Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Monostable Multivibrator Using Transistors
Uploaded by
Hemantha DalugamaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Monostable Multivibrator Using Transistors
Uploaded by
Hemantha DalugamaCopyright:
Available Formats
electrosome.
com/monostable-multivibrator-transistors/
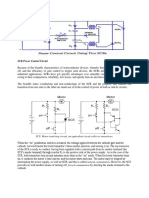
Monostable Multivibrator using
Transistors – Circuit Diagram
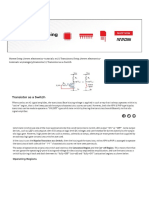
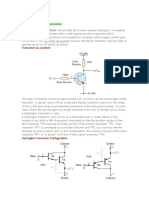
In the below circuit diagram we can find two transistors which are wired as switches.
Please read the article Transistor as a Switch to know more about it. When a transistor
is ON, it works in saturation region and its collector – emitter acts as a short circuit.
When a transistor is OFF, it works in cut off region and its collector – emitter acts as an
open circuit. So in the above circuit, when a transistor is in OFF state, its collector will
have voltage equal to supply voltage Vcc and when the a transistor is in ON state, its
collector will be grounded.
Function of resistor R is to limit collector current of both transistors Q1 and Q1.
Resistors R1 & R2 will provide base current for transistors Q2 & Q1 respectively during
ON condition. Capacitor C3 and Resistor R3 is designed as a differentiator circuit to
provide sharp trigger pulses to the base of the transistor Q1. The diode D allows only
positive pulses to the base. Capacitor C2 is optional, which is called as Speed Up
capacitor. It is used for speedy bypassing of signal transitions (LOW to HIGH and HIGH
to LOW) at the collector of Q2 to the base of Q1.
When the circuit is switched ON, transistor Q1 will be OFF and Q2 will be ON, which is its stable
state. Transistor Q2 is ON since the base of the transistor is connected to Vcc via R1. Transistor
Q1 will be OFF because base of the transistor is at 0v since transistor Q2 is ON.
You might also like
- Industrial Electronics: Understanding Thyristors and SCR OperationDocument4 pagesIndustrial Electronics: Understanding Thyristors and SCR Operationtinonoy KulitlitNo ratings yet
- Aim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsDocument6 pagesAim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsShahrukh PinjariNo ratings yet
- Bistable MultivibratorsDocument9 pagesBistable MultivibratorsihtishamuddNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORSDocument13 pagesTRANSISTORSAbad Kurt ChristianNo ratings yet
- Fpe (1) AkDocument39 pagesFpe (1) AkAnchal YewaleNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document99 pagesMod 2SREEHARI V ANo ratings yet
- Transistor CircuitsDocument9 pagesTransistor CircuitsYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3_Part 2_NotesDocument17 pagesUNIT 3_Part 2_NotesmourjyasanyNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document8 pagesTransistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Fariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- ELEC-SPD-S3 - Thyristor or Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument4 pagesELEC-SPD-S3 - Thyristor or Silicon Controlled RectifierHiren H. PatelNo ratings yet
- Thyristor TutorialDocument9 pagesThyristor Tutorialhamza malik100% (1)
- Em ReportDocument7 pagesEm Reportkashafnasir9977No ratings yet
- Rain AlarmDocument15 pagesRain AlarmTARIT DAS100% (4)
- Class 1 Transistor As A SwitchDocument11 pagesClass 1 Transistor As A Switchermaheshkumar4No ratings yet
- Lecture Week 03Document54 pagesLecture Week 03عبدالله قيس محمود الحيدريNo ratings yet
- Relay Switch Circuit and Relay Switching CircuitDocument10 pagesRelay Switch Circuit and Relay Switching CircuitidatscribdNo ratings yet
- BJT vs FET: Key Differences Between the Two Transistor TypesDocument13 pagesBJT vs FET: Key Differences Between the Two Transistor TypesSivarajanRajendranNo ratings yet
- Types of TransistorDocument13 pagesTypes of Transistorkipkoech_rotichNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDocument11 pagesTransistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDilpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Transistor&IcDocument66 pagesTransistor&IcmythonyNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentMohamed SaberNo ratings yet
- IC 555 ProjectsDocument14 pagesIC 555 ProjectsParth Lad100% (1)
- Substation ComponentsDocument62 pagesSubstation Componentsahmed75% (4)
- Transistor As A Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning AssignmentDocument5 pagesTransistor As A Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning AssignmentAmanNo ratings yet
- AE Unit - 4Document7 pagesAE Unit - 4aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- 3Document48 pages3j4xzj8vx4No ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrincipleDocument24 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrinciplesixfacerajNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Modern Power Electronics Components and SystemsDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Modern Power Electronics Components and SystemsdanimannyNo ratings yet
