Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Activity of Cansat Project in Keio University
Uploaded by
jjaavvmmOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
An Activity of Cansat Project in Keio University
Uploaded by
jjaavvmmCopyright:
Available Formats
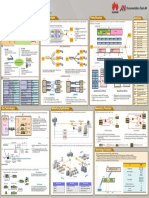
An Activity of CanSat Project
in Keio University
Keio University CanSat 2006 Team Wolve Z
Yuta Nakajima, Yasuyuki Nanamori, Shota Tobimatsu, Naoko Matsubara, Junya Kitade, Masataka Tanaka,
Taichi Saguchi, Hiromasa Masuda, Yohsuke Tohma, Masaki Takahashi, Kazuo Yoshida
2006 History
April Keio CanSat 2006 “Wolve’z”
Project Start
• We are from the department of system design engineering, Keio University.
August
• Our first challenge of CanSat activity started in 2006.
Noshiro Competition
• We developed an Open Class CanSat for Noshiro Comeback Competition in 2006
October
SPAIN Demonstration
148mm Based on our concept of “simple and robust”,
we improved the followings:
Comeback CanSat 1) To get accurate flight records, we
elaborated the format of record data and
A nano-scale (350-1050 g) satellite model.
168mm
made redundancy by using ROM and
CanSat is released from a rocket or a balloon, Radio communication.
and uses Para foil to fly toward the target on Para foil
the ground autonomously. 2) To open a Para foil without fail and to fly
towards the goal points, we tested to
Motor adjust our Para foil again and again.
1050g
ROM Battery
(motor) Para Foil
On Board Computer
GPS GPS
Motor
(right)
ROM OBC
Digital
System of Wolve’Z CanSat compass
motor
(left)
GPS and Digital compass are used as the
navigation source, and guidance and control Battery
Battery Radio Grand station
calculation is made on OBC (On Board Circuit transmitter
Board
Computer), whose output actuates the control Radio Electric signal
Radio
PC
transmitter
surface of the Para foil. Transmitter Digital Compass
Fig.1 Keio CanSat Wolvez
Power Supply
Mechanical connect
Fig.1 Architecture of Wolve’Z CanSat Fig.2 Block diagram
System Engineering
User Requirements Working group
System Demonstration
& Concept of
& Validation
Operations
• To develop a CanSat needs interdisciplinary
knowledge like Mechanics, Structure, Electronics, System System Integration
System Electronics Structure
Requirements & Engineering
Computer Science, Fluid Mechanics, etc… Architectures
& Test
Domain
OBC Para foil
• A holistic view is important because many Component Sensor Body structure
Component
Component Design
elements are complicated. Integration & Test Engineering Battery Para foil control system
Domain
Motor( Control ) Motor( mechanics )
Procure, Build / Code, Communication Control Algorithm
Like a real satellites project, we develop CanSat & Assemble Parts
ROM
with an approach of system engineering.
Fig.3 System development Fig.4 Working Group
2006 Noshiro Comeback Competition
In Comeback Competition, a CANSAT with a certain control mechanism such as Para foil is, after
release from a balloon in 100-200 m altitude, to come back to a certain target point autonomously
without human interaction, and the one which can come nearest to the target point becomes the winner.
Flight Path
Flight Path
Foot Print
Helium Balloon Release Point Projection
Release 200
Height 100-
Mechanism
with Timer 150
Y-Z plane
We won the Noshiro Comeback competition
100-150m
Height
Redundant CanSat flying (Z) 100
Flight Path
Nylon Wire towards target After that, we had a
50
X-Z plane Landing Point chance to demonstrate
0 our CanSat to introduce
X-Y plane
50
0
50 Japanese CanSat Activity
0 06/08/19 1st Flight
-50 -50 @Noshiro in Japan
in the IAF conference in
Reel Mechanism Test Zone: φ300 m North (Y) East (X)
Valencia, SPAIN.
