33% found this document useful (3 votes)
21K views6 pagesCarburetor Parts and Functions Explained
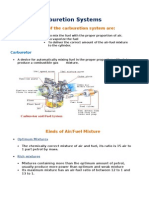
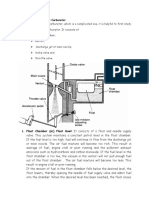
The document discusses the components and functions of a carburetor. It describes 13 main parts of a carburetor including the inlet hose, needle valve, float chamber, jets, throttle valve, venturi, choke valve, and screws. It explains what each part does and how it contributes to regulating air and fuel flow to enable the carburetor to mix fuel and air ideally under different engine conditions.
Uploaded by
Celso AmotoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
33% found this document useful (3 votes)
21K views6 pagesCarburetor Parts and Functions Explained
The document discusses the components and functions of a carburetor. It describes 13 main parts of a carburetor including the inlet hose, needle valve, float chamber, jets, throttle valve, venturi, choke valve, and screws. It explains what each part does and how it contributes to regulating air and fuel flow to enable the carburetor to mix fuel and air ideally under different engine conditions.
Uploaded by
Celso AmotoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd