Professional Documents
Culture Documents
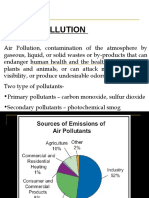
Pollution Causes and Effects in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Thapelo JeremiahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pollution Causes and Effects in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Thapelo JeremiahCopyright:
Available Formats
POLLUTION
- It is the release of substances from human activities that are harmful to the
environment
- It refers to the harm done to the environment by the release of substances produced by
human activities.
- The substance that is released and causes harm to the environment is a pollutant
pollutant Source(s) Harm to the environment
Carbon dioxide Burning of fossil
Enhanced greenhouse effect (global warming)
(CO2) fuels
Methane (CH4) Cattle, paddy fields,
extraction of coal Enhanced greenhouse effect
and oil
Fertilizers
Arable Agriculture Eutrophication
herbicides Can kill harmless plants. Persist in the
Arable Agriculture
environment as well
pesticides Agriculture (both Kills harmless species. Bioaccumulation in food
arable and livestock) chains
sewage Human and Reduces concentration of oxygen in rivers.
livestock waste Destroy freshwater communities
Nuclear fall-out Leaks/accidents at
(beta and nuclear power Cancers in humans, mutations in non-human
gamma stations, nuclear species
radiation) tests, atomic bomb
Industrial
chemical waste Can be fatal to wildlife and humans. Causes
(heavy metals bioaccumulation. Lead harms the nervous
factories
such as lead, system. Mercury and silver can result in the
mercury and birth of idiots and malformed children
cyanide)
Discarded solid Landfills reduce productive land and produce
waste methane gas. Eye sore if scattered on land.
(biodegradable Domestic and Rubbish can leak toxic liquids which leach into
and non- industrial waste the ground. Plastics can choke livestock. Plastic
biodegradable bags can choke sea turtles. Plastic nets in water
rubbish) can entangle marine organisms like dolphins
- Biodegradable plastics are those that can be broken down by decomposers. These
usually have starch incorporated into their structures and the starch is digested by
bacteria in the soil
- Non-biodegradable plastics cannot be broken down by decomposers
EUTROPHICATION OF WATER DUE TO OVER-USE OF FERTILIZERS
- Most fertilizers used by farmers to increases crop yields contain nitrates, phosphates
and potassium ions.
- Nitrates are highly soluble (they quickly dissolve in water). The nitrates that are not
immediately taken up (absorbed) by plants get washed away in drainage water. This is
called leaching.
- The leached nutrients (mainly nitrates and phosphates) get washed into rivers, streams,
dams and other water bodies.
- The nutrients stimulate the vigorous and rapid growth of algae (water plant)
- The algal leaves cover the water surface and block out sunlight from plants submerged
in water, resulting in their death.
- The vigorous growth of algae also causes stiff competition among the algae for
resources and some die.
- The dead plants and algae are decomposed by aerobic bacteria which multiplies rapidly
due to the availability of food resources.
- The bacteria uses up the dissolved oxygen (through aerobic respiration) and marine
organisms like fish die of lack of oxygen (suffocation).
*** By definition, eutrophication is algal bloom caused by water pollution, resulting in death
of marine organisms (polluted by fertilizers, organic waste or untreated sewage).
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
- Greenhouse gases naturally contained in the atmosphere include carbon dioxide,
methane and water vapour.
- Made-made greenhouse gases are mainly chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) like carbon
tetrachloride and chloroform, which are usually used as solvents, aerosol propellants
and refrigerator coolants
- The greenhouse gases act as a blanket surrounding the earth, keeping it warm.
- The gases are transparent to short-wave UV radiation from the sun allowing it to freely
pass through to the ground. The ground is warmed up by this radiation.
- In turn, the ground radiates heat back into space as longer wave length infra-red
radiation. The greenhouse gases do not allow all of this infra-red radiation to pass
through. Much of it is absorbed by the gases and reflected back towards the earth,
making the air above it warm.
- This trapping of long wave radiation resulting in it warming the atmospheric air is the
greenhouse effect. The temperature could rise by about 320C above what normally
happens without greenhouse gases.
Importance of the greenhouse effect
- If it did not happen, the earth would be too cold for life and living systems to exist.
- The earth’s surface temperature would be so low that the rate of biochemical reactions
would not sustain life.
