Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
asifali juttOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Uploaded by
asifali juttCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Biological molecules (proteins) which catalyze a biochemical reaction and remain unchanged
after completion of reaction are called
A. Cofactor B. Coenzymes
C. Activator D. Enzymes
Which statement about enzyme is incorrect:
Some of them consist solely of protein with They catalyze a chemical reaction without
A. B.
no non protein part. being utilized.
They without their cofactor are called
C. All enzymes are fibrous Proteins. D.
apoenzyme.
In which of the following location enzymes controlling cellular respiration are present?
A. Nucleus B. Chlorophast
C. Milochondria D. Ribosome
An activated enzyme consisting of polypeptide chain and a cofactor is called:
A. Apoenzyme B. Holoenzyme
C. Activated enzyme D. Both b and c
Which one forms the raw material for coenzymes?
A. Vitamins B. Carbohydrates
C. Proteins D. Metals
A cofactor made of inorganic ion which is detachable is called
A. Prosthetic group B. Coenzyme
C. Activator D. Cofactor
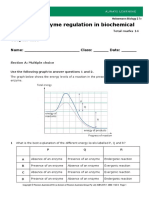
Enzymes _________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction
A. Increases B. Decreases
Increases or decreases depending upon
C. Does not effect D.
individual enzyme
A three dimensional dcavity bearing a specific charge by which the enzyme reacts with its substrate
is called
A. Active site B. Binding site
C. Catalytic site D. Allosteric site
Which step causes activation of catalytic site of an enzyme?
A. Change in pH of the surroundings. B. Formation of Enzyme Susstrate complex.
C. Change in the charge of the active site. D. Change in temperature
Lock and Key model was proposed by
A. Emil Fischer B. Koshland
C. Robin Williams D. Rudolph Virchow
Which statement is incorrect about Lock and Key Model?
Specific enzyme can transform only a Active site of an enzyme is a non flexible
A. B.
specific substrate structure.
Active site does not change before during It explains the mechanism of every
C. D.
or even after the reaction. chemical reaction.
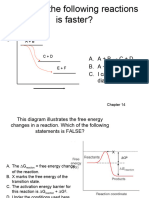
The rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of an enzyme which statement
is incorrect in this respect:
Increase in enzyme molecule increases This relation is for unlimited time period
A. B.
the available active sites. with unlimited enzyme concentration
If the concentration is doubled the rate
C. D. None of these.
will become two fold.
If the concentration of enzyme is kept constant and amount of substrate is increased a point is
reached where increase in substrates concentration does not affect the reaction rate because of
Enzymes get denatured at higher substrate Rate of reaction is indirectly proportional to
A. B.
conc. substrate concentration at this point.
All the active sites on enzyme molecule are
C. D. None of these.
occupied.
If more substrate to already occurring enzymatic reaction is added more enzyme activity is seen
because:
There is probably more substrate present There is probably more enzayme available
A. B.
than there is enzyme. than there is substrate.
There is probably more product present The enzyme substrate complex is probably
C. D.
than there is either substrate or enzyme. failing to form during the reaction.
If more substrate to already occurring enzymatic reaction is added and there is no effect on the
rate of the reaction what is the form given to this situation:
A. Saturation B. Denaturation
C. Composition D. Inhibition
The active site of an enzyme:
A. Never changes B. Forms no chemical bond with substrate
Determined by structure and the specificity
C. D. They are non specific in their action.
of the enzyme.
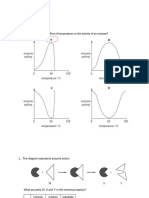
Excessive increase in temperature of medium causes the enzyme molecule to
A. Activate B. Unaffected
C. Denatured D. None of these.
Extreme change in pH results in:
Change in ionization of amino acids at the
A. B. Change in the ionization of the substrate.
active site of the enzyme.
C. Denaturation of the enzyme D. Increase in the reaction rate.
A chemical substance which can react (in place of substrate) with the enzyme but is not transformed
into product/s and thus blocks the active site temporarily or permanently is called
A. Co-enzyme B. Blocker
C. Inhibitor D. Cofactor
Inhibitors which block the enzyme by forming weak bond are called
A. Competitive inhibitors. B. Non-competitive inhibitors
C. Irreversible inhibitors. D. Both a and b
A substance which binds at the active site of the enzyme but does not result in the formation of the
products is called:
A. Irreversible inhibitor B. Reversible inhibitor
C. Competitive inhibitor D. Non-competitive inhibitor
The structure of an enzyme is altered by:
A. Irreversible inhibitor B. Reversible inhibitor
C. Competitive inhibitor D. Non-competitive inhibitor
Malonic acid is an example of:
A. Irreversible inhibitor B. Reversible inhibitor
C. Competitive inhibitor D. Non-competitive inhibitor
If enzyme concentration is low than substrate pH and temperature values are equal to requirement
then which of the following will increase rate of reaction.
