Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Displacement Change Valve
Uploaded by
Allan LariosaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Displacement Change Valve
Uploaded by
Allan LariosaCopyright:
Available Formats
Previous Screen
Welcome: j370alx
Product: EXCAVATOR
Model: 323D L EXCAVATOR NZF00001
Configuration: 323D L Excavator NZF00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY
C6.6 Engine
Systems Operation
320D and 323D Excavators Hydraulic System
Media Number -RENR7294-12 Publication Date -01/09/2012 Date Updated -24/09/2012
i04360194
Displacement Change Valve
SMCS - 3220
Small Displacement Change Operation
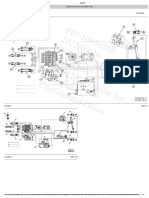
Illustration 1 g02571576
Travel motor (partial diagram)
(1) Swashplate
(2) Piston
(3) Piston chamber
(4) Passage
(5) Displacement change valve
(6) Port (pilot system oil pressure)
(7) Port (supply oil or return oil)
(8) Check valve
(9) Check valve
(10) Port (supply oil or return oil)
(11) Passage
(12) Piston chamber
(13) Piston
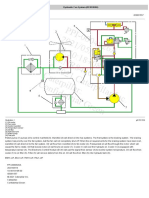
Illustration 2 g02571578
Small displacement change operation
(1) Swashplate
(2) Piston
(3) Piston chamber
(4) Passage (return oil)
(5) Displacement change valve
(6) Port (pilot system oil pressure)
(7) Port (supply oil or return oil)
(8) Check valve
(9) Check valve
(10) Port (supply oil or return oil)
(11) Passage (pump delivery flow)
(12) Piston chamber
(13) Piston
(14) Spool
(15) Spring
(16) Body
(17) Spool chamber
(18) Spool chamber
(19) Passage (return oil)
(20) Hydraulic tank
When the travel speed control switch on the control panel is pushed, a rabbit appears on the display. The machine is in HIGH SPEED MODE. In this condition, an input signal from the
travel speed control switch is sent to the machine ECM.
The pressure sensor for the pump delivery also provides an input signal to the machine ECM. When the travel load is light and the pump delivery pressure is below a certain level, the
signal from the pump delivery pressure sensor is below a certain level. When the pump delivery pressure is below a certain level, the machine ECM energizes the travel speed solenoid.
When the travel speed solenoid is energized, pilot system oil flows into pilot port (6) of displacement change valve (5). Spool (14) moves to the right against the force of spring (15) until
the spool contacts body (16).
Main pump oil flows from passage (7) of the travel motor through check valve (8). The main pump oil then flows through spool chamber (17) and passage (11) to piston chamber (12).
The oil in piston chamber (12) moves piston (13) against swashplate (1). Swashplate (1) forces piston (2) into piston chamber (3). The oil in piston chamber (3) flows through passage
(4), spool chamber (18), and passage (19) to hydraulic tank (20). As a result, the angle of swashplate (1) is decreased and the motor displacement is decreased. The travel speed is
maximum in this condition.
Large Displacement Change Operation
Illustration 3 g02571580
Large displacement change operation
(1) Swashplate
(2) Piston
(3) Piston chamber
(4) Passage (return oil)
(5) Displacement change valve
(6) Port (pilot system oil pressure)
(7) Port (supply oil or return oil)
(8) Check valve
(9) Check valve
(10) Port (supply oil or return oil)
(11) Passage (pump delivery flow)
(12) Piston chamber
(13) Piston
(14) Spool
(15) Spring
(16) Body
(17) Spool chamber
(18) Spool chamber
(19) Passage (return oil)
(20) Hydraulic tank
(21) Stopper
(22) Center passage
When the angle of swashplate (1) in the travel motor increases, the displacement of the travel motor increases. The angle of swashplate (1) in the travel motor will increase and the travel
speed will decrease during the following two conditions.
1. The angle of swashplate (1) in the travel motor will increase and the travel speed will decrease when an increase in pump pressure occurs.
When the machine is in HIGH SPEED MODE and the pump delivery pressure increases above a certain level, the travel speed solenoid is de-energized. When the travel speed
solenoid is de-energized, pilot system oil stops flowing into pilot port (6) of displacement change valve (5). Spool (14) moves to the left by the force of spring (15) until the spool
contacts stopper (21). Main pump oil flows from port (7) of the travel motor through check valve (8). The main pump oil then flows through spool chamber (18) and passage (4)
into piston chamber (3). The oil in piston chamber (3) moves piston (2) against swashplate (1). The angle of swashplate (1) increases. Swashplate (1) forces piston (13) into piston
chamber (12). The oil in piston chamber (12) flows through passage (11), spool chamber (17), and center passage (22) of spool (14). The oil then flows through passage (19) to
hydraulic tank (20). As the angle of swashplate (1) increases, the displacement of the travel motor increases and the travel speed decreases.
2. In LOW SPEED MODE, the angle of swashplate (1) will increase and the travel speed will decrease.
When the travel speed control switch on the control panel is pushed, a tortoise appears on the display. The machine is in LOW SPEED MODE. In this condition, an input signal
from the travel speed control switch is sent to the machine ECM. The machine ECM de-energizes the travel speed solenoid. The angle of swashplate (1) increases and the
displacement of the travel motor increases. The travel speed decreases.
Copyright 1993 - 2019 Caterpillar Inc. Sun Mar 03 2019 01:44:35 GMT+0800 (Philippine Standard Time)
All Rights Reserved.
j370alx
Private Network For SIS Licensees.
You might also like
- 374F Displacement Change Valve CAT EXCAVATORDocument4 pages374F Displacement Change Valve CAT EXCAVATOROscar TelloNo ratings yet
- Displacement Change ValveDocument5 pagesDisplacement Change ValveJuan Daniel Martinez Montoya100% (1)
- Control Valve Straight TravelDocument5 pagesControl Valve Straight TravelSteven Y.MNo ratings yet
- Travel Parking BrakeDocument4 pagesTravel Parking BrakeAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Power Train Hydraulic System (SENR9159-10)Document3 pagesPower Train Hydraulic System (SENR9159-10)Anderson Oliveira SilvaNo ratings yet
- Electrovalvula 928GDocument7 pagesElectrovalvula 928Garnoldmec100% (1)
- Transmission Hydraulic SystemDocument3 pagesTransmission Hydraulic Systemcristian chuquicondor torres100% (1)
- Control Valve (Straight Travel)Document5 pagesControl Valve (Straight Travel)Steven ManuputtyNo ratings yet
- 330C Excavator Hydraulic Syste1Document4 pages330C Excavator Hydraulic Syste1john ayengahNo ratings yet
- Transmission: Hydraulic ControlDocument4 pagesTransmission: Hydraulic Controlardan fadilah100% (1)
- Control Hidraulico de La Transmision D6NDocument7 pagesControl Hidraulico de La Transmision D6NDavid manjarresNo ratings yet
- Relief Valve CrossoverDocument5 pagesRelief Valve CrossoverSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- Motor de Direccion Operacion de Sistemas KPZ D8TDocument3 pagesMotor de Direccion Operacion de Sistemas KPZ D8Talmag0167No ratings yet
- Transmission Hydraulic Control OperationDocument8 pagesTransmission Hydraulic Control OperationRwan MarymNo ratings yet
- 966H Fan SystemDocument3 pages966H Fan SystemSaidou COULIBALYNo ratings yet
- Power Train Hydraulic System d7gDocument3 pagesPower Train Hydraulic System d7gcristian chuquicondor torres100% (2)
- Hydraulic Schematic (Steering System) : Fonctionnement Des SystèmesDocument4 pagesHydraulic Schematic (Steering System) : Fonctionnement Des SystèmesOUMJRANNo ratings yet
- Transmission Hydraulic System 966Document5 pagesTransmission Hydraulic System 966Walid HouranNo ratings yet
- Valvula de Control DireccionDocument5 pagesValvula de Control DireccionRafael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Transmission Hydraulic SystemDocument4 pagesTransmission Hydraulic SystemEdgarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System Operation for D11N Track-Type TractorDocument43 pagesHydraulic System Operation for D11N Track-Type Tractormiguel_catNo ratings yet
- Steering Control Valve - HMU Steering 950G 2002Document15 pagesSteering Control Valve - HMU Steering 950G 2002ssinokrotNo ratings yet