- All the water on earth would be frozen
Negative effects
- A lot of the ice that is locked up in Polar Regions and on high mountains would start to
melt. There would be melting of ice caps, releasing more water into oceans. This would
cause a rise in sea levels and flooding of many low lying areas of land.
- There will be more violent storms in some countries
- Some countries would become hotter, drier and develop into deserts
- Plants and animals in certain areas might become extinct
- Some areas might not sustain crop growth
- A significant rise in surface temperature causes changes in the distribution pattern and
intensity of the major planetary systems and the distribution of organisms.
ACID RAIN
- Gases that cause acid rain are sulphur dioxide (SO2) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
- The SO2 is formed when fossil fuels like coal are burnt and the sulphur that is produced
combines with oxygen. This happens in large industries that burn coal, such as power
stations.
- The oxides of nitrogen (nitrogen oxides) are released as exhaust fumes from cars and
trucks
- These gases can be drifted over large distances and be deposited as solid, dry particles
on plant leaves or in water bodies.
- The gases in the atmosphere dissolve in rain water to form acids (sulphuric acid and
nitric acid) which lower the pH of the rain water to as low as 3 in some places. Generally,
acid rain has a pH of less than 5.
Effects of acid rain on the environment
- Sulphur dioxide irritates the linings of the breathing system. Those with asthma and
bronchitis can suffer attacks.
- Sulfur dioxide particles can be absorbed into the plant through the stomata, damage
leaf cells and reduce their disease resistance
- When acid rain falls on soils, it causes leaching of ions like calcium ions and magnesium
ions. These become deficient.
- Aluminium becomes soluble (dissolves in water) and gets absorbed by plant roots,
resulting in the poisoning of those roots (Aluminium toxicity). The dissolved aluminium
can also poison aquatic life
- Phosphates become insoluble (as it forms insoluble compounds) and cannot be
absorbed by plants
- Soils become acidic and this reduces microbial activity, resulting in accumulation of
organic matter and reduced nitrogen fixation
- Fish eggs are killed as acid rain dissolves the egg shells (calcium carbonate)
- Buildings, especially built from limestone rock, get eroded
- Marine organisms with chalky shells get affected as the shells dissolve in acidic
conditions
How to reduce effects of acid rain
- Use of low sulfur fuels. Coal can be crushed and then washed with a solvent to dissolve
the sulfur compounds, hence reducing its sulfur content
- Rather burn more oil than sulfur to reduce sulfur dioxide
- Flue gas desulfurization can be used where sulfur from power station chimneys is
removed by treating waste gases with wet powdered limestone which neutralizes the
gases before they can escape. This can be done by passing gases from industries
through a fine spray of lime (scrubbing)
- Use of catalytic converters fitted in exhaust pipes to reduce nitrogen oxides in exhaust
fumes.
You might also like
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyMuhamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- What Is Deforestation?: Endangered EcosystemDocument7 pagesWhat Is Deforestation?: Endangered Ecosystemkhaty95No ratings yet
- Recycling of Water: by Sewage TreatmentDocument36 pagesRecycling of Water: by Sewage TreatmentHtet Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- Pollution: Cigarette SmokingDocument4 pagesPollution: Cigarette Smokinghh rickyNo ratings yet
- Session 8: Understanding Pollution Types and SolutionsDocument10 pagesSession 8: Understanding Pollution Types and SolutionsOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- EVS - Unit 3 - Environmental PollutionDocument32 pagesEVS - Unit 3 - Environmental Pollutionr1u2No ratings yet
- Environmental Studies - Life SciencesDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Studies - Life SciencesTally LeachNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Environmental Pollution Notes, MCQ & QuestionsDocument11 pagesUnit-4 Environmental Pollution Notes, MCQ & QuestionsMohana NNo ratings yet
- Causes of Wildlife ExtinctionDocument13 pagesCauses of Wildlife ExtinctionAshlie MarieNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument2 pagesPollutionRuno OmughelliNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - PollutionDocument4 pagesTopic 7 - Pollutionashley bedassieNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain NotesDocument2 pagesAcid Rain Notesapi-268159571No ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument42 pagesEnvironmental PollutionGood DoogNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Causes, Effects and Solutions in 40 CharactersDocument45 pagesAir Pollution: Causes, Effects and Solutions in 40 CharactersprashantbaraskarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution & Sold Waste Management: UNIT-3Document26 pagesEnvironmental Pollution & Sold Waste Management: UNIT-3sarfarzNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument16 pagesPollutionPrasanth KNo ratings yet