A. increase in concentration of enzyme B. increase in concentration of substrate
C. increase in pH D. increase in temperature
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions, Revised EditionFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- A.P. Chapter 8 WebTestDocument9 pagesA.P. Chapter 8 WebTestNick PirainoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Enzyme Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Enzyme Practice QuestionsSunwoo YooNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymesfalcon girl100% (2)
- MCQS CH 3 Bio Part 1 1Document2 pagesMCQS CH 3 Bio Part 1 1All kinds of information on channelNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Chapter 8 2Document12 pagesQuizlet Chapter 8 2EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of EnzymesDocument3 pagesNomenclature of EnzymesJanjan GarcesNo ratings yet
- 2020 UST MBR BiochemistryDocument77 pages2020 UST MBR BiochemistryLorealLunaNo ratings yet
- Enzymology Quiz: Contributed by Sindhe Veere Shivaji, C/o Shivaji Steel & General Stores, MarketDocument2 pagesEnzymology Quiz: Contributed by Sindhe Veere Shivaji, C/o Shivaji Steel & General Stores, MarketBarish RoyNo ratings yet
- (Fold/Cover If You Don'T Wanna See The Answers Yet) BDocument43 pages(Fold/Cover If You Don'T Wanna See The Answers Yet) BManila Med100% (2)
- Activity 14 - Biochemical EngineeringDocument3 pagesActivity 14 - Biochemical EngineeringJeanne Roselle Dulatre CortezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Prepared By: SIR SARWAR AZIZDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics: Prepared By: SIR SARWAR AZIZEliza BethNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Quizzes by Ronnie BaticulonDocument20 pagesBiochemistry Quizzes by Ronnie BaticulonMhartin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Practice Clinical Chemistry 2 CFUDocument7 pagesPractice Clinical Chemistry 2 CFUReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- Enzymes SL Quiz: The Part of The Enzyme Where The Substrate Binds Is Known As The ....Document2 pagesEnzymes SL Quiz: The Part of The Enzyme Where The Substrate Binds Is Known As The ....ShruthiNo ratings yet
- BCH MCQs1Document304 pagesBCH MCQs1moxdegr8100% (1)
- A. B. C. D. A. B. C. A. B. C.: Enzyme That Differ in Amino Acid Sequence But Catalyze The Same Reaction AreDocument1 pageA. B. C. D. A. B. C. A. B. C.: Enzyme That Differ in Amino Acid Sequence But Catalyze The Same Reaction AreYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymesJica MedrosoNo ratings yet
- Bio-Preview Biochemistry Part B: EnzymesDocument5 pagesBio-Preview Biochemistry Part B: EnzymesYealshaday BirhanuNo ratings yet
- AP Biology 1st Semester Final Exam Review-2011.2012Document13 pagesAP Biology 1st Semester Final Exam Review-2011.2012Jessica ShinNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: OutlineDocument10 pagesEnzymes: OutlineManila MedNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Enzyme - Check - in - Quiz - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesKami Export - Enzyme - Check - in - Quiz - ANSWER KEYNicholas UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- C4 (Biocatalysis)Document12 pagesC4 (Biocatalysis)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Enzymes MCQ QPDocument8 pages2.4 Enzymes MCQ QPnurjahaan valliNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Are Always: Compressed Notes Chapter 4: Biocatalysis Sb025Document7 pagesEnzymes Are Always: Compressed Notes Chapter 4: Biocatalysis Sb025LIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Quiz - BiologyDocument2 pagesCH 8 Quiz - Biologybmunroe1968No ratings yet
- 04 Lec - Bio024 EnzymesDocument11 pages04 Lec - Bio024 EnzymesAlliah YamitNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesPharmacology QuestionnaireWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- CH6 Pt. 2Document6 pagesCH6 Pt. 2Ken LaguiabNo ratings yet
- Tutorial FD Biochem (Enzymes)Document5 pagesTutorial FD Biochem (Enzymes)ANIS HUMAIRA ABDUL HAFIZNo ratings yet
- Paper Biology: Test Chapter. 3 Class 1st Year Total Marks 30 Time: 50 Mints Chose The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesPaper Biology: Test Chapter. 3 Class 1st Year Total Marks 30 Time: 50 Mints Chose The Correct Answermuhammad ayyazNo ratings yet
- Biology WS AnswersDocument17 pagesBiology WS AnswersKazeNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 - Module 11Document12 pagesBio 1 - Module 11Judah CaballerøNo ratings yet
