Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Apparatus For Four-Point Bend Testing
Uploaded by
MudassarHashmi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesApparatus for four-point bend testing
Original Title
Apparatus for four-point bend testing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentApparatus for four-point bend testing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesApparatus For Four-Point Bend Testing
Uploaded by
MudassarHashmiApparatus for four-point bend testing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
2) United States Patent
Clark
(54) APPARATUS FOR FOUR-POINT BEND.
TESTING
(7) Applicant: ROLL
S-ROYCE PLC, London (GB)
(72) Inveator: Bryne Clark, Bristol (GB)
(93) Assignee: ROL
|S-ROYCE ple, Derby (GB)
(4) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer the tem of this
pateat is extended of adjusted under 35
USC. 1S4¢b) by O days.
(21) Appl. No. 14/631,280
(22) Filed: Feb, 25,2018
ws) Prior Publication Data
$ 2015/0268144 A1 Sep. 24, 2015
G0) Fore
Application Priority Data
Mar. 21,2014 (GB) 1405073.6
Gb neck
GoInv20
GUN v3
(2006.01)
(2006.01)
(2006.01),
(GOIN 3/20 (2013.01); GOIN 3/32 (2013.01)
GOIM S016 (2013.01); GOIN 220370023
(2013.01): GOIN 2208/0282 2013.01)
Field of Classification Search
CPC oe GOIN 3/20; GOIM SI0016; PIGC 35/06
usp 731852, 849
See application file for complete search history
(58)
36) References Cited
US. PATENT DOCUMENTS
331885 A * 511962 Larson coin 338
T810
AMOI A * T1964 Baker oin'320
‘US009354151B2
(10) Patent No.
4s) Date of Patent:
US 9,354,151 B2
May 31, 2016
S032 A * 21965 Slivan own 33s
450286 4 ¢ S198 Pomee oi 320
AOTISS A+ 71987 Fischer Goins
73850
(Continsed)
FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
be
Ge
ton29 012 aL 1/2005
A ios
(Continved)
(OTHER PUBLICATIONS
Sep. 11, 2014 Seuch Repow issued in Bish Application No
MOS073.6,
Primary Examiner — Lisa Casto
Tran M Tran
oun PLC
Assistant Examiner
(4) Attornes, Agent, or Firm
on
Arig for testing an aerofil component in four-point bending,
‘whieh includes first and second fixtures movable relative 10
cach other to apply # eyelically varying load to opposing
aerofoil surfaces of the component. The frst fxture has (Wo
fist loading formations positioned to apply the load to one
surface ofthe component, the formations being spaced apart
inthe spanwise direction of the component. The second fx-
ture has two second loading formations positioned to apply
the load tothe other surfaeeof the component, which are aso
spaced apart in the spanwise direction ofthe component and
positioned reatve tothe is loading Formsaons to apply the
Toad ina four-point bending arrangement. The second fixture
‘scontinuously adjustable so that its loading formations move
relative to cachotherin the direction of application of te load
tobalancethe load between the formations ring theeyclical
load variation,
ABSTRACT
13 Claims, 1 Drawing Sheet
US 9,354,151 B2
Page 2
0) References led names m+ S200 cna
mas
US. PATENT DOCUMENTS abit mo 42007 Doak avin
4730408 A+ B88 Bash coyago 730280 BL 2007 LN cons
Ne ;
ae eee contd T8!08t a 2007 ate con it
N80 ei
4981399 A+ 71090 Quin conta) 81664 m2 4200 ong cals
nt a a
