ACA Interface Page 1 of 2
Administrator User Guide 12 Series
Chapter: Data Access Control (DAC)
ACA Interface
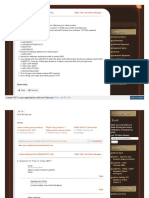
The ACA interface is split into a top and bottom panel and all data is clearly arranged under four distinct tabs
inside each panel. For more on working with panels, please refer to Copying, Moving and Assigning Elements.
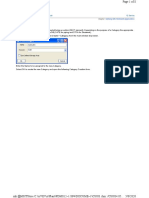
Click picture to enlarge
Figure 11:1. Overview of the ACA user interface
To work on data inside the top or bottom panel, click anywhere inside the panel. Click on any one of the four
tabs to make your selection:
• Users - shows Users along with ACRs and ACR groups, and Teams together with Users grouped under
these Teams,
• ACRs - shows all ACRs defined in the database along with assigned Scopes and Roles, and ACR
Groups,
• Scopes - shows all defined Scopes,
• Roles - shows all defined Roles with Perops belonging to those Roles.
For more information on the above terminology, please refer to Data Access Control (DAC).
The tabs are particularly beneficial as database information can be extensive and viewing everything inside a
single window can be unwieldy. With the help of tabs, it is possible to view elements of one particular ACR or
Scope inside its own dedicated tab; it is also convenient when making assignments between each element.
Each tab contains a tree structure consisting of nodes, where each node represents a database element.
Each node in turn displays children representing elements related to their parent.
The following types of database nodes found in the ACA:
• User - contains children of type ACR or ACR Group representing ACR elements assigned to the User,
• Team - contains children of type User representing Users involved in the Team,
• ACR - contains children of types Scope and Role representing assigned access control right elements,
• ACR Group - contains ACR nodes representing ACRs involved in the group,
• Scope - nodes of this type do not have any child nodes,
• Role - contains Perop nodes that the Role consists of,
• Perop - nodes of this type do not have any child nodes.
The above relationships between nodes are recursive. This means that when a Team node contains User
mk:@MSITStor[Link]\AVEVA\Plant\PDMS12~1.SP4\DOCUME~1\[Link]::/AUG12.1... 5/3/2020
�ACA Interface Page 2 of 2
nodes, those nodes in turn, have will have ACR nodes, which again contain Scopes and Roles etc.
The advantage of this approach is that you can see all access control elements connected with a specific
database element in one single view.
For example, it is possible to view complete information about access rights for a single User including all
assigned ACRs and ACR Groups with Scope and Role information along with Perop definitions, all in one
place.
Moreover, it is possible to edit this information, singly or collectively.
Copyright 1974 to current year. AVEVA Solutions Limited and its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
mk:@MSITStor[Link]\AVEVA\Plant\PDMS12~1.SP4\DOCUME~1\[Link]::/AUG12.1... 5/3/2020