- Biochem Quiz 1 2021Document6 pagesBiochem Quiz 1 2021Michelle MariposaNo ratings yet
- Compiled Quiz BiochemistryDocument38 pagesCompiled Quiz BiochemistryAdrianNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document7 pagesCH 14Roberto RullerNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology Basic Principles 10th Edition Talaro Test BankDocument35 pagesFoundations in Microbiology Basic Principles 10th Edition Talaro Test Bankhieudermotjm7w100% (28)
- Enzymes Classified Past Paper 2 Solved GCSE O Levels Biology 0610Document40 pagesEnzymes Classified Past Paper 2 Solved GCSE O Levels Biology 0610IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Ezyme 2Document3 pagesEzyme 2Nini Besi100% (1)
- Enzymes Are: A. Biocatalysts B. Proteins Except Ribozymes C. Products of Genes D. All of The AboveDocument1 pageEnzymes Are: A. Biocatalysts B. Proteins Except Ribozymes C. Products of Genes D. All of The AboveNini BesiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document20 pagesEnzymes 1Saad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalDocument71 pagesBiochemistry FinalJanie-Vi Gorospe100% (2)
- Chapter 9 Chemical Kinetics Question BankDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Chemical Kinetics Question Bankmymegaacc111No ratings yet
- Enzyme QuizDocument9 pagesEnzyme Quizerin_slatenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesChemistry of Life Practice QuestionsAmerican ArmyNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument2 pagesNoteHSUAN-ER LONo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument23 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Unit 3Document10 pagesBiology VCE Unit 3nidhi patelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: Prepared By: SIR SARWARDocument3 pagesChemical Equilibrium: Prepared By: SIR SARWAREliza BethNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - PharmacologyDocument10 pagesModule 4 - PharmacologyKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Specific Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical: Constituents of Enzyme MoleculeDocument6 pagesEnzyme: Specific Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical: Constituents of Enzyme MoleculeAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Fpgee Study Guide GurudattaDocument31 pagesFpgee Study Guide GurudattaWINSOMETAB33% (3)
- 491 Exam 1 KEYDocument10 pages491 Exam 1 KEYLily M Mo100% (1)
- GOGOBIORANGERSDocument2 pagesGOGOBIORANGERSkingds2006No ratings yet
- Biology An Australian Focus 5th Edition Knox Test BankDocument30 pagesBiology An Australian Focus 5th Edition Knox Test BankAndrewMorrisbknaf100% (16)
- Test Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 14th Edition Michael T Madigan Download DownloadDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 14th Edition Michael T Madigan Download Downloadstevenstevensjgzaryxbdp100% (22)
- Newspaper Index: A Monthly Publication of Newspaper's ArticlesDocument32 pagesNewspaper Index: A Monthly Publication of Newspaper's Articlesasifali juttNo ratings yet
- Functions and Limits: Q1.Tick ( The Correct Answer. (10) FunctionDocument2 pagesFunctions and Limits: Q1.Tick ( The Correct Answer. (10) Functionasifali juttNo ratings yet
- Functions and Limits: Q1.Tick ( The Correct Answer. (10) FunctionDocument2 pagesFunctions and Limits: Q1.Tick ( The Correct Answer. (10) Functionasifali juttNo ratings yet
- Ex 10 3 FSC Part1 Ver3Document8 pagesEx 10 3 FSC Part1 Ver3Abdul Basit JavedNo ratings yet
- Functions and Limits: Q1.Tick ( The Correct Answer. (10) FunctionDocument2 pagesFunctions and Limits: Q1.Tick ( The Correct Answer. (10) Functionasifali juttNo ratings yet
- The Educators School Abdul Hakim: Muhammad Zubair MukhtarDocument1 pageThe Educators School Abdul Hakim: Muhammad Zubair Mukhtarasifali juttNo ratings yet
- 1............. 3 CH Bio 1st YearDocument4 pages1............. 3 CH Bio 1st Yearasifali juttNo ratings yet
- تائی ایسری (کرشن چندر) کا فنی فکری جائزہ. شاہد حفیظ۔میلسیDocument9 pagesتائی ایسری (کرشن چندر) کا فنی فکری جائزہ. شاہد حفیظ۔میلسیasifali jutt100% (2)
- 9 General Math (Arts) Guess Papers by MNA GhummanDocument2 pages9 General Math (Arts) Guess Papers by MNA Ghummanasifali jutt50% (2)
- 11th Maths Important Sums Study Material English Medium PDFDocument2 pages11th Maths Important Sums Study Material English Medium PDFasifali juttNo ratings yet
