Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro
Uploaded by
Geraldine Marie SalvoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro
Uploaded by
Geraldine Marie SalvoCopyright:
Available Formats
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
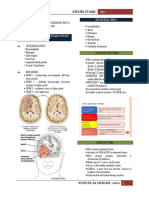
ADDITIONAL NOTES IN PEDIA NEURO (PART 1) Generalized Seizure: Previously called primary
DR. DIAZ generalized , these engage or involve network or side of the
brain at the onset
ILAE 2017 CLASSIFICATION OF SEIZURE TYPES BASIC VERSION Unknown Onset: If the onset of as seizure is not known,
the unknown onset category. Later on, the seizure type can
FOCAL ONSET be changed if the beginning of a person’s seizure becomes
Aware / Impaired Awareness clear.
Motor/ Non-motor Onset
Focal to Bilateral Tonic Clonic
Focal to Bilateral Seizure: A seizure that starts in one
side or part of the brain and spreads to both sides has
GENERALIZED ONSET
been called a secondary generalized seizures. Now the
Motor (Tonic Clonic, Other Motor)
term generalized refers only to the start of a seizure. The
Non-Motor (Absence)
new term for secondary generalized seizure would be focal
to bilateral seizure.
UNKNOWN ONSET
Motor (Tonic Clonic, Other Motor)
Non-Motor 2. LEVEL OF AWARENESS DURING THE SEIZURE
Unclassified
Focal Aware: If awareness remains intact even if the
person is unable to talk or respond during a seizure, the
seizure would be called a focal aware seizure. This
replaces the term simple partial.
Focal Impaired Awareness: If awareness is impaired or
affected at any time during a seizure, even if a person has
a vague idea of what happened, the seizure would be called
focal impaired awareness. This replaces the term complex
partial seizure.
Awareness Unknown: Sometimes it’s not possible to know
2017 REVISED CLASSIFICATION OF SEIZURE - THE NEW BASIC if a person lives alone or has seizures only at night. In this
CLASSIFICATION situation, the awareness term may not be used or it would
be described as awareness unknown.
3 KEY FEATURES
1. Where seizures begin in the brain
Generalized Seizures: These are all presumed to affect a
2. Level of awareness during a seizure
person’s awareness or consciousness in some way. Thus
3. Other features of seizures
no special terms are needed to describe awareness in
generalized seizures.
1. WHERE SEIZURES BEGIN
3. DESCRIBING MOTOR AND OTHER SYMPTOMS
The type of seizure onset is important because it affects
choice of Seizure medication, possibilities for epilepsy
surgery, outlook, and possible causes. Focal Motor Seizure: This means that some type of
movement occurs during the event. For example twitching,
jerking, or stiffening movements of a body part or autisms
Focal Seizures: Previously called partial seizures, these
start in an area or network of cells on one side of the (automatic movements such as licking lips, rubbing hands,
walking, or running)
brain.
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 1
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
Focal Non-motor Seizure: This type of seizure has other ILAE 2017 CLASSIFICATION OF SEIZURE TYPES EXPANDED
symptoms that occur first such as change in sensation, VERSION
emotions, thinking, or experiences.
It’s also possible for a focal aware or impaired awareness
seizure to be sub-classified as motor or non-motor onset.
Auras: The term aura, which described symptoms a person
may feel in the beginning is seizure, is not in the new
classification. Yet people may continue to use this term. It’s
important to know that in most cases, these early
symptoms may be the start of a seizure.
DESCRIBING GENERALIZED ONSET SEIZURES
Generalized Motor Seizures: The generalized tonic-clonic
seizure term is still used to describe seizures with
stiffening (tonic) and jerking (clonic). This loosely
corresponds to “grand mal”. Other forms of generalized
motor seizures may happen. Many of these terms have not THE 2017 SEIZURE CLASSIFICATION
changed, and a few new terms have been added.
Classification of a seizure type is only of the seizure
Generalized Non- Motor Seizures: These are primarily description. This new system will make it easier to describe
absence seizures, and the term corresponds to the old seizures and using common language to talk about them.
term “petit mal”. These seizures involve brief changes in
awareness, staring, and some may have automatic or The new classification is designed to have some flexibility.
repeated movements like lipsmacking. Use of other descriptive terms or even text is encouraged.
DESCRIBING UNKNWON ONSET SEIZURES Most seizures can be classified by signs and symptoms that
happen during a seizure. However, other information is
When the beginning of a seizure is not known, this useful when available. For example, phone videos, EEG
classification still gives away to describe whether features (elelctroencephalogram), MRI (magnetic resonance
are motor or non-motor. imaging), and other brain imaging, blood tests, or gene
tests maybe helpful.
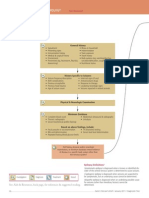
THE NEW EXPANDED CLASSIFICATION
This seizure classification does not change the definition of
The expanded classification keeps the framework of the epilepsy or epilepsy syndromes. The epilepsy classification
basic classification, but adds more seizure types of includes the whole clinical picture, with information on
features under motor and non-motor seizures are listed seizure types, causes, EEG pattern, brain imaging, genetics,
for all types: focal, generalized, and unknown onset. and epilepsy syndromes, such as Lennox-Gastaut
Syndrome.
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 2
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
EPILEPTIC EEG
TREATMENT
CORTICOSTEROID USE…
Corticosteroid inhibits the synthesis of interleukin 1
BACTERIAL MENINGITIS and TNF.
There is convincing evidence that corticosteroids
decrease mortality rates and long term neurologic
sequelae in some patients with tuberculous
meningitis by: reducing vasculitis, inflammation,
and ultimately intracranial pressure; lowering the
intracranial pressure limits tissue damage and
favors circulation and anti-tuberculosis drugs
through the brain and meninges.
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 3
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mental HealthDocument59 pagesMental HealthGeraldine Marie Salvo97% (29)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Thief 2 The Metal Age ManualDocument33 pagesThief 2 The Metal Age ManualMordenGreyNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument5 pagesStages of LaborGeraldine Marie Salvo100% (4)
- Tiki Taka Notes Final PDFDocument104 pagesTiki Taka Notes Final PDFAditiSahak62No ratings yet
- Meniere DiseaseDocument16 pagesMeniere DiseaseNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Periampullary CarcinomaDocument35 pagesPeriampullary Carcinomaminnalesri100% (2)
- Board Review Questions: Pharmacology and Therapeutics MCQsDocument15 pagesBoard Review Questions: Pharmacology and Therapeutics MCQsVince Cabahug100% (4)
- Yoga Poses Help Manage EpilepsyDocument7 pagesYoga Poses Help Manage EpilepsyRekha SharmaNo ratings yet
- A2A Comanche250 Pilot's ManualDocument102 pagesA2A Comanche250 Pilot's ManualMiguel Simo100% (1)
- Handout On First Aid, Rescue & Water Safety: Dr. Jezreel B. VicenteDocument39 pagesHandout On First Aid, Rescue & Water Safety: Dr. Jezreel B. Vicentewy100% (2)
- Critical appraisal of journal articlesDocument13 pagesCritical appraisal of journal articlesMaria MarcellaNo ratings yet
- Junqueira's Basic Histology Text & Atlas (14th Ed.), Anthony Mescher PDFDocument16 pagesJunqueira's Basic Histology Text & Atlas (14th Ed.), Anthony Mescher PDFsha.and0% (1)
- Case Study on Epilepsy Patient's Treatment and RecoveryDocument11 pagesCase Study on Epilepsy Patient's Treatment and RecoveryHarry Sivia100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresKwini Jeyn50% (2)
- Difficulty in MobilityDocument16 pagesDifficulty in MobilityAbbeygale Galan100% (1)
- Chest Trauma Diagnosis and ManagementDocument27 pagesChest Trauma Diagnosis and ManagementGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- LARYNX ANATOMYDocument83 pagesLARYNX ANATOMYGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- LEGALMED DEception DetectionDocument9 pagesLEGALMED DEception DetectionGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Histology Case #3Document19 pagesGroup 1: Histology Case #3Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Immunochemistry Part 2 NotesDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Immunochemistry Part 2 NotesAnthea AllamNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders PDFDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorders PDFGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Case 1 NeuroDocument11 pagesCase 1 NeuroGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Family Case Presentation: Abat FamilyDocument80 pagesFamily Case Presentation: Abat FamilyGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro2Document4 pagesAdditional Notes in Pedia Neuro2Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- AdrenocorticosteroidsDocument64 pagesAdrenocorticosteroidsGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Protein Chemistry Part 1.1Document13 pages1.1 Protein Chemistry Part 1.1Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy VIDocument4 pagesAnatomy VIGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Enzyme Chemistry Part 1Document7 pages4.1 Enzyme Chemistry Part 1Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Immunochemistry Part 1Document7 pagesImmunochemistry Part 1Anthea AllamNo ratings yet
