson Etext Package 14th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Auditing The Art and Science of Assurance Engagements Fourteenth Canadian Edition Plus Mylab Accounting With Pearson Etext Package 14th Edition PDF Full Chaptersiccaganoiddz6x100% (15)
- SOGA, 1930. Topic - Contract of Sale.Document3 pagesSOGA, 1930. Topic - Contract of Sale.Adarsh TripathiNo ratings yet
- CMPC Quiz 1Document5 pagesCMPC Quiz 1Mae-shane SagayoNo ratings yet
- 2 Cash Budget Cash Flows and Cash BudgetDocument1 page2 Cash Budget Cash Flows and Cash BudgetMark Lawrence YusiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On: Rattan Professional Education College Sohana, Sas Nagar (Mohali)Document48 pagesSeminar Report On: Rattan Professional Education College Sohana, Sas Nagar (Mohali)Bharat AhujaNo ratings yet
- Aika Mbuya Final Research PDFDocument42 pagesAika Mbuya Final Research PDFElisheba EnaelNo ratings yet
- Report of The President B/A Keith D. Hill OCTOBER 2021Document29 pagesReport of The President B/A Keith D. Hill OCTOBER 2021Chicago Transit Justice CoalitionNo ratings yet
- Type The Document Title: Stocklayouts NavdeepDocument36 pagesType The Document Title: Stocklayouts Navdeepnavi_one100% (1)
- Striking OffDocument8 pagesStriking OffNur Amalina MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Tai Tong ChuacheDocument2 pagesTai Tong Chuachechappy_leigh118No ratings yet
- FY23 Budget RequestsDocument3 pagesFY23 Budget RequestsWVXU NewsNo ratings yet
- Trading Journal For 60 Days ChallangeDocument17 pagesTrading Journal For 60 Days Challangemuin aliNo ratings yet
- Anec 45 - TrigoDocument5 pagesAnec 45 - TrigoOperaciones CotecnaNo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument3 pagesBalance SheetTukaram PawarNo ratings yet
- Mario Blejer - Fiscal Policy and Economic Reform - Essays in Honor of Vito Tanzi (Routledge Studies in The Modern World Economy, 6) (1997)Document324 pagesMario Blejer - Fiscal Policy and Economic Reform - Essays in Honor of Vito Tanzi (Routledge Studies in The Modern World Economy, 6) (1997)Hector J. RubiniNo ratings yet
- Contributions To Arabic MetrologyDocument87 pagesContributions To Arabic MetrologyDigital Library Numis (DLN)No ratings yet