Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Frequency?
Uploaded by
Katherine Gomez BastianOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Frequency?
Uploaded by
Katherine Gomez BastianCopyright:
Available Formats
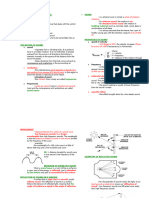
What is Frequency?
Frequency is the number of times the cycle of compression and rarefaction of air
occurs in a given unit of time is describe as the frequency of a sound. For example,
if there are 1000 cycles in the period of one second the frequency is 1000 cps
(1000 Hertz-Hz in the new standard nomenclature.
Rate of repetition of a periodic phenomenon (determines the pitch of a sound)
Number of displacement or oscillations that a particle undergoes in one sound.
Unit of frequency = Hertz (Hz)
Normal responds to sound within the audio frequency range of about 20 – 20000 Hz
Airborne Noise is due to fluctuations of air pressure about the mean atmospheric pressure.
Flanking Paths
F1– Open plenums over wall and through
suspended ceilings
F2 – Common ductwork
F3 – Adjacent exterior windows
F4 – Common floor heaters
F5 – Open vents
F6 – Louvered Doors
F7 – Under doors
Noise Leaks
L1 – Poor seal at wall/ceiling connection
L2 – Poor seal at wall/wall connection
L3 – Poor seal at wall/mullion connection
L4 – Poor seal around outlet penetration (also
avoid back-to-back outlets
L5 – Poor seal wall penetration
L6 – Poor seal floor penetration
L7 – Poor seal wall/floor connection
Structural borne noise is the
vibration of elastic bodies. It
travels through walls, floor, and
columns.
Liquid borne noise is cause by pulsations
of liquid pressure about the mean static
pressure. Rapid pressure changes
produce more noise. Large and rapid
changes in pressure produce
"cavitation" sound.
Ultrasound is noises of
frequency greater than 20,000
cyc/sec. Sounds in the range
20-100kHz are commonly used
for communication and
navigation by bats, dolphins,
and some other species
Infrasound is noise of frequency less
than 2- cyc/sec. (below the normal lower
limit of the human ear). Sources of
infrasound in nature include volcanoes,
avalanches, earthquakes and meteorites.
You might also like
- SoundDocument9 pagesSoundpuneetNo ratings yet
- Use of Mines in Trench Warfare (From the French School of St. Cyr)From EverandUse of Mines in Trench Warfare (From the French School of St. Cyr)No ratings yet
- RRLDocument15 pagesRRLjerry elizagaNo ratings yet
- Bs 3 Unit 5aDocument28 pagesBs 3 Unit 5aPavithra SivasankaranNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and Lighting: FrequenciesDocument15 pagesAcoustics and Lighting: FrequenciesPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- Echoes and Room FlutterDocument6 pagesEchoes and Room FlutterRinsha MgNo ratings yet
- Building Services IV Module 04Document38 pagesBuilding Services IV Module 04hardik MajethiyaNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Speech RoomsDocument6 pagesCriteria For Speech RoomsJohn Vincent ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesAcoustics and LightingSam AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Hands On Electronic SurveillanceDocument57 pagesHands On Electronic SurveillanceЕлизабет Петрова100% (4)
- Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesAcoustics and LightingNeslie Joy AgotoNo ratings yet
- Building services-IV Module-04Document38 pagesBuilding services-IV Module-04hardik MajethiyaNo ratings yet
- AR-407 Building Services-III: Assignment-5Document17 pagesAR-407 Building Services-III: Assignment-5MOHD NAZEEF KHANNo ratings yet
- Acoustics: Air Borne Noise and Structure Borne NoiseDocument11 pagesAcoustics: Air Borne Noise and Structure Borne NoiseVISHAL SHARMA100% (1)
- Reveiw Arch-2010 Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesReveiw Arch-2010 Acoustics and LightingiloilocityNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 AcousticDocument37 pagesUnit 2 AcousticAbhi VallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Audio ShortsDocument4 pagesMultimedia Audio Shortsعلی احمدNo ratings yet
