Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lal Das Rahul Kumar (19SF32100) 库马尔
Lal Das Rahul Kumar (19SF32100) 库马尔
Uploaded by
Rahul Kumar Lal DasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lal Das Rahul Kumar (19SF32100) 库马尔
Lal Das Rahul Kumar (19SF32100) 库马尔
Uploaded by
Rahul Kumar Lal DasCopyright:
Available Formats
Lal Das Rahul Kumar (19SF32100)
库马尔
➢ Q1.
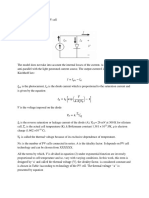
The energy dissipated by a viscous damper per sinusoidal cycle is given by,
Wnc = -πωCXp2 ------ (1)
now the hysteretic damping or structural damping force is given by,
Wnc = -πhXp2 ------ (2)
If we equate the two equations we get:
C = h/ω ------ (3)
This is known as equivalent damping. Damping is rarely viscous but we can
often model the appropriate type of damping using equivalent viscous
damping. Hence, we replace the C with Ceq for the modeling purpose, the
equation for the energy dissipated by a viscous damper per sinusoidal cycle is
given by,
Wnc = -πωCeqXp2 ------ (4)
➢ Q2.
𝑚𝑥̈ + 𝑐𝑥̇ + 𝑘𝑥 = 𝐹0 cos 𝜔𝑡
we know;
then equation becomes
The solution of the above equation (2nd order differential equation) is,
the special solution is
Lal Das Rahul Kumar (19SF32100)
库马尔
The general solution of nonhomogeneous equation is:
For initial condition the equation reduces to
by substituting the solution into the differential equation, we get:
Then,
Where
is called frequency ratio.
➢ Q3
Laplace transform is tool to model a complex system into mathematically
suitable system of equation which adequately represents the original recorded
response of any system. This is used for solution of complex frequency
domain functions.
Frequency response function is the function that represents the system
characteristics. It is used to calculate the dynamic response of the system.
➢ Q4
impulse response function, of a dynamic system is its output when presented
with a brief input signal, called an impulse.
You might also like
- Introduction To Alternating Current - Grade 12 - by Irfan HaiderDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Alternating Current - Grade 12 - by Irfan HaiderIrfan Haider100% (1)
- Mechanical Vibration - MSD - Part 2Document9 pagesMechanical Vibration - MSD - Part 2Mohammad Saad SalimNo ratings yet
- LCR CircuitDocument14 pagesLCR CircuitCOSM-OS50% (2)
- 230 Power System Stability PDFDocument31 pages230 Power System Stability PDFBelayneh Tadesse100% (1)
- Lecture 21Document38 pagesLecture 21yakwetuNo ratings yet
- Random VibrationsDocument20 pagesRandom VibrationsVivek PandeyNo ratings yet
- 18CS06 Structural Dynamics: Duhamel'S IntegralDocument29 pages18CS06 Structural Dynamics: Duhamel'S Integral20MC06 - SORNAMUGI KNo ratings yet
- Viscous Damped Vibration PDFDocument19 pagesViscous Damped Vibration PDFReyman SolasNo ratings yet
- Lecture #5 Root Locus PDFDocument40 pagesLecture #5 Root Locus PDFسيف الدين SaifEddinNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady State Response SlideDocument19 pagesTransient and Steady State Response SlideMd. Shahriar MohtasimNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPreparatory Problems PDFGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPreparatory Problems PDFGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPreparatory Problems PDFGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Viscous DampingDocument32 pagesChapter-2 Viscous DampingMuhammad haider AyazNo ratings yet
- Series and Shunt CompensationDocument55 pagesSeries and Shunt Compensationk rajendraNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Bee Sem 1Document24 pagesQuestion Paper Bee Sem 1Roshan SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Phasor Method - Resonance and PowerDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Phasor Method - Resonance and PowerTu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Goal of This LabDocument9 pagesGoal of This LabAli AsgerovNo ratings yet
- On Standardised Moments of Force Distribution in Simple LiquidsDocument11 pagesOn Standardised Moments of Force Distribution in Simple LiquidsStatistics Office MakwanpurNo ratings yet
- Paper JUREDocument11 pagesPaper JUREPrathamNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions LecDocument32 pagesNuclear Reactions Lecjon alex100% (1)
- SYSC 3600 - Assignment #9: Outputs and Is Changing at 0.5 Outputs/sec. Initially There Is No Input, But at Time T 2 ADocument2 pagesSYSC 3600 - Assignment #9: Outputs and Is Changing at 0.5 Outputs/sec. Initially There Is No Input, But at Time T 2 AbjpwongNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Laboratory: Project ReportDocument10 pagesStructural Mechanics Laboratory: Project ReportJayanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Group-10 (ID 182 183) EEE212 Project ReportDocument40 pagesGroup-10 (ID 182 183) EEE212 Project ReportShamsul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - 1st and 2nd Order Transient Analysis ElectricalDocument54 pagesChapter 6 - 1st and 2nd Order Transient Analysis ElectricalDouglas OngomNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Resonance Lecture 6: Resonance: 6.1 Electrical CircuitsDocument3 pagesModule 6: Resonance Lecture 6: Resonance: 6.1 Electrical CircuitsDr Srini vasanNo ratings yet
- Step Response Unit ResponseDocument6 pagesStep Response Unit ResponsetirsollantadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4amanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Transformerless Photovoltaic Systems Using Neutral Point Clamped Multilevel InvertersDocument6 pagesTransformerless Photovoltaic Systems Using Neutral Point Clamped Multilevel InvertersKarim EfthuNo ratings yet
- UPFC Model Documentation: Figure 1. General Architecture of The UPFC DeviceDocument10 pagesUPFC Model Documentation: Figure 1. General Architecture of The UPFC DeviceTerrorTricolorFCNo ratings yet
- Exp3 2021Document11 pagesExp3 2021Priyanka kataria [IIT DELHI]No ratings yet
- EE6508 - Power Quality - AG - Lecture - 2 (2) .PDDocument31 pagesEE6508 - Power Quality - AG - Lecture - 2 (2) .PDwing fatt hiewNo ratings yet
- DispersionDocument18 pagesDispersionGanesh RamNo ratings yet
- 3 - 2b Transformer Energization - ModelingDocument7 pages3 - 2b Transformer Energization - ModelingNalex GeeNo ratings yet
- Damped Free VibrationDocument26 pagesDamped Free VibrationPriyamvada BijuNo ratings yet
- 2 Free Vibration: Any System Possessing Mass and Elasticity Is Capable of VibrationDocument11 pages2 Free Vibration: Any System Possessing Mass and Elasticity Is Capable of VibrationNumkang KangNo ratings yet
- Methodology and Modeling of PV CellDocument4 pagesMethodology and Modeling of PV CellbilalNo ratings yet
- Linear Coupled OscillatorsDocument21 pagesLinear Coupled OscillatorsanonymousxxNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Modeling and Analysis of Synchronverters: Zhou Wei, Chen Jie and Gong ChunyingDocument5 pagesSmall Signal Modeling and Analysis of Synchronverters: Zhou Wei, Chen Jie and Gong ChunyingEnimien AymenNo ratings yet
- MECH463 Tutorial 08Document1 pageMECH463 Tutorial 08adelNo ratings yet
- Ehvac P.balakishan Eee PDFDocument23 pagesEhvac P.balakishan Eee PDFFAHAD IQBALNo ratings yet
- 21PHY12 MODULE 1 Oscillations and WavesDocument32 pages21PHY12 MODULE 1 Oscillations and WavesAshesh Krishna AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lecture PowerPointDocument34 pagesChapter 5 Lecture PowerPointKarthik IlangoNo ratings yet
- EE530 231 Lect 04Document19 pagesEE530 231 Lect 04SosoNo ratings yet
- QLabs Controls Instructor Resources Sample QUBE Servo 2 Position Control PDFDocument6 pagesQLabs Controls Instructor Resources Sample QUBE Servo 2 Position Control PDFBite RamanNo ratings yet
- ( (Overdamped Voltage Response) )Document12 pages( (Overdamped Voltage Response) )Hayder AliNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Physics 15bDocument9 pagesElectromagnetism: Physics 15bnalliminiNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Control of A BuckDocument6 pagesSliding Mode Control of A BuckAdvika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Two Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesTwo Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsAshutoshMishraNo ratings yet
- Slua671 Compensation Design With TL431 For UCC28600Document13 pagesSlua671 Compensation Design With TL431 For UCC28600Phạm Văn Tưởng100% (1)
- Power System Engineering-II Question Bank (3rd and 4th Units) - 12-19Document8 pagesPower System Engineering-II Question Bank (3rd and 4th Units) - 12-19Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Calculation of The Efficiency Limit For Solar CellsDocument30 pagesTheoretical Calculation of The Efficiency Limit For Solar CellsVianney TyzeNo ratings yet
- Double Pendulum Power - AC Power From A Mechanical OscillatorDocument20 pagesDouble Pendulum Power - AC Power From A Mechanical Oscillatoranonymousdpp100% (1)
- Exercises of Integrals and Integro-Differentials EquationsFrom EverandExercises of Integrals and Integro-Differentials EquationsNo ratings yet
- SPTC14.2 21 F N+WangDocument56 pagesSPTC14.2 21 F N+WangRahul Kumar Lal DasNo ratings yet
- First Lecture Cable Stayed BridgeDocument51 pagesFirst Lecture Cable Stayed BridgeRahul Kumar Lal DasNo ratings yet
- xianlin2012ramayanaInChina PDFDocument13 pagesxianlin2012ramayanaInChina PDFRahul Kumar Lal DasNo ratings yet
- Effect of Dominant Parameters For Conical Basin: Gravitational Water Vortex Power PlantDocument8 pagesEffect of Dominant Parameters For Conical Basin: Gravitational Water Vortex Power PlantRahul Kumar Lal DasNo ratings yet
- 10 28 0 15Document1 page10 28 0 15Rahul Kumar Lal Das0% (1)
- BeiDaHuang ReportDocument9 pagesBeiDaHuang ReportRahul Kumar Lal DasNo ratings yet