- 24M Motor Grader B9300001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY C18 Engine (SEBP6378 - 46) - Controle Hidráulico de TransmissãoDocument3 pages24M Motor Grader B9300001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY C18 Engine (SEBP6378 - 46) - Controle Hidráulico de TransmissãoDouglas GomesNo ratings yet
- Lubrication System: Systems OperationDocument4 pagesLubrication System: Systems OperationHasby Potter100% (1)
- Hydraulic Shematic FonctionDocument10 pagesHydraulic Shematic FonctionatelierNo ratings yet
- Electrohydraulic Pilot ManifoldDocument5 pagesElectrohydraulic Pilot ManifoldBroCactusNo ratings yet
- 785D Off-Highway Truck Hydraulic System Systems OperationDocument24 pages785D Off-Highway Truck Hydraulic System Systems Operation1No ratings yet
- Transmision D6D PDFDocument72 pagesTransmision D6D PDFJose Luis Garcia Blanco100% (3)
- d6h Power TrainDocument55 pagesd6h Power TrainLuis Carlos Ramos100% (7)
- Transmission Hydraulic Control OperationDocument8 pagesTransmission Hydraulic Control Operationzawmoe aungNo ratings yet
- Funcionamiento Convertido 960 FDocument54 pagesFuncionamiento Convertido 960 FMiguel Huaman PolarNo ratings yet
- Nguyên lý làm việc hệ thống đi chuyển ủi d7gDocument70 pagesNguyên lý làm việc hệ thống đi chuyển ủi d7gDu TrầnNo ratings yet
- 938F Wheel Loader 7SN00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3116 Engine (SEBP2374 - 53) - Sistemas y ComponentesDocument15 pages938F Wheel Loader 7SN00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3116 Engine (SEBP2374 - 53) - Sistemas y ComponentesCarlos Andres Campos TorresNo ratings yet
- Sys - Opert. Steering Control Valve HmuDocument17 pagesSys - Opert. Steering Control Valve HmuDidi PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Valvula Selectora Trans.Document4 pagesValvula Selectora Trans.enriqueNo ratings yet
- 446D Valvula de Prioridad. Operacion de SistemaDocument8 pages446D Valvula de Prioridad. Operacion de SistemaCarlos IrabedraNo ratings yet
- Digrama d6h FrenosDocument63 pagesDigrama d6h FrenosRODRIGO HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Transmision Retroexcavadora VilavilaDocument30 pagesTransmision Retroexcavadora VilavilaRZ EmiNo ratings yet
- Travel Motor System OperationDocument9 pagesTravel Motor System OperationAllan Lariosa100% (1)
- General Information (Brake, Hydraulic Fan System)Document5 pagesGeneral Information (Brake, Hydraulic Fan System)EVER DAVID SAAVEDRA HUAYHUA0% (1)
- Hydraulic Fan SystemDocument4 pagesHydraulic Fan SystemEVER DAVID SAAVEDRA HUAYHUA100% (1)
- Piston Pump (Brake, Hydraulic Fan)Document7 pagesPiston Pump (Brake, Hydraulic Fan)EVER DAVID SAAVEDRA HUAYHUANo ratings yet
- U3 - 2-D4E Power Shift OperacionDocument35 pagesU3 - 2-D4E Power Shift Operacionchristian vergaray gonzales100% (1)
- Steering Control Valve (HMU Steering) 962HDocument13 pagesSteering Control Valve (HMU Steering) 962HAngelito MuñozNo ratings yet
- Systems Operation (Senr7046-00) d9h TransmisionDocument56 pagesSystems Operation (Senr7046-00) d9h TransmisionAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Operacion de Sis EmasDocument50 pagesOperacion de Sis EmasAlfredo Guzmán100% (1)
- Sistema Control Trans 140hDocument7 pagesSistema Control Trans 140hFernando Ortiz86% (7)
- Перенаправленный документ принтера удаленного рабочего столаDocument9 pagesПеренаправленный документ принтера удаленного рабочего столаANDREI26No ratings yet
- Lubrification 3412Document37 pagesLubrification 3412Mirabeau Tchio DasseNo ratings yet
- Piston Pump (Brake, Hydraulic Fan)Document7 pagesPiston Pump (Brake, Hydraulic Fan)kiddrix gamerNo ratings yet
- AndresitoDocument25 pagesAndresitoJoan VasquezNo ratings yet
- D9R Hydraulic SystemDocument24 pagesD9R Hydraulic SystemMarta TiaNo ratings yet
- Power Train Hydraulic System 740Document16 pagesPower Train Hydraulic System 740Jesus Almanzar Santos100% (4)
- 11 Main Hydraulic PumpDocument4 pages11 Main Hydraulic PumpZawminhtun100% (1)
- Hydraulic System: Operación de SistemasDocument5 pagesHydraulic System: Operación de Sistemasmiguel_catNo ratings yet
- SO - Pilot Hydraulic SystemDocument8 pagesSO - Pilot Hydraulic Systemisaac989No ratings yet
- Transmission Hydraulic Control Operation 966Document12 pagesTransmission Hydraulic Control Operation 966Walid HouranNo ratings yet
