Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Multiple Choice Questions
Uploaded by
Ramagya SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Multiple Choice Questions
Uploaded by
Ramagya SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.
com/
CHAPTER 13
Magnetic Effects of
Electric Current
Multiple Choice Questions
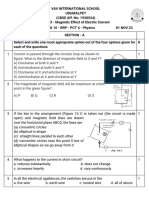
1. Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding
magnetic lines of field
(a) The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the
direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle
points
(b) Magnetic field lines are closed curves
(c) If magnetic field lines are parallel and
equidistant, they represent zero field strength
(d) Relative strength of magnetic field is shown by
the degree of closeness of the field lines
2. If the key in the arrangement (Figure 13.1) is taken
out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field
lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD,
the lines are
(a) concentric circles
(b) elliptical in shape
(c) straight lines parallel to each other
(d) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical
shapes as we go away from it
3. A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the
plane of paper carries a current when the key is ON.
The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane
of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anti clockwise
and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines
point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet
is on the face close to
(a) A (b) B
(c) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small and A if the current is large
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/ Courtesy : NCERT
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/
4. For a current in a long straight solenoid N- and S-poles are created
at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect
statement is
(a) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight
lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all
points inside the solenoid
(b) The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can
be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft
iron, when placed inside the coil
(c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid
is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a
bar magnet
(d) The N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of
current through the solenoid is reversed
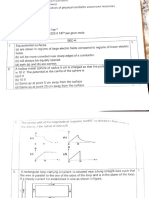
5. A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of
paper pointing from left to right as shown in
Figure 13.3. In the field an electron and a proton
move as shown. The electron and the proton
experience
(a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
(b) forces both pointing out of the plane of paper
(c) forces pointing into the plane of paper and
out of the plane of paper, respectively
(d) force pointing opposite and along the
direction of the uniform magnetic field
respectively
6. Commercial electric motors do not use
(a) an electromagnet to rotate the armature
(b) effectively large number of turns of conducting
wire in the current carrying coil
(c) a permanent magnet to rotate the armature
(d) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound
7. In the arrangement shown in Figure 13.4 there are
two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod.
Initially the key is not inserted. Then the key is
inserted and later removed. Then
(a) the deflection in the galvanometer remains zero
throughout
(b) there is a momentary deflection in the
galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is
no effect when the key is removed
98 E XEMPLAR PROBLEMS – SCIENCE
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/ Courtesy : NCERT
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/
(c) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out
shortly; the deflections are in the same direction
(d) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out
shortly; the deflections are in opposite directions
8. Choose the incorrect statement
(a) Fleming’s right-hand rule is a simple rule to know the direction
of induced current
(b) The right-hand thumb rule is used to find the direction of
magnetic fields due to current carrying conductors
(c) The difference between the direct and alternating currents is
that the direct current always flows in one direction, whereas
the alternating current reverses its direction periodically
1
(d) In India, the AC changes direction after every 50 second
9. A constant current flows in a horizontal wire in the plane of the
paper from east to west as shown in Figure 13.5. The direction
of magnetic field at a point will be North to South
(a) directly above the wire
(b) directly below the wire
(c) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the north side
of the wire
(d) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the south
side of the wire
10. The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying
straight solenoid is
(a) more at the ends than at the centre
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) same at all points
(d) found to increase from one end to the other
11. To convert an AC generator into DC generator
(a) split-ring type commutator must be used
(b) slip rings and brushes must be used
(c) a stronger magnetic field has to be used
(d) a rectangular wire loop has to be used
12. The most important safety method used for protecting home
appliances from short circuiting or overloading is
(a) earthing
(b) use of fuse
(c) use of stabilizers
(d) use of electric meter
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 99
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/ Courtesy : NCERT
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/
Short Answer Questions
13. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane of paper near
point A as shown in Figure 13.6. In which plane should a straight
current carrying conductor be placed so that it passes through A
and there is no change in the deflection of the compass? Under
what condition is the deflection maximum and why?