- MultivibratorsDocument14 pagesMultivibratorsMuhammadSajidNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three System Driver 3.1 MOSFET Control CircuitDocument11 pagesChapter Three System Driver 3.1 MOSFET Control CircuitAlhussain EmbarkNo ratings yet
- Electronics by TakDocument7 pagesElectronics by Taktak2020No ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument2 pagesTransistor As A Switchjojo1216No ratings yet
- SCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsDocument5 pagesSCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsMark Kenneth Apuyan100% (1)
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument10 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- The Darlington Transistor: Transistor As A SwitchDocument3 pagesThe Darlington Transistor: Transistor As A SwitchCol Sanjay BajpaiNo ratings yet
- THYRISTORDocument26 pagesTHYRISTORLovely Jaze SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Darlington Transistor and The Sziklai Darlington PairDocument8 pagesDarlington Transistor and The Sziklai Darlington PairSylvester WasongaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument30 pagesModule 1 NotesSoxamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Power Semiconductor DevicesJibril JundiNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- The Transistor As A SwitchDocument8 pagesThe Transistor As A Switchmajstor100% (1)
- Semiconductor Power Switching DevicesDocument30 pagesSemiconductor Power Switching Devicesबृजभूषणशर्माNo ratings yet
- PDF Book For TrainingDocument111 pagesPDF Book For TrainingSeam LukNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument62 pagesPower Semiconductor DevicesMD. SADEKUL ISLAM RIMON 1502084No ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDocument5 pagesComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Multivibrators OverviewDocument15 pagesMultivibrators OverviewAchuilNo ratings yet
- HV Resonance CollectionDocument4 pagesHV Resonance CollectionfreiwildNo ratings yet
- Multi Vibrato RssDocument6 pagesMulti Vibrato RssRamanujam O SNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits: Unit 1 Single Stage AmplifiersDocument58 pagesAnalysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits: Unit 1 Single Stage AmplifiersjeevithaNo ratings yet
- project2018Document4 pagesproject2018negikrishna9627No ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2Document92 pagesLab Manual 2Joyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Thyristors and Triacs PDFDocument30 pagesThyristors and Triacs PDFCristianNo ratings yet
- Experiment in ElectronicsDocument8 pagesExperiment in ElectronicsPercival Cylas CabralesNo ratings yet
- Practical Electronics For InventorsDocument14 pagesPractical Electronics For InventorsphillamxNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument5 pagesTransistor As A SwitchGeorge NGNo ratings yet
- Over-Under Voltage Cut-Off With On-Time Delay PROJECT REPORTDocument35 pagesOver-Under Voltage Cut-Off With On-Time Delay PROJECT REPORTSumit Agarwal75% (4)
- The Transistor Astable Multi VibratorDocument6 pagesThe Transistor Astable Multi VibratorTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- TRAY4Document1 pageTRAY4Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Monostable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument4 pagesMonostable Multivibrator Using TransistorsHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Tray 2Document2 pagesTray 2Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic BrakeDocument6 pagesHydraulic BrakeHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- TRAY4Document1 pageTRAY4Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Production UNIT 5HandoutHemanthaDocument25 pagesProduction UNIT 5HandoutHemanthaHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Air Brake (Road Vehicle)Document2 pagesAir Brake (Road Vehicle)Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Tray 2Document2 pagesTray 2Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Oh M 1Document26 pagesPresentation Oh M 1Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Disc brake technology: A concise historyDocument13 pagesDisc brake technology: A concise historyHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Thevenin HemanthaDocument9 pagesThevenin HemanthaHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- 71 2Document46 pages71 2Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Basic Hand Tools GuideDocument26 pagesBasic Hand Tools GuideHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- 1Document32 pages1Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Divinaguma Doc1Document7 pagesDivinaguma Doc1Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Faraday Any 1Document16 pagesPresentation Faraday Any 1Hemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet