Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.3 Electrical Resistivity Test Aim & Scope of Investigation
Uploaded by
parthOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.3 Electrical Resistivity Test Aim & Scope of Investigation
Uploaded by
parthCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
3 Electrical Resistivity Test
Aim & Scope of Investigation
The main objectives of the Resistivity Survey and Investigation are as under.
• To collect the basic data on sub-surface geological formation.
• To know the resistance of the sub-surface layers.
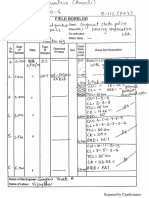
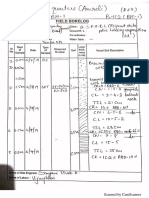
Total four Nos. of Electrical Resistivity tests are conducted at pre marked locations in the plot
area. In the geophysical resistivity survey Wenner configuration method is used. The main aim
of the present survey is to know engineering properties of the formation and its resistivity at
different depth.
In the Wenner four pin method, four electrodes are driven into the earth along a straight line
at equal interval. Current ‘I’ is passed through the two outer electrodes and the voltage
difference ‘V’ is observed between the two inner electrodes. The current ‘I’ flowing into the
earth produces an electric proportional to its density and to the resistivity of the soil. The
voltage ‘V’ measured between the inner electrodes is therefore, proportional to the field
condition. Resistivity thus will be proportional to the ratio of the voltage to the current.
Pa = 2 II a V Ohm.m
I
Where Pa = Apparent Resistivity of the formation / Soil (Ohm.m.)
a = Distance between two electrodes (m.)
V = Voltage ( milli volt.)
I = Current (milli Ampere.), (V/I= Measured Resistance in Ohm.)
Resistivity set up electrical circuit for resistivity survey
At the selected point in the chosen direction i.e. North – South and East – West four electrodes
are driven into the earth up to required depth along a straight line at equal intervals. The D.C.
resistivity meter is placed in the steady and level base. The current and potential electrodes
are connected to the instrument terminals. By passing current from the battery box, readings
are taken.
NORTH
WEST EAST
SOUTH
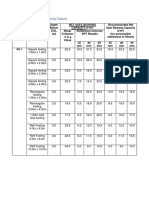
The resistivity data of the sub-surface layers at different depth are calculated and tabulated in
the table 3/1 to 3/4 of report.
You might also like
- Soil Resistivity MeasurementDocument3 pagesSoil Resistivity Measurementsaravanakumarpalani100% (1)
- 12 - Chapter 5 PDFDocument67 pages12 - Chapter 5 PDFPranav. ThubeNo ratings yet
- Morales Jefferjunegyner Geol-401bDocument10 pagesMorales Jefferjunegyner Geol-401bAnika Gaudan PonoNo ratings yet
- Geophysics (Electric Method)Document79 pagesGeophysics (Electric Method)Vaqas Ali Khan100% (1)
- Assignment 04 GSIDocument4 pagesAssignment 04 GSISyeda L RNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodDocument22 pagesLecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodNamwangala Rashid NatinduNo ratings yet
- Method Statement FOR Earth Resistivity TestDocument9 pagesMethod Statement FOR Earth Resistivity TestTARUNNo ratings yet
- Chapter23Geoelectrical MethodsDocument53 pagesChapter23Geoelectrical MethodsImranNo ratings yet
- Ves Bayelsa SHMBRG MethDocument9 pagesVes Bayelsa SHMBRG MethWadadiNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Investigations: Electrical Methods: The Resistivity MethodDocument22 pagesGeophysical Investigations: Electrical Methods: The Resistivity MethodtoudouNo ratings yet
- Geo-Resistivity & IP Survey DiscussionDocument4 pagesGeo-Resistivity & IP Survey DiscussionCris SosaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resisitivity Method For Subsurface Competency at Simawa, Redeem CampDocument26 pagesElectrical Resisitivity Method For Subsurface Competency at Simawa, Redeem CampTaiwo OlapadeNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Exploration OF Ground Water: B.Rajkumar Asst. HydrogeologistDocument18 pagesGeophysical Exploration OF Ground Water: B.Rajkumar Asst. HydrogeologistRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Resistivity MethodssDocument17 pagesResistivity MethodssNatoRenatoNo ratings yet
- SchlumbergerDocument10 pagesSchlumbergerRuby PermataNo ratings yet
- Resistivity LectureDocument39 pagesResistivity LectureAFRIADMA AULIA PERDANANo ratings yet
- Tabletop ModelsDocument8 pagesTabletop ModelsChuck_YoungNo ratings yet
- 12 Earthing SystemDocument6 pages12 Earthing SystemMightier PrakharNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Investigation: Electrical MethodsDocument25 pagesGeophysical Investigation: Electrical Methodsghassen laouiniNo ratings yet
