Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infographic On Charitable Trust
Uploaded by
LavernyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infographic On Charitable Trust
Uploaded by
LavernyaCopyright:
Available Formats
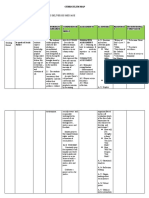
Definition and Requirements of a Charitable Trust
Definition Commissioners of Special Purposes of Income Tax v Pemsel [1891]
Charity has 4 principle divisions (Lord MacNagthen)
Relief of poverty
Advancement of education
Advancement of religion
Other purposes beneficial to the communities
Purpose:
Charitable Nai Seng Hiang v The Trustees of the
Presbyterian Church in Singapore
Public Registered & Ors [1988]:
Benefit Benefit whole community/ a section of
community & not a small group/ private
individuals
Requirements
Gift = Wholly &
exclusively for
charitable
Exclusively Connecting Word:
Charitable
"Charitable or other purposes": Not
Charitable - Houston v Burns [1981]
"Charitable and other purpose":
Charitable - Re Sutton (1885)
Re Scarisbrick (1951) – Need not satisfy public benefit requirement
so long as the settlor has a genuine charitable intention.
Relief of
Re Gwyon (1930) – Foundation for clothing of boy but failed to
Poverty exclude more affluent children. Held, benefit must be restricted to
4 Principle Divisions (Lord MacNagthen)
the poor.
I. Research (must benefit the public) – Re Shaw [1957]: The
settlor left money for the development of a 40-letter alphabet
and the translation of one of his plays into this new alphabet.
Held, not charitable as there was no element of teaching or
education and the mere acquisition of knowledge would not per
se be a charitable object.
Advancement of
Education
Advancement of
Religion
Re South Place
Ethical Society
[1980] – held:
“Religion” = Man’s
relation with God
“Ethics” = Man’s
relation with man
Thus, both are not
the same.
United Grand Lodge
of Ancient Free &
Accepted Masons of
England v Holborn
Other purposes Test: What the law treats as charitable Borough Council
and not what the testator thought was
beneficial to [1957] – Held:
charitable.
the Advancement of
EX: Welfare of animals – Re religion means to
communities Wedgwood (1915), Welfare of elderly, promote it and
Relief of sickness etc. increase religious
belief.
Effect: Enables trust property to be used for other purpose which
resembles the donor’s original purpose. – AG v Lim Poh Neo
(W) & Ors [1976]
2 situation of failure:
a. Initial failure (gift does not take effect due to donor’s
charitable purpose) – Biscoe v Jackson: there was
sufficient intention thus allowed cy-pres.
b. Subsequent Failure (gift failed after it has taken effect) – Cy-pres
Re Slevin Doctrine
Lavernya (A166528)
You might also like
- Week 13 Charitable Trust 2.0Document20 pagesWeek 13 Charitable Trust 2.0Ram Erfan Z. NuqmanNo ratings yet
- Charities Structure Plan - Equity and TrustsDocument4 pagesCharities Structure Plan - Equity and TrustsRowenaNo ratings yet
- Equity and TrustsDocument11 pagesEquity and TrustsValentina KiritaNo ratings yet
- Charitabletrustshortnotes 160121152230 PDFDocument5 pagesCharitabletrustshortnotes 160121152230 PDFluvshot1No ratings yet
- A Sixfold Biblical Approach To Social TransformatiDocument9 pagesA Sixfold Biblical Approach To Social TransformatiAvinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Ministry of Giving TeachersDocument7 pagesThe Ministry of Giving TeachersAlex PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Charitable TrustsDocument30 pagesCharitable TrustsDominic Grell100% (1)
- Church Planting and Community DevelopmentDocument5 pagesChurch Planting and Community DevelopmentEverything new100% (1)
- The Social Teaching of The ChurchDocument39 pagesThe Social Teaching of The ChurchMark Francis VillegasNo ratings yet
- Catholic Social Teaching PowerPoint PDFDocument55 pagesCatholic Social Teaching PowerPoint PDFKRISHABELLENo ratings yet
- Economic Principles of The Kingdom of God: Bryan Johnson, May 2007Document23 pagesEconomic Principles of The Kingdom of God: Bryan Johnson, May 2007ntv2000No ratings yet
- Be Inexplicably GenerousDocument2 pagesBe Inexplicably GeneroustingrizalNo ratings yet
