Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obstructive Jaundice
Uploaded by
Matt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageObstructive Jaundice
Uploaded by
MattCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
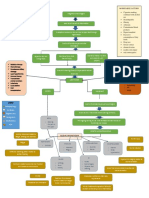
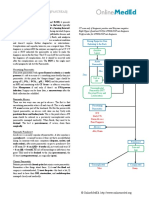
General Surgery [OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE]
Etiology of Jaundice Malignant Obstructive
Jaundice is a problem of bilirubin production (hemolysis), Physical Palpable nontender Tender Gallbladder
conversion (liver disease, acute or chronic), or excretion Exam Gallbladder
(obstruction). These are covered in depth in the medicine topics. Ultrasound Thin-Walled Distended Thick-Walled rigid
In surgery it’s important to recognize the laboratory findings Gallbladder gallbladder
(production: ↑ unconjugated bilirubin only; conversion: Stones Ø Stones Stones
↑unconjugated bilirubin and LFTs; obstruction: ↑ conjugated Diagnosis MRCP then ERCP
bilirubin and LFTs and Alk Phos, and Pancreatic Enzymes) and ERCP or EUS = Bx
know the difference between Viral (AST and ALT in the 1000s) CT scan stage
and EtOH Hepatitis (AST:ALT > 1.5). The rest is the topic at Treatment Surgery ERCP
hand - obstructive jaundice.
Obstructive Jaundice Prehaptic – Hemolysis
When the biliary tree is blocked the liver does what it’s (Hemolysis) Hematomas
supposed to do: conjugate bilirubin. There will be an elevated EtOH Hepatitis
conjugated bilirubin in obstructive jaundice. That means it’s Viral Hepatitis
water-soluble; it will be excreted in the urine turning it the IntraHepatic
Other Hepatitis
color of bilirubin (making dark urine). The stool will lose its (Hepatitis) Cirrhosis /Hepatitis
pigment (clay colored stools). Other signs of obstruction may Childhood Disease
be present (pruritus or icterus, for example) but the patient is
going to be yellow (jaundice). The decision is if it is an acute PostHepatic Gallstones
inflammatory process or a chronic malignant one. The first (Obstructive) Pancreatic Cancer
PBC
step is in the physical exam. A palpable, nontender
PSC
gallbladder generally means a cancer (the gall bladder produces
Stricture
fluid but there’s nowhere for it to go, so it just blows up like a
balloon). A tender gallbladder (Murphy’s Sign) is indicative of
an inflammatory process, cholecystitis, making the likely culprit
a stone. The next step is an Ultrasound: a thin walled, dilated
gallbladder walls free of inflammation with a distal obstruction
(cancer), while a thick-walled rigid (porcelain) gallbladder is
from chronic inflammation. In addition, it might even be
possible to see the stones in the gallbladder (but rarely, if ever,
the offending stone).
Choledocholithiasis and Cholangitis (see gallbladder lecture)
If there’s a stone in the common bile duct, there’s no time for
the biliary tree to adapt. Mild dilation of ducts on ultrasound, Normal Gallbladder Cancer Choledocholithiasis
gallstones in the gallbladder (you rarely see the gallstones in the
duct), and jaundice will be seen. If nontoxic (choledoco) get an
MRCP to confirm, then ERCP to treat. If toxic (cholangitis) give
antibiotics and skin MRCP for ERCP first.
Weight Loss Migratory Thin-walled,
Cancer
There are three tumors that can present with painless jaundice, and Jaundice Thrombophlebitis distended
a palpable gallbladder, and usually weight loss. 1Pancreatic Gallbladder
cancer (adeno from the head of pancreas strangles the biliary but no stones
tree) is diagnosed with an EUS with biopsy; it requires a
Whipple procedure (pancreado-duodeno-jejunostomy) to treat.