- Evs Assignment 3Document18 pagesEvs Assignment 3AasthaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiogeochemical ReviewerAlyssa Harriet MartinezNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Environmental Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesHsslive XI Environmental Chemistry NotesAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- Cycles Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCycles Cheat Sheetapi-368121935No ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution-Causes, Effects and Control MeasuresDocument59 pagesEnvironmental Pollution-Causes, Effects and Control MeasuresArcchhit ThhakkareNo ratings yet
- Causes of industrial air pollutionDocument18 pagesCauses of industrial air pollutionGopiKrishnan PlakkatNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Shivjeet Mam-1Document5 pagesEnvironmental Management Shivjeet Mam-1Arshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Types and Control MeasuresDocument65 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Types and Control MeasuressabarinathmuruganNo ratings yet
- Name: Aina Najwa Binti Amir Class: 4 RossaDocument15 pagesName: Aina Najwa Binti Amir Class: 4 RossaAina NajwaNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE PollutionDocument2 pagesENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE PollutionEdralin dalgo jrNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument10 pagesPollutionlohith.ganeshkumarNo ratings yet
- EutrophicationDocument2 pagesEutrophicationlaracassar22No ratings yet
- How Environmental Pollution Affects Balance in NatureDocument10 pagesHow Environmental Pollution Affects Balance in Nature秀珍100% (1)
- Acid Rain and Ozone DepletionDocument40 pagesAcid Rain and Ozone DepletionmalarNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: The Problem Continues: Presented by Navjot Singh Roll No. 95222454108 Bba 6 SemesterDocument38 pagesAcid Rain: The Problem Continues: Presented by Navjot Singh Roll No. 95222454108 Bba 6 SemesterlovleshrubyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document11 pagesPresentation 4Hawra SafriNo ratings yet
- Sains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Document11 pagesSains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Noorain MohammadNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity NotesDocument1 pageBiodiversity NotesTJ FortoNo ratings yet
- Env 203/geo 205: Introduction To Geography: Moupia Rahman (MPR), PHDDocument37 pagesEnv 203/geo 205: Introduction To Geography: Moupia Rahman (MPR), PHDMalihaNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument25 pagesAcid RainNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Water PollutionDocument40 pagesEnvironmental and Water PollutionmediquipNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Human Activities That Endanger An EcosystemDocument7 pages9.1 Human Activities That Endanger An EcosystemMuhamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument38 pagesChemistry NotesTedNo ratings yet
- Marinepollution 190103155704Document48 pagesMarinepollution 190103155704sure2004No ratings yet
- Module 5- E & EDocument15 pagesModule 5- E & ECRAZY ಕನ್ನಡಿಗNo ratings yet
- Pollution: Ashutosh Jaiswal Ravi Mishra Shishir Jaiswal Gaurav Verma Anshul RathoreDocument47 pagesPollution: Ashutosh Jaiswal Ravi Mishra Shishir Jaiswal Gaurav Verma Anshul RathoreAshutosh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Envi LT1Document10 pagesEnvi LT1crezatNo ratings yet
- 1) A) State The Human Activities That Threaten An EcosystemDocument49 pages1) A) State The Human Activities That Threaten An EcosystemSarannya KengkathranNo ratings yet
- Soil Pollution and Chemical IndustriesDocument4 pagesSoil Pollution and Chemical Industriesnur100% (1)
- Environmental PollutionDocument90 pagesEnvironmental Pollutiondhanuka jiNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Air PollutionDocument33 pagesAir Pollution Air PollutionHridiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Industry and TechnologyDocument33 pagesImpact of Industry and TechnologyFarhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- 16 Environmental Issues - FOCUS AREA 2021Document2 pages16 Environmental Issues - FOCUS AREA 2021viswanathpm79No ratings yet