4986180 A UBBL Gaomio sons GORD SOT BD 620) U4 3
hae sitet
ee ee con 1sm718 82 6200 Chima nn GOES
Sis
886361 A * 10191 Robes Goimgoe: ——TS2LIST B2* 11200 Camas
ni i
S4M688 4 * $192 Hoon mesons GOIR IR ——149OBSE DF 42010 Cp
ne
23188 A+ 8190 Bonde cones 7866465 2+ 12011 Ate
Se
5,280,730 A * 1/1994 Peres: eae 7,974,803 B2* 7/2011 Logan GOIN 3545,
Te 7 703104
5424834 A * 6198 cold con's So BI 22011 Sah colk tne
seat 0
$2000 A * 41906 Bosh BERN asesoo mas 22018 Doser ant
Moo Rano mae 33013 Rin ink vot
590728 A + 121998 Fin oon'tso Ss
Sih) RAO BOY 62019 Kim con sont
908205 A+ $1909 chy cons thasoL
Palo gezigne met 12014 Foe cannot
4967 B1* 112002 a outttlt a
TSS) xasoane 02+ 102014 hase cone
6908129 82° VO) Sarso¥e nnn TNS ae
ore ee
4101 82° 112003 ak oing ——S80.S85 BOP 102016 ang coun
oN 2
ot eee a GSH oupisi7 nat 72015 finan caunsot
ossi94 Bae Lam a ONDE Sr Bos AIS see 20M seme
ee ane Tasca mar 82013 Nope ais sot
Seeuz mas 12mm se NNR ag dba AI B018 Behe” GOIN RS
sekx2 82" 122008 tk oath Nat
mas
6.81618 62° 04 Hak ooistat PORPIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
mas
68n409 R2* 42005 Kavate costes Gp nate A+ Woe conse
Mase gotta A "OIE
osioe Be* 82005 Unik coonttae
T3853
* cited by examiner
US 9,354,151 B2
May 31, 2016
U.S, Patent
US 9,354,151 B2
1
APPARATUS FOR FOUR-POINT BEND
TESTING
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
“The present invention relates trig for esting an serail
‘component in foti-point bending.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Gas turbine engine aerofoil components (ie. blades oF
vanes) are traditionally assessed for high eycle fatigue (HCE)
by carrying out fatigue tests on sample ei
‘entails clamping the vanrblade at
mechanically exeting one of the component's modal fre-
‘quencies. The exciting foree ean be provided by a mechanical
‘Saker or by a pulsed or constant ait et, Large amplitudes of
vibration are generally required inorder to prodice desied
HCP fares
‘Onn matrix composite (OMC) erofoil components are
‘becoming more widely incorporated into gas turbine engines.
However, conventional methods of exciting bladevane vibra-
tion modes can be inadequate for such component. In par-
ticular, OMCs tend to have high intrinsic damping and hence
it can be difficult to excite their vibeation modes to high
‘enough amplitudes to cause HCP failure.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It would be desirble to provide an altemative testing
method, particularly for OMC aerofoil components.
“Accordingly. ina first aspect, the present invention pro-
vides a rig fr testing an serofoil component in four-point
bending, the sig including first and second fixtures movable
relative to each other to apply a cyclically varying load to
‘opposing aeroFoil surices of the aerooil component,
the first fixture having two firs loading formations which
are positioned to apply the load to one of the aerofoit
surfaces of the component, the fist loading formations
being spaced apart inthe spanwise direction ofthe com
ponent, and
the second fixtre having two second loading formations
‘which are positioned to apply the lod to the oer aeo-
foil surface of the component, the second loading for.