14. Under what conditions permanent electromagnet is obtained if a
current carrying solenoid is used? Support your answer with the
help of a labelled circuit diagram.
15. AB is a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as
shown in Figure 13.7. What are the directions of magnetic fields
produced by it at points P and Q? Given r1 > r2, where will the
strength of the magnetic field be larger?
16. A magnetic compass shows a deflection when placed near a
current carrying wire. How will the deflection of the compass get
affected if the current in the wire is increased? Support your
answer with a reason.
17. It is established that an electric current through a metallic
conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Is there a similar
magnetic field produced around a thin beam of moving (i) alpha
particles, (ii) neutrons? Justify your answer.
18. What does the direction of thumb indicate in the right-hand thumb
rule. In what way this rule is different from Fleming’s left-hand
rule?
19. Meena draws magnetic field lines of field close to the axis of a
current carrying circular loop. As she moves away from the centre
of the circular loop she observes that the lines keep on diverging.
How will you explain her observation.
20. What does the divergence of magnetic field lines near the ends of
a current carrying straight solenoid indicate?
21. Name four appliances wherein an electric motor, a rotating device
that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, is used as
an important component. In what respect motors are different
from generators?
22. What is the role of the two conducting stationary brushes in a
simple electric motor?
23. What is the difference between a direct current and an alternating
current? How many times does AC used in India change direction
in one second?
100 E XEMPLAR PROBLEMS – SCIENCE
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/ Courtesy : NCERT
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/
24. What is the role of fuse, used in series with any electrical
appliance? Why should a fuse with defined rating not be replaced
by one with a larger rating?
Long Answer Questions
25. Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing North and South
in the absence of a nearby magnet get deflected when a bar magnet
or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient
features of magnetic lines of field concept.
26. With the help of a labelled circuit diagram illustrate the pattern
of field lines of the magnetic field around a current carrying
straight long conducting wire. How is the right hand thumb rule
useful to find direction of magnetic field associated with a current
carrying conductor?
27. Explain with the help of a labelled diagram the distribution of
magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop. Why is it
that if a current carrying coil has n turns the field produced at
any point is n times as large as that produced by a single turn?
28. Describe the activity that shows that a current-carrying conductor
experiences a force perpendicular to its length and the external
magnetic field. How does Fleming’s left-hand rule help us to find
the direction of the force acting on the current carrying conductor?
29. Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a simple electric motor and
explain its working. In what way these simple electric motors are
diffferent from commercial motors?
30. Explain the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Describe
an experiment to show that a current is set up in a closed loop
when an external magnetic field passing through the loop
increases or decreases.
31. Describe the working of an AC generator with the help of a labelled
circuit diagram. What changes must be made in the arrangement
to convert it to a DC generator?
32. Draw an appropriate schematic diagram showing common
domestic circuits and discuss the importance of fuse. Why is it
that a burnt out fuse should be replaced by another fuse of
identical rating?