- Environmental Degradation Is The Deterioration of The Environment Through Depletion ofDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Degradation Is The Deterioration of The Environment Through Depletion ofMelissa A. BernardoNo ratings yet
- Human Activities and The EnvironmentDocument10 pagesHuman Activities and The EnvironmentAnna Daniella LunaNo ratings yet
- Management of Resources & Humand and ForestsDocument4 pagesManagement of Resources & Humand and Forestslaracassar22No ratings yet
- Air, Water and Soil: University of California College Prep University of CaliforniaDocument6 pagesAir, Water and Soil: University of California College Prep University of CaliforniaRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgD7Njual8g4UlQfjeOytV8-MRUu8Z7EC2rvqDhwcO7HcaLQL TjOa-nezIrniHZuk1o7h jQGNDqoOiDQ 5vIiznve0EHLeamU2QS4uOGh3z7f2HWoPQJMUpyA PDFDocument254 pagesACFrOgD7Njual8g4UlQfjeOytV8-MRUu8Z7EC2rvqDhwcO7HcaLQL TjOa-nezIrniHZuk1o7h jQGNDqoOiDQ 5vIiznve0EHLeamU2QS4uOGh3z7f2HWoPQJMUpyA PDFPushpender BajajNo ratings yet
- Types of PollutionDocument12 pagesTypes of PollutionAavika MishraNo ratings yet
- Impact of Industrialization & Modernization On EnvironmentDocument98 pagesImpact of Industrialization & Modernization On EnvironmentYogesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere GVJDocument8 pagesThe Atmosphere GVJEsai StephenNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 & 3 Environmental PollutionDocument8 pagesTopic 2 & 3 Environmental Pollutiongraciewambuimugo11No ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry - Environmental Pollution, Atmospheric Pollution and Green ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry - Environmental Pollution, Atmospheric Pollution and Green ChemistryRishabh Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Behavior of ColumnsDocument15 pagesFundamental Behavior of ColumnsThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- The Clay Cooking Pot: An Exploration of A Women's TechnologyDocument13 pagesThe Clay Cooking Pot: An Exploration of A Women's TechnologyThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Design of Building Structures To Improve Their Resistance To Progressive CollapseDocument13 pagesDesign of Building Structures To Improve Their Resistance To Progressive CollapseOmar Ricardo CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Marker Assisted Selection of Stress-Tolerant CassavaDocument19 pagesMarker Assisted Selection of Stress-Tolerant CassavaThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- E.M WavesDocument22 pagesE.M WavesashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Genetics ReviewDocument12 pagesNon-Mendelian Genetics ReviewIan TabNo ratings yet
- Enhancing resilience of communities in Solomon Islands to climate change impactsDocument69 pagesEnhancing resilience of communities in Solomon Islands to climate change impactsDaniel AgiruNo ratings yet
- Steel-Concrete Composite Beams For Slim Floors-SpeDocument6 pagesSteel-Concrete Composite Beams For Slim Floors-SpeThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Radio Activity M/C QuestionsDocument11 pagesForm 5 Radio Activity M/C QuestionsThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Rwanda - GAFSP Proposal (Part 1 and 2)Document44 pagesRwanda - GAFSP Proposal (Part 1 and 2)Thapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Field Crop Production GuideDocument52 pagesField Crop Production GuideThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2020 1 Hour 15 MinutesDocument10 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2020 1 Hour 15 MinutesThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Bismuth-214 Half-Life and DecayDocument9 pagesBismuth-214 Half-Life and DecayThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Youth Empowerment Fo Development Ministries (Yedem) International Sierra Leone - Project 002Document7 pagesYouth Empowerment Fo Development Ministries (Yedem) International Sierra Leone - Project 002chandru683No ratings yet
- Ex 5 Reversible ReactionsDocument3 pagesEx 5 Reversible ReactionsThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMuhammad Imran SaeedNo ratings yet
- Form 5 HW Design Chem QuestionsDocument4 pagesForm 5 HW Design Chem QuestionsThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 4Document18 pages2020 Specimen Paper 4bdsisiraNo ratings yet
- Database NotesDocument14 pagesDatabase NotesThapelo Jeremiah100% (1)
- 0510 m18 QP 22Document16 pages0510 m18 QP 22IamEnszNo ratings yet