- 12th Phy ch#16 Test (SEA) PDFDocument4 pages12th Phy ch#16 Test (SEA) PDFasifali jutt100% (1)
- پنجاب میں اردو۔ شاہد حفیظ۔ میلسی PDFDocument8 pagesپنجاب میں اردو۔ شاہد حفیظ۔ میلسی PDFasifali juttNo ratings yet
- 100% Guess Math 9th For All Board PDFDocument2 pages100% Guess Math 9th For All Board PDFasifali juttNo ratings yet
- 11th Maths Important Sums Study Material English MediumDocument2 pages11th Maths Important Sums Study Material English Mediumasifali juttNo ratings yet
- 100% Guess Math 9th For All Board PDFDocument2 pages100% Guess Math 9th For All Board PDFasifali juttNo ratings yet
- 10th 1st Half BiologyDocument2 pages10th 1st Half Biologyasifali juttNo ratings yet
- Ewing Dian Setyadi - Artikel Ilmiah - PpjpiDocument17 pagesEwing Dian Setyadi - Artikel Ilmiah - PpjpiewingsetyadiNo ratings yet
- Axonal Degeneration: Nerve RegenerationDocument1 pageAxonal Degeneration: Nerve RegenerationYogi drNo ratings yet
- EdiblevaccinesDocument11 pagesEdiblevaccinesAbduNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders Screening and PreventionDocument36 pagesGenetic Disorders Screening and PreventionManovaPrasannaKumarNo ratings yet
- Gmo EssayDocument4 pagesGmo Essayapi-270707439No ratings yet
- Fates of PyruvateDocument20 pagesFates of PyruvatedanyalNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Pharmacognostical and Physicochemical Standardization of Peperomia Pellucida (L.) Hbk.Document4 pagesPhytochemical Pharmacognostical and Physicochemical Standardization of Peperomia Pellucida (L.) Hbk.ayi-zidaneNo ratings yet
- The Role of Free Radicals in Health and DiseaseDocument9 pagesThe Role of Free Radicals in Health and Diseasehumera0% (1)
- The Changing Context of Hepatitis D: ReviewDocument12 pagesThe Changing Context of Hepatitis D: ReviewHadi KuriryNo ratings yet
- Gender Role: Kenth Joel CardenteDocument7 pagesGender Role: Kenth Joel CardenteKenth Joel CardenteNo ratings yet
- Title: Production of Alkaline Protease Using Cow DungDocument35 pagesTitle: Production of Alkaline Protease Using Cow DungAlisha ZafarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2nd Quarter (Photosynthesis)Document3 pagesGen Bio 2nd Quarter (Photosynthesis)Andrei Joshua AngellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 DNA Viruses That Infect HumansDocument64 pagesChapter 24 DNA Viruses That Infect HumansJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Angiogenesis in CancerDocument4 pagesAngiogenesis in CanceranonymousNo ratings yet
- History of Plant Ecology PDFDocument3 pagesHistory of Plant Ecology PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Instruction For Medicinal Use: PhagepyDocument4 pagesInstruction For Medicinal Use: PhagepyjagadeeshbhatNo ratings yet
- Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay (Eclia)Document12 pagesElectrochemiluminescence Immunoassay (Eclia)Maliq Arif100% (1)
- Transgenic AnimalsDocument4 pagesTransgenic AnimalsRiza Joy PalomarNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument25 pagesAntiviral Drugss.k. kubraNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument19 pagesNitrogen CycleSophia SyNo ratings yet
- Charles Darwin and Natural SelectionDocument10 pagesCharles Darwin and Natural Selectionninaabraham500No ratings yet
- Pharmanutrition: Yoichi Sunagawa, Yasufumi Katanasaka, Koji Hasegawa, Tatsuya MorimotoDocument5 pagesPharmanutrition: Yoichi Sunagawa, Yasufumi Katanasaka, Koji Hasegawa, Tatsuya MorimotoRizky AmaliaNo ratings yet
- The Roles of Organisms in The Cycling of MaterialsDocument27 pagesThe Roles of Organisms in The Cycling of Materialsdhanicadones29No ratings yet
- Staphylococcus and MicrococcusDocument4 pagesStaphylococcus and MicrococcusAmador GielasNo ratings yet
- Capture-Based, Cell-Based and Tissue-Based SensorsDocument11 pagesCapture-Based, Cell-Based and Tissue-Based SensorsNetra Agarkar100% (1)
- Algae NotesDocument20 pagesAlgae NotesDHARMARAj100% (2)
- Fbioe 08 599674Document16 pagesFbioe 08 599674Tanishka AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 13 E0007Document5 pages13 E0007sheraNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiotechnologyDocument40 pagesMolecular BiotechnologyBhaskar GangulyNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Branched Chain Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesBenefits of Branched Chain Amino AcidsparidhiNo ratings yet