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 101
Downloaded From : http://cbseportal.com/ Courtesy : NCERT
You might also like
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current Multiple Choice QuestionsShishir AnandNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Exemplar Chapter 13Document5 pages10 Science Exemplar Chapter 13senjicsNo ratings yet
- Physics Magnetic EffectsDocument30 pagesPhysics Magnetic Effects12345678vbsNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 13Document15 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 13Utkrist ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Magnetic Effects of Current Exam Style SolutionDocument14 pagesCh13 Magnetic Effects of Current Exam Style SolutionRiyansh WarikooNo ratings yet
- MCQs Moving Charge and MagnetismDocument9 pagesMCQs Moving Charge and MagnetismnilusclassesNo ratings yet
- 10 Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument5 pages10 Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentKhushbu BarnwalNo ratings yet
- 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument20 pages13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 4 Ans - Ch.13 - 01 Nov 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 4 Ans - Ch.13 - 01 Nov 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- 4867935-CLASS 10 - SCIENCE - PHY - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT - WS WITH ANS. - SHYNIDocument7 pages4867935-CLASS 10 - SCIENCE - PHY - MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT - WS WITH ANS. - SHYNIEducation PointNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current DPP1Document5 pagesClass 10 Science MCQs Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current DPP1Paarth BansalNo ratings yet
- SG_Test3MCQ_64ac8bc86f1720.64ac8bcaa19898.54250131Document34 pagesSG_Test3MCQ_64ac8bc86f1720.64ac8bcaa19898.54250131390108263No ratings yet
- DPP - Magnetic Effects of Electricity Current (Prashant Kirad)Document11 pagesDPP - Magnetic Effects of Electricity Current (Prashant Kirad)superherosunny13No ratings yet
- TB_Test3MCQ_64ac8bb425db33.64ac8bb6501d86.10150019Document33 pagesTB_Test3MCQ_64ac8bb425db33.64ac8bb6501d86.10150019390108263No ratings yet
- Module Test (MT 02) Class - X: "Project Abhyudaya"Document13 pagesModule Test (MT 02) Class - X: "Project Abhyudaya"Tarun SoniNo ratings yet
- 4 - Moving Charges & MagnetismDocument15 pages4 - Moving Charges & MagnetismAawesh BackupsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current - Practice SheetDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current - Practice Sheetanchalnagori807No ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH - 04Document5 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH - 04Arunima SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document30 pagesCH 4terasaini77No ratings yet
- QP - PreBoard - 1 - PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP - PreBoard - 1 - PhysicsABHIK THE GHOULNo ratings yet
- Magnets & Moving Charges: Chapter 4 & 5 ReviewDocument2 pagesMagnets & Moving Charges: Chapter 4 & 5 ReviewHarishankar SNo ratings yet
- 10 Questions MagneticDocument13 pages10 Questions Magneticanupam9932642No ratings yet
- Class X Physics - Magnetism QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass X Physics - Magnetism Questionsavp sNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions 2022-23Document34 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions 2022-23Rohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- 10 Science TP 13 1Document7 pages10 Science TP 13 1KSP Classes GondiaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board MS PHY CLASS X 2022Document8 pagesPre Board MS PHY CLASS X 2022Anugrah Kumar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentHarsh JuyalNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics MCQs (CH 4) NCRTDocument5 pages12th Physics MCQs (CH 4) NCRTRock StudiesNo ratings yet
- CH-6Document11 pagesCH-6terasaini77No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Lesson: Magnetic Fields and InductionDocument11 pagesElectromagnetism Lesson: Magnetic Fields and InductionqueenjoseNo ratings yet
- CH13 Magnetism WSDocument5 pagesCH13 Magnetism WSViswasNo ratings yet