- Methodology - Electrical Resitivity MethodDocument12 pagesMethodology - Electrical Resitivity Methodtejaswini shahapurkarNo ratings yet
- LR2 Electric Field Plotting Part IDocument5 pagesLR2 Electric Field Plotting Part IabeermousaNo ratings yet
- Electrical ResistivityDocument58 pagesElectrical Resistivityعبد الرحمن القيسيNo ratings yet
- Low-Cost Resistivity Meter For Groundwater Exploration Using High Voltage ExperimentationsDocument5 pagesLow-Cost Resistivity Meter For Groundwater Exploration Using High Voltage ExperimentationsjaimemanNo ratings yet
- ERS REPORT OF Com Site 3Document20 pagesERS REPORT OF Com Site 3Areeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ert Sunsorce Tuljapur Maharashtra 15.11.2021Document32 pagesErt Sunsorce Tuljapur Maharashtra 15.11.2021Satyajit MalikNo ratings yet
- Equipotential Surfaces and Electric FieldDocument18 pagesEquipotential Surfaces and Electric FieldARABELLE CONCEPCIONNo ratings yet
- Experiment OnDocument7 pagesExperiment Onকাওমিউজ্জামান কাব্যNo ratings yet
- 02 Tss Resist I VityDocument2 pages02 Tss Resist I VitygoomeyNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Methods - Environmental GeophysicsDocument36 pagesResistivity Methods - Environmental GeophysicsYong Praz50% (2)
- Electricty and Magnitism Lab Manual: January 2019Document31 pagesElectricty and Magnitism Lab Manual: January 2019Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and Electric Field Mapping - VillanuevaDocument22 pagesElectric Potential and Electric Field Mapping - VillanuevaCristy Mae U. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document6 pagesLecture 2none. xNo ratings yet
- gh2 Industries Survey ReportDocument26 pagesgh2 Industries Survey ReportAreeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Active Method "Electrical Resistivity" and "D.C Resistivity" Are Used Synonymously Measure Earth ResistiviDocument26 pagesActive Method "Electrical Resistivity" and "D.C Resistivity" Are Used Synonymously Measure Earth ResistiviZeeshan ahmed100% (1)
- Dhev Emt 1Document12 pagesDhev Emt 1CharavanaNo ratings yet
- 6.question Bank With Answers (2 Marks) - 1Document10 pages6.question Bank With Answers (2 Marks) - 1Durgesh DhoreNo ratings yet
- 061cardimona Resistivity OverviewDocument10 pages061cardimona Resistivity OverviewgoomeyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistivity Tests On RocksDocument29 pagesElectrical Resistivity Tests On Rocksanshu832No ratings yet
- BEE - Manual ODD 2021Document44 pagesBEE - Manual ODD 2021Deekshith raiNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Earth ResistanceDocument12 pagesMeasurement of Earth ResistanceMuhammad Saif AmirNo ratings yet
- Elogs Megger 097-11Document13 pagesElogs Megger 097-11dbrown_786859No ratings yet
- Methology For Earth Resisitivity of SoilDocument4 pagesMethology For Earth Resisitivity of Soilmohd waseemNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Electric Field Data Sheet Group 1 June 8Document6 pagesExperiment 7 Electric Field Data Sheet Group 1 June 8Airesheale VillancioNo ratings yet
- Electric Field LinesDocument4 pagesElectric Field LinesPappu PriyaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Electrodes in IP ArraysDocument17 pagesA Comparison of Electrodes in IP ArraysLuis Alonso SANo ratings yet
- Pole PoleDocument13 pagesPole PoleraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Electric Potential and Field Mapping: Florida Institute of Technology © 2020 by J. GeringDocument8 pagesExperiment 2 Electric Potential and Field Mapping: Florida Institute of Technology © 2020 by J. GeringHafizSikandarNo ratings yet
- Geophysical MethodsDocument12 pagesGeophysical Methodstommad3691No ratings yet
- Configuration and Specification of Equipments Used in DC Resistivity SurveyDocument43 pagesConfiguration and Specification of Equipments Used in DC Resistivity SurveyAditya Kumar AnandNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsFrom EverandPrinciples of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Geophysical Investigations: Electrical Methods: The Resistivity MethodDocument15 pagesGeophysical Investigations: Electrical Methods: The Resistivity MethodtoudouNo ratings yet
- Resistivity MethodsDocument27 pagesResistivity MethodsRoxanneDequinaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 ReviewerDocument22 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Reviewercharydel.oretaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Electrical Method Field ProcedureDocument9 pagesLecture 13 Electrical Method Field ProcedureShadi Garma100% (1)
- Electrical Equipment: by M.Eng CHEA KimsairngDocument25 pagesElectrical Equipment: by M.Eng CHEA KimsairngKimsairng CheaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodDocument22 pagesLecