Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plants Physiology
Uploaded by
Priya DarshiniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plants Physiology
Uploaded by
Priya DarshiniCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
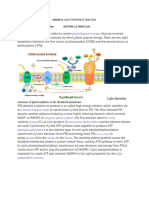
List the products of light dependent reaction
NADPH,ATP ,Oxygen
2. Define photophosphorylation
Process of adding phosphate to ADP to form ATP by using the energy from sunlight via electron
transport chain and chemiosmosis .
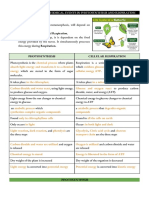
3. Compare Cyclic and Noncyclic photophosphorylation Now, answer these questions:
Cyclic photophosphorylation Noncyclic photophosphorylation
Involve cyclic electron flow Involve non-cyclic electron flow
Only produce ATP Produce ATP, oxygen and NADPH + H+
Involves PS I (P700) only Involves PS I (P700) and PS II (P680)
First electron donor is PS I First electron donor is water
Last electron acceptor is PS I Last electron acceptor is NADP+
No oxygen release Oxygen is released
4. Compare Photosystem I and Photosystem II
Photosystem I Photosystem II
The photocenter is P700 The photocenter is P680
Pigments absorb longer wavelengths of light Pigments absorb shorter wavelengths of light
(more than 680 nm) (less than 680 nm)
Involved in both cyclic and non- cyclic Only involved in cyclic photophosphorylation
photophosphorylation
No photolysis of water occurs Photolysis of water occurs
Main function is NADPH synthesis Main function is ATP synthesis and hydrolysis
of water
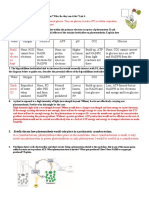
5. Definition of chemiosmosis.
Chemiosmosis is the process that use energy stored in the form of proton (H+) gradient across
the inner mitochondrial membrane to produce ATP from ADP and Pi. Proton (H+) across
membrane is known as proton motive force.
6. Why is it called oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria?
It is because hydrogen ions in the matrix space can only pass through the inner mitochondrial
membrane through a membrane protein called ATP synthase. As protons move through ATP
synthase, ADP is turned into ATP. The production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in
mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation
You might also like
- Unit 5. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationsDocument16 pagesUnit 5. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationsShoaib Ahmed SamNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pages4.3.1 PhotosynthesisMariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Photosystems I&iiDocument49 pagesPhotosystems I&iiObiajulu Crystal OnyinyechiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGI UMUM 2007:: Photosynthesis Lecture 4-5: Introduction and The Light ReactionsDocument32 pagesBIOLOGI UMUM 2007:: Photosynthesis Lecture 4-5: Introduction and The Light ReactionsZainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Photosynthesiswkwhui100% (6)
- Unit III BSWDocument37 pagesUnit III BSWAshwinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument14 pagesBiologyPrincyNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio1 ReviewerStevenzel EstellaNo ratings yet
- CHP 5 PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesCHP 5 PhotosynthesisSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- MRFM Q63 H SMR 5 WZRVCJ RKDocument5 pagesMRFM Q63 H SMR 5 WZRVCJ RKBalbeer KaurNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Part 1Document27 pagesPhotosynthesis Part 1m4h1rstNo ratings yet
- Light and Dark Reaction - 1Document15 pagesLight and Dark Reaction - 1Louie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- BFE Unit 3Document22 pagesBFE Unit 3tanvichalke17No ratings yet
- Nbio1 FionnahDocument2 pagesNbio1 FionnahlyravixxNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio ReviewerhahatdogNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis March - AprilDocument40 pagesPhotosynthesis March - AprilIbrahim TurayNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument65 pagesPhotosynthesisVinz Arvhil MatagayNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument11 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISDRISTIE KALITANo ratings yet
- 17 3Document30 pages17 3Lim ZjianNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent ReactionDocument19 pagesLight Dependent Reactionefesonbantillo18No ratings yet
- 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument9 pages13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsAarushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 5.2.1Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis 5.2.1bexNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument16 pagesPhotosynthesisMohamed RizwanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAditya VenkatNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyKomana SangarNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleBernadette PasionNo ratings yet
- BFE Unit 3Document22 pagesBFE Unit 3DanielNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 MOD 1 - ATP ProductionDocument43 pagesQTR 2 MOD 1 - ATP ProductionCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2Document58 pagesPhotosynthesis 2Jemimah Carmelle DoradoNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsDocument25 pagesPatterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsMar'J0% (1)
- Summary of Notes About Light Dependent ReactionDocument4 pagesSummary of Notes About Light Dependent ReactionGilbert AmanNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Light Reaction Event in PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesUnveiling The Light Reaction Event in Photosynthesiszbplayer8No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesisepick7No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Photorespiration 02Document15 pagesPhotosynthesis and Photorespiration 02simamkelemqina4No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Inihibitors ReviewDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Inihibitors Reviewapi-521773978No ratings yet
- FY B.Sc. Light Reactions IDocument5 pagesFY B.Sc. Light Reactions IVijendraNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument35 pagesPhotosynthesisPark EunyaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis A Level BiologyDocument88 pagesPhotosynthesis A Level Biologyeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Class: 11 Sub: Biology Chapter - 13Document7 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants: Class: 11 Sub: Biology Chapter - 13kuldeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Esci 2Document3 pagesEsci 2Victor Gojo CruzNo ratings yet
- ATP Production: AP BiologyDocument20 pagesATP Production: AP BiologyCamille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionDocument29 pagesQuarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionKarl Patrick PachecoNo ratings yet
- PhotophosphorylationDocument18 pagesPhotophosphorylationLorri - Ann LamontNo ratings yet
- Biotech Pres 29032016Document36 pagesBiotech Pres 29032016Marza ZareenNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Bio Topic 5Document6 pagesEdexcel Bio Topic 5quesntinmoorsNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent ReactionsDocument2 pagesLight Dependent ReactionsDuaa Saqri RamahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants PDFAdityaNo ratings yet
- L10 2023 - Photosynthesis IDocument10 pagesL10 2023 - Photosynthesis Imaddie.jngNo ratings yet
- CAPE. Photosystems & Photophosphorylation.Document41 pagesCAPE. Photosystems & Photophosphorylation.Rocheal WhittinghamNo ratings yet
- Hotosynthesis Chapter Outline: 7.1 Photosynthetic OrganismsDocument4 pagesHotosynthesis Chapter Outline: 7.1 Photosynthetic Organismsrommel benamirNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAjay JamwalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 6.0 2024Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 6.0 2024jagartidubey5842No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument10 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISNur SafirahNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document32 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Allihannah PhillipsNo ratings yet
- XAVI PHOTOSYNTHESIS - Lecture BIOUMUMDocument47 pagesXAVI PHOTOSYNTHESIS - Lecture BIOUMUMPrita YhuniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975From Everand25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the 25th International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Jerusalem, Israel 6–11 July 1975Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)