Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 3 FL Geo
Uploaded by
Bijay Ketan Miahra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThe document summarizes key aspects of river drainage systems and India's major river systems. It describes four common drainage patterns - dendritic, trellis, radial, and rectangular - and features formed by river erosion like gorges, meanders, and deltas. It then outlines India's two major river systems - the Himalayan and peninsular rivers. The Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus river systems of the Himalayas are described as well as four major peninsular basins - Godavari, Narmada, Krishna, and Kaveri. Rivers play important roles like irrigation, navigation, domestic water supply, and hydroelectricity.
Original Description:
mind map class 10
Original Title
ch 3 fl geo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of river drainage systems and India's major river systems. It describes four common drainage patterns - dendritic, trellis, radial, and rectangular - and features formed by river erosion like gorges, meanders, and deltas. It then outlines India's two major river systems - the Himalayan and peninsular rivers. The Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus river systems of the Himalayas are described as well as four major peninsular basins - Godavari, Narmada, Krishna, and Kaveri. Rivers play important roles like irrigation, navigation, domestic water supply, and hydroelectricity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageCH 3 FL Geo
Uploaded by
Bijay Ketan MiahraThe document summarizes key aspects of river drainage systems and India's major river systems. It describes four common drainage patterns - dendritic, trellis, radial, and rectangular - and features formed by river erosion like gorges, meanders, and deltas. It then outlines India's two major river systems - the Himalayan and peninsular rivers. The Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus river systems of the Himalayas are described as well as four major peninsular basins - Godavari, Narmada, Krishna, and Kaveri. Rivers play important roles like irrigation, navigation, domestic water supply, and hydroelectricity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
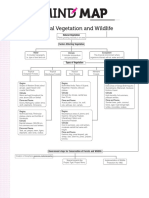
MIND
Drainage
River System
Consists of Features Formed
Tributaries, streams and drainage basin Gorges, meanders,
Ox-bow lakes, deltas
Drainage Pattern
Rectangular Drainage Trellis Drainage Radial Drainage
Dendritic Drainage
Tributaries display Tributaries often intersect Tributaries flow
Streams and
right angle bends and at right angles and are in different directions
tributariesjoin like
are widely spaced. closely spaced. from a central peak.
branches of a tree.
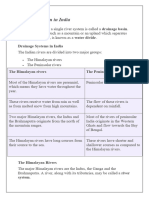
River System in India
Himalayan Rivers Peninsular Rivers
(perennial) (seasonal)
Ganga River System Brahmaputra River System
Indus River System
2500 kms, rises from 2900 kms, rises from
2900 kms, rises in
Gangotri glacier and drains Tibet and drains in
Tibet and drains
in Bay of Bengal forming Bay of Bengal forming
in Arabian sea
Sundarban delta. Sundarban delta.
Godavari Basin Narmada Basin Krishna Basin Kaveri Basin
1500 kms, rises from 1300 kms, rises from 1400 kms, rises from 760 kms, rises from
Western Ghats and Amarkantak hills and a spring in Western Ghats Brahmagiri range and
drains in Bay of Bengal drains in Arabian sea and drains in Bay of Bengal. falls in Bay of Bengal
Role of Rivers
Irrigation Navigation Domestic Uses Hydroelectricity
You might also like
- Lesson 1-Land and Physical Geography of NorthDocument2 pagesLesson 1-Land and Physical Geography of NorthMohammed Nahyan100% (1)
- Indian River SystemDocument40 pagesIndian River SystemRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Anthropology, Space, and Geographic Information Systems (Spatial Information Systems) PDFDocument305 pagesAnthropology, Space, and Geographic Information Systems (Spatial Information Systems) PDFe-cevikNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Climate Activity KEYDocument2 pagesFactors That Affect Climate Activity KEYAbdallah Almekawy100% (2)
- Earth Science Quiz 1Document2 pagesEarth Science Quiz 1Neptune LopezNo ratings yet
- Geomatics Engineering - A Practical Guide To Project Design 2010Document298 pagesGeomatics Engineering - A Practical Guide To Project Design 2010Tan50% (2)
- Class 9 DrainageDocument52 pagesClass 9 DrainageJoe Calvin Rossario86% (7)
- Geography Chapter 3 DrainageDocument22 pagesGeography Chapter 3 Drainage41 Shaivya ManaktalaNo ratings yet
- Rivers of India PDFDocument16 pagesRivers of India PDFSugundan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- DRAINAGEDocument26 pagesDRAINAGESarvagya ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Rainage: Rainage Ystems IN NdiaDocument9 pagesRainage: Rainage Ystems IN NdiavijayNo ratings yet