It carries a dismal prognosis. 2Cholangiocarcinoma (cancer of Pancreatic Cancer
the duct itself) can be the source of obstruction, which would be
diagnosed on ERCP with Bx and is capable of ruling out a
Ampullary CT scan Cholangio-
stricture. 3Ampulla of Vater cancer, which can bleed into the
GI lumen, presents with an FOBT+ but with a -Colonoscopy. Cancer carcinoma
START WITH AN MRCP which should always precede the FOBT +, Colo - PSCCancer
biopsy test (either ERCP or EUS). CT scans are still used to ERCP with Bx ERCP with Bx
stage lesions and surgical resection is usually the treatment. Resection Resection
Pancreatic Cancer
Migratory thrombophlebitis (described as palpation of “rigid
cords” of superficial veins that come and go) is essentially Migratory Thrombophlebitis
pathognomonic for pancreatic cancer. EUS with BX
Whipple
© OnlineMedEd. http://www.onlinemeded.org
You might also like
- Kholesistis & Kholelitiasis 30-11-14Document67 pagesKholesistis & Kholelitiasis 30-11-14Dian AzhariaNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- Case of Obstructive JaundiceDocument38 pagesCase of Obstructive JaundiceadiNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Seminar Under The Guidance Of-Dr. Shiva NarangDocument47 pagesJaundice: Seminar Under The Guidance Of-Dr. Shiva NarangMiguel MansillaNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument29 pagesColorectal CancerLeeyanBhadzzVagayNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFDocument2 pagesPediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFJasmine KangNo ratings yet
- Hepato-Billiary Diseases: Tutor: DR SocdaalDocument32 pagesHepato-Billiary Diseases: Tutor: DR SocdaalOmar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 2-Acute Abdominal PainDocument24 pages2-Acute Abdominal Painabdalmajeed alshammaryNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Rectal CarcinomaDocument25 pagesPathophysiology: Rectal CarcinomaCristina CristinaNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)MattNo ratings yet
- Calculous Biliary DiseaseDocument71 pagesCalculous Biliary DiseaseMinnossNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastrointestinal Bleeding, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Large Bowel Obstruction by Nic MDocument42 pagesLarge Bowel Obstruction by Nic MRisky OpponentNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Bleeding in AdultsDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of Gastrointestinal Bleeding in AdultsSaeed Al-YafeiNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Lump Right HypochondriumDocument22 pagesCase Presentation Lump Right HypochondriumNANDAN RAINo ratings yet
- PR BleedDocument20 pagesPR BleedCathy KayNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument19 pagesAcute AbdomenNazmi Z. MehmetiNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument53 pagesJaundiceAbhishiktaAbhiNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease of The ColonDocument38 pagesDiverticular Disease of The Colonapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain MS LectureDocument63 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain MS Lectureheka_amrongNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Cancer: Aziz Ahmad, MD Surgical Oncology Mills-Peninsula Hospital April 23, 2011Document18 pagesPancreatic Cancer: Aziz Ahmad, MD Surgical Oncology Mills-Peninsula Hospital April 23, 2011mywifenoor1983No ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Staging of Colorectal Cancer - UpToDate PDFDocument41 pagesClinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Staging of Colorectal Cancer - UpToDate PDFVali MocanuNo ratings yet
- 1 LiverDocument10 pages1 LiverAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- Acute Abdominal Pain: Associate Professor, Dept. of Surgery Mti, KMC, KTHDocument45 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain: Associate Professor, Dept. of Surgery Mti, KMC, KTHWaleed MaboodNo ratings yet
- Bile Duct InjuryDocument21 pagesBile Duct InjuryParul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Ascites PresentationDocument19 pagesAscites PresentationDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis DoneDocument91 pagesLiver Cirrhosis DoneGiorgi PopiashviliNo ratings yet
- Ascitic Fluid AnalysisDocument3 pagesAscitic Fluid AnalysisLohJNo ratings yet
- Absite CH 32 BilliaryDocument14 pagesAbsite CH 32 BilliaryJames JosephNo ratings yet
- Surgery II - Pancreas 2014Document20 pagesSurgery II - Pancreas 2014Medisina101No ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: Causes and PathologyDocument12 pagesCholecystitis: Causes and PathologySher KhanNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: DefinitionDocument4 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease: Definitionkarl abiaadNo ratings yet
- HBV HCV Cirrhosis Gender Perinatal Transmission Age Family HX RaceDocument2 pagesHBV HCV Cirrhosis Gender Perinatal Transmission Age Family HX RaceKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- Colon Cancer: Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesColon Cancer: Risk FactorsAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea 2016Document37 pagesDiarrhea 2016oli garkiNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder EmpyemaDocument17 pagesGallbladder EmpyemaYayut 18No ratings yet
- Right Ventricular Myocardial InfarctionDocument43 pagesRight Ventricular Myocardial Infarctionrudresh m g0% (2)
- Gall Stone Disease: DR M.farhad General SurgeonDocument56 pagesGall Stone Disease: DR M.farhad General SurgeondrelvNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Treatment & ManagementDocument8 pagesCholelithiasis Treatment & ManagementRayhanun MardhatillahNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynDocument29 pagesCholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynCams BonoanNo ratings yet
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC, Also Called Malignant Hepatoma) Is The MostDocument10 pagesHepatocellular Carcinoma: Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC, Also Called Malignant Hepatoma) Is The MostNurul An NisaNo ratings yet
- Spleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementDocument53 pagesSpleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Perforated Peptic UlcerDocument68 pagesPerforated Peptic UlcerSaibo BoldsaikhanNo ratings yet