Fig.4 Regulation Fig.5 Flight path of Wolve’Z CanSat
You might also like
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 4: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 4: MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Buck 1948Document9 pagesBuck 1948Carlos Mora100% (1)
- Yak-130 MJ 5-inch model plane assembly guideDocument1 pageYak-130 MJ 5-inch model plane assembly guideAlejandro Lablée0% (2)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Harmonic Excitation and Response Spectrum AnalysisDocument54 pagesHarmonic Excitation and Response Spectrum AnalysisAayisha S AHAMED100% (1)
- An Introduction To Closed Loop MarketingDocument40 pagesAn Introduction To Closed Loop MarketingGeorgiana VasilescuNo ratings yet
- Comparative ratings of heavy duty cablesDocument1 pageComparative ratings of heavy duty cablesshivani76% (25)
- Colorful Chalkboard Classroom Labels and OrganizersFrom EverandColorful Chalkboard Classroom Labels and OrganizersNo ratings yet
- Training MatrixDocument2 pagesTraining MatrixAmeerHamzaWarraichNo ratings yet
- PBN Manual - ICAO Doc 9613 Final 5.10.08Document294 pagesPBN Manual - ICAO Doc 9613 Final 5.10.08Liviu Per100% (4)
- PLC BASIC 1 AutomationDocument21 pagesPLC BASIC 1 AutomationYogi wimi syaputraNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Eléctrico 773BDocument2 pagesDiagrama Eléctrico 773BLucia BarrazaNo ratings yet
- YASHICA MAT-124 User's ManualDocument34 pagesYASHICA MAT-124 User's Manuallegrandew100% (1)
- Mesuring Tape HE - mt.001Document2 pagesMesuring Tape HE - mt.001Chethan Nagaraju KumbarNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Law IntroductionDocument8 pagesHuman Rights Law IntroductionXander ZingapanNo ratings yet
- SM-A102N Manual de Servicio Anibal Garcia IrepaiDocument37 pagesSM-A102N Manual de Servicio Anibal Garcia IrepaiJoaquin Koki Ventura100% (1)
- Timer Quick Start Guide: 2. Mount Timer 8. Additional Features 7. Program Timer Download The Orbit B-Hyve Lite AppDocument2 pagesTimer Quick Start Guide: 2. Mount Timer 8. Additional Features 7. Program Timer Download The Orbit B-Hyve Lite AppScott WNo ratings yet
- Wrong Way Soreboard - Tabellenblatt1Document3 pagesWrong Way Soreboard - Tabellenblatt1Hrvoje PizekNo ratings yet
- Eve PI Diagrams v1 4Document6 pagesEve PI Diagrams v1 4Gustavo Alexandre SchefferNo ratings yet
- Example Ship SheetDocument2 pagesExample Ship SheetmatthaeusbmNo ratings yet
- Mondelez International (Formerly Cadbury India LTD.) : Project at A GlanceDocument15 pagesMondelez International (Formerly Cadbury India LTD.) : Project at A GlanceKSXNo ratings yet
- Fini - Mci - 50hp - PDF FiniDocument4 pagesFini - Mci - 50hp - PDF FinisebastianNo ratings yet
- Quantum Autoencoders With Enhanced Data EncodingDocument7 pagesQuantum Autoencoders With Enhanced Data EncodingfoobarukNo ratings yet
- 315b L PDFDocument2 pages315b L PDFДрагиша Небитни ТрифуновићNo ratings yet
- Winidea Build 9.17.172.0.109652 Test Report: Renesas Rh850Document2 pagesWinidea Build 9.17.172.0.109652 Test Report: Renesas Rh850mohammedNo ratings yet
- SOSIALISASI PEMAKAIAN BBM DAN JURNAL KAPAL Rev.1Document13 pagesSOSIALISASI PEMAKAIAN BBM DAN JURNAL KAPAL Rev.1Gusti RahmidaNo ratings yet
- ERAC DATASHEET WW en-GBDocument1 pageERAC DATASHEET WW en-GBJavier LópezNo ratings yet
- 785C Plano Hidraulico PDFDocument2 pages785C Plano Hidraulico PDFChristian Vásquez BasilioNo ratings yet
- Huaweigpon PDFDocument1 pageHuaweigpon PDFRobNo ratings yet
- 6 Urban Cruiser (Cont. Next Page) : Engine Control (1NR-FE)Document4 pages6 Urban Cruiser (Cont. Next Page) : Engine Control (1NR-FE)HEMIL ROBERTO RODRIGUEZ HERRERANo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual for StealthCam STC-ZX36NG CameraDocument54 pagesInstruction Manual for StealthCam STC-ZX36NG CameraCarlos ZaniniNo ratings yet