- VTApr 11Document1 pageVTApr 11maya_metzNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Final Version - TGP - EdDocument6 pagesGrade 9 - Final Version - TGP - EdroseNo ratings yet
- Law 3711 - 07 Charitable TrustDocument6 pagesLaw 3711 - 07 Charitable TrustNasha DzulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Rom 12.6-8Document2 pagesRom 12.6-8Blaine RogersNo ratings yet
- 12 Steps To Starting A CMCDocument22 pages12 Steps To Starting A CMCChanel ANo ratings yet
- Where Do We Bring Our Tithe in Search of The Storehouse by G Edward Reid EbookDocument68 pagesWhere Do We Bring Our Tithe in Search of The Storehouse by G Edward Reid EbookKBanteilang NonglangNo ratings yet
- An Act Of: WorshipDocument24 pagesAn Act Of: WorshipGlizza BergadoNo ratings yet
- The Church: Church Is A GroupDocument1 pageThe Church: Church Is A GroupjerikvNo ratings yet
- WealthDocument1 pageWealthfredglass7No ratings yet
- Should Christians Tithe? Exploring The Grace That Keeps The Windows of Heaven OpenFrom EverandShould Christians Tithe? Exploring The Grace That Keeps The Windows of Heaven OpenNo ratings yet
- Keller Integrative MinistryDocument28 pagesKeller Integrative MinistrycoburNo ratings yet
- Catholic Social Teaching PowerPointDocument33 pagesCatholic Social Teaching PowerPointJerico Ortega SantosNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM MAP Grade 7 2020-2021 2nd QuaterDocument10 pagesCURRICULUM MAP Grade 7 2020-2021 2nd QuaterKARLO MARKO VALLADORESNo ratings yet
- Module 1 RE 3Document3 pagesModule 1 RE 3Kean LonggayNo ratings yet
- Nelson, Professor Emeritus of Pastoral Studies, North Park Theological SeminaryDocument10 pagesNelson, Professor Emeritus of Pastoral Studies, North Park Theological Seminaryjesuszabaleta5810No ratings yet
- Charitable TrustsDocument41 pagesCharitable TrustsALI SHAMMOONNo ratings yet
- Man of FAITH by George MüllerDocument47 pagesMan of FAITH by George MüllerVictor OnovohNo ratings yet
- Tithe - Ellen G. White EstateDocument20 pagesTithe - Ellen G. White EstatejorgenmokNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document7 pagesModule 1Ray Cris TemarioNo ratings yet
- ACTS BiblicalGiftsDocument39 pagesACTS BiblicalGiftsChipanta SikaluzweNo ratings yet
- ACTS BiblicalGiftsDocument39 pagesACTS BiblicalGiftsChipanta SikaluzweNo ratings yet
- CR June PagesDocument4 pagesCR June PagesColorado Christian UniversityNo ratings yet
- Project The Ministerial Life 1Document59 pagesProject The Ministerial Life 1milson IncNo ratings yet
- Nkd-Discretionary, Protective N Charitable TrustDocument35 pagesNkd-Discretionary, Protective N Charitable TrustJinghui LimNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Lesson 1: The Growing Up of Youth MinistryDocument4 pagesSession 1 Lesson 1: The Growing Up of Youth MinistryMatheus Motta Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Mission: A Universal Mandate MR Z N SironbouDocument4 pagesMission: A Universal Mandate MR Z N SironbouSironbou Zui NewmaiNo ratings yet
- Catholic Identity Catholic Charities Portland, Oregon Senior Managers RetreatDocument62 pagesCatholic Identity Catholic Charities Portland, Oregon Senior Managers RetreatTina Bates BalderaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Concept of Man and SocietyDocument3 pagesLecture 3 - Concept of Man and SocietyANDREA NICOLE FLORESNo ratings yet
- Archivetempgrade 9 - Final Version - TGP - EdDocument20 pagesArchivetempgrade 9 - Final Version - TGP - EdJESSIE ERIC HEYRANANo ratings yet
- FCC Newsletter May 09Document1 pageFCC Newsletter May 09Faith Community ChurchNo ratings yet
- Releasing The Ministry Of All God's People: A holistic Spirit-led modelFrom EverandReleasing The Ministry Of All God's People: A holistic Spirit-led modelNo ratings yet
- Pelayo Rotchell - Module 2 - Historical Evolution of Social WorkDocument12 pagesPelayo Rotchell - Module 2 - Historical Evolution of Social WorkRotchell Abila PelayoNo ratings yet
- 12 Characteristics of Parish Social MinistryDocument4 pages12 Characteristics of Parish Social MinistryCatholic Charities USA100% (1)
- Bible Study Acts 5 and 6Document6 pagesBible Study Acts 5 and 6theintrepiddodgerNo ratings yet
- FaithDocument43 pagesFaithMarilou Chalanao EstebanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ministry of Helps NotesDocument1 pageUnderstanding Ministry of Helps Notesgift chindaNo ratings yet
- Crestyl Faye Rodrigo Cagatan - Reading Log 2 - Denominational History and Prophetic HeritageDocument3 pagesCrestyl Faye Rodrigo Cagatan - Reading Log 2 - Denominational History and Prophetic HeritageFaatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Welfare Caring For Those in Need 2022 Annual ReportDocument48 pagesWelfare Caring For Those in Need 2022 Annual Reportabelsoto932No ratings yet
- To Serve: Global Children'S DayDocument6 pagesTo Serve: Global Children'S DayMaria Rose Tariga AquinoNo ratings yet
- Barnabas Community Ministry International (BACOMI) : 1. VisionDocument14 pagesBarnabas Community Ministry International (BACOMI) : 1. Visionpastorwmagaya4416No ratings yet
- Grace, Virtue, Sin, ConversionDocument31 pagesGrace, Virtue, Sin, ConversionBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Dons Spirituels RenouveauDocument26 pagesDons Spirituels RenouveauLewis AKISSINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument24 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionAparna SahasrabudheNo ratings yet
- FM - Session 11Document20 pagesFM - Session 11api-27168445No ratings yet
- The Trumpet Call: Our VisionDocument4 pagesThe Trumpet Call: Our VisionEast Stroudsburg United Methodist ChurchNo ratings yet
- The Trumpet Call: Our VisionDocument4 pagesThe Trumpet Call: Our VisionEast Stroudsburg United Methodist ChurchNo ratings yet
- IRA Amendment - ChartDocument1 pageIRA Amendment - ChartLavernyaNo ratings yet
- TRAVELSIGHT (M) SDN BHD & ANOR V ATLAS CORP SDN BHDDocument23 pagesTRAVELSIGHT (M) SDN BHD & ANOR V ATLAS CORP SDN BHDLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Zulhairy KamaruzamanDocument17 pagesZulhairy KamaruzamanLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Dang Chooi Ping V Lim Eng KokDocument10 pagesDang Chooi Ping V Lim Eng KokLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Revised Compendium FOR PERSONAL INJURY AWARDS 2018 Revised Compendium FOR PERSONAL INJURY AWARDS 2018Document52 pagesRevised Compendium FOR PERSONAL INJURY AWARDS 2018 Revised Compendium FOR PERSONAL INJURY AWARDS 2018LavernyaNo ratings yet
- Duty To ClientDocument32 pagesDuty To ClientLavernya100% (1)
- Lai Meng v. Toh Chew LianDocument20 pagesLai Meng v. Toh Chew LianLavernyaNo ratings yet
- CPC 5 (Case Study)Document3 pagesCPC 5 (Case Study)LavernyaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Tutorial, Question 14 - Lavernya Bala Subramaniam (A166528), Firm 11Document4 pagesEvidence Tutorial, Question 14 - Lavernya Bala Subramaniam (A166528), Firm 11LavernyaNo ratings yet
- Baheerathy Ap Arumugam V V Gunaselan Al V VisvanathanDocument37 pagesBaheerathy Ap Arumugam V V Gunaselan Al V VisvanathanLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Police Investigation Part 1Document16 pagesPolice Investigation Part 1LavernyaNo ratings yet
- Syarahan Ketiga CPC PDFDocument30 pagesSyarahan Ketiga CPC PDFLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Pearce V BrooksDocument3 pagesPearce V BrooksLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Paramoo V Zeno LTDDocument3 pagesParamoo V Zeno LTDLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Crime Part 2: Muhamad Helmi MD Said Tatacara Jenayah 1 UUK4033Document21 pagesInvestigation of Crime Part 2: Muhamad Helmi MD Said Tatacara Jenayah 1 UUK4033LavernyaNo ratings yet
- Tatacara Jenayah 1 UUUK4033: Dr. Muhamad Helmi Bin Md. Said, Fuu UkmDocument36 pagesTatacara Jenayah 1 UUUK4033: Dr. Muhamad Helmi Bin Md. Said, Fuu UkmLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Tenancy in MalaysiaDocument2 pagesTenancy in MalaysiaLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis AssignmentDocument7 pagesCase Analysis AssignmentLavernyaNo ratings yet
- Layos vs. VillanuevaDocument2 pagesLayos vs. VillanuevaLaura MangantulaoNo ratings yet
- The John Molson School of Business MBA 607 Final Exam June 2013 (100 MARKS)Document10 pagesThe John Molson School of Business MBA 607 Final Exam June 2013 (100 MARKS)aicellNo ratings yet