- GIT Fully DoneDocument14 pagesGIT Fully DoneTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- 008 Plain X-Ray AbdomenDocument7 pages008 Plain X-Ray AbdomenAthul GurudasNo ratings yet
- Diverticular DiseaseDocument30 pagesDiverticular Diseasept.mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation:: DR - Amra Farrukh PG.T Su.IDocument75 pagesCase Presentation:: DR - Amra Farrukh PG.T Su.IpeeconNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Pancreatitis - DBarilDocument25 pagesNecrotizing Pancreatitis - DBarilataner1991No ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen &peritonitisDocument63 pagesAcute Abdomen &peritonitisSamar Ahmad100% (1)
- SURGERYFinals - 1. The AppendixDocument10 pagesSURGERYFinals - 1. The AppendixRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Jaundice: DR Nanteza SumayiyaDocument26 pagesObstructive Jaundice: DR Nanteza SumayiyaNinaNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Ca PresentationDocument25 pagesColorectal Ca Presentationapi-399299717No ratings yet
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument3 pagesRenal Cell CarcinomaSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Upper GIT BleedingDocument69 pagesUpper GIT BleedingSoleh Ramly100% (1)
- An Updated Review of Cystic Hepatic LesionsDocument8 pagesAn Updated Review of Cystic Hepatic LesionsMayerlin CalvacheNo ratings yet
- Pre-Op Eval PDFDocument1 pagePre-Op Eval PDFMattNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Postop Fever)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Postop Fever)MattNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Other Postop CXNS)Document2 pagesGeneral Surgery: (Other Postop CXNS)MattNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument1 pagePancreasMattNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Gallbladder Disease)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Gallbladder Disease)Matt100% (1)
- General Surgery: (Leg Ulcers)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Leg Ulcers)MattNo ratings yet
- ColorectalDocument1 pageColorectalMattNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Esophageal Disorders)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Esophageal Disorders)MattNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)MattNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2006 AnswersDocument29 pagesHematology 2006 AnswersMattNo ratings yet
- GIT-III Module PDFDocument9 pagesGIT-III Module PDFFaiz MansoorNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal: Bleeding in Infants and ChildrenDocument16 pagesGastrointestinal: Bleeding in Infants and ChildrenAdelia AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Gambar RadiologiDocument3 pagesGambar RadiologiLoudry Amsal EGNo ratings yet
- Testing For Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: VOL. 2, NO. 2 Clinical ReviewDocument13 pagesTesting For Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: VOL. 2, NO. 2 Clinical ReviewPaulina Fernanda ToledoNo ratings yet
- Case No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVDocument17 pagesCase No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVPremiums of the RoseNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: Complications & TreatmentDocument28 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Complications & Treatmentsimi yNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver Disease and Liver Failure PDFDocument39 pagesChronic Liver Disease and Liver Failure PDFDr.Tapash Chandra Gope50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of HemorrhoidsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of HemorrhoidsTrixie FayeNo ratings yet
- CPLD Final ProgramDocument3 pagesCPLD Final ProgramsriNo ratings yet
- Case Report Peritonitis WordDocument4 pagesCase Report Peritonitis WordMufidatul UmmahNo ratings yet
- GITDocument14 pagesGITEssam ZayedNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument19 pagesAbdominal PainAudricNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Surgery PresentationDocument191 pagesPediatric Surgery PresentationdanoonotNo ratings yet
- Parikartika (Fissure in Ano) Defination ParikartanDocument9 pagesParikartika (Fissure in Ano) Defination ParikartanGAURAV100% (1)
- Book 1Document166 pagesBook 1Puput HepitasariNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CholelitiasisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of CholelitiasisJASMINENICHOLE �GALAPONNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Fat StrandingDocument16 pagesPatterns of Fat StrandingMiguel SanJuanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry-2 (MLT 302) Liver Function and The Biliary Tract Lecture Three Dr. Essam H. AljiffriDocument18 pagesClinical Chemistry-2 (MLT 302) Liver Function and The Biliary Tract Lecture Three Dr. Essam H. AljiffriKadek Widhiana UtamiNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument5 pagesJaundiceshyft1611No ratings yet
- Recognizing Bowel Obstruction and IleusDocument35 pagesRecognizing Bowel Obstruction and IleusmustikaNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & PreventionDocument2 pagesAppendicitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & PreventionJr MateoNo ratings yet
- WJGEv 4 I 6Document82 pagesWJGEv 4 I 6Duane BrooksNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder Diseases Are Most Often Caused by GallstonesDocument8 pagesGallbladder Diseases Are Most Often Caused by GallstonesCharlie C. SanchezNo ratings yet
- IHHC NRSG FORM 0035-16 Nursing PlansDocument2 pagesIHHC NRSG FORM 0035-16 Nursing PlansJess GoNo ratings yet
- Whipple Procedure Case Study PresentationDocument30 pagesWhipple Procedure Case Study Presentationapi-315408947100% (3)
- The SGOT/SGPT Ratio - An Indicator of Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument4 pagesThe SGOT/SGPT Ratio - An Indicator of Alcoholic Liver DiseaseSahara MaindokaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Evaluation TemplateDocument2 pagesGastroenterology Evaluation Templatee-MedTools86% (7)
- Intestinal Obstruction 4Document25 pagesIntestinal Obstruction 4Muvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- Surgery EORDocument76 pagesSurgery EORAndrew BowmanNo ratings yet
- Children Part I Continuation TABLEDocument5 pagesChildren Part I Continuation TABLEMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet