Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale
Uploaded by
Joshua Villarba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesOriginal Title
Pneumothorax NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesPrioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale
Uploaded by
Joshua VillarbaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
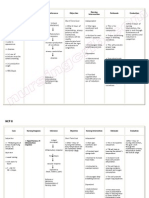
PRIORITIZED NURSING PROBLEM FOR PNEUMOTHORAX
Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale
Ineffective breathing Independent
pattern related to 1. Elevate head of bed as Facilitates lung expansion and
airway obstruction permitted and position on ventilation, and reduces risk of
secondary to sides, as indicated. airway obstruction by tongue.
Pneumothorax. Upright position allows increased
diaphragmatic excursion secondary
to downward shift of internal
organs from gravity.
2. Encourage deep breathing if Inhaling through nose allows air to
client is conscious be filtered, warmed and humidified.
3. Monitor rate, rhythm, and Changes may indicate onset of
depth of respiration. Note pulmonary complications.
breathing irregularities, for Deviations may also suggest
example, apneustic, ataxic, or respiratory problems if neglected
cluster breathing. could worsen patient’s state of
health.
4. Note competence of gag and Ability to mobilize or clear
swallow reflexes and client’s secretions is important to airway
ability to protect own airway. maintenance. Loss of swallow or
cough reflex may indicate need for
artificial airway or intubation.
5. Auscultate breath sounds, Identifies pulmonary problems
noting areas of such as atelectasis, congestion, and
hypoventilation and presence airway obstruction, which may
of adventitious sounds. jeopardize cerebral oxygenation.
Breath sounds may be diminished
or absent in a lobe, lung segment,
or entire lung field (unilateral).
Atelectatic area will have no breath
sounds, and partially collapsed
areas have decreased sounds.
6. Instruct the patient to avoid Consuming gas forming foods can
over-eating and gas forming cause bloating and discomfort by
foods. pushing on the diaphragm, making
it difficult and uncomfortable to
breathe.
7. Maintain calm attitude while To promote good environment
dealing with the patient. necessary to improve patient’s
health. Assists patient to deal with
the physiological effects of
hypoxia, which may be manifested
as anxiety and/or fear.
Dependent
To follow patient’s therapeutic
8. Administer pain killer
regimen to stabilize her wellness of
/sedative/ antipyretic as
health.
prescribed by the doctor
CTT maintains prescribed
intrapleural negativity, which
Collaborative
promotes optimum lung expansions
9. Assist in reclogging of the and fluid drainage.
Chest tube thoracostomy
Monitors progress of resolving
pneumothorax and re-expansion of
lung. Can identify malposition of
10. Review serial chest x-rays. endotracheal tube (ET) affecting
lung re-expansion.
Aids in reducing work of breathing;
promotes relief of respiratory
distress and cyanosis associated
with hypoxemia.
11. Administer supplemental
oxygen via
cannula/mask/mechanical
ventilation as indicated.
References:
https://nurseslabs.com/pneu
mothorax/
https://nurseslabs.com/3-
hemothoraxpneumothorax-
nursing-care-plans/
https://www.coursehero.co
m/file/39940631/nursing-
care-plan-
pneumothoraxpdf/
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan - Pneumothorax PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Pneumothorax PDFJanine Joy Orpilla76% (25)
- Inside The Living BodyDocument9 pagesInside The Living BodySteve Marville Aguinaldo70% (10)
- Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsDocument1 pagePneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsJoshua Villarba80% (5)
- Dynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization TechniquesDocument20 pagesDynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization TechniquesAnanda Kartika P.100% (3)
- Emt National Practice ExamDocument42 pagesEmt National Practice Examdebbiemedic3557100% (12)
- Impaired Liver FunctionDocument1 pageImpaired Liver FunctionShop Dzubiri Here75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation - NCPDocument5 pagesOxygenation - NCPCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Document2 pagesNcp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce67% (3)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- 1 Bagua and The Sixteen NeigongDocument45 pages1 Bagua and The Sixteen Neigongredpete1100% (5)
- Introduction To Tantric MeditationDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Tantric MeditationJelena VukicevicNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215No ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Sample NCPDocument1 pageSample NCPemrith100% (5)
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans in 40 CharactersDocument1 pagePneumonia Nursing Care Plans in 40 Charactersjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP LocDocument2 pagesNCP LocMel RodolfoNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJezza RequilmeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanMiguelito Galagar GultianoNo ratings yet
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation for Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNcp-Ineffective Airway Clearancelouanne0550% (2)
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesNo ratings yet
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Managing Anxiety After Heart AttackDocument6 pagesManaging Anxiety After Heart AttackRen VillenaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion FdarDocument1 pagePleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraNo ratings yet
- Impaired mobility assessmentDocument2 pagesImpaired mobility assessmentVhin Lim100% (2)
- Multiodular non toxic goiter nursing care planDocument1 pageMultiodular non toxic goiter nursing care plankzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizNo ratings yet
- NCP AfDocument3 pagesNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotNo ratings yet
- Assessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As VerbalizedDocument2 pagesAssessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalizedmayla_jordan3666No ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCP Increased IcpDocument2 pagesNCP Increased IcphelloaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Assessment, Interventions & OutcomesDocument1 pagePneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Assessment, Interventions & Outcomesjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document2 pagesCourse Task 3Geraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Ventilatory Assistance MechanicalDocument18 pagesVentilatory Assistance Mechanicalmardsz100% (5)
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument34 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsMenard Velasco100% (1)
- Airway ManagementDocument11 pagesAirway Managementmegayani santosoNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument33 pagesPneumothoraxjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Blood Pleural EffusionDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plans: Blood Pleural Effusionjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumonitisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for PneumonitisYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document1 pageCourse Task 3Jurielyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Cancer Cancer LungsDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plans: Cancer Cancer Lungsjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Assessment and Care PlanDocument7 pagesPneumonia Assessment and Care PlanAkun NyampahNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Lec Course Task CU3Document2 pagesNCMB 312 Lec Course Task CU3Mushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- MS CourseTask8Document3 pagesMS CourseTask8Aria100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure: EtiologyDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: EtiologyJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Acute Bacterial Sinusitis Pathophysiology: Obstruction of Sinus OstiaDocument1 pageAcute Bacterial Sinusitis Pathophysiology: Obstruction of Sinus OstiaJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Prioritized Nursing For Problem For Rheumatic Fever Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument3 pagesPrioritized Nursing For Problem For Rheumatic Fever Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Concept Map PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesTuberculosis Concept Map PathophysiologyJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Prioritized Nursing for Bacterial Infection ProblemsDocument2 pagesPrioritized Nursing for Bacterial Infection ProblemsJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Assignment in MHCNDocument7 pagesAssignment in MHCNJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Patient Education on Anemia and Iron-Rich FoodsDocument3 pagesPatient Education on Anemia and Iron-Rich FoodsJoshua Villarba100% (2)
- A Case Presentation: Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesA Case Presentation: Ectopic PregnancyJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- 5 Doh ProgramsDocument3 pages5 Doh ProgramsJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Social functions of artworksDocument1 pageSocial functions of artworksJoshua Villarba83% (30)
- Gestational DiabetesDocument3 pagesGestational DiabetesJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Route and Site of Administration: Age of The ChildDocument2 pagesRoute and Site of Administration: Age of The ChildJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Drug ManualDocument1 pageDrug ManualJoshua VillarbaNo ratings yet
- LabDocument6 pagesLabapi-462581208No ratings yet
- Simultaneous Measurements of Pressure, Flow and Sound During Trumpet PlayingDocument7 pagesSimultaneous Measurements of Pressure, Flow and Sound During Trumpet PlayingSzymon ŚledzińskiNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Bellavista Icu Complete 2021Document3 pagesSpesifikasi Bellavista Icu Complete 2021Ervan FutrantoNo ratings yet
- Medif Information Sheet For Passengers Requiring Medical Clearence - Part 1-2 - Tarom From 4122 - 2Document2 pagesMedif Information Sheet For Passengers Requiring Medical Clearence - Part 1-2 - Tarom From 4122 - 2ViolleteMorenaNo ratings yet
- A2 BIOLOGY CORE PRACTICAL SUMMARYDocument3 pagesA2 BIOLOGY CORE PRACTICAL SUMMARYSQ100% (2)
- Consciously Controlled Breathing RubricDocument3 pagesConsciously Controlled Breathing RubricEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument79 pagesControlDavidou15100% (2)
- Voice Therapy For The Professional VoiceDocument17 pagesVoice Therapy For The Professional Voiceapi-19500641100% (5)
- Rtho Ind: Nemir AdjinaDocument46 pagesRtho Ind: Nemir AdjinaNemir AdjinaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Respiratory SystemDocument52 pagesDrugs Acting On Respiratory SystemIrwan M. Iskober100% (4)
- Asthma Management Tips for Congestion TypeDocument57 pagesAsthma Management Tips for Congestion TypeRahulsinghoooo100% (1)
- COPD and Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument138 pagesCOPD and Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentMonique Reyes0% (1)
- Science Grade 9 Learning MaterialsDocument417 pagesScience Grade 9 Learning Materialsnorthernsamar.jbbinamera01No ratings yet
- Borax MsdsDocument5 pagesBorax MsdsBlue Ofo-ob TJNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPDocument12 pagesGas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPtanishqa bhujbalNo ratings yet
- NREMT Study Guide ProjectDocument12 pagesNREMT Study Guide ProjectGabriel SionsNo ratings yet
- How Chakras Interact with the Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesHow Chakras Interact with the Endocrine SystemNalini Muniyendi100% (2)
- Material Safety Data Sheet For Hobas PipeDocument3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet For Hobas Pipejunhe898No ratings yet
- Share the World's Leading Anesthesia MachineDocument6 pagesShare the World's Leading Anesthesia MachineSurta DevianaNo ratings yet
- Youth Impacted by Rising Pollution EssayDocument8 pagesYouth Impacted by Rising Pollution EssayGajalakshmi KumaresanNo ratings yet
- The Food and Supplement Guide For The Coronavirus Version 7Document59 pagesThe Food and Supplement Guide For The Coronavirus Version 7alexpla37No ratings yet
- Have You Known Love?Document4 pagesHave You Known Love?Raana KhanNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument41 pagesCOPDsanalcrazy100% (3)
- 2nd Puc Biology Reasoning Questions ZoologyDocument4 pages2nd Puc Biology Reasoning Questions ZoologynomanNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness ACBT and PLBT breathing techniques increase COPD oxygen levelsDocument4 pagesEffectiveness ACBT and PLBT breathing techniques increase COPD oxygen levelsI Putu Yoga PrasetyaNo ratings yet