- Udgam School For Children: SUBJECT: Science Worksheet CH-13Document10 pagesUdgam School For Children: SUBJECT: Science Worksheet CH-13YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument5 pagesMagnetismstrips25042001No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism - DPP 03 (Of Lec 04) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)Document3 pagesElectromagnetism - DPP 03 (Of Lec 04) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)pragnakrishnan5No ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 4 CASE STUDY Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument17 pagesPhysics XII CH 4 CASE STUDY Moving Charges and MagnetismNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- M1 TESTDocument3 pagesM1 TESTsehajpahwa0009No ratings yet
- 50Q - Electromagnetic InductionDocument10 pages50Q - Electromagnetic InductionshobhasunilsinghNo ratings yet
- Ripical Test 2 (Magnetism) NNNDocument2 pagesRipical Test 2 (Magnetism) NNNYousef AminNo ratings yet
- 2021 P For Kjrrent - Magnetism - Chapter - TestDocument6 pages2021 P For Kjrrent - Magnetism - Chapter - TestRSNo ratings yet
- WS1 - Reinforcement - Magnetic EffectsDocument2 pagesWS1 - Reinforcement - Magnetic EffectsOshin TiwariNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics MCQs (CH 6) NCRTDocument6 pages12th Physics MCQs (CH 6) NCRTRock StudiesNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Sahodaya Schools Complex Pre Board Examination 2021 Grade 12 (SET-1) (Subject: PhysicsDocument7 pagesBangalore Sahodaya Schools Complex Pre Board Examination 2021 Grade 12 (SET-1) (Subject: PhysicsTPG CLANNo ratings yet
- CBSE- magnetic effects of electric current-Document5 pagesCBSE- magnetic effects of electric current-sera anilNo ratings yet
- Document - 2023-09-03 - 150327 (2 Files Merged)Document2 pagesDocument - 2023-09-03 - 150327 (2 Files Merged)Gagan .SNo ratings yet
- CBSE-Class-10-Science MCQ Magnetic-Effects-of-Electric-CurrentDocument8 pagesCBSE-Class-10-Science MCQ Magnetic-Effects-of-Electric-CurrentManisha KanawadeNo ratings yet
- Case Study CH 4 12thDocument9 pagesCase Study CH 4 12thmanish bhatNo ratings yet
- Summary and Review of ElectromagentismDocument3 pagesSummary and Review of ElectromagentismterrylimNo ratings yet
- Agnetic Effects of CurrentDocument3 pagesAgnetic Effects of CurrentNaveen ShankarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism MCQDocument14 pagesElectromagnetism MCQHira FiazNo ratings yet
- 6502f6725f8c830018c5d3ba - ## - Magnetic Effect of Current & EMI 12 Theory Notes PDF OnlyDocument18 pages6502f6725f8c830018c5d3ba - ## - Magnetic Effect of Current & EMI 12 Theory Notes PDF Onlyanubhav79068No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electricity QB PDFDocument17 pagesMagnetism and Electricity QB PDFGopa BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism ExerciseDocument44 pagesMagnetism ExerciseChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentMohan SuyalNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 4 MCQ Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument12 pagesPhysics XII CH 4 MCQ Moving Charges and MagnetismM SNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Sahodaya Schools Complex Pre Board Examination 2021 Grade 12 (SET-2) Subject: PhysicsDocument8 pagesBangalore Sahodaya Schools Complex Pre Board Examination 2021 Grade 12 (SET-2) Subject: Physicsdick kumarNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Law - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument4 pagesKirchhoff's Law - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismCristian Camilo Ostos CharryNo ratings yet
- Magnetism To Transformer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)Document10 pagesMagnetism To Transformer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)6C09 FUNG CHI LAMNo ratings yet
- THE MIDNIGHT VISITOR'S QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesTHE MIDNIGHT VISITOR'S QUESTIONSRamagya Singh100% (1)
- Two Stories About Flying 1 RTC PDFDocument2 pagesTwo Stories About Flying 1 RTC PDFRamagya SinghNo ratings yet
- The Ball Poem Practice QsDocument2 pagesThe Ball Poem Practice QsRamagya SinghNo ratings yet
- The Thief's Story PB QsDocument1 pageThe Thief's Story PB QsRamagya SinghNo ratings yet
- RTC His First Flight AnswerDocument3 pagesRTC His First Flight AnswerRamagya SinghNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesElectricity: Multiple Choice QuestionsRamagya SinghNo ratings yet