- fda225a3bc8662db188cc33c8c14fa1d939bb2f58cb69bc1a538e0fb0485a8c7_optimDocument3 pagesfda225a3bc8662db188cc33c8c14fa1d939bb2f58cb69bc1a538e0fb0485a8c7_optimmartin.ca2117No ratings yet
- Eve PI Diagrams v1 4Document6 pagesEve PI Diagrams v1 4chrismaccNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Yak 130 PRDocument1 pageToaz - Info Yak 130 PRPaul DanielNo ratings yet
- Yak-130 MJ 5-inch model plane assembly guideDocument1 pageYak-130 MJ 5-inch model plane assembly guideHuascar CandiaNo ratings yet
- Cansat Kit Project: Yoshino TsuchiyaDocument28 pagesCansat Kit Project: Yoshino Tsuchiyaanon-449909No ratings yet
- 120H (ES Version)Document2 pages120H (ES Version)Leonardo NunesNo ratings yet
- Katni End to Singrauli End Foot Over Bridge DesignDocument1 pageKatni End to Singrauli End Foot Over Bridge Designdeepak singhNo ratings yet
- List Gambar Penerimaan Klas Rev2Document14 pagesList Gambar Penerimaan Klas Rev2Dolok Joko KenconoNo ratings yet
- Pre101013 2303Document2 pagesPre101013 2303Ching FanNo ratings yet
- Arquitectura Rev. 7.1 OvationDocument1 pageArquitectura Rev. 7.1 Ovationeduard ramosNo ratings yet
- Electrical System 793C Off-Highway Truck: Machine Harness Connector and Component LocationsDocument2 pagesElectrical System 793C Off-Highway Truck: Machine Harness Connector and Component LocationsJerry Alejos GuardapucllaNo ratings yet
- AR-M160 - M205 Circuit PDFDocument20 pagesAR-M160 - M205 Circuit PDFLân SharpNo ratings yet
- DMZ Switches: Wireless SwitchDocument1 pageDMZ Switches: Wireless SwitchAir TopNo ratings yet
- SelectDocument12 pagesSelectAshoka NarayananNo ratings yet
- Sensor Periodic Table 2022Document1 pageSensor Periodic Table 2022plpdspNo ratings yet
- 797Document4 pages797RossellPumaNo ratings yet
- Copernicus Programme Space Component OverviewDocument1 pageCopernicus Programme Space Component OverviewGemmaNo ratings yet
- 320D FMDocument2 pages320D FMFabio AlvesNo ratings yet
- Maxx Force DTusaDocument1 pageMaxx Force DTusaffralbertoNo ratings yet
- NECMicrocontroller GuideDocument8 pagesNECMicrocontroller GuideAldemir Fernando BattagliaNo ratings yet
- PLDT and GLOBE Home Internet ComparisonDocument1 pagePLDT and GLOBE Home Internet ComparisonAir TopNo ratings yet
- Top View: Resultant Consulting EnginersDocument1 pageTop View: Resultant Consulting EnginersEnrique RafaelNo ratings yet
- BMRCL Route Map - New-10-06-2019-Incl Airport PDFDocument1 pageBMRCL Route Map - New-10-06-2019-Incl Airport PDFvinay_mdrNo ratings yet
- Bike ComputerDocument2 pagesBike ComputerpapadoperakisNo ratings yet
- BMRCL Route Map - New-10-06-2019-Incl Airport PDFDocument1 pageBMRCL Route Map - New-10-06-2019-Incl Airport PDFvinay_mdrNo ratings yet
- 315C CFTDocument4 pages315C CFTelectricista85No ratings yet
- 5230 Excavator Electrical System: Machine Harnes Connector and Component LocationsDocument2 pages5230 Excavator Electrical System: Machine Harnes Connector and Component LocationsGilvan JuniorNo ratings yet
- Component Locations: Hydraulic System 730 Ejector Articulated TruckDocument2 pagesComponent Locations: Hydraulic System 730 Ejector Articulated Truckmrcruzito_2099No ratings yet
- SP2582-1-15-3 UmDocument141 pagesSP2582-1-15-3 UmMihai LefterNo ratings yet
- Ecom System Diciembre 2020Document1 pageEcom System Diciembre 2020gamer creativoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sodi Rental Brochure EnglishDocument23 pages2017 Sodi Rental Brochure Englishjordy gonzalezNo ratings yet