- 2.behaviour of SoundDocument45 pages2.behaviour of SoundSaransh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics FirstDocument80 pagesAcoustics FirstRekha SNo ratings yet
- Architectural Acoustic: Prepared By:-Rushit PatelDocument32 pagesArchitectural Acoustic: Prepared By:-Rushit PatelSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Sessional IN Acoustics: Submitted To: Submitted By: Prof. Sanjay Jadon Kushal PawaiyaDocument6 pagesSessional IN Acoustics: Submitted To: Submitted By: Prof. Sanjay Jadon Kushal PawaiyaShaileshNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURAL ACOUSTICS-module 2-Part2Document65 pagesARCHITECTURAL ACOUSTICS-module 2-Part2ardra m oNo ratings yet
- Acoustics-2 (Sound in Enclosed Spaces)Document24 pagesAcoustics-2 (Sound in Enclosed Spaces)disha100% (1)
- AcousticsDocument56 pagesAcousticsRaheman SaiyedNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Acoustics (12 Hours) : Characteristics of SoundDocument12 pagesUnit I Introduction To Acoustics (12 Hours) : Characteristics of SoundRupa RajNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 01Document15 pagesAcoustics 01Ybette Anorico VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and LightingDocument16 pagesAcoustics and LightingDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- BMC-4 Inverted BeamDocument23 pagesBMC-4 Inverted BeamDarshan KansaraNo ratings yet
- Acoustical Analysis 1. Sound CharacteristicDocument2 pagesAcoustical Analysis 1. Sound CharacteristicGerald Paul FelongcoNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Sound in An EnclosureDocument7 pagesBehaviour of Sound in An EnclosureAnusha IvaturiNo ratings yet
- Acoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCDocument14 pagesAcoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCKomal ChopadaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics of Buildings: Applications in The PentagonDocument5 pagesAcoustics of Buildings: Applications in The PentagonMudrikaNo ratings yet
- Wave Behavior at Boundaries, Refraction, Interference, and DiffractionDocument13 pagesWave Behavior at Boundaries, Refraction, Interference, and DiffractionTianjiao ZhangNo ratings yet
- Auditorium AcousticsDocument17 pagesAuditorium AcousticsTanyaNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 4 RSWDocument14 pagesBuilding Utilities 4 RSWMartina Jeunesse FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 1Document10 pagesAcoustics 1Anusha IvaturiNo ratings yet
- Sound Absorption, Reflection & Transmission, Mechanism of Absorption Reverberation TimeDocument31 pagesSound Absorption, Reflection & Transmission, Mechanism of Absorption Reverberation TimeAnonymous 5kOS4tNo ratings yet
- Wave PropDocument32 pagesWave PropChamondi Aswini Kumar GadigeNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Module 1B StudentsDocument11 pagesAcoustics Module 1B StudentsKrupa NidhiNo ratings yet
- Architectural AccousticsDocument25 pagesArchitectural AccousticsJOTHINo ratings yet
- Glossary of Important Acoustical TermsDocument3 pagesGlossary of Important Acoustical TermsFranMarkNo ratings yet
- Acoustics ARCH 255 - Liapu Wasif 11 21Document11 pagesAcoustics ARCH 255 - Liapu Wasif 11 21Aurka JamanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 06 - Shankhapratim BhattacharyaDocument17 pagesLecture - 06 - Shankhapratim Bhattacharyapushpakbhawgati27No ratings yet
- Acoustic NotesDocument21 pagesAcoustic NoteschriziafreeNo ratings yet
- 05A - Sound InsulationDocument17 pages05A - Sound InsulationRitikaNo ratings yet
- RF (Radio Frequency) Signal: Medium. Bounded Medium Contains or Confines TheDocument10 pagesRF (Radio Frequency) Signal: Medium. Bounded Medium Contains or Confines TheMasterArvinNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument28 pagesAcousticsKanika Maheshwari100% (1)