- Hid Fan 966fDocument5 pagesHid Fan 966fSyahdiNo ratings yet
- Graphic Color CodesDocument2 pagesGraphic Color CodesAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- System Configuration ParametersDocument3 pagesSystem Configuration ParametersAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Fuel System C7 and C9 - Caterpillar Electronic Engine - Blog - TeknisiDocument19 pagesFuel System C7 and C9 - Caterpillar Electronic Engine - Blog - TeknisiAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Fuel System C7 and C9 - Caterpillar Electronic Engine - Blog - TeknisiDocument19 pagesFuel System C7 and C9 - Caterpillar Electronic Engine - Blog - TeknisiAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Engine Oil Pressure Sensor - Remove and Install - Intake Valve Actuator (RENR9705) C13Document2 pagesEngine Oil Pressure Sensor - Remove and Install - Intake Valve Actuator (RENR9705) C13Allan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Training Equipment: Common Rail Diesel EngineDocument80 pagesVehicle Training Equipment: Common Rail Diesel Enginestrumf381No ratings yet
- Caterpillar Machines With Acert Technology: For More Information VisitDocument4 pagesCaterpillar Machines With Acert Technology: For More Information VisitAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Machines With Acert Technology: For More Information VisitDocument4 pagesCaterpillar Machines With Acert Technology: For More Information VisitAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Crankshaft Position Sensor - Remove and Install (RENR9705) C13Document2 pagesCrankshaft Position Sensor - Remove and Install (RENR9705) C13Allan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Engine Control FundamentalsDocument29 pagesEngine Control FundamentalsVikrant SharmaNo ratings yet
- ACERT Engine Brochure PDFDocument13 pagesACERT Engine Brochure PDFtruckman1000No ratings yet
- Graphic Color CodesDocument2 pagesGraphic Color CodesAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- 14m Hydraulic Fan SystemDocument1 page14m Hydraulic Fan SystemAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Competitive Bulletin: Caterpillar ACERT™ vs. Volvo V-ACT Tier 3 EnginesDocument12 pagesCompetitive Bulletin: Caterpillar ACERT™ vs. Volvo V-ACT Tier 3 EnginesAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Graphic Color CodesDocument2 pagesGraphic Color CodesAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Coconut Water Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsDocument3 pagesCoconut Water Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 2: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument19 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 2: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyBill Villon79% (58)
- Engine Control FundamentalsDocument29 pagesEngine Control FundamentalsVikrant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cauliflower Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsDocument3 pagesCauliflower Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Asparagus Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsDocument3 pagesAsparagus Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Cucumber Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsDocument3 pagesCucumber Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- ADM-MIL-SHS-Module 3 Reviewed Nov 26 Sir YujinDocument26 pagesADM-MIL-SHS-Module 3 Reviewed Nov 26 Sir Yujinjohn_mateo75% (12)
- Media and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Types of Media (Print, Broadcast, New Media)Document27 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Types of Media (Print, Broadcast, New Media)Bill Villon63% (30)
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument24 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyBill Villon100% (5)
- How To Be A Better Driver - 14 Easy Steps (With Pictures)Document5 pagesHow To Be A Better Driver - 14 Easy Steps (With Pictures)Allan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3: Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument21 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3: Responsible Use of Media and InformationBill Villon76% (17)
- 1 Functions Math111Document82 pages1 Functions Math111Allan LariosaNo ratings yet