‘mations also being spaced apart in the spanie direc-
tioa of the component and being positioned relative to
the first loading formations to apply the Toad in Tour
point bending arangement;
wherein the second fixture is continuously adjustable so
‘that its loading. formations move relative to each other in
the direction of application of the load to balance the
Joad betwen the loading formations during theeyelical
Toad variation,
In general, bladesivanes do not have syrimetric ross soo
tions and hence they deform in an uneven way. Advanta-
_gcousl the continous adjustability ofthe second fixturcean,
‘ensure that all the leading formations carry equal load
throughout the loading cycle. The four-point bending
‘erangement ensures that the maxinnim beading stress inthe
‘component occurs in the centre section of the component
away fom the fixtures. The fg also allows high loads to Be
applied
“The rig may have any one of, tothe extent that they are
‘compatible, any combination of the following optional fea
‘Conveniently, the scone loading formations may be sap=
ported st opposite ends ofa set of first balancing beams ofthe
0
o
2
secon fist the oa being transmit the second ode
dng formations top he et it baling beams which
rock o produce the relative movement ofthe second lading
formations inthe dreto of application of he lend
Fach loading fomation may have two pas which make
toadingcontet with that formation's aero sre at
respective positions spaced apa nthe chordvisedieton
bithecomponent Eachof throttling formations an
thenbecontinovsly adjustable ota tsps move eave
to cach other inthe diction of application ofthe lad
atc that ending formations share othe Toad between
the pods during the ejlical load variion, The ws of sch
ra allows the fod to applied more unifomiy across the
Ehovisedeson ofthe component. Conveniently, each of
the three adjustable loading fomationscan havea respective
Set of second haleing beams hich spor tha loadin
formation’s pads st opposite ends thereof, the adjustable
Jean formations share th oad being tans tots
pat through the st of econ balancing Dems, whi rock
{Sprodice the eave movement of th pods nthe decon
Siappicaton ofthe oad. Theloang amy be imal
So that they can Bre follow the slopes of the srfces on
‘whic they boar
Typically, one ofthe fist and second fixtures may boo
tower fxr andthe ther theft an secon fxn sy
bean upper ites Tn use the component can then exten
Substantially orizonaly Between the ites ith upward
fiving and’ doynward-aing.aerofol surfaces, Such an
arrangement allows the lower nar to soppon ie compe
nen dng song up thea For example the ist fixe
maybe the lower fixture and the socom ire may Bethe
‘pp intr
Comenicnty the irst loading fomations may provide the
cuter loading pont ofthe fouepoit bending srangeme:
Sint te sscond lang fomatcas provide the inne baa.
Pointe fourpoit bending arrangement. Tat heist
Fading formations may be spaced a grater distance apart in
the spanwise direction ofthe component than the second
leading formations. Parcalarly when the fit Gntre s 0
Joe inte, sichanarrangementeanimprovehestppor of
thecomponent doing sting up af the oe
na scond aspect, th preset ivention provides the se of
ther acoring tothe ist aspect foe trting (ee ati
testing) an seofuil component ea stb engine
bade or vang) in four bending by applying aeycbcally
‘arying load o opposing eof srfoes ofthe component
Ta thin sapet the present isentonprovidesa metho of
setng (fave esting) an eof component e023
Turbine eagine blade or vane) i fourpotnt Bening the
tethod inci:
Providing the ig according to the ist ppt
Ihouning the component n ther 30 thet the fist and
‘cctod louding formations are posiined wo apply the
Ioadto he opposing seo srfaces of the component
arplving a eyeialy varying load the opposing sei
Surices though the fist and second ong forma
ions, where the second Fate continu ass
+0 tht the scond long formations move relative fo
‘ch oor nthe diction of application ofthe fod 0
Balance the load bebween the loading formations ding
the eylical lod variation
‘Themethod may haveanyeneto the exet that they are
compatible, any combination of the following optional
inthe example when cach loading formation as two pads
cs make Iecing-contct wath that Fomation's ace
$helace a respective positions spaced aa in he chordwise
US 9,354,151 B2
3
direction ofthe component, the components mounted so that
the pads of each loading fonnation make loading-contaet
with that formation'sseeofol surface, and on application of
the eyelically varying load, each adjustable looding formation
‘continuously adjusts so tht its pads move relative to each
‘ther inthe direction of application ofthe lad o balance that
Jong formation’s shar of the load between the pads during
the eyelical load variation
‘The aerofeil component may be an organi matrix com=
posite component, such as a component formed of eabat
{ibee enforced plastic andor las fibre reinforced plastic.
“The method may include enclosing the rig in an exviron=
rental chamber eg. for hot oF wet testing. Suc testing is
«difficult o perform using conventional forced modal excita.
tion approche.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS.
Embodiments of the invention will now be described by.
way of example with reference to the aocompanying dras-
ings in which
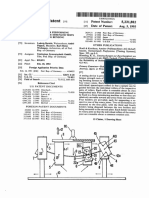
TIG. 1 shows schematically a rig for vesting an verofoil
‘component in four-point bending.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION AND FURTHER
OPTIONAL FEATURES OF THE INVENTION
With reference to FIG. 1, «rig for testing an sero
‘component in four-point bending is generally indicated a 10
tnd has a direction of application of load which is in the
Vertical dtcction ofthe drawing,
“The rig has ower (fst) fixtre 12 and an upper (second)
‘Oxture 14, Lower fixture is securely and rigidly mountable t©
a immovable base, while dhe upper fixture Mf is movable up
‘and down ia the vertical direction, forexampleby a hydeaulic
‘or electrically driven jack or eross-head of @ universal testing
machine. gas turbitie engine arofoilcomponent 16, suchas
a fan blade, is located between the lower and upper fixtures,
‘supported on the lower fixture. The component extends b=
stantially horizontally with ts opposing aerofil surfaces fac-
‘ng upwards and downwards. Guide posts 17 serve to locate
‘component in the cect postion om the lower Fixture
‘The component 16 lus a complex shape, which also
‘deforms ina complex and uneven manner under Loading. The
rig is adapted to be able provide balanced loading during
‘our-point bending, especially during eyelical variation ofthe
out-point bending Toa.
‘More partiulaey, the lower fixture has wo first loading
formations 18, 20 which ace positioned to apply the load t0
the underside serofoil surface, the frst loading formations
being spiced distance , apart in the spanwise direction of
the component (ce. the direction of the componeat which
spans working gas annulus of the engine). Similarly, the
Upper fixture 14 has two second loading formations 22, 24
‘shih are positioned to apply the load to the topside sero
surface, the second loading formations being spaced a dis-
tance S, apart inthe spanwise direction of the component.
Distance 5, is greater than distance S,, with the first loading
formations providing the outer loading points ofthe four
point bending arrangement and the second loading forma-
fions providing the inner loading points of the four-point
bending arrangement.
ach loading formation 18, 20, 22,24 has wo gimballed
pads 26 which make looding-contact with that formation’s
Beto surface at respective positions spaced a distance C
‘apart in the chordwise dieetion of the component, BY
4
balling te pads, they are beter able follow the slopes ofthe
surlaces on which they bear during loading.
“The upper fixture 14 has a set o fist balancing beams 28,
‘with the two second loading formations 22,24 being at oppo”
site ends ofthe beams. The load is wansmitted from the ck
‘retoss-head through the first balancing beams to the second
loading formations. The beams ean rock about central pivot
points 30 so that the second loading formations move relative
fo exch other in the diction of application of the load,
thereby balancing the load between al the loading formations
‘during the cyclical load variation
‘One ofthe fis loading formations 18 has a simple support,
£32 for its pads 26. In contest, the other fist loading. forma-
tions 20, and the two second loading formations 22,24 have
respoctve sets of second balancing beams 34 for their pads
26, More particularly, in each of these three loading forma
‘ions 20, 22,24, the respoctve pas are supported at opposite
ends of the second balancing beams, which can rock about
‘ental pivot points 36 so thatthe pads move relative teach
‘other inthe direction of application ofthe lod, thereby bal-
fncing that loading formation’s share ofthe load between the
pads during the eyelical load variation. The share of the load
‘fhe Fist loading formation 18 having the simple support 32
is also thereby balanced between its pads 26
Tus the “ire structure” ofthe upper fixture 14 in which
the load is transmitted to each loading pad 26 via two sets of
Joad balancing beams 28, 34, in combination with the addi-
‘ional set of balaneing beams 34 of the fist loading forma
tions 200 the lower fixture 12, balance the loa fet and right,
and front and rear, thereby ensuring that al pads carry equal
shares ofthe Inad throughout the loading eye, even as the
component deflects asymmetrically and unevenly. In addi
tion, the nse ofa four-point hending arrangement can ensire
that the maximum bending tress occurs in the centre section
ofthe component away from the loading formations 18, 20
22,24
‘The rig ean thas be used to perform fatigue testing in a
‘manner that does not depend on exciting the componeat’s
vibration modes, making the rig particularly suitable fr test
jing OMC components. The rig salso compatible with fst set
up times, which is desirable when testing many components
In addition, the rig ean earry high applied loads, allowing
‘component fate failures to be achieved in resonable time
scales. Further, the rig can be enclosed in an environmental
chamber, eg. for hot or wet testing
‘While the invention has been described in conjunction with
the exemplary embodiments desribed above, many’ equiva
lent medications and variations will be apparent to those
stalled in the art when given this disclosure. Accordingly, the
‘exemplary embodiments othe invention set forth abave are
‘considered o be illusrative and not limiting. Various changes
to the deseribod embodiments may be made without depar-
ing from the spirit and seope ofthe invention,
“The invention claimed is:
1. A rig for testing an aerofail component in four-point
bending, the aerofoil component having a first aerofol sur-
‘ace and an oppositely-facing second serofoil surface, the rig
including a first fixture and a second fixture movable relative
to each other to apply a eyelcally varying load to the first
erofol surface andthe secondaerofol surface ofthe aero
‘compontent,
the frst fixture having two first oading mations whieh
‘re positioned to apply the load to the first arofoil
surfce of the component, the two first loading forma-
tions being spaced apart in # spanwise direction ofthe
‘component, and
US 9,354,151 B2
5
the second fixture having two second loading formations
‘which are positioned to apply the load to the second
aerofol surface of the component, the two second Toad-
‘ng formations also being spaced apart inthe spanssise
direction of the component, the spanwise spacing of the
{so socond loading formations being less an the span=
‘wise spacing ofthe two frst loading formations, and the
‘sso second loading formations being positioned relative
to the two first loading formations such that the first
fixtures and the second fixtures apply the lood in a Fore
point bending arrangement;
wherein the second fixture is configured so thatthe oo
‘second loading. formations are movable relative to each
‘ther indirection of application ofthe Toad to balance
the load between the two second loading formations
during the eyetical load variation,
2. The rig according to claim 1, wherein the two second
loading formations are supported at opposite ends ofa set of
first balancing beams ofthe second fixture, the load being
transmitted to the second loading formations through the set 2
‘of first balancing beams, which rock to produce the relative
‘movement of theo second loading formations in the diree-
tion of application ofthe lad
3. The rig according to claim 1, wherein:
‘each foding, formation has two pads which make lodin
‘contact With tht formation's aerofil surface at respec:
tive postions spaced apart in the chondwvise direction of
the component; and
cach of three the loading formations is configured so that
its pads move relative fo each other in the direction of
application of the load to balance that loading forma-
tion's share of the load between the pads during the
cyclical load variation,
4. The rig acconding to claim 3, wherein each of said three
loading formations has «respective set of second balancing
beams which support tht loading formation’ pads at oppo-
site ends thoroof, each of sid thre loading formations share
‘of the lead being transmitted to its pads through the set of
second balancing beams, which mck to price the relative
‘movement ofthe pads in the direction of application of the
oad.
'. The rig according to claim 3, wherein the pads of the
loading formations are gimbal.
6, The rig according to claim 1, wherein,
fone ofthe first fixture and the second fixture isa lower
fixture, and the other ofthe first fixture and the second.
fixture isan upper fixture,
{in use, the component extends substantially horizontally
‘hetween the lower fixture and the upper fixture with
‘upward-facing and downwardfacing aerofoil succes
6
7. The rig according to claim 6, wherein the frst fixture is
the lower fisture and the second fixture isthe upper fixture,
8. The rig according to claim 1, wherein the fist loading
formations provide outer loading points of the four-point
bending arrangement and the second loading formations pro-
vide inne loading points ofthe four-point bending armnge-
°
9. A method of testing an aeofoil component in four-point
bending, the method including:
providing the rig according to claim 1
‘mounting the component in the rg so that the fis loading
formations and the second loading formations are pos
tioned to apply the load to the oppositely-facing eof
surfaces ofthe component,
applying a eyclically varying load wo the oppositely-facing
‘2erofoil surfaces through the first loating formations
‘and second loading formations, whereby the second fix-
‘ure continuously adjusts so thatthe second loading,
formations move relative to eachother in the direction of
application ofthe loa to balance the oad between the
loading formations during the eylical load variation,
10, The method of testing an aerofil component according
{0 claim 9, wherein: eaet loading formation has two pads
configured to make loading-contact with that foemation's
aecofoil surface a respective positions spaced apart in the
‘hordwisediretion the component cach of three ofthe frst
and second leading formations is configured so that it pads
‘move relative o each other in the direction of application of
the load to balance that loading formation’s share of load
‘between the pads during the eylical load variation; the com-
ponent is mount so thatthe pas of each loading formation
‘make loadcontaet with tha formation’s aro surface; and
‘on application of the cyclical varying load, each of said three
ofthe ist and second loading formations continuously adjust
‘so that it pads move relative to each other inthe direction of
‘application of the load to balance that loading formations
share ofthe Toad between the pads during the eyelical load
variation,
11, Themethod of testing an aerofoil component according
toelsim 9, wherein the testis fatigue tes.