- Drainage Systems in IndiaDocument13 pagesDrainage Systems in IndiaTawseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Social Science Class 9 FT 2022-23Document9 pagesSocial Science Class 9 FT 2022-23Shruti ParasherNo ratings yet
- Economic Geography IndiaDocument86 pagesEconomic Geography Indianilofer shallyNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - DrainageDocument9 pagesCh3 - DrainageHussainNo ratings yet
- Indian River Systems: For Different Government ExamsDocument13 pagesIndian River Systems: For Different Government ExamsDeepti SinglaNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 8Document24 pagesGeography Handout 8Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Maxfort School, Dwarka: Recognised Senior Secondary School Affiliated To CBSEDocument18 pagesMaxfort School, Dwarka: Recognised Senior Secondary School Affiliated To CBSELasya ThakurNo ratings yet
- Iess 103Document9 pagesIess 103Abhiroop DasNo ratings yet
- Indian River SystemDocument34 pagesIndian River Systemboranihar34No ratings yet
- I: D S H & P: Ndia Rainage Ystem Imalayan EninsularDocument38 pagesI: D S H & P: Ndia Rainage Ystem Imalayan EninsularSandhya KRNo ratings yet
- Rainage: Rainage Ystems IN NdiaDocument9 pagesRainage: Rainage Ystems IN NdiaHavyash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indian GeographyDocument36 pagesIndian GeographyRamNo ratings yet
- 2607 Topper 21 101 1 23 7334 Drainage Up201807191143 1531980807 6187Document6 pages2607 Topper 21 101 1 23 7334 Drainage Up201807191143 1531980807 6187Deepa MundadaNo ratings yet
- 11 GeographyDocument14 pages11 Geographygolichamolu6No ratings yet
- Drainage System - PDF 20Document11 pagesDrainage System - PDF 20Jagdeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Rivers and Drainage PDFDocument9 pagesRivers and Drainage PDFAnirban BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Drainage: India: Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata Class Ix SESSION 2022-23 Geography: Study MaterialDocument5 pagesDrainage: India: Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata Class Ix SESSION 2022-23 Geography: Study MaterialOishi GoswamiNo ratings yet
- DRAINAGE CLASS 9TH GeographyDocument21 pagesDRAINAGE CLASS 9TH GeographyShipra agrawalNo ratings yet
- L-9, India-Location, Extent, Political and Physical FeaturesDocument11 pagesL-9, India-Location, Extent, Political and Physical FeaturesAlfiya PathanNo ratings yet
- Pages From Kegy103Document10 pagesPages From Kegy103Rishabh KashyapNo ratings yet
- Rainage Ystem: Geography - Part IDocument11 pagesRainage Ystem: Geography - Part IAmarnath WadwaleNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Geography Gist of The Lesson Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageDocument7 pagesClass Ix Geography Gist of The Lesson Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageMadhusudan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Drainage: Peninsular Rivers. The Himalayan RiversDocument4 pagesDrainage: Peninsular Rivers. The Himalayan RiverssimsamsmartNo ratings yet
- Drainage System IghjjjDocument8 pagesDrainage System IghjjjAkhilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Rainage Ystem: Geography - Part IDocument11 pagesRainage Ystem: Geography - Part Ijagriti kumariNo ratings yet
- Drainage NotesDocument5 pagesDrainage NotesSarika RawatNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Geography Gist of The Lesson Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageDocument7 pagesClass 9 Geography Gist of The Lesson Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageMadhusudan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- DrainageDocument34 pagesDrainageAthar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - (Philoid-IN)Document11 pagesChapter 3 - (Philoid-IN)Siddharth KumarNo ratings yet
- Drainage Systems of IndiaDocument7 pagesDrainage Systems of IndianifmsNo ratings yet
- DRAINAGEDocument60 pagesDRAINAGEsy96024902No ratings yet
- Geo11 3 India Drainage SystemDocument11 pagesGeo11 3 India Drainage Systemsuperman_universeNo ratings yet
- Peninsular Rivers of India - WbpscupscDocument30 pagesPeninsular Rivers of India - Wbpscupscram choudharyNo ratings yet
- Drainage System in IndiaDocument4 pagesDrainage System in IndiaJosya CLS2RNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Geography Gist of The Lessons Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageDocument7 pagesClass Ix Geography Gist of The Lessons Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageMadhusudan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Drainage Pattern of IndiaDocument8 pagesDrainage Pattern of IndiaBaroNo ratings yet