- ADM-MIL-SHS-Module 2 Reviewed Nov 26 Sir YujinDocument23 pagesADM-MIL-SHS-Module 2 Reviewed Nov 26 Sir Yujinjohn_mateo90% (10)
- How To Drive Defensively - 9 Easy Steps (With Pictures)Document4 pagesHow To Drive Defensively - 9 Easy Steps (With Pictures)Allan LariosaNo ratings yet
- 21 PavementMarkingsDocument4 pages21 PavementMarkingsOladunni AfolabiNo ratings yet
- EN DX140W-7 DX160W-7 Brochure D4600863 04-2023Document28 pagesEN DX140W-7 DX160W-7 Brochure D4600863 04-2023Kormaw FilfiluNo ratings yet
- Compact BOP Section 7 - Maintenance + TestingDocument9 pagesCompact BOP Section 7 - Maintenance + TestingLawrence FernandesNo ratings yet
- Tou 43-02Document30 pagesTou 43-02Hajirashid26No ratings yet
- Mechanical Pressure Switches MDS: FluidcontrolDocument6 pagesMechanical Pressure Switches MDS: FluidcontrolLeninNo ratings yet
- Cummins Diessel Engine m11 Troubleshooting and Repair ManualDocument20 pagesCummins Diessel Engine m11 Troubleshooting and Repair Manualevelyn100% (48)
- Hydraulic Cylinder Honing PDFDocument36 pagesHydraulic Cylinder Honing PDFFredy Alvarez CespedesNo ratings yet
- Re 15224Document12 pagesRe 15224Ahmed Abd ElhakeemNo ratings yet
- Multihead Hydraulic Swaging Unit (MHSU) : Setup and Operating InstructionsDocument6 pagesMultihead Hydraulic Swaging Unit (MHSU) : Setup and Operating InstructionslerdoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Four-Stroke - Engine - BasicsDocument47 pagesLecture 3 - Four-Stroke - Engine - BasicsArwa HusseinNo ratings yet
- Tata 207 Di LHD Cat PDFDocument253 pagesTata 207 Di LHD Cat PDFkaustubh s100% (2)
- Condensate & Feedwater System - Steam Turbine & Condenser PDFDocument37 pagesCondensate & Feedwater System - Steam Turbine & Condenser PDFjhchung1110% (1)
- K3V112DT Instruction Manual OverviewDocument40 pagesK3V112DT Instruction Manual Overviewjuanchis650100% (7)
- Rebar Bender ManualDocument23 pagesRebar Bender ManualMahmoud AliNo ratings yet
- Piston and Rings: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument9 pagesPiston and Rings: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenalonsoNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Engine Thermodynamic CycleDocument16 pages4 Stroke Engine Thermodynamic CycleNatallia NatalliaNo ratings yet
- PneumaticclampsDocument36 pagesPneumaticclampsHector Serrano SantosNo ratings yet
- 11528918-Ford Tw10 Tw20 Tw30 Workshop ManualDocument111 pages11528918-Ford Tw10 Tw20 Tw30 Workshop Manualmrbazha80% (15)
- L20 Series: Service and Repair ManualDocument28 pagesL20 Series: Service and Repair ManualJoe CorreaNo ratings yet
- Effect Mechanism and Quantitative Analysis of Injector Faults On Diesel Engine PerformanceDocument22 pagesEffect Mechanism and Quantitative Analysis of Injector Faults On Diesel Engine Performancefabio1199No ratings yet
- Reliability Assessment of Rolling Piston Rotary CompressorsDocument89 pagesReliability Assessment of Rolling Piston Rotary CompressorsSundaraPandiyanNo ratings yet
- Delfino Service ManualDocument107 pagesDelfino Service ManualDavid BenitoNo ratings yet
- Rok 3lt enDocument2 pagesRok 3lt enJesus SanchezNo ratings yet
- Kta 38 g12 Parts CatlogDocument198 pagesKta 38 g12 Parts CatlogVinesh Vineshb100% (3)
- Putzmeister-Mortar Technology-P13 - EN PDFDocument2 pagesPutzmeister-Mortar Technology-P13 - EN PDFAlexandru NutuNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat 336E L Excavator (Prefix TEG) Service Repair Manual (TEG00001 and Up)Document29 pagesCaterpillar Cat 336E L Excavator (Prefix TEG) Service Repair Manual (TEG00001 and Up)kfsmmeNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Powerhead Specifications and RepairDocument30 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Powerhead Specifications and RepairBaxter LoachNo ratings yet
- ATR-1 Antilock Traction Relay Valve (SD-13-4811)Document12 pagesATR-1 Antilock Traction Relay Valve (SD-13-4811)emmanuelNo ratings yet
- MGB COMPETITION PREPARATION MANUALDocument39 pagesMGB COMPETITION PREPARATION MANUALasrwNo ratings yet
- Ex110 (697na Bsii 2016) PDFDocument32 pagesEx110 (697na Bsii 2016) PDFGyanprakash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual 2T Rotax Aircraft EngineDocument57 pagesMaintenance Manual 2T Rotax Aircraft Enginellovar100% (2)