- Form No. 10-I: Certificate of Prescribed Authority For The Purposes of Section 80DDBDocument1 pageForm No. 10-I: Certificate of Prescribed Authority For The Purposes of Section 80DDBIam KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 2501 Mathematics Paper+with+solution EveningDocument10 pages2501 Mathematics Paper+with+solution EveningNenavath GaneshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Political ScienceDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Political Sciencecyrene cayananNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design Using PROKONDocument114 pagesConcrete Design Using PROKONHesham Mohamed100% (2)
- D8.1M 2007PV PDFDocument5 pagesD8.1M 2007PV PDFkhadtarpNo ratings yet
- India: SupplyDocument6 pagesIndia: SupplyHarish NathanNo ratings yet
- Ground Rules 2019Document3 pagesGround Rules 2019Jeremiah Miko LepasanaNo ratings yet
- 800 Pharsal Verb Thong DungDocument34 pages800 Pharsal Verb Thong DungNguyễn Thu Huyền100% (2)
- Peter Lehr Militant Buddhism The Rise of Religious Violence in Sri Lanka Myanmar and Thailand Springer International PDFDocument305 pagesPeter Lehr Militant Buddhism The Rise of Religious Violence in Sri Lanka Myanmar and Thailand Springer International PDFIloviaaya RegitaNo ratings yet
- The Final Bible of Christian SatanismDocument309 pagesThe Final Bible of Christian SatanismLucifer White100% (1)
- The Cognitive Enterprise For HCM in Retail Powered by Ibm and Oracle - 46027146USENDocument29 pagesThe Cognitive Enterprise For HCM in Retail Powered by Ibm and Oracle - 46027146USENByte MeNo ratings yet
- The Personal Law of The Mahommedans, According To All The Schools (1880) Ali, Syed Ameer, 1849-1928Document454 pagesThe Personal Law of The Mahommedans, According To All The Schools (1880) Ali, Syed Ameer, 1849-1928David BaileyNo ratings yet
- K.M Nanavati v. State of MaharashtraDocument6 pagesK.M Nanavati v. State of MaharashtraPushpank PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Ulverstone Show ResultsDocument10 pages2019 Ulverstone Show ResultsMegan PowellNo ratings yet
- Effect of Intensive Health Education On Adherence To Treatment in Sputum Positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis PatientsDocument6 pagesEffect of Intensive Health Education On Adherence To Treatment in Sputum Positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis PatientspocutindahNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics For The BlindDocument8 pagesErgonomics For The BlindShruthi PandulaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Politik Dan Cinta Tanah Air Dalam Perspektif IslamDocument9 pagesJurnal Politik Dan Cinta Tanah Air Dalam Perspektif Islamalpiantoutina12No ratings yet
- Favis vs. Mun. of SabanganDocument5 pagesFavis vs. Mun. of SabanganAyra CadigalNo ratings yet
- Test Statistics Fact SheetDocument4 pagesTest Statistics Fact SheetIra CervoNo ratings yet
- 30 Linux System Monitoring Tools Every SysAdmin Should Know - NixcraftDocument90 pages30 Linux System Monitoring Tools Every SysAdmin Should Know - Nixcraftvignesh05No ratings yet
- CN and OS Lab ManualDocument53 pagesCN and OS Lab Manualsudheer mangalampalliNo ratings yet
- Economic Value Added in ComDocument7 pagesEconomic Value Added in Comhareshsoni21No ratings yet
- Thesis Statement VampiresDocument6 pagesThesis Statement Vampireslaurasmithdesmoines100% (2)
- Sayyid Jamal Al-Din Muhammad B. Safdar Al-Afghani (1838-1897)Document8 pagesSayyid Jamal Al-Din Muhammad B. Safdar Al-Afghani (1838-1897)Itslee NxNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 5 Quarter 2: Answer KeyDocument4 pagesMathematics Grade 5 Quarter 2: Answer KeyApril Jean Cahoy100% (2)
- 4 Major Advantages of Japanese Education SystemDocument3 pages4 Major Advantages of Japanese Education SystemIsa HafizaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Risk ManagementDocument46 pagesStrategic Risk ManagementNuman Rox100% (1)
- EdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 5 Mark Scheme Jan 2000Document3 pagesEdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 5 Mark Scheme Jan 2000Nabeeha07No ratings yet