Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Postpartum Infection
Postpartum Infection
Uploaded by
Amiraah MasriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Postpartum Infection
Postpartum Infection
Uploaded by
Amiraah MasriCopyright:
Available Formats
Postpartum Infection
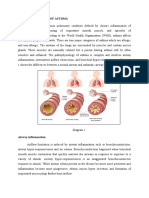
Puerperal or postpartum infection is common infection in the uterus that happens after
delivery. After delivery, the uterus may develop infection if the amniotic sac are
infected. The uterine infection are included endometritis (infection of uterine lining),
myometritis (infection of uterine muscle) and parametritis (infection around uterus
area). (Moldenhouer, 2020)
Pathophysiology of Postpartum Infection
The vagina contains a large number of microorganism in proximity to the normally
upper sterile genital tract. These organisms from vagina may introduce into uterus
during labor and delivery process. Moreover, the uterine cavity also has two
characteristic that may contribute to the possibility of infection which is a large
surface area that allow infection to occur and during placenta delivery, there is large
open venous channels under the placenta that are directly accessible to bacteria enable
the infections (Eschenbach, 2018). Although the uterus serves barrier to any infection,
once the barrier is break, it is easy the infection to occur which commonly happen
during cesarean section, urinary catheter placement, and intravenous line placement.
Sign and Symptoms of Postpartum Infection
I Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic
II Fever within 1 to 3 days after delivery
III General feeling illness or discomfort
IV Headache
V Loss of appetite
VI Tachypnea (rapid heart rate)
VII Swollen or tenderness at uterus
VIII Foul smelling vaginal discharge
IX Paleness and chills
Causes of Postpartum Infection
I A long delay (often more than 18 hours) between ruptured membrane and
delivery.
II Internal monitoring of the fetus (which require ruptured membranes
containing the fetus)
III Prolonged labor (low progression labor)
IV Cesarean delivery
V Repeated vaginal examination during labor
VI Placental fragments remaining in the uterus after delivery
VII Bacterial vaginosis
Risk factors of Postpartum Infection
I Anemia
II Obesity
III Women with sexual transmitted disease
IV Multiple vaginal examinations during labor
V Women undergo Caesarean section
VI Delay between ruptured amniotic sac ruptured and delivery
VII Having remained placenta in the uterus after delivery
VIII Excessive bleeding after delivery
References
Moldenhauer, J. S., Last full review/revision May 2020| Content last modified May
2020. (2020). Postpartum Infections of the Uterus - Women's Health Issues. Retrieved
June 15, 2020, from https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-
issues/postdelivery-period/postpartum-infections-of-the-uterus
Eschenbach, D. (2018). Serious Postpartum Infections. Retrieved June 2020, from
https://www.glowm.com/section_view/item/177
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- OB 1 - 1.02 Physiology of Menstruation and Decidua PDFDocument11 pagesOB 1 - 1.02 Physiology of Menstruation and Decidua PDFMDreamerNo ratings yet
- Puberty - GirlsDocument37 pagesPuberty - Girlsjonathan100% (1)
- Applied Veterinary Gynaecology and Obste1 PDFDocument377 pagesApplied Veterinary Gynaecology and Obste1 PDFHamza AlviNo ratings yet
- Precipitate and Prolonged LabourDocument16 pagesPrecipitate and Prolonged LabourN. Siva100% (3)
- S5LT-IIc-3.3.1-THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE PDFDocument5 pagesS5LT-IIc-3.3.1-THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE PDFMelyn BustamanteNo ratings yet
- MCQ ReproductionDocument2 pagesMCQ Reproductionwanderer_1010100% (1)
- A Network On Chip Architecture and Design MethodologyDocument8 pagesA Network On Chip Architecture and Design MethodologyAmiraah MasriNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Female Reproductive System The Ovarian CycleDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Female Reproductive System The Ovarian CycleAmiraah MasriNo ratings yet
- Retained PlacentaDocument2 pagesRetained PlacentaAmiraah MasriNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Asthma Trigger 1Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Asthma Trigger 1Amiraah MasriNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Asthma Trigger 1Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Asthma Trigger 1Amiraah MasriNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesReproductive SystemA.S.A. QuerubinNo ratings yet
- The Gynaecological ExaminationDocument3 pagesThe Gynaecological ExaminationpogimudaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJade AltarejosNo ratings yet
- PartogramDocument31 pagesPartogramRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Physiology NotesDocument5 pagesReproductive System Physiology NotesKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Amenorrhea UpdatedDocument30 pagesAmenorrhea UpdatedAbdi fatah ali1No ratings yet
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- MCN PPT PostpartumDocument30 pagesMCN PPT PostpartumJohn MajanNo ratings yet
- 010 - Female Reproductive System IIIDocument3 pages010 - Female Reproductive System IIIRaffy GutmanNo ratings yet
- Lab - Stages of The Human Menstrual CycleDocument15 pagesLab - Stages of The Human Menstrual CycleJohn gamingNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System AssessmentDocument116 pagesFemale Reproductive System AssessmentJeno MNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. Chapter 12. Human Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesWorksheet. Chapter 12. Human Reproductive SystemLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- GYN Sakshi Arora 9edDocument54 pagesGYN Sakshi Arora 9edHigh Class Education (H.C.Education)No ratings yet
- Emergency ChildbirthDocument12 pagesEmergency ChildbirthCharles Reginald K. HwangNo ratings yet
- Patriarchy in The Workplace: A Woman's OppressionDocument4 pagesPatriarchy in The Workplace: A Woman's OppressionCasandra SobczakNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Debates Over Female Genital CuttingDocument12 pagesThe Evolution of Debates Over Female Genital CuttingLMhae CalderonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Microscopic Anatomy of The Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesExperiment 1: Microscopic Anatomy of The Reproductive Systemharman parmarNo ratings yet
- Literatur Review Pijat Oksitosin Dan Aroma TerapyDocument11 pagesLiteratur Review Pijat Oksitosin Dan Aroma TerapySalman FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Neutralizes The Acidity of The UrethraDocument12 pagesNeutralizes The Acidity of The Urethracresia hidalgoNo ratings yet
- Abortus Spontaneous Incomplete With Previous Curettage InfectionDocument4 pagesAbortus Spontaneous Incomplete With Previous Curettage InfectionNofita AizzaNo ratings yet
- CiplaMed - Contraception Cafeteria - 2019-06-21Document12 pagesCiplaMed - Contraception Cafeteria - 2019-06-21Ayushman UjjawalNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Pit (Fer Room)Document3 pagesJadwal Pit (Fer Room)Dwi Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Model Asuhan Kebidanan Berbasis Teori Helen Varney Dalam Deteksi Dini Preeklampsia Kehamilan Di RSIA Citra Keluarga Kota KediriDocument12 pagesModel Asuhan Kebidanan Berbasis Teori Helen Varney Dalam Deteksi Dini Preeklampsia Kehamilan Di RSIA Citra Keluarga Kota Kedirirosha yuliantiNo ratings yet
- Superfetation - April Mae SumacoDocument36 pagesSuperfetation - April Mae SumacoDaniel TomnobNo ratings yet