Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pulse Code Modulation
Uploaded by
عبدالله سعد محمدصالح0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views26 pagesOriginal Title
pulsecodemodulation-130331092752-phpapp02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views26 pagesPulse Code Modulation
Uploaded by
عبدالله سعد محمدصالحCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Pulse Code Modulation
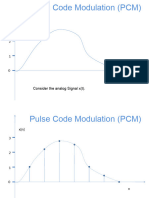
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
Analog voice data must be translated into a series of
binary digits before they can be transmitted.
With Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), the amplitude of
the sound wave is sampled at regular intervals and
translated into a binary number.
The difference between the original analog signal and
the translated digital signal is called quantizing error.
PCM
PCM uses a sampling rate of 8000 samples per
second.
Each sample is an 8 bit sample resulting in a
digital rate of 64,000 bps (8 x 8000).
Converting Samples to Bits
Quantizing
Similar concept to pixelization
Breaks wave into pieces, assigns a value in a
particular range
8-bit range allows for 256 possible sample
levels
More bits means greater detail, fewer bits
means less detail
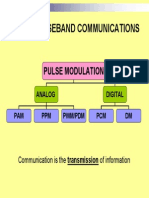
MULTIPLEXING TYPES
Frequency Division Multiplexing
Time Division Multiplexing
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
Categories of multiplexing
FDM
Is the process of translating
individual speech circuits (300-
3400Hz) into pre assigned slots
within the bandwith of transmission
medium. and, the preassigned slots
are always available to each user
FDM
FDM process
FDM demultiplexing example
TDM
The process where a transmission
medium is shared by a number of circuits
in time domain by establishing a
sequence of time slots during which
individual channels can be transmitted…
Thus the entire bandwidth is periodically
available to each channel
TDM
TDM frames
PCM PROCESSES
Filtering
Sampling
Quantization
Encoding
Line coding
SAMPLING
SAMPLING THEOREM
“ If a band limited signal is sampled at regular
intervals of time and at a rate equal to or more
than twice the highest signal frequency in the
band, then the sample contains all the
information of the original signal”
Fs= >2fH
PULSE CODE MODULATION
• Voice Frequency range 0- 4 Khz
• Sampling the Voice Signal @ 8 Khz
(Double the Max. Frequency as per
sampling theorem) i.e. 8000s/sec
• Sampling time period Ts=1sec/8000
• Ts= 125 microsec
• Time available for sampling each channel,
when we have N total channels=125/N
• In PCM, Time frame=125microsec ;time
available per chl=125/32 =3.9microsec.
QUANTIZING
The process of measuring the numerical
values of the samples and giving them a
table value in a suitable scale
The finite number of amplitude intervals is
called the ‘quantizing interval’ like
quantizing interval no.1 is 10-20mV; 2 is
20-30mV etc. in a case of 1V signal.
Linear quantizing is where the quantizing
intervals are of the same size
QUANTIZING
Quantization intervals are coded in binary
form, and so the quantization intervals will be
in powers of 2.
In PCM, 8 bit code is used and so we have 256
intervals for quantizing (128 levels in the
positive direction and 128 levels in negative
direction)
QUANTIZATION DISTORTION
The deviation between the amplitude of
samples at the transmitter and receiving ends
In linear quantization, the distortion is more
and to decrease the distortion, the no. of steps
in the given amplitude range has to be
increased.
Due to BW limitations, more quantum levels in
small amplitude region are planned results to
Non linear (uniform) quantization
COMPANDING
Is the process where non uniform quantization
is achieved using segmented quantization
In companding, to specify the location of
sample value, the following are necessary…
sign of the sample, the segment no., the
quantum level within the segment.
PCM ENCODING
FRAME STRUCTURE
In PCM we have 32 Ts and Ts 0 (FAW)
carries the synchronization signals and FAW
digit value is X 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 . FAW
transmitted in alternate frame. In FAW unused
frames, supervisory and alarm signals are
transmitted
Ts 16 carries the signalling information (for 2
channels)
FRAME STRUCTURE
For carrying the signalling for all 30 chls and
for carrying sync. Data for all frames, in PCM
16 frame pattern is used and it is known as
multi frame
Duration of multi frame is 2msecs.