- Maths June 2017 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Maths IGCSEDocument20 pagesMaths June 2017 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Maths IGCSEThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMuhammad Imran SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Accounting Paper 1 May June 2016 12 PDFDocument20 pagesAccounting Paper 1 May June 2016 12 PDFThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2020Document4 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2020Thapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Maths November 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Maths IGCSEDocument20 pagesMaths November 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Maths IGCSEThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Maths November 2016 (v2) QP - Paper 4 CIE Maths IGCSEDocument20 pagesMaths November 2016 (v2) QP - Paper 4 CIE Maths IGCSEThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument12 pages2020 Specimen Paper 4 Mark Schemeande wala boorgerNo ratings yet
- Mil-Prf-85285e T2 PDFDocument3 pagesMil-Prf-85285e T2 PDFLuis Barrios ArandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Is Fun Vol 4 PDFDocument257 pagesPhysics Is Fun Vol 4 PDFAarzomand HabibNo ratings yet
- Bs en 485 2 2007 PDFDocument70 pagesBs en 485 2 2007 PDFKeven Montgemry50% (2)
- Schott Optical Glass Pocket Catalog Europe October 2011 Eng PDFDocument114 pagesSchott Optical Glass Pocket Catalog Europe October 2011 Eng PDFradwan137No ratings yet
- Carboguard 60 LH PDSDocument4 pagesCarboguard 60 LH PDSRicardo SantosNo ratings yet
- SKIN CLEANSING PRODUCTSDocument6 pagesSKIN CLEANSING PRODUCTSAmber LugtuNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Electrical Technology Vol. 2 - Theraja-P1Document29 pagesA Textbook of Electrical Technology Vol. 2 - Theraja-P1Muhammad TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Line Sizing GuidelinesDocument32 pagesLine Sizing Guidelinesyunjun12100% (2)
- IsoCore Flange Isolation Gaskets and Kits Provide Cost Effective Alternative to PhenolicDocument4 pagesIsoCore Flange Isolation Gaskets and Kits Provide Cost Effective Alternative to PhenolicShenhua Kronen SohneNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Study Guide - AP BiologyDocument6 pagesUnit 3 - Study Guide - AP BiologyMishaNo ratings yet
- API 570 – DAY 3 BOOKDocument106 pagesAPI 570 – DAY 3 BOOKmelvinNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Operating Parameters and Conditions in Hydrocyclones For Enhanced SeparationsDocument18 pagesAn Overview of Operating Parameters and Conditions in Hydrocyclones For Enhanced SeparationsAlex MaximasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0963996918308329 Main PDFDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0963996918308329 Main PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document4 pagesSheet 2Yasmin RedaNo ratings yet
- Nannaya University 4th Sem Subject ResultsDocument150 pagesNannaya University 4th Sem Subject ResultsLalithaa LaliiNo ratings yet
- Upaya Meminimalisir Dampak Lingkungan Dari Penggunaan Pestisida Dalam Pertanian (Dampak Lingkungan Dan Penanggulangannya)Document9 pagesUpaya Meminimalisir Dampak Lingkungan Dari Penggunaan Pestisida Dalam Pertanian (Dampak Lingkungan Dan Penanggulangannya)HafizNo ratings yet
- ISO-4063-List of Welding ProcessesDocument7 pagesISO-4063-List of Welding ProcessesGM100% (1)
- MUCLecture 2021 1013529Document10 pagesMUCLecture 2021 1013529mugentsukiyomi31No ratings yet
- NCR 18650aDocument1 pageNCR 18650aAlan ReisNo ratings yet
- New Scientist Essential Guide - No11 - Life On EarthDocument100 pagesNew Scientist Essential Guide - No11 - Life On EarthHieu TrinhNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Patinas: A Guide to Chemical PatinationDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Patinas: A Guide to Chemical PatinationparaziteNo ratings yet
- Energrease HTG 2 PDFDocument2 pagesEnergrease HTG 2 PDFLê Duy PhongNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Oxygen Electrochemical Sensors: Product Use: Supplier Name: AddressDocument3 pagesSafety Data Sheet Oxygen Electrochemical Sensors: Product Use: Supplier Name: AddressMario Ricardo CambraiaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule Summative TestDocument6 pagesMacromolecule Summative Testapi-2670792390% (2)
- Expansi Valve DanfossDocument12 pagesExpansi Valve Danfossgie_tehnikNo ratings yet
- Isplen PB180G2MDocument1 pageIsplen PB180G2MTaoufik KheddarNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Elements03 - : God BlessDocument101 pagesMachine Design Elements03 - : God BlessReynald de VeraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of PharmacologyDocument113 pagesNursing Care of PharmacologyEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Removal and Recovery (1975)Document225 pagesSulfur Removal and Recovery (1975)Ahmed Soliman100% (1)
- Corrosion Protection For Steel StructuresDocument10 pagesCorrosion Protection For Steel StructuresmaxxmaxxyNo ratings yet