- Architectural Acoustics.Document14 pagesArchitectural Acoustics.maniNo ratings yet
- Science - Sound DiffractionDocument12 pagesScience - Sound DiffractionElissah S PabilonaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: List of Acoustical DefectsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2: List of Acoustical DefectsRaj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 05 Digital DelayDocument7 pages05 Digital DelayAlex SantosNo ratings yet
- EngPhy Module III&IVDocument96 pagesEngPhy Module III&IVSanjeevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Insulation: Sound - IntroductionDocument14 pagesChapter 4: Insulation: Sound - IntroductionYu HanaNo ratings yet
- Su1c2 by Adel KhamisDocument12 pagesSu1c2 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On The Seminar: Acoustics and Basic Principle of Sound ProofingDocument5 pagesReaction Paper On The Seminar: Acoustics and Basic Principle of Sound Proofingstephen2buizonNo ratings yet
- Active Learning AssignmentDocument15 pagesActive Learning AssignmentIndhu JayavelNo ratings yet
- Sound: Behavior in Closed SpacesDocument48 pagesSound: Behavior in Closed SpacesSharanya100% (1)
- Kinesthetic, Dimension, ScaleDocument11 pagesKinesthetic, Dimension, ScaleKatherine Gomez BastianNo ratings yet
- Fajardo, Max, Jr. - Plumbing Design and Estimate 2nd Edition PDFDocument175 pagesFajardo, Max, Jr. - Plumbing Design and Estimate 2nd Edition PDFKatherine Gomez Bastian100% (1)
- COR CZO Article 13-1 About DuplexDocument4 pagesCOR CZO Article 13-1 About DuplexKatherine Gomez BastianNo ratings yet
- Plumbing and Sanitary (Utilities 1)Document216 pagesPlumbing and Sanitary (Utilities 1)Alex Dulay100% (4)
- Proposed Designs: For Internal Use Only For Internal Use OnlyDocument5 pagesProposed Designs: For Internal Use Only For Internal Use OnlyKatherine Gomez BastianNo ratings yet
- Major Issues in Mass Housing in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesMajor Issues in Mass Housing in The PhilippinesKatherine Gomez Bastian33% (3)
- Private HEIs Faculty Student RatioDocument39 pagesPrivate HEIs Faculty Student RatioKatherine Gomez BastianNo ratings yet
- Clark Green City ProjectDocument40 pagesClark Green City ProjectKatherine Gomez Bastian100% (6)
- Bloomberg Certification FAQ BMC (Bloomberg Market Concepts) : Goizueta Business LibraryDocument3 pagesBloomberg Certification FAQ BMC (Bloomberg Market Concepts) : Goizueta Business LibrarySarah Raquel Bozo Herrera100% (1)
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology Gapan Academic Extension CampusDocument4 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology Gapan Academic Extension CampusErmercadoNo ratings yet
- Ric RG90 y RG60Document1 pageRic RG90 y RG60GabrielConsentidoNo ratings yet
- Resistive Capacitive Inductive and Magnetic Sensor Technologies by Winncy Y Du PDFDocument400 pagesResistive Capacitive Inductive and Magnetic Sensor Technologies by Winncy Y Du PDFlocthaiquoc83% (6)
- Assign#1Document2 pagesAssign#1Edrielle ValdezNo ratings yet
- ¿Cómo Se Utilizan Las Partituras en La Enseñanza y El Aprendizaje de La Música?Document15 pages¿Cómo Se Utilizan Las Partituras en La Enseñanza y El Aprendizaje de La Música?manaimanaNo ratings yet
- Experiments With An Axial Fan: Page 1/3 10/2010Document3 pagesExperiments With An Axial Fan: Page 1/3 10/2010Priyam ParasharNo ratings yet
- CMA Building Foundation Beams PDFDocument13 pagesCMA Building Foundation Beams PDFRegie NojaldaNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study On Drilling of Metals Through Microwave HeatingDocument6 pagesA Feasibility Study On Drilling of Metals Through Microwave HeatingT J GNo ratings yet
- E85005-0126 - FireShield Plus Conventional Fire Alarm Systems PDFDocument8 pagesE85005-0126 - FireShield Plus Conventional Fire Alarm Systems PDFLuis TovarNo ratings yet