PCM Standards
THERE ARE TWO STANDARDS OF PCM
NAMELY
1) THE EUROPEAN 2 ) THE AMERICAN.
THEY DIFFER SLIGHTLY IN THE DETAIL OF
THEIR WORKING BUT THE PRINCIPLES ARE
THE SAME.
EUROPEAN PCM = 30 CHANNELS
NORTH AMERICAN PCM = 24 CHANNELS
JAPANESE PCM = 24 CHANNELS
IN INDIA WE FOLLOW THE EUROPEAN PCM
OF 30 CHANNELS SYSTEM WORKING.
JUSTIFICATION TYPES
Positive justification: Common
synchronization bit rate offered at each
tributary is higher than the bit rate of
individual tributary.
Positive-negative justification
Negative justification
You might also like
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument26 pagesPulse Code Modulationbree789No ratings yet
- Pondicherry UniversityDocument17 pagesPondicherry Universitygood updaterNo ratings yet
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- PCM Agenda for Electronics Engineering DepartmentDocument17 pagesPCM Agenda for Electronics Engineering Departmentjohn billy balidioNo ratings yet
- PCM PrincipleDocument31 pagesPCM PrincipleSachin PatelNo ratings yet
- PCM PrinciplesDocument45 pagesPCM PrinciplesKapil BhutaniNo ratings yet
- PCM PriniciplesDocument36 pagesPCM PriniciplesbhagNo ratings yet
- PCM Digital MUX ConceptsDocument38 pagesPCM Digital MUX ConceptsGireesh Chowdary GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- PCM Telecommunication System EngineeringDocument49 pagesPCM Telecommunication System EngineeringAliImranNo ratings yet
- PCM MUX Hierarchy NewDocument16 pagesPCM MUX Hierarchy NewJason RogersNo ratings yet
- Pulse-code modulation (PCM) for digitizing analog signalsDocument54 pagesPulse-code modulation (PCM) for digitizing analog signalsdiversity_86No ratings yet
- Transmission System: Lecture # 1 by Sajjad KarimDocument26 pagesTransmission System: Lecture # 1 by Sajjad KarimMohsin NisarNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument16 pagesDigital CommunicationAli Najim Al-AskariNo ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) ExplainedDocument45 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM) ExplainedKunal KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Conversion (A/D) : Engr. Francis B. MalitDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital Conversion (A/D) : Engr. Francis B. MalitJuliene ArganaNo ratings yet
- PCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberDocument77 pagesPCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberTao Thích Màu ĐenNo ratings yet
- Week 3 1 PDFDocument33 pagesWeek 3 1 PDFosmanriazNo ratings yet
- EE 3206, Exp 03Document3 pagesEE 3206, Exp 03Tahsin Zaman TalhaNo ratings yet
- Pcs Module 5 NotesDocument47 pagesPcs Module 5 NotesYogeshwar SNo ratings yet
- Transmission: N No of LevelsDocument14 pagesTransmission: N No of LevelsAshwani BhallaNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument14 pagesSwitchingPikesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission: Analog-to-Digital Conversion TechniquesDocument15 pagesDigital Transmission: Analog-to-Digital Conversion TechniquesAkash RajNo ratings yet
- PCM AdcsDocument47 pagesPCM Adcspmbrahvee115No ratings yet
- Baseband Formatting TechniquesDocument89 pagesBaseband Formatting TechniquesKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- William Stallings: Digital Data Communications TechniquesDocument49 pagesWilliam Stallings: Digital Data Communications TechniquesRekha V RNo ratings yet
- Analog To DigitalDocument14 pagesAnalog To DigitalHarshit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationsDocument39 pagesDigital Communicationsmakomdd100% (1)
- DC Lab ManualDocument24 pagesDC Lab Manualvidyae100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Ecm413 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Ecm413 PDFCaha yANo ratings yet
- Exp. PCMDocument9 pagesExp. PCMsairajdreamNo ratings yet