- Cable Specification P S REV 04Document81 pagesCable Specification P S REV 04Ramagya Singh100% (1)
- HVCatalogueLowRes PDFDocument38 pagesHVCatalogueLowRes PDFMahmoud GwailyNo ratings yet
- ETR Part A Course FrameworkDocument13 pagesETR Part A Course Frameworkkenneth dancesNo ratings yet
- Bhel Block 3Document35 pagesBhel Block 3Aditya Aggarwal62% (13)
- Ac Generators: Compiled and Presented by Doren NedrickDocument20 pagesAc Generators: Compiled and Presented by Doren Nedrickadamwaiz100% (1)
- DCMT - Set 4 GR14 SuppleDocument2 pagesDCMT - Set 4 GR14 SuppleP Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Diseases of The Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat (1912)Document618 pagesElectricity in Diseases of The Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat (1912)JamesNo ratings yet
- IgnitionDocument64 pagesIgnitionKarthigaiselvan Shanmuganathan100% (6)
- 8MAN100072-0001 A en Technical Description Onboard DC Grid™ System Sales PDFDocument30 pages8MAN100072-0001 A en Technical Description Onboard DC Grid™ System Sales PDFStefanitaNo ratings yet
- Electric Generator - WikipediaDocument16 pagesElectric Generator - WikipediaPye PhyoNo ratings yet
- Summary Form 3Document26 pagesSummary Form 3Prakkash RajanNo ratings yet
- Lorentz Psk2 Cs FDocument51 pagesLorentz Psk2 Cs FSINES France100% (1)
- IEEE Standard ListDocument18 pagesIEEE Standard ListanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current ExplainedDocument13 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current ExplainedMai ka ChachaNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram Dse 7320 Amf PDF FreeDocument1 pageWiring Diagram Dse 7320 Amf PDF FreeSemih GençNo ratings yet
- The Design of A Test Rig and Study of The Performance and Efficiency of A Tesla Disc TurbineDocument15 pagesThe Design of A Test Rig and Study of The Performance and Efficiency of A Tesla Disc Turbinearturo ortegaNo ratings yet
- BHELDocument20 pagesBHELRaghavendra SattigeriNo ratings yet
- Experiment Validation of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Control System Based On Wind Energy Utilization Coefficient CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesExperiment Validation of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Control System Based On Wind Energy Utilization Coefficient CharacteristicsErick Lettra de MouraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power System Simulator For EngineeringDocument1,048 pagesIntroduction To Power System Simulator For Engineeringpirindola123No ratings yet
- Gulfstream g150 Pilot Training Manual Volume 2 Aircraft Syst PDFDocument474 pagesGulfstream g150 Pilot Training Manual Volume 2 Aircraft Syst PDFrubenaris100% (3)
- Physics On The Guitar - Jim Overhiser & Luke Donev PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics On The Guitar - Jim Overhiser & Luke Donev PDFValter DiasNo ratings yet
- BERSABAL, CEGROW BER - EE 435AL (6535) 1st Exam, 2020-2021Document3 pagesBERSABAL, CEGROW BER - EE 435AL (6535) 1st Exam, 2020-2021Cegrow Ber BersabalNo ratings yet
- ModelsDocument716 pagesModelsshyamda100% (2)
- CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Machinery Principles: EE321 Electrical Machines 1 Notes For Chapter 1Document27 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Machinery Principles: EE321 Electrical Machines 1 Notes For Chapter 1Rehan SadiqNo ratings yet
- MepDocument3 pagesMephsWSNo ratings yet
- Avr Conversion InstructionsDocument2 pagesAvr Conversion InstructionsJose PirulliNo ratings yet
- Time-Domain Models For Power System Stability and UnbalanceDocument135 pagesTime-Domain Models For Power System Stability and UnbalanceDanielAlejandroRamosQueroNo ratings yet
- Power On The Move: Portable GeneratorsDocument12 pagesPower On The Move: Portable GeneratorsElisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- Bidding Documents for Laboratory EquipmentDocument22 pagesBidding Documents for Laboratory EquipmentRavid YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Generator PM ChecklistDocument2 pagesGenerator PM ChecklistYan's Senora Bescoro100% (3)
- Literature Review On Vertical Axis Wind TurbineDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Vertical Axis Wind Turbineaflsodoam100% (1)
- Ee 6604 Design of Electrical Machines Question BankDocument12 pagesEe 6604 Design of Electrical Machines Question BankAlex Neo XanderNo ratings yet