12. The method of esting an aerofol component according
to claim 9, wherein the aerofoil component is an organic
‘mateix composite component.
13, The rig of claim 1, wherein the (wo second loading
{Formations ate disposed between the wo first leading forma
tions in the spanwise direction ofthe component.
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Pure Bending Mechanical Test Device and Method For Implementing SameDocument15 pagesPure Bending Mechanical Test Device and Method For Implementing SameMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Turbine With Cooled Turbine Guide VanesDocument10 pagesTurbine With Cooled Turbine Guide VanesMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Turbine Rotor and Steam TurbineDocument15 pagesTurbine Rotor and Steam TurbineMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Turbine Blow Down Starter For Turbine EngineDocument8 pagesTurbine Blow Down Starter For Turbine EngineMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Turbine Blade, Turbine, and Gas Turbine Having The SameDocument16 pagesTurbine Blade, Turbine, and Gas Turbine Having The SameMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Fully Articulated Four-Point-Bend Loading FixtureDocument7 pagesFully Articulated Four-Point-Bend Loading FixtureMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Labyrinth Seal For Gas Turbine Engine TurbineDocument12 pagesLabyrinth Seal For Gas Turbine Engine TurbineMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Steam Turbine and Turbine RotorDocument13 pagesSteam Turbine and Turbine RotorMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Testing Device For Performing Four-Point Fatigue Strength Tests Under Alternating Bending StressesDocument6 pagesTesting Device For Performing Four-Point Fatigue Strength Tests Under Alternating Bending StressesMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- BISE Gujranwala Board SSC and HSSC Certificate Verification Process and RequirementsDocument2 pagesBISE Gujranwala Board SSC and HSSC Certificate Verification Process and RequirementsMudassarHashmi57% (7)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Method and Ultrasonic Meter System For Determining Pipe RoughnessDocument13 pagesMethod and Ultrasonic Meter System For Determining Pipe RoughnessMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness MeterDocument6 pagesSurface Roughness MeterMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Low Flow Safety ValveDocument12 pagesLow Flow Safety ValveMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 1.A - EPR Design Description - v3 PDFDocument185 pages1.A - EPR Design Description - v3 PDFMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Degree Attestation CH All An FormDocument1 pageDegree Attestation CH All An FormMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pressure Relief Valve Engineering HandbookDocument93 pagesPressure Relief Valve Engineering Handbookakrouti92% (12)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Certificate Attestation Form (IBCC)Document1 pageCertificate Attestation Form (IBCC)MudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- NDPL Safety ManualDocument103 pagesNDPL Safety ManualvntjbpNo ratings yet
- IBCC FormDocument2 pagesIBCC FormshafxNo ratings yet
- Combustion Modelling Using Ansys CFXDocument61 pagesCombustion Modelling Using Ansys CFXMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- NRC 1.116Document2 pagesNRC 1.116MudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Mental Fitness Certificate for Mudassar Hussain HashmiDocument1 pageMental Fitness Certificate for Mudassar Hussain HashmiMudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Cable Laying SpecificationDocument16 pagesCable Laying SpecificationdavidgarciavazquezNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Epp 0500-See-11-07-04Document20 pagesEpp 0500-See-11-07-04MudassarHashmiNo ratings yet
- Straight JointDocument1 pageStraight JointdillehNo ratings yet
- Megger Cable Fault Finding SolutionsDocument44 pagesMegger Cable Fault Finding SolutionsMudassarHashmi100% (3)
- Brugg Cables User GuideDocument27 pagesBrugg Cables User GuideMehdi_Mashayekhi_172No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)