- PCM: Pulse Code Modulation GuideDocument9 pagesPCM: Pulse Code Modulation GuideMd.Robin MridhaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Chapter 1Document43 pagesDigital Communication Chapter 1aarushibawejajiNo ratings yet
- Analog To DigitalDocument17 pagesAnalog To DigitalI KaizokuNo ratings yet
- 3 CH 4Document49 pages3 CH 4Amanman WubetNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument53 pagesIntroduction to Digital Modulation TechniquesMuhamad Fuad100% (1)
- 8thpracticalDocument8 pages8thpracticalShubham RathodNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission (Pulse Modulation)Document61 pagesDigital Transmission (Pulse Modulation)Fritz FatigaNo ratings yet
- Analog To DigitalDocument15 pagesAnalog To DigitalMani SandeepNo ratings yet
- 3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Document34 pages3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Brian Edward HarrisNo ratings yet
- PCM PDFDocument43 pagesPCM PDFjain niragNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation TechniquesDocument43 pagesPulse Modulation Techniquesyohans shegawNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATION 2 (Reviewer)Document22 pagesCOMMUNICATION 2 (Reviewer)Jovel Jhon Opiana100% (1)
- Digital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDFDocument39 pagesDigital Communications - Fundamentals & Applications (Q0) PDFMohamd barcaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications - H.AN PDFDocument12 pagesDigital Communications - H.AN PDFMohamd barca100% (1)
- Digital Transmission: PCM ProcessesDocument28 pagesDigital Transmission: PCM ProcessesLharie Mae BecinaNo ratings yet
- PCM BahaaDocument50 pagesPCM BahaaNazar liveNo ratings yet
- Poc Unit 3Document26 pagesPoc Unit 3aashishscribdNo ratings yet
- PCM and Digital ModulationDocument72 pagesPCM and Digital ModulationPhan TranNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: Aim:-Apparatus: - MATLAB. Theory of Pulse Code Modulation & DemodulationDocument6 pagesExperiment No.: Aim:-Apparatus: - MATLAB. Theory of Pulse Code Modulation & DemodulationSujal GolarNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersDocument33 pagesDigital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersMukesh100% (5)
- 6 PCM DM DPCMDocument33 pages6 PCM DM DPCMWidyaninurul HidayantiNo ratings yet
- Data Communication - 8Document43 pagesData Communication - 8Md Khairum MonirNo ratings yet
- Analog to Digital Conversion Using PCMDocument17 pagesAnalog to Digital Conversion Using PCMShakeel AminNo ratings yet
- Data Communication (PCM)Document234 pagesData Communication (PCM)Siddhartha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Techniques ExplainedDocument34 pagesDigital Transmission Techniques Explainedposktova100% (1)
- Introduction To Digital Communication (Lectures)Document13 pagesIntroduction To Digital Communication (Lectures)Arnav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Bab 7 Multimedia Kompresi AudioDocument52 pagesBab 7 Multimedia Kompresi AudioElektro ForceNo ratings yet
- A Power Point Presentation by Sagar & PradeepDocument12 pagesA Power Point Presentation by Sagar & Pradeepعبدالله سعد محمدصالحNo ratings yet
- 2009-CPE-03 Uce&T Bzu MultanDocument20 pages2009-CPE-03 Uce&T Bzu Multanعبدالله سعد محمدصالحNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument13 pagesPulse Code ModulationShakeel AminNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code ModulationDocument17 pagesPulse Code Modulationعبدالله سعد محمدصالحNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub - All Commands in Ms Dos PDFDocument44 pagesIdoc - Pub - All Commands in Ms Dos PDFAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- AocvDocument5 pagesAocvgowripNo ratings yet