- TH-56415277 Lamtakhong System Configuration R2Document1 pageTH-56415277 Lamtakhong System Configuration R2Panupan ThakongNo ratings yet
- ICE Integrated Concurrent EngineeringDocument60 pagesICE Integrated Concurrent EngineeringEduardo MenaNo ratings yet
- Ficha OrdesaDocument1 pageFicha Ordesaluigi schiavoneNo ratings yet
- OMEGA AIR-CNG Product Overview - EN - 950123Document2 pagesOMEGA AIR-CNG Product Overview - EN - 950123Junaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- International CanSat Workshop - List of Presentation FilesDocument1 pageInternational CanSat Workshop - List of Presentation FilesjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- International CanSat Workshop - Program and AbstractsDocument30 pagesInternational CanSat Workshop - Program and AbstractsjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Norwegian Cansat Competiton and Future Plans: - OutlineDocument9 pagesNorwegian Cansat Competiton and Future Plans: - OutlinejjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Kita University Tudent Pace Roject (ASSP) and The Noshiro Space EventDocument22 pagesKita University Tudent Pace Roject (ASSP) and The Noshiro Space EventjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Cansat Activities in University of Tokyo - Excellent Training For Real Satellite ProjectDocument39 pagesCansat Activities in University of Tokyo - Excellent Training For Real Satellite ProjectjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Cansat - Malaysian Plan: Malaysia National Space Agency (Angkasa)Document24 pagesCansat - Malaysian Plan: Malaysia National Space Agency (Angkasa)jjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- The Results Obtained by The YASHAGO Team at ARLISS 2006Document16 pagesThe Results Obtained by The YASHAGO Team at ARLISS 2006jjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Cansat Development Program in Tokyo Institute of TechnologyDocument16 pagesCansat Development Program in Tokyo Institute of TechnologyjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- JAXA-Colombia International CanSat Workshop AgendaDocument27 pagesJAXA-Colombia International CanSat Workshop AgendajjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- ICW-23) Kagawa Univ PDFDocument1 pageICW-23) Kagawa Univ PDFjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- ICW 04) AeropacDocument19 pagesICW 04) AeropacjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Experiment on Attitude Control for Solar Power GenerationDocument19 pagesExperiment on Attitude Control for Solar Power GenerationjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Nano-Satellite Payload Development at The University of SydneyDocument29 pagesNano-Satellite Payload Development at The University of SydneyjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- LEEM National CanSat CompetitionDocument12 pagesLEEM National CanSat CompetitionjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- The Results Obtained by The YASHAGO Team at ARLISS 2006Document16 pagesThe Results Obtained by The YASHAGO Team at ARLISS 2006jjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- First Fly-back of Tohoku University at ARLISS 2006Document8 pagesFirst Fly-back of Tohoku University at ARLISS 2006jjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- CSW Offers Can-Sat Launch Experiment OpportunitiesDocument16 pagesCSW Offers Can-Sat Launch Experiment OpportunitiesjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Brosch SmartBird en 8s RZ 110311 LoDocument8 pagesBrosch SmartBird en 8s RZ 110311 LoBagsFNo ratings yet
- SM Chapter1 PDFDocument14 pagesSM Chapter1 PDFgoc1794No ratings yet