- Drainage One ShotDocument23 pagesDrainage One ShotkashvikayNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Drainage Class 9th GeographyDocument5 pagesCH 3 Drainage Class 9th GeographySnehasish PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Geography 7 Drainage SystemDocument4 pagesGeography 7 Drainage SystemKankana BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Drainage SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Drainage SystemGaurav SInghNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 DrainageDocument3 pagesCH - 3 DrainageVeena VermaNo ratings yet
- Drainage SystemDocument8 pagesDrainage SystemPralay DasNo ratings yet
- Drainage System of IndiaDocument16 pagesDrainage System of IndiaAju 99Gaming100% (1)
- DRAINAGEDocument4 pagesDRAINAGERitvik GoyalNo ratings yet
- Fkdm. JDocument4 pagesFkdm. JPritthiraj ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Peninsular River System or Peninsular Drainage: Theory 1Document4 pagesPeninsular River System or Peninsular Drainage: Theory 1Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- DrainageDocument37 pagesDrainageSanjay SwamynathanNo ratings yet
- Himalayan River SystemsDocument6 pagesHimalayan River SystemsGauri Sanjeev ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Rainage Ystem: Geography - Part IDocument11 pagesRainage Ystem: Geography - Part IChithra ThambyNo ratings yet
- Samina 4104 Lec 2Document12 pagesSamina 4104 Lec 2Sakib MhmudNo ratings yet
- Rivers of India: By: Sharadha SrinivasanDocument18 pagesRivers of India: By: Sharadha SrinivasanSuhailHaqueNo ratings yet
- 9 SocSc DrainageDocument6 pages9 SocSc DrainageAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- India-Size and Location Class 9 Extra Questions Social Science Geography Chapter 1Document5 pagesIndia-Size and Location Class 9 Extra Questions Social Science Geography Chapter 1Bijay Ketan MiahraNo ratings yet
- CH 4 FL GeoDocument1 pageCH 4 FL GeoBijay Ketan MiahraNo ratings yet
- CH 5 FL GeoDocument1 pageCH 5 FL GeoBijay Ketan MiahraNo ratings yet
- CH 2 FL GeoDocument1 pageCH 2 FL GeoBijay Ketan MiahraNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 4 Climate - Class 9th GeographyDocument5 pagesNotes of CH 4 Climate - Class 9th GeographyBijay Ketan MiahraNo ratings yet
- Report Land SurveyDocument14 pagesReport Land SurveySyedjamelNo ratings yet
- Spatial Data Presentation and VisualizationDocument8 pagesSpatial Data Presentation and VisualizationEng Bagaragaza RomualdNo ratings yet
- New Let TosDocument2 pagesNew Let TosRhailla NOORNo ratings yet
- Relative BearingsDocument2 pagesRelative Bearingskhebiloğlu100% (2)
- Lecturer 2 - Geomorphology and Weathering - 14Document21 pagesLecturer 2 - Geomorphology and Weathering - 14Joseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Program Scheme For BA ReportDocument13 pagesProgram Scheme For BA ReportAnonymous JphxcjzCgbNo ratings yet
- Geocentric Datum, GDM2000 For MalaysiaDocument15 pagesGeocentric Datum, GDM2000 For Malaysialegion1437100% (6)
- B Plan Syllabus Copy SPA - JNAFAUDocument43 pagesB Plan Syllabus Copy SPA - JNAFAUJagadeesh PrakashNo ratings yet
- Population GeographyDocument27 pagesPopulation Geographywebsalesbonn19No ratings yet
- The Magnetic Poles From 1590Document8 pagesThe Magnetic Poles From 1590Aldo Jose Zeas CastroNo ratings yet
- Peran Dan Fungsi IPCNDocument36 pagesPeran Dan Fungsi IPCNFahiraNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson 3 Study GuideDocument1 pageSocial Studies Lesson 3 Study Guideapi-682816189No ratings yet
- Overview of ISO 19100 Series: ISO/TC211 Geographic Information/geomaticsDocument31 pagesOverview of ISO 19100 Series: ISO/TC211 Geographic Information/geomaticsJericko Tejido100% (1)
- Social Studies First LessonDocument3 pagesSocial Studies First LessonAljean M. MiradorNo ratings yet
- Geography 1esoDocument4 pagesGeography 1esomagrotasNo ratings yet
- Ms LYNETTE ADHIAMBO OBAREDocument5 pagesMs LYNETTE ADHIAMBO OBAREdylonochiengNo ratings yet
- K07Document1 pageK07Noore Alam Sarkar100% (1)
- Vcaa 2017 ExamDocument17 pagesVcaa 2017 ExamNikki ChenNo ratings yet
- MMDocument994 pagesMMJM HalinaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: Marquina, Myca Lyn March 2, 2021 BS in Accountancy GED105Document1 pageActivity 3: Marquina, Myca Lyn March 2, 2021 BS in Accountancy GED105sharalyn100% (1)
- Social Sciences - Intermediate PhaseDocument14 pagesSocial Sciences - Intermediate PhaseSongeziwe Alex HlatiNo ratings yet
- Gyro Error GuideDocument2 pagesGyro Error GuideFrancis ParisNo ratings yet
- Scope of Geography HssliveDocument6 pagesScope of Geography Hsslivemonika singh100% (1)
- The Tip of The Iceberg of Great Polar Reads!Document4 pagesThe Tip of The Iceberg of Great Polar Reads!Na TiNo ratings yet
- Cycle-Of-Erosion - UG - I - AI - 1Document28 pagesCycle-Of-Erosion - UG - I - AI - 1vaishnavi chandakNo ratings yet