- Draft SemestralWorK Aircraft2Document7 pagesDraft SemestralWorK Aircraft2Filip SkultetyNo ratings yet
- GCSE Current and Charge AnswersDocument2 pagesGCSE Current and Charge AnswersLakhan VaishnavNo ratings yet
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument24 pages8086 Microprocessorsamrat kumar100% (1)
- Loan Prediction SystemDocument31 pagesLoan Prediction SystemFakorede Akinwande alexNo ratings yet
- Resume Akila BanuDocument7 pagesResume Akila BanuAkila BanuNo ratings yet
- HANS - Udyam Registration CertificateDocument2 pagesHANS - Udyam Registration Certificateshivi mishraNo ratings yet
- Oxford University Press Mind AssociationDocument29 pagesOxford University Press Mind AssociationTran Thi ThaoNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision and Action Recognition A Guide For Image Processing and Computer Vision Community For Action UnderstandingDocument228 pagesComputer Vision and Action Recognition A Guide For Image Processing and Computer Vision Community For Action UnderstandingWilfredo MolinaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Weather StationDocument8 pagesAutomatic Weather StationMyat Tun OoNo ratings yet
- IvaraEXPIntegration OracleDocument175 pagesIvaraEXPIntegration OracleAlejandroZappaNo ratings yet
- Anomaly Detection Using A Self-Sufficient Ad Hoc Electrical Impedance Tomography Sensor Deployed Within Imaged SpaceDocument5 pagesAnomaly Detection Using A Self-Sufficient Ad Hoc Electrical Impedance Tomography Sensor Deployed Within Imaged Spaceaibramai3No ratings yet
- Hypermesh Basic TrainingDocument84 pagesHypermesh Basic TrainingJohnNo ratings yet
- First American Grand Prix - The Savannah Auto Races, 1908-1911, The - Tanya A. BaileyDocument239 pagesFirst American Grand Prix - The Savannah Auto Races, 1908-1911, The - Tanya A. BaileyFilipeBouraNo ratings yet
- Battery StorageDocument46 pagesBattery StorageKishore MuluguNo ratings yet
- Ei CompendexDocument2 pagesEi CompendexHashim Zameer SanghiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: PRE - Test in Empowerment Technologies (Shs - G11)Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: PRE - Test in Empowerment Technologies (Shs - G11)c- msNo ratings yet
- Context DrivenDocument18 pagesContext DrivenRajib BoseNo ratings yet
- Multiple Vacancies With MENAISCO in Jazan - Saudi ArabiaDocument5 pagesMultiple Vacancies With MENAISCO in Jazan - Saudi ArabiaViiq Corpse GrinderNo ratings yet
- La Flaca - Jarabe de Palo (Drums Only) - Piano TutorialDocument1 pageLa Flaca - Jarabe de Palo (Drums Only) - Piano TutorialLaura Martínez CasorránNo ratings yet
- SSG - FlashSystem 5035 Data SheetDocument13 pagesSSG - FlashSystem 5035 Data SheetpipatlNo ratings yet
- Combo Smart: Compact, Single-Step, Full-Page Scanner Series With Versatile FunctionsDocument2 pagesCombo Smart: Compact, Single-Step, Full-Page Scanner Series With Versatile Functionsminhdung.pham4713No ratings yet
- Ina 122Document14 pagesIna 122Wasang Juwi PracihnoNo ratings yet
- VMware Compatibility Guide Servidores DELL R720 - Vmware 6.5Document2 pagesVMware Compatibility Guide Servidores DELL R720 - Vmware 6.5Emanuel TavaresNo ratings yet
- Simatic S7-PDIAG For S7-300 and S7-400 Configuring Process DiagnosticsDocument198 pagesSimatic S7-PDIAG For S7-300 and S7-400 Configuring Process DiagnosticsOleksandr HusievNo ratings yet
- CCW332 - Digital Marketing - SyllabusDocument2 pagesCCW332 - Digital Marketing - SyllabusV ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design (II) - Sheet 3Document2 pagesEngineering Design (II) - Sheet 3Mohamed SaidNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - Ozone Generator Water SystemDocument3 pagesData Sheet - Ozone Generator Water SystemleeNo ratings yet
- TEC3r Manual 1.9.FDocument130 pagesTEC3r Manual 1.9.FerasmolsdiasNo ratings yet