Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ch2 Force Vectors'
Uploaded by
Laith Jaber0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views37 pagesOriginal Title
ch2 force vectors'
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views37 pagesch2 Force Vectors'
Uploaded by
Laith JaberCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 37
FUNCTIONAL PHYSICS
Statics- Force Vectors
Finding a Resultant Force
Finding the Components of a Force.
Addition of Several Forces.
Important Rules
Addition of a System of Coplanar
Forces
For analytical work we can represent these
components in one of two ways, using either
•Scalar notation
•Cartesian vector notation.
Scalar Notation
Cartesian Vector Notation
Coplanar Force Resultants
Example 1
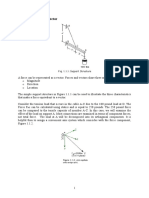
The screw eye is subjected to two forces, F1 and F2 .
Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
Example 1
The screw eye is subjected to two forces, F1 and F2 .
Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
Example 2
Resolve the horizontal 600-lb force into components acting along the u and v axes and
determine the magnitudes of these components.
Example 4
It is required that the resultant force acting on the eyebolt be directed along the positive x axis
and that F2 have a minimum magnitude. Determine this magnitude, the angle theta, and the
corresponding resultant force.
Example 7
The end of the boom is subjected to three concurrent and coplanar forces. Determine the
magnitude and direction of the resultant force
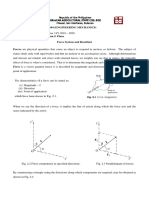
Right-Handed 3D Coordinate System
Right-Handed 3D Coordinate System
A rectangular coordinate system is said to be
right-handed if the thumb of the right hand
points in the direction of the positive z axis
when the right-hand fingers are curled about
this axis and directed from the positive x
towards the positive y axis
Rectangular Components of a Vector
Cartesian Unit Vectors
Cartesian Unit Vectors
Direction of a Cartesian Vector-1-
Direction of a Cartesian Vector-2-
Direction of a Cartesian Vector-3-
Example 8
Express the force F as a Cartesian vector.
Example 10
Express the force F as a Cartesian vector
Addition of Cartesian Vectors
Addition of Cartesian Vectors
Example 2.9
Determine the magnitude and the coordinate direction angles of
the resultant force acting on the ring
Example 2.11
Two forces act on the hook. Specify the magnitude of F2 and its coordinate
direction angles so that the resultant force FR acts along the positive y axis and
has a magnitude of 800 N.
Vector Directed along a line
Example 2.15
The roof is supported by
cables as shown in the
photo. If the cables exert
forces FAB = 100 N and
FAC = 120 N on the wall
hook at A, determine the
resultant force acting at A .
Express the result as a
Cartesian vector
You might also like
- Force Vectors: Add and Resolve Coplanar ForcesDocument20 pagesForce Vectors: Add and Resolve Coplanar Forcesdanaluca2753No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Chapter 2 - Force Systems 2DDocument61 pagesLecture 3 Chapter 2 - Force Systems 2Drobel metikuNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 FORCE VECTOR (Mechanic)Document41 pagesCHAPTER 2 FORCE VECTOR (Mechanic)Afiq NajmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document78 pagesChapter 02Bảo Tín TrầnNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Statics: Force VectorsDocument77 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Statics: Force VectorsnabilahNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Strength of Materials - 1Document93 pagesLecture Notes in Strength of Materials - 1Rhea MambaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Force Vector-OdatDocument101 pagesChapter 2-Force Vector-OdatMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Physical QuantitiesDocument24 pagesPhysical QuantitiesMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Resultant and Equilibrant Forces ExperimentDocument3 pagesResultant and Equilibrant Forces ExperimentIan Garcia0% (1)
- Forces in 3DDocument11 pagesForces in 3DAdeboye BusayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document78 pagesChapter 02Giang ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Scalars and Vectors: ScalarDocument22 pagesScalars and Vectors: Scalarsuwilanji kawambaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture (1) : Vectors and ScalarsDocument20 pagesLecture (1) : Vectors and ScalarsAhmad DaqaladNo ratings yet
- Topic 2. Force VectorDocument18 pagesTopic 2. Force VectorArnold Apostol Jr.No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Statics: Course OverviewDocument51 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Statics: Course OverviewNazmus Sakib AlinNo ratings yet
- Statics 2Document54 pagesStatics 2Arjun TaugNo ratings yet
- g481 1 1 2 Scalars and VectorsDocument7 pagesg481 1 1 2 Scalars and Vectorsapi-236179294No ratings yet
- 02 Me1 PDFDocument5 pages02 Me1 PDFvat007No ratings yet
- Static Module 2 PDFDocument151 pagesStatic Module 2 PDFMac KYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Mechanics of Engineering by HCMUTDocument78 pagesChapter 02 Mechanics of Engineering by HCMUTB NamNo ratings yet
- KR10203 Chapter 1Document64 pagesKR10203 Chapter 1RINA RINANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Chapter 2 - Part IDocument60 pagesLecture 2 Chapter 2 - Part IFeye MumichaNo ratings yet
- Force System and ResultantDocument20 pagesForce System and ResultantMyra GarciaNo ratings yet
- Exp (2) - Vectors (Lab Report)Document12 pagesExp (2) - Vectors (Lab Report)Mansoor Al TunijiNo ratings yet
- Statics Week-1 2014Document25 pagesStatics Week-1 2014OzanCanSubaşıNo ratings yet
- Chapter+2Document24 pagesChapter+2Mary Jane SañoNo ratings yet
- CE201 Statics Chap2Document49 pagesCE201 Statics Chap2taniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document84 pagesChapter 2Ijal HaizalNo ratings yet
- 7 Force AnalysisDocument19 pages7 Force AnalysisEn Eskay100% (1)
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration - 1Document114 pagesSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration - 1qussai salahNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Scalar Quantities: Chapter ObjectivesDocument56 pagesVectors and Scalar Quantities: Chapter ObjectivesLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Force SystemsDocument28 pagesChapter 2: Force SystemsFawad KhanNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors: ESCI 211 - Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument24 pagesForce Vectors: ESCI 211 - Statics of Rigid BodiesVv ZoidNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Statics: Force SystemsDocument77 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Statics: Force SystemsTalal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Chapter 2: Force VectorsDocument42 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies: Chapter 2: Force VectorsRyan Philip CatapangNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Force SystemsDocument30 pagesEquivalent Force SystemsEhreenNo ratings yet
- Statics of Particle: - Forces in PlaneDocument36 pagesStatics of Particle: - Forces in PlaneNorsahira Binti MaslazimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force VectorsDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Force Vectorsaweertt80% (5)
- Eg 231 Tutorial Sheet 1Q - 230118 - 105359Document19 pagesEg 231 Tutorial Sheet 1Q - 230118 - 105359NINEBO MWEWANo ratings yet
- Force VectorDocument47 pagesForce Vectoradeliene 25No ratings yet
- IE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 2 Force VectorsDocument13 pagesIE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 2 Force VectorsBernadeth MontardeNo ratings yet
- Statics Mechanics GuideDocument210 pagesStatics Mechanics Guideabdul khader100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Force VectorsDocument56 pagesChapter 2 Force VectorsMUHAMMAD HASSAAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition of Forces 2D & 3DDocument51 pagesForce Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition of Forces 2D & 3DparklNo ratings yet
- Part1 EmotionDocument46 pagesPart1 EmotionhohoNo ratings yet
- Vector Addition and Resultant ForcesDocument24 pagesVector Addition and Resultant ForcesM Jamshaid TahiriNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium of Concurrent ForcesDocument5 pagesStatic Equilibrium of Concurrent ForcesAhmed AbuNasserNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Engineering MechanicsDocument35 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies: Engineering MechanicsJoylyn BeranNo ratings yet
- Review of Statics Solutions For ExamplesDocument53 pagesReview of Statics Solutions For ExamplesAnisyahira khalidNo ratings yet
- Addition of Forces in A PlaneDocument25 pagesAddition of Forces in A PlaneLancel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document10 pagesExperiment 2Abas Kyla Avril CaballesNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 - Force SystemDocument15 pagesCHP 2 - Force SystemSagheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter2-Resultants of Force SystemsDocument28 pagesChapter2-Resultants of Force SystemsIana LeynoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-3Document18 pagesChapter 2-3Ishin MatoiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Topic 1 - Systems of Coplanar ForcesDocument22 pagesLesson 2-Topic 1 - Systems of Coplanar ForcesNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Eng MechDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Eng Mechtewodrosbasie26No ratings yet
- Adding Forces Resultant and Equilibrium, Resolving Forces ComponentDocument18 pagesAdding Forces Resultant and Equilibrium, Resolving Forces ComponentHisyamAl-MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Forces and EquilibriumDocument57 pagesForces and EquilibriumUnknown_unknown_unknownNo ratings yet
- Prepare Job InterviewDocument1 pagePrepare Job InterviewLaith JaberNo ratings yet
- Olympic History Timeline (1370)Document1 pageOlympic History Timeline (1370)Laith JaberNo ratings yet
- Design of Human-Powered Vehicles - (Mark Archibald-2016) PDFDocument324 pagesDesign of Human-Powered Vehicles - (Mark Archibald-2016) PDFLaith Jaber100% (2)
- Electrical Engineering Program Map: HNC HNC HNCDocument1 pageElectrical Engineering Program Map: HNC HNC HNCLaith JaberNo ratings yet