- New Avionics Concepts: Yves Saint-Upery Eyak Cockpit OperationsDocument36 pagesNew Avionics Concepts: Yves Saint-Upery Eyak Cockpit OperationsjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Run-Back RoversDocument46 pagesEvolution of Run-Back RoversjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- SM Chapter3 PDFDocument20 pagesSM Chapter3 PDFJuan perezNo ratings yet
- ICW-02) Prof TwiggsDocument27 pagesICW-02) Prof TwiggsjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Space System 2002 2003Document46 pagesSpace System 2002 2003jjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Satellite Market SurveyDocument9 pagesSatellite Market Surveyjjaavvmm0% (1)
- Air Traffic Surveillance Data StandardDocument29 pagesAir Traffic Surveillance Data StandardjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- University Tokyo CUBESAT CanSat projects suborbital experimentsDocument51 pagesUniversity Tokyo CUBESAT CanSat projects suborbital experimentsjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- Alumni Speaks... : Axay GandhiDocument4 pagesAlumni Speaks... : Axay GandhiSajal MorchhaleNo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire 1710 (Quanta DT3) PDFDocument35 pagesAcer Aspire 1710 (Quanta DT3) PDFMustafa AkanNo ratings yet
- Organization Management and LeadershipDocument26 pagesOrganization Management and LeadershipOtilia BadeaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Quiz 1 ResultsDocument27 pagesPrelim Quiz 1 Resultsgummy bearNo ratings yet
- Fugacity CoefficientDocument4 pagesFugacity Coefficientsigit1058No ratings yet
- Domestic Water-Supply - TheoryDocument19 pagesDomestic Water-Supply - Theoryyarzar17No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming (OOPS) : Java Means Durga SirDocument2 pagesObject Oriented Programming (OOPS) : Java Means Durga SirROHIT JAINNo ratings yet
- The Nigerian Marketing System Its Development - Problems and ProspectsDocument8 pagesThe Nigerian Marketing System Its Development - Problems and ProspectsNwakor Maco Sochi100% (1)
- Pre-Admission Interview Slip TemplateDocument1 pagePre-Admission Interview Slip TemplateLeaniel SilvaNo ratings yet
- Study of NanofibresDocument237 pagesStudy of NanofibresGerardo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Compendium 2004jan RadiographyDocument11 pagesCompendium 2004jan RadiographyAgus SusilaNo ratings yet
- AlumaCore OPGWDocument1 pageAlumaCore OPGWlepouletNo ratings yet
- Organograma ASME IX Art. I PDFDocument4 pagesOrganograma ASME IX Art. I PDFfabiocorreasilvaNo ratings yet
- Murray NYC Group MeteringDocument5 pagesMurray NYC Group MeteringKannon TamNo ratings yet
- Castro DW 32Document3 pagesCastro DW 32Jeetu GosaiNo ratings yet
- Did You Ever Meet Shattered Illusions?Document5 pagesDid You Ever Meet Shattered Illusions?Junjie HuangNo ratings yet
- Trends in Maternal Mortality: Executive SummaryDocument16 pagesTrends in Maternal Mortality: Executive SummarykansaNo ratings yet
- Toshiba SMMS-7 VRF CatalogueDocument106 pagesToshiba SMMS-7 VRF CatalogueMyo Sein67% (3)
- Lean-burn gas generator sets technical specificationsDocument2 pagesLean-burn gas generator sets technical specificationsHector IuspaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5: Engineering Utilities IiDocument4 pagesAssignment 5: Engineering Utilities IiRex SabersonNo ratings yet
- International Emergency Nursing: Karen Hammad, Lingli Peng, Olga Anikeeva, Paul Arbon, Huiyun Du, Yinglan LiDocument5 pagesInternational Emergency Nursing: Karen Hammad, Lingli Peng, Olga Anikeeva, Paul Arbon, Huiyun Du, Yinglan LiRuly AryaNo ratings yet
- Agile Assignment 2Document2 pagesAgile Assignment 2Sameen ShakeelNo ratings yet