- Engg Prospect1usDocument20 pagesEngg Prospect1usArun KumarNo ratings yet
- SKANDIX - Order EditDocument2 pagesSKANDIX - Order EditmehNo ratings yet
- U-Joint Shaft PDFDocument5 pagesU-Joint Shaft PDFAdrian SantosNo ratings yet
- Power Network Telecommunication: Powerlink - Technical DataDocument10 pagesPower Network Telecommunication: Powerlink - Technical Datawas00266No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Rajeev RanjanDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Rajeev RanjanPratik AnandNo ratings yet
- Animal and Human Brain Work With Treatment Its Malfunction: Pijush Kanti BhattacharjeeDocument6 pagesAnimal and Human Brain Work With Treatment Its Malfunction: Pijush Kanti BhattacharjeeNilakshi Paul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Acoples Hidraulicos Serie 60 ParkerDocument2 pagesAcoples Hidraulicos Serie 60 ParkerAntonio MoralesNo ratings yet
- Coomaraswamy, SarpabandhaDocument3 pagesCoomaraswamy, SarpabandhakamakarmaNo ratings yet
- Service Pack 2Document149 pagesService Pack 2billwong169No ratings yet
- 2018 Academic Sector Annual Report PDFDocument213 pages2018 Academic Sector Annual Report PDFEsperanza ReyesNo ratings yet
- David Beard Composer CV ShortDocument2 pagesDavid Beard Composer CV ShortEhsan KarimyNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With ATV310: DangerDocument4 pagesGetting Started With ATV310: DangerAdnan Naeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Multi Split and Single Split Systems BrochureDocument32 pagesToshiba Multi Split and Single Split Systems Brochurethanhlong2005No ratings yet
- Infineon IKFW50N65DH5Document15 pagesInfineon IKFW50N65DH5nithinmundackal3623No ratings yet
- Attempt 1 OrgDocument19 pagesAttempt 1 OrgMohammed Irfan SheriffNo ratings yet
- Advanced English Communication Skills LaDocument5 pagesAdvanced English Communication Skills LaMadjid MouffokiNo ratings yet
- SAP Fiori Deployment OptionsDocument16 pagesSAP Fiori Deployment OptionsVinaykumar PJNo ratings yet
- Econ 103 - 01Document3 pagesEcon 103 - 01perrerNo ratings yet
- 15mm K115 GW-S CUP STD (SH005 1014 B)Document2 pages15mm K115 GW-S CUP STD (SH005 1014 B)Ionut BucurNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Sui Asset Department (FROM 29 JUNE 2016 TO 24 JULY 2016)Document13 pagesInternship Report Sui Asset Department (FROM 29 JUNE 2016 TO 24 JULY 2016)Jawaid HussainNo ratings yet
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Interactive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookFrom EverandInteractive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- AI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The School Garden Curriculum: An Integrated K-8 Guide for Discovering Science, Ecology, and Whole-Systems ThinkingFrom EverandThe School Garden Curriculum: An Integrated K-8 Guide for Discovering Science, Ecology, and Whole-Systems ThinkingNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)From EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- Common Core Science 4 Today, Grade 3: Daily Skill PracticeFrom EverandCommon Core Science 4 Today, Grade 3: Daily Skill PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- How to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasFrom EverandHow to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- RASPBERRY PI FOR BEGINNERS: TIPS AND TRICKS TO LEARN RASPBERRY PI PROGRAMMINGFrom EverandRASPBERRY PI FOR BEGINNERS: TIPS AND TRICKS TO LEARN RASPBERRY PI PROGRAMMINGNo ratings yet
- Stay Curious and Keep Exploring: 50 Amazing, Bubbly, and Creative Science Experiments to Do with the Whole FamilyFrom EverandStay Curious and Keep Exploring: 50 Amazing, Bubbly, and Creative Science Experiments to Do with the Whole FamilyNo ratings yet
- How Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksFrom EverandHow Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksNo ratings yet