Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Indian Constitution
Uploaded by
Suman Sahu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThe Indian Constitution is the world's longest written constitution containing 395 articles and 8 schedules. It was passed on November 26, 1949 by the Constituent Assembly and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution draws from Western legal traditions like liberal democracy, a British parliamentary system, and fundamental rights inspired by the US Bill of Rights. India has a federal system with residual powers held by the central government similar to systems in Canada, Australia, and Ireland. The constitution can be amended through a process requiring two-thirds majority votes in both houses of parliament.
Original Description:
Original Title
introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Indian Constitution is the world's longest written constitution containing 395 articles and 8 schedules. It was passed on November 26, 1949 by the Constituent Assembly and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution draws from Western legal traditions like liberal democracy, a British parliamentary system, and fundamental rights inspired by the US Bill of Rights. India has a federal system with residual powers held by the central government similar to systems in Canada, Australia, and Ireland. The constitution can be amended through a process requiring two-thirds majority votes in both houses of parliament.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesIntroduction To Indian Constitution
Uploaded by
Suman SahuThe Indian Constitution is the world's longest written constitution containing 395 articles and 8 schedules. It was passed on November 26, 1949 by the Constituent Assembly and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution draws from Western legal traditions like liberal democracy, a British parliamentary system, and fundamental rights inspired by the US Bill of Rights. India has a federal system with residual powers held by the central government similar to systems in Canada, Australia, and Ireland. The constitution can be amended through a process requiring two-thirds majority votes in both houses of parliament.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Introduction to Indian Constitution
The Constitution of India is the world's lengthiest
written constitution with 395 articles and 8 schedules. It contains
the good points taken from the constitution's of many countries in the
world. It was passed on 26 Nov 1949 by the 'The Constituent
Assembly' and is fully applicable since 26 Jan 1950. The Constituent
Assembly had been elected for undivided India and held its first
sitting on 9th Dec.1946, re-assembled on the 14th August 1947, as The
Sovereign Constituent Assembly for the dominion of India. In regard
to its composition the members were elected by indirect election by
the members of The Provisional Legislative Assemblies (lower house
only). At the time of signing 284 out of 299 members of the Assembly
were present.
The constitution of India draws extensively from Western legal
traditions in its outline of the principles of liberal democracy. It
follows a British parliamentary pattern with a lower and upper house.
It embodies someFundamental Rights which are similar to the Bill of
Rights declared by the United States constitution. It also borrows the
concept of a Supreme Court from the US.
India is a federal system in which residual powers of legislation remain
with the central government, similar to that in Canada. The
constitution provides detailed lists dividing up powers between central
and state governments as in Australia, and it elaborates a set of
Directive Principles of State Policy as does the Irishconstitution.
The constitution has provision for Schedules to be added to the
constitution by amendment. The ten schedules in force cover the
designations of the states and union territories; the emoluments for
high-level officials; forms of oaths; allocation of the number of seats
in the Rajya Sabha. A review of the constitutionneeds at least two-
thirds of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha to pass it.
The Indian constitution is one of the most frequently amended
constitutions in the world. Infact the firstamendment to it was passed
after only a year of the adoption of the constitution and instituted
numerous minor changes. Many more amendments followed, a rate of
almost two amendments per year since 1950. Most of the
constitution can be amended after a quorum of more than half of the
members of each house in Parliament passes an amendment with a two-
thirds majority vote. Articles pertaining to the distribution of
legislative authority between the central and state governments must
also be approved by 50 percent of the state legislatures.
You might also like
- Session 4 (Alternative and Other Circumstances)Document3 pagesSession 4 (Alternative and Other Circumstances)Noel Ephraim Antigua100% (1)
- Constitution of IndiaDocument24 pagesConstitution of IndiajnturajNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Indian Constitutional Scheme With That of Other Countries by BHASKAR JYOTIDocument10 pagesComparison of The Indian Constitutional Scheme With That of Other Countries by BHASKAR JYOTIJaiGanesh100% (1)
- Al-Ameen College of Law: Important Question With Answers December - 2018Document67 pagesAl-Ameen College of Law: Important Question With Answers December - 2018rohanNo ratings yet
- Define and Explain The Meaning of CONSTITUTIONDocument24 pagesDefine and Explain The Meaning of CONSTITUTIONImran PathanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Indian Constitutional Scheme With That of Other CountriesDocument26 pagesComparison of The Indian Constitutional Scheme With That of Other CountriesbhuneeNo ratings yet
- Al-Ameen College of Law: Important Question With Answers DECEMBER - 2018Document67 pagesAl-Ameen College of Law: Important Question With Answers DECEMBER - 2018GïŘï Yadav Rastha100% (3)
- Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument5 pagesSalient Features of Indian ConstitutionShreya Ghosh Dastidar100% (1)
- The 1987 Constitution The Constitution of The Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesThe 1987 Constitution The Constitution of The Republic of The PhilippinesHardy Allen Leviste VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis Template 22Document17 pagesRisk Analysis Template 22Abobakr ElomdaNo ratings yet
- Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument11 pagesFeatures of Indian ConstitutionMamatha RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- AHB Hong KongDocument46 pagesAHB Hong KongPraveen SankaranNo ratings yet
- The 1973 Constitution of Pakistan Was Adopted On April 12Document11 pagesThe 1973 Constitution of Pakistan Was Adopted On April 12Sheraz AliNo ratings yet
- Workplace Harassment Preventation PolicyDocument2 pagesWorkplace Harassment Preventation PolicyJohn Leo De LeusNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Loss (Books)Document1 pageAffidavit of Loss (Books)nildafvicenteNo ratings yet
- Contemp IndiaDocument20 pagesContemp IndiaPranav BajajNo ratings yet
- M.L Chapter-3Document36 pagesM.L Chapter-3Shivankar sukulNo ratings yet
- Law of Pakistan: HistoryDocument8 pagesLaw of Pakistan: Historyسلطان علی طارقNo ratings yet
- Constitutional LAW-1 Assignment: Submtted By: Alvin Paul P S R18BL003 Bba LLB (H) 3 SemesterDocument11 pagesConstitutional LAW-1 Assignment: Submtted By: Alvin Paul P S R18BL003 Bba LLB (H) 3 SemesterAnonymous CSH2EsZkNo ratings yet
- Major Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument11 pagesMajor Features of Indian Constitutionaayushmaan agnihotriNo ratings yet
- INDIAN POLITY M. LAXMIKANT pdf-74-78Document5 pagesINDIAN POLITY M. LAXMIKANT pdf-74-78omshrihareNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction and Basic Information About Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction and Basic Information About Indian ConstitutionNishchaiya BaylaNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India - Study Material For IPO ExamDocument6 pagesConstitution of India - Study Material For IPO ExamDur TurNo ratings yet
- Q # 1: Indian Constitution Is The Lengthiest Constitution of The World. Discuss Its Sources, Constitution Making Process and Distinctive FeaturesDocument5 pagesQ # 1: Indian Constitution Is The Lengthiest Constitution of The World. Discuss Its Sources, Constitution Making Process and Distinctive FeaturesXain RanaNo ratings yet
- This Article Lists The 18 Major Features of The Constitution and Comprehensively Covers Each of The Features in The ArticleDocument10 pagesThis Article Lists The 18 Major Features of The Constitution and Comprehensively Covers Each of The Features in The ArticleShaswatNo ratings yet
- Quote: What Does The Word The Constitution Means The Composition of SomethingDocument14 pagesQuote: What Does The Word The Constitution Means The Composition of Somethingmalay majhiNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument35 pagesIndian ConstitutionZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Indian Political SystemDocument81 pagesIndian Political SystemManish SoniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument15 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: Submitted By: Submitted ToAnimeshNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument35 pagesIndian Constitutionpavithra kNo ratings yet
- Constituent AssemblyDocument3 pagesConstituent Assemblythinklegal2212No ratings yet
- Constitution Unit 1 & 2Document28 pagesConstitution Unit 1 & 2shreyas dasNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India NotesDocument4 pagesConstitution of India NotesRee QNo ratings yet
- 1.05 Constitutional Development - 4Document10 pages1.05 Constitutional Development - 4Roshan JibhakateNo ratings yet
- Impotent Feachers of Indial ConstitutionDocument8 pagesImpotent Feachers of Indial Constitutionchhatrapal sahuNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 Constitution of 1956 (Fall)Document15 pagesLec-11 Constitution of 1956 (Fall)Taef Hossain 1531416630No ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ConstitutionDocument4 pagesSalient Features of The ConstitutionNarayanan BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- 8th and 18th AmendmentsDocument8 pages8th and 18th AmendmentsYousaf AliNo ratings yet
- 1.meaning of The Constitution Law and ConstitutionalismDocument29 pages1.meaning of The Constitution Law and Constitutionalism19tk1ao222 md faisal aliNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Notes For LectureDocument38 pagesIndian Constitution Notes For Lecturepooja kumarNo ratings yet
- Ic NotesDocument25 pagesIc NotesNandeesha K RNo ratings yet
- Constitutional HistoryDocument4 pagesConstitutional HistorynithyaaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Has Had Three Constitutions Since Its Inception in 1947Document8 pagesPakistan Has Had Three Constitutions Since Its Inception in 1947muhammad shahgeerNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India: Prof. ShivashankarDocument24 pagesConstitution of India: Prof. Shivashankarshivashankar sgNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan - WikipediaDocument97 pagesConstitution of Pakistan - WikipediaMehran HaloNo ratings yet
- Political Sci - 4TH Semester - L03 - LLB - 191342Document21 pagesPolitical Sci - 4TH Semester - L03 - LLB - 191342Riyashree DasNo ratings yet
- Krutika Ravindra Mane Bms Department Community Development and Corporate Social Responsibility ROLL NO. 127 Indian Constitution SystemDocument14 pagesKrutika Ravindra Mane Bms Department Community Development and Corporate Social Responsibility ROLL NO. 127 Indian Constitution SystemKrutika ManeNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Notes Unit - I & IiDocument32 pagesIndian Constitution Notes Unit - I & Iikumar.abhinav1015No ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument10 pagesConstitution of IndiaDr.V.Bastin JeromeNo ratings yet
- Blog SatendraDocument3 pagesBlog SatendraSatendraNo ratings yet
- Features of The Constitution of IndiaDocument4 pagesFeatures of The Constitution of IndiaMriganga SarmaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument19 pagesSalient Features of Indian ConstitutionPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity MaterialDocument45 pagesIndian Polity MaterialstalinkbcNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity MaterialDocument45 pagesIndian Polity Materialsuresh100% (2)
- Constitution of Pakistan - WikipediaDocument23 pagesConstitution of Pakistan - WikipediaAhmed RajpootNo ratings yet
- Constitution Law New Syllabus 2020Document36 pagesConstitution Law New Syllabus 2020arjun0505No ratings yet
- Constitution 1973Document8 pagesConstitution 1973vu softNo ratings yet
- Holland - 17th CenturyDocument17 pagesHolland - 17th CenturyAbhinava GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Constitution Chapter 2Document7 pagesConstitution Chapter 2Mohd SuhailNo ratings yet
- Kishore: Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesKishore: Salient Features of Indian ConstitutionShahran SanuNo ratings yet
- Govt of India Act 1935 Has A Significant Role in The Constitutional History of PakistanDocument6 pagesGovt of India Act 1935 Has A Significant Role in The Constitutional History of PakistanIrtaza HassanNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesSalient Features of The Indian Constitutionmanukar404No ratings yet
- Basic Features of The Indian ConstitutionDocument5 pagesBasic Features of The Indian ConstitutionKashish RajputNo ratings yet
- 7852Document6 pages7852Neil PlayzNo ratings yet
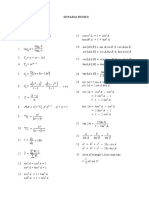
- Formula Addmath SPM KSSMDocument1 pageFormula Addmath SPM KSSMMasrupawan AsmaranyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conveyancing Lecture 1Document18 pagesIntroduction To Conveyancing Lecture 1Judge and Jury.No ratings yet
- Delhi Airport: E-Visa Application FormDocument3 pagesDelhi Airport: E-Visa Application FormBismilNo ratings yet
- Social Justice Society Vs Dangerous Drugs Board, GR No. 157870, November 3, 2008Document2 pagesSocial Justice Society Vs Dangerous Drugs Board, GR No. 157870, November 3, 2008Dotecho Jzo EyNo ratings yet
- Reinstatement FormDocument1 pageReinstatement FormHanzell Faith Bayawa DaculaNo ratings yet
- Pearce v. FBI Agent Doe 5th Circuit Unpublished DecisionDocument6 pagesPearce v. FBI Agent Doe 5th Circuit Unpublished DecisionWashington Free BeaconNo ratings yet
- Nims School of Law: Is Criminology A ScienceDocument9 pagesNims School of Law: Is Criminology A ScienceAdarsha MaityNo ratings yet
- Information Technology For Management by Ramesh BehlDocument1 pageInformation Technology For Management by Ramesh BehlSubir Chakrabarty0% (1)
- Sharia - POLICY BRIEF ONE Final VersionDocument12 pagesSharia - POLICY BRIEF ONE Final VersionTemitopeNo ratings yet
- Home Insurance - Google SearchDocument1 pageHome Insurance - Google Searchayesha wahidNo ratings yet
- 15 Lourdes Hospital Vs CapanzanaDocument8 pages15 Lourdes Hospital Vs CapanzanaBeau BautistaNo ratings yet
- CDD - Semi Finals Examination - RFBT SalesDocument20 pagesCDD - Semi Finals Examination - RFBT SalesFeelingerang MAYoraNo ratings yet
- Government of Kerala: ChainDocument12 pagesGovernment of Kerala: ChaingigopulikkottilNo ratings yet
- Standard Fire & Special Perils Policy Schedule: Page 1 of 3Document4 pagesStandard Fire & Special Perils Policy Schedule: Page 1 of 3asdfNo ratings yet
- Instructions / Checklist For Filling KYC FormDocument18 pagesInstructions / Checklist For Filling KYC FormTushar Prakash ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Article 1160Document3 pagesArticle 1160Eliza Jayne Princess VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Y%S, XLD M Dka %SL Iudcjd Ckrcfha .Eiü M %H:, Yq Ifr Rdehaf Nrhryprf Fbaur Tu J JKHDG GJ JpupifDocument8 pagesY%S, XLD M Dka %SL Iudcjd Ckrcfha .Eiü M %H:, Yq Ifr Rdehaf Nrhryprf Fbaur Tu J JKHDG GJ JpupifRamesh RKNo ratings yet
- BADRI UAE Annual Preliminary Industry Report 2022 Q4Document13 pagesBADRI UAE Annual Preliminary Industry Report 2022 Q4Monica AhujaNo ratings yet
- Poplack 2004Document10 pagesPoplack 2004Rodion KsnNo ratings yet
- American Slavery DissertationDocument8 pagesAmerican Slavery DissertationWriteMyPaperInApaFormatCanada100% (1)
- Case Comment On Rajiv Raturi v. Union of India The Dawn of Disability Rights in IndiaDocument6 pagesCase Comment On Rajiv Raturi v. Union of India The Dawn of Disability Rights in IndiaInquisitive MindNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Writing PromptsDocument8 pagesPersuasive Writing PromptsvivNo ratings yet
- EH Students Essays Subjects 2022Document5 pagesEH Students Essays Subjects 2022Алтынгуль ЕрежеповаNo ratings yet
- Grade-7 Attendance SheetDocument54 pagesGrade-7 Attendance SheetJimsley BisomolNo ratings yet