Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonitis
Uploaded by
Yuvi Rociandel LUARDOOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonitis
Uploaded by
Yuvi Rociandel LUARDOCopyright:
Available Formats
MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Level II AACUP Accredited
Student Name: Level:
Group:
PNEUMONITIS
NURSING CARE PLAN
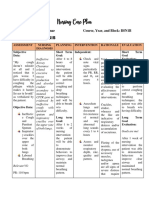
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Airway Clearance
Expected Outcomes:
Short Term Objective:
Within 8 hours of comprehensive nursing interventions, the patient will be able to
identify/demonstrate behaviors to achieve airway clearance.
Long Term Objective:
Within 3 days of comprehensive nursing interventions, the patient will be able to
display/maintain a clear airway with breath sounds clearing; absence of dyspnea, cyanosis,
as evidenced by keeping a patent airway and effectively clearing secretions.
Signs and Symptoms:
● Changes in rate, depth of respirations
● Abnormal breath sounds (rhonchi, bronchial lung sounds, egophony)
● Use of accessory muscles
● Dyspnea, tachypnea
● Cough, effective or ineffective; with/without sputum production
● Cyanosis
● Decreased breath sounds over affected lung areas
● Ineffective cough
● Purulent sputum
● Hypoxemia
● Infiltrates seen on chest x-ray film
Interventions Rationale Evaluation
1. Assess the rate, Altered breathing Short Term:
rhythm, and depth of patterns may occur
MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Level II AACUP Accredited
respiration, chest together with accessory Goal met. Within 8 hours of
movement, and use of muscles to increase comprehensive nursing
accessory muscles. chest excursion to interventions, the patient was able
facilitate effective to identify/demonstrate behaviors to
breathing. achieve airway clearance.
Long Term:
2. Assess cough Coughing is the most
effectiveness and effective way to remove Goal met. Within 3 days of
productivity secretions. comprehensive nursing
interventions, the patient was able
3. Auscultate lung fields, Decreased airflow occurs to display/maintain a clear airway
noting areas of in areas with with breath sounds clearing;
decreased or absent consolidated fluid. absence of dyspnea, cyanosis, as
airflow and adventitious Bronchial breath sounds evidenced by keeping a patent
breath sounds: crackles, can also occur in these airway and effectively clearing
wheezes. consolidated areas. secretions.
Crackles, rhonchi, and
wheezes are heard on
inspiration and/or
expiration due to fluid
accumulation, thick
secretions, and airway
spasms and obstruction.
4. Observe the sputum Changes in sputum
color, viscosity, and odor. characteristics may
Report changes. indicate infection.
5. Assess the patient’s Airway clearance is
hydration status. hindered with inadequate
hydration and thickening
of secretions.
6. Elevate the head of the Doing so would lower
bed, change position the diaphragm and
frequently. promote chest
MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Level II AACUP Accredited
expansion, aeration of
lung segments,
mobilization, and
expectoration of
secretions.
7. Teach and assist the Deep breathing
patient with proper deep- exercises facilitates
breathing exercises. maximum expansion of
the lungs and smaller
airways, and improves
the productivity of
cough.
8. Suction as indicated: Stimulates cough or
frequent coughing, mechanically clears
adventitious breath airway in a patient who
sounds, desaturation cannot do so because of
related to airway ineffective cough or
secretions. decreased level of
consciousness.
9. Maintain adequate Fluids, especially warm
hydration by forcing liquids, aid in the
fluids to at least 3000 mobilization and
mL/day unless expectoration of
contraindicated. secretions. It helps
maintain hydration and
increases ciliary action to
remove secretions, and
reduces the viscosity of
secretions.
10. Monitor serial chest Follows progress and
x-rays, ABGs, pulse effects and extent of
oximetry readings. pneumonia.
You might also like
- NCMB 312 Lec Course Task CU3Document2 pagesNCMB 312 Lec Course Task CU3Mushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanDenise Garcia MolinaNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document1 pageCourse Task 3Jurielyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention Diagnose 1 Purpose and Criteria Results Intervention Rational NIC Labels Respiratory MonitoringDocument10 pagesNursing Intervention Diagnose 1 Purpose and Criteria Results Intervention Rational NIC Labels Respiratory MonitoringFhicholy Davied VanrioNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument33 pagesPneumothoraxjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 3Document2 pagesWeek 3 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 302 - DIMAYUGA, BRYANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceEricka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - MS1 COURSE TASK - CU 3Document2 pagesWeek 3 - MS1 COURSE TASK - CU 302 - DIMAYUGA, BRYANNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document2 pagesCourse Task 3Geraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Chona NCP 1Document5 pagesChona NCP 1Jan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Effective Airway Clearance Nursing DiagnosisDocument30 pagesEffective Airway Clearance Nursing DiagnosisReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- Bukidnon State University: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument1 pageBukidnon State University: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermSimbo Ralph JulesNo ratings yet
- Intervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixDocument5 pagesIntervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixRizki ArifNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- CT3, Obstructive Lung DisordersDocument3 pagesCT3, Obstructive Lung DisordersAlondra VelascoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPRuth MontebonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientMG CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument34 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsMenard Velasco100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Assisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingDocument3 pagesAssisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document1 pageNursing Care Plan 2JOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Promoting Effective Breathing and Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesPromoting Effective Breathing and Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- NCP Room 303 TelarmaDocument2 pagesNCP Room 303 TelarmaasdasdNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care PlanElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Task NCPDocument12 pagesTask NCPferdy ilhamNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions - RespiratoryDocument4 pagesNursing Interventions - Respiratorymanager.intelligentsolutionsNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataNo ratings yet
- NCP (Baluyot Jason Lee) Group17Document3 pagesNCP (Baluyot Jason Lee) Group17Jasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 pagesNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- Bronchial Asthma (Parinas Rhoanne)Document10 pagesBronchial Asthma (Parinas Rhoanne)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- DULNUANDocument2 pagesDULNUANJB tindonganNo ratings yet
- Improving airway clearance and managing activity intoleranceDocument2 pagesImproving airway clearance and managing activity intoleranceAva VierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care Planalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Holy Name University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Tagbilaran City, BoholDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Holy Name University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Tagbilaran City, BoholAllison CrookeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- Assess The Rate, Rhythm, and Depth of Respiration, Chest Movement, and Use of Accessory MusclesDocument4 pagesAssess The Rate, Rhythm, and Depth of Respiration, Chest Movement, and Use of Accessory MusclesjkfgNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToFrudz OrjalezaNo ratings yet
- Checklist Using Nasopharengeal and Oropharengeal SuctioningDocument4 pagesChecklist Using Nasopharengeal and Oropharengeal SuctioningKristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy Benefits and SafetyDocument5 pagesOxygen Therapy Benefits and SafetyZamora HazelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Funda Notes Nca MidtermDocument9 pagesFunda Notes Nca MidtermAICEL A. ABILNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument3 pagesSeptic ShockYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for SIADHDocument5 pagesNursing care plan for SIADHYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Cancer PreventionDocument1 pageActivity 6 - Cancer PreventionYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Activity 7 - Diagnostics and LaboratoryDocument1 pageActivity 7 - Diagnostics and LaboratoryYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Activity 5 - Cellular AberrationDocument2 pagesActivity 5 - Cellular AberrationYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Cancer PreventionDocument1 pageActivity 6 - Cancer PreventionYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Cancer ActivityDocument1 pageActivity 4 - Cancer ActivityYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - MVGO ACTIVITYDocument1 pageActivity 1 - MVGO ACTIVITYYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideDocument7 pagesAP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideVal HathiramaniNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology-IiDocument19 pagesI. Objectives:: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology-IiMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesRespiratory System - Print - QuizizzosamaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Identify The Key Parts of The Breathing System Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Identify The Key Parts of The Breathing System Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolNo ratings yet
- t3 SC 307 ks3 Gas Exchange Homework Activity Sheet - Ver - 2 PDFDocument4 pagest3 SC 307 ks3 Gas Exchange Homework Activity Sheet - Ver - 2 PDFMahima JNo ratings yet
- The Microscopic Structure and Functions of the Respiratory SystemDocument67 pagesThe Microscopic Structure and Functions of the Respiratory SystemADE DWINATA SUSILO PUTRINo ratings yet
- S8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestDocument2 pagesS8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestWilliam Anthony56% (9)
- Science 9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory and Circulatory System Ver FinalDocument33 pagesScience 9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory and Circulatory System Ver FinalNoah SmithNo ratings yet
- Y8 RespirationDocument26 pagesY8 RespirationJohan Sukweenadhi100% (3)
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument3 pages8c Summary SheetsAreeba Inam Rao80% (5)
- Chapter-6-Rescue Apparatus and Rescue OperationsDocument13 pagesChapter-6-Rescue Apparatus and Rescue OperationsFaizal Anwar KhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular EnergyDocument3 pagesCellular EnergyEvelyn KimNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Parts of The Upper Respiratory TractDocument2 pagesRespiratory System: Parts of The Upper Respiratory TractGRascia OnaNo ratings yet
- Copd Copd: What Is COPD? Risk FactorsDocument1 pageCopd Copd: What Is COPD? Risk FactorsSirikit MaddelaNo ratings yet
- Respi ReviewerDocument5 pagesRespi ReviewerDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument31 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseIVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- Hypoxia: Moderator: DR Meera Balasubramanyam Professor Dept of Anaesthesiology MMCRI Speaker: DR Nandhini.K.S.KaratDocument65 pagesHypoxia: Moderator: DR Meera Balasubramanyam Professor Dept of Anaesthesiology MMCRI Speaker: DR Nandhini.K.S.KaratAnn Susan MathewNo ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument63 pagesSpirometryAries DocNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument34 pagesRespiration in PlantsPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Mechanical VentilationDocument34 pagesBasic Principles of Mechanical VentilationMohamed KorieshNo ratings yet
- Scan 17-Nov-2021Document6 pagesScan 17-Nov-2021Savita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chest RetractionDocument11 pagesChest RetractionJURY LEIGH SALUQUENNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesSUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Respiratory FunctionDocument6 pagesDisturbances in Respiratory FunctionSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Child Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Child Respiratory Systemmanju talluriNo ratings yet
- ArdsDocument53 pagesArdsSophy Sony100% (3)
- Icu Initial Ventilator SettingsDocument40 pagesIcu Initial Ventilator SettingsantreaspetsasNo ratings yet
- UCSD Internal Medicine Handbook 2011Document142 pagesUCSD Internal Medicine Handbook 2011ak100007100% (5)
- IndianJAnaesth602137-1073061 025850Document3 pagesIndianJAnaesth602137-1073061 025850ramukolakiNo ratings yet