Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parazitologija Protozoa Helminti: Nematoda (Okrugli Crvi) Platyhelminthes - CESTODE (Pljosnati Crvi) Trematoda (Metilji)
Parazitologija Protozoa Helminti: Nematoda (Okrugli Crvi) Platyhelminthes - CESTODE (Pljosnati Crvi) Trematoda (Metilji)
Uploaded by
saraahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parazitologija Protozoa Helminti: Nematoda (Okrugli Crvi) Platyhelminthes - CESTODE (Pljosnati Crvi) Trematoda (Metilji)
Parazitologija Protozoa Helminti: Nematoda (Okrugli Crvi) Platyhelminthes - CESTODE (Pljosnati Crvi) Trematoda (Metilji)
Uploaded by
saraahCopyright:
Available Formats
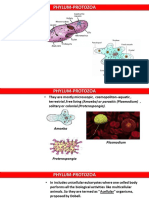
PARAZITOLOGIJA
PROTOZOA HELMINTI
NEMATODA PLATYHELMINTHES – TREMATODA
1. AMAEBE
(okrugli crvi) CESTODE (pljosnati crvi) (Metilji)
2. FLAGELATI
(MASTIGOPHORE)
3. SPOROZOASIDA
(PLAZMODIUM)
Protozoa are free-living, single celled, eucaryotic cells with a cytoplasmic membrane and cellular
organelles, including 1 or 2 nuclei, mitochondria, food vacuoles, and endoplasmic reticulum. They come in
many sizes, from 5 micrometers to 2 millimeters. They have an outer layer of cytoplasm (ectoplasm) and
an inner layer (endoplasm), which appear different from each other under the microscope.
The protozoa ingest solid pieces of food through a small mouth called the cytostome. For example, amoe
bas (Entamoeba histolitica) can ingest human red blood cells into their cytoplasm. The protozoa reproduce
asex ually, undergoing DNA replication followed by division into 2 cells. They also reproduce sexually by the
fusion of 2 cells, followed by the exchange of DNA and separa tion into 2 cells again.
When exposed to new environments (such as temper ature changes, transit down the intestinal tract, or
chemical agents), the protozoa can secrete a protective coat and shrink into a round armored form, called
the cyst. It is this cyst form that is infective when ingested by humans. Following ingestion it converts back
into the motile form, called the trophozoite.
You might also like
- Habit, Habitat, Structure, Reproduction and Importance of Slime Molds, Comparison With ProtozoaDocument66 pagesHabit, Habitat, Structure, Reproduction and Importance of Slime Molds, Comparison With ProtozoaAsfi Raian OmeNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument59 pagesParasitology NotesGiorgos Doukas KaranasiosNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue ProtozoansDocument12 pagesBlood and Tissue ProtozoansHumayun ArshadNo ratings yet
- Electronic Atlas of ParasitologyDocument650 pagesElectronic Atlas of Parasitologystormyccs100% (7)
- Atlas Electrónico de ParasitologíaDocument650 pagesAtlas Electrónico de ParasitologíaSoledad Rod100% (1)
- ProtozoaDocument25 pagesProtozoanupur.kmcNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument29 pagesWeek 8 Phylum PlatyhelminthesAlyssa Jane AbellonNo ratings yet
- Animal DiversityDocument26 pagesAnimal DiversityUzochukwu OnyemaNo ratings yet
- The Phorbol 12-Myristate-13-Acetate Differentiation Protocol Is Critical To The Interaction of THP-1 Macrophages With Salmonella TyphimuriumDocument13 pagesThe Phorbol 12-Myristate-13-Acetate Differentiation Protocol Is Critical To The Interaction of THP-1 Macrophages With Salmonella TyphimuriumMaria SunflowerNo ratings yet
- Plastids and Genome Interactions 1. Types of PlastidsDocument15 pagesPlastids and Genome Interactions 1. Types of PlastidsB. Rajeev KungurNo ratings yet
- DissertationDocument5 pagesDissertationIX17-41 Suvayu ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Cell Division MeiosisDocument4 pagesReproductive Cell Division Meiosisspnandan1903No ratings yet
- General Characteristics of The Trematoda: Worms. The Third Class Is Mongenea (Parasites To TheDocument10 pagesGeneral Characteristics of The Trematoda: Worms. The Third Class Is Mongenea (Parasites To Theruben6mNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell Cyclesatheeshpharma6No ratings yet
- Life-Cycle of Primate Malaria Parasites R S Bray & P C C GarnhamDocument6 pagesLife-Cycle of Primate Malaria Parasites R S Bray & P C C GarnhamppdatNo ratings yet
- Crozatier Et Al-2007-Cellular MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesCrozatier Et Al-2007-Cellular MicrobiologyVINEET KUREELNo ratings yet
- Tripanozoma Cruzi PDFDocument13 pagesTripanozoma Cruzi PDFDaniel CruzNo ratings yet
- List of ParasitesDocument11 pagesList of ParasitesRaashed RamzanNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Gene or Point Mutation Chromosomal MutationDocument6 pagesMutation: Gene or Point Mutation Chromosomal MutationGeo NalobNo ratings yet
- Flagellates 1 & 2: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesFlagellates 1 & 2: ObjectivesJustine EscobalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Protists: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesOverview of Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Protists: ObjectivesMethi KishmishNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document58 pagesLecture 02Lib PalmaresNo ratings yet
- 8.0 HaemoflagellatesDocument11 pages8.0 HaemoflagellatesHenry KarokiNo ratings yet
- Parasito First YearDocument2 pagesParasito First Yearyam pdNo ratings yet
- Actividad Telomerasa C2C12Document8 pagesActividad Telomerasa C2C12Nacido para BendcirNo ratings yet
- Protozoans ParasitesDocument29 pagesProtozoans Parasitespotatopurple009No ratings yet
- Amoeba, Flagellates, Ciliates and SporozoansDocument7 pagesAmoeba, Flagellates, Ciliates and SporozoansHani HairullaNo ratings yet
- Saulet Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug ResearchDocument67 pagesSaulet Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug ResearchHafiz Muhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas HominisDocument1 pageTrichomonas HominisFebriarini dwi nandaNo ratings yet
- Host Immune System Evasion by The Protozoan Parasites TrypanosomaDocument12 pagesHost Immune System Evasion by The Protozoan Parasites TrypanosomaEDGAR AXEL GONZALEZ DUENASNo ratings yet
- 2 PARA 1 - Protozoa - FlagellatesDocument13 pages2 PARA 1 - Protozoa - FlagellatesTricia LlorinNo ratings yet
- Genital, Intestinal, Oral FlagellaDocument7 pagesGenital, Intestinal, Oral Flagellaxofoh43003No ratings yet
- Protozoa KuliahDocument45 pagesProtozoa KuliahWally RedsNo ratings yet
- The Intestinal ProtozoaDocument15 pagesThe Intestinal ProtozoaKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIUNo ratings yet
- Week14 Protozoa1 Transcript PDFDocument23 pagesWeek14 Protozoa1 Transcript PDFrabiaNo ratings yet
- ON Plasmodium Vivax (Malarial Parasite)Document10 pagesON Plasmodium Vivax (Malarial Parasite)Raja Marudut SimatupangNo ratings yet
- PlasmodiumFalciparum New InformationDocument3 pagesPlasmodiumFalciparum New InformationJustin Jim SalazarNo ratings yet
- Plant Path104 Exer 2Document3 pagesPlant Path104 Exer 2Casey Jon VeaNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycles of Cryptogams: Peter BellDocument14 pagesThe Life Cycles of Cryptogams: Peter BellArchana YadavNo ratings yet
- Austin Journal of Molecular and Cellular BiologyDocument7 pagesAustin Journal of Molecular and Cellular BiologyAustin Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Ciliates FlagellatesDocument4 pagesParasitology Ciliates FlagellatesarvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document19 pagesPresentation 3Gift Maganga100% (1)
- Introduction of ProtozoaDocument31 pagesIntroduction of ProtozoaEINSTEIN2D100% (2)
- Hemofl - AgellatesDocument46 pagesHemofl - Agellatesمحمد رحيم حسن محمودNo ratings yet
- Protozoa Plasmodium VivaxDocument23 pagesProtozoa Plasmodium VivaxDS MeherNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Testicular Germ Cell Tumours: Leendert H. J. Looijenga and J. Wolter OosterhuisDocument11 pagesPathogenesis of Testicular Germ Cell Tumours: Leendert H. J. Looijenga and J. Wolter OosterhuisLatansa DinaNo ratings yet
- Shape Variations of Trichomonas Vaginalis in Presence of Different SubstratesDocument4 pagesShape Variations of Trichomonas Vaginalis in Presence of Different SubstratesIonela RobertaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment: Microbial Diversity MollicutesDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Assignment: Microbial Diversity MollicutesVidushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2-Introduction To ProtozoaDocument4 pages2-Introduction To ProtozoaNur LiyanaNo ratings yet
- Role of Apoptosis-Related Factors in Follicular Atresia: ReviewDocument10 pagesRole of Apoptosis-Related Factors in Follicular Atresia: ReviewLiliz D'Luph RamaNo ratings yet
- Rab27a Regulates Exocytosis of Tertiary and Specific Granules in Human NeutrophilsDocument11 pagesRab27a Regulates Exocytosis of Tertiary and Specific Granules in Human NeutrophilsJavier HerreroNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument38 pagesParasitology NotesEdoardo CitarellaNo ratings yet
- General Concepts ProtozoaDocument9 pagesGeneral Concepts ProtozoaRoshan PMNo ratings yet
- Amoeba and FlagellatesDocument1 pageAmoeba and FlagellatesJoseph DavidNo ratings yet
- Kebidahan 1Document10 pagesKebidahan 1Siti IntanksNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument5 pagesBlood and Tissue FlagellatesChristine BuenNo ratings yet
- Phylum ProtozoaDocument15 pagesPhylum ProtozoaRiddhima SinghalNo ratings yet
- The Intestinal Protozoa: A. IntroductionDocument32 pagesThe Intestinal Protozoa: A. Introductionهاني عقيل حسين جوادNo ratings yet