Lange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e > Medications Affecting Cardiac and Renal Function
Catherine E. Pelletier-Dattu+
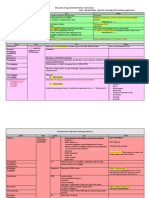
Drug Pharmacokinetics Mechanism of Action Clinical Uses Drawbacks and Side Effects
Class IA
•Antimuscarinic activity can suppress
vagal tone leading to an increase in
AV conduction which may cause
tachycardia
•Inhibit fast Na+ channel by blocking •Refractory heterogenicity: Depressed
•All types of arrhythmias
•A: PO, IV activated Na+ channels conduction can further lead to torsade
•Especially useful for conversion of a
•M: Hepatic (P450) •Weakly block K+ channels (reduces de pointes and eventual quinidine
Quinidine fib/flutter to sinus rhythm and
•E: Parent drug and metabolites repolarization), which increases AP syncope (due to QT prolongation)
maintenance in patients with
excreted in urine duration (manifested as lengthening •GI irritation (nausea, vomiting,
paroxysmal fib/flutter
of QT interval) diarrhea)
•Increased mortality especially
associated with structural heart
disease
•Inhibits P450 enzymes
•GI irritation (nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea)
•A: IM, IV •All types of arrhythmias
•Drug-induced lupus-like syndrome
•M: Hepatic (P450) metabolism to N- •Especially useful for
•Blood dyscrasias (agranulocytosis,
Procainamide acetylprocainamide (NAPA) hemodynamically stable
bone marrow suppression,
•E: Parent drug and metabolite monomorphic VT or preexcited atrial
neutropenia, thrombocytopenia,
excreted primarily in urine fibrillation
anemia)
•Hypotension
•Antimuscarinic activity can suppress
vagal tone leading to an increase in
•A: PO
AV conduction which may cause
•M: Hepatic (P450)
Disopyramide (Norpace) •Ventricular arrhythmias tachycardia
•E: Parent drug and metabolite
•Constipation
excreted primarily in urine
•Xerostomia
•Urinary hesitancy
Class IB
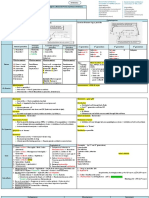
•Inhibit both inactive and active Na+
•A: IV, ET tube •CNS side effects (tremor, light-
channels
•M: Hepatic (P450) •Suppression of recurrent ventricular headedness, nausea of central origin,
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) •Act preferentially on depolarized,
•E: Primarily excreted as metabolites tachycardia and fibrillation paresthesias)
arrhythmogenic tissue
in urine •Inhibits P450 enzymes
•Shorten AP duration
•A: PO •GI side effects (nausea, vomiting)
•M: Hepatic (P450) •Neurologic side effects (light-
Mexiletine •Ventricular arrhythmias
•E: Parent drug and metabolites headedness, dizziness, tremor,
excreted in urine nervousness)
•Cardiovascular collapse (esp with
•A: PO, IV rapid infusion)
•M: Hepatic (P450) •Ventricular tachycardia and •Vertigo
Phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek)
•E: Primarily excreted as metabolites paroxysmal atrial tachycardia •Gingivitis gingival hyperplasia
in urine •Systemic lupus erythematosus
•Induces P450 enzymes
� Class IC
•Proarrhythmic
•Inhibit fast Na+ channels •CNS side effects (dizziness, visual
•A: PO and IV; well absorbed •Especially effective in the His- disturbances)
•Ventricular arrhythmias
•M: Hepatic (P450) Purkinje system (widens QRS •Increased mortality in patients with
Flecainide (Tambocor) •Paroxysmal supraventricular
•E: Parent drug and metabolites complex) recent myocardial infarction and
arrhythmias
excreted in urine •Usually little effect on AP duration non–life-threatening ventricular
•Prolongation of refractory periods arrhythmias
•Inhibits P450 enzymes
•Prolongation of QRS interval
•A: PO and IV
•Supraventricular arrhythmias •Proarrhythmia
•M: Hepatic (P450)
Propafenone (Rythmol) •Ventricular arrhythmias •GI side effects (constipation, metallic
•E: Parent drug and metabolites
•Prevention of a fib recurrence taste, nausea, vomiting)
mainly excreted in urine
•Inhibits P450 enzymes
Date of download: 05/31/20 from AccessPharmacy: accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.