- EASL Guidelines on Gallstone Prevention, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument36 pagesEASL Guidelines on Gallstone Prevention, Diagnosis, and TreatmentGabo Bravo RodríguezNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Enzyme Chemistry Part 2Document6 pages4.2 Enzyme Chemistry Part 2Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- EPIDEMIOLOGY & GEOGRAPHIC DistributionDocument2 pagesEPIDEMIOLOGY & GEOGRAPHIC DistributionGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect Smooth MuscleDocument90 pagesDrugs That Affect Smooth MuscleGeraldine Marie Salvo100% (1)
- Form 2D Health Plan Implementation Pregnancy Prenatal CareDocument2 pagesForm 2D Health Plan Implementation Pregnancy Prenatal CareLora CarpioNo ratings yet
- OLFU Family Case Study on the Flores FamilyDocument12 pagesOLFU Family Case Study on the Flores FamilyGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Case 3 - Biochem VIDocument5 pagesCase 3 - Biochem VIGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Microbiology, Pathology & Pharmacology Review ResourcesDocument1 pageAnatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Microbiology, Pathology & Pharmacology Review ResourcesGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- AudioRounds GonorrheaDocument1 pageAudioRounds GonorrheaIlham DarmawanNo ratings yet
- The New Definition and Classification of Seizures and EpilepsyDocument7 pagesThe New Definition and Classification of Seizures and EpilepsyCarlos Andrés BernalNo ratings yet
- Understanding Non-Epileptic SeizuresDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Non-Epileptic SeizuresKaram Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Ethel LepkyDocument2 pagesEthel LepkyAli MullaNo ratings yet
- Semiologi Epilepsi: Nama Pasien: No CM: Tanggal: Diagnosis Awal: PemeriksaDocument7 pagesSemiologi Epilepsi: Nama Pasien: No CM: Tanggal: Diagnosis Awal: Pemeriksaanton MDNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tree of Seizures in DogsDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Tree of Seizures in DogsBethany CrawfordNo ratings yet
- NNGN3780 ClinicalDocument26 pagesNNGN3780 ClinicalErica Dianne VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Common ProblemsDocument33 pagesPediatric Nursing Common ProblemsMaricel Agcaoili GallatoNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Malaria (CM) Prof. WBP Matuja, MuhasDocument20 pagesCerebral Malaria (CM) Prof. WBP Matuja, MuhasAnonymous TCZf45C10No ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument12 pagesHemiplegiaalexandra 007No ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF EPILEPSY IN PREGNANCYDocument24 pagesMANAGEMENT OF EPILEPSY IN PREGNANCYClaudio UdjajaNo ratings yet
- Counseling and Management of The RIskis of Living With EpilepsyDocument15 pagesCounseling and Management of The RIskis of Living With Epilepsynight.shadowNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation 2Document11 pagesCase Presentation 2Angel Jonele ManongsongNo ratings yet
- Preclinical Evaluation of Anti-Epileptics: S K Kanthlal Dept of Pharmacology Amrita School of Pharmacy KochiDocument24 pagesPreclinical Evaluation of Anti-Epileptics: S K Kanthlal Dept of Pharmacology Amrita School of Pharmacy Kochigunuputi sushmaNo ratings yet
- Gears of War ManualDocument18 pagesGears of War Manualarfan1984No ratings yet
- Acute Viral Encephalitis in ChildrenDocument16 pagesAcute Viral Encephalitis in ChildrenCF PonceNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Case StudyDocument13 pagesMechanisms Case Studyshane_tin143No ratings yet
- Kibera Mirror MayDocument8 pagesKibera Mirror Mayvincent achuka maisibaNo ratings yet
- Common Symptoms Partial SeizuresDocument2 pagesCommon Symptoms Partial SeizuresAnonymous qm1o8YcNo ratings yet
- History and Classification of EpilepsyDocument9 pagesHistory and Classification of Epilepsygoo99No ratings yet
- Battle of The Gods ManualDocument10 pagesBattle of The Gods ManualaawaredNo ratings yet
- 3 - pg.51-113Document63 pages3 - pg.51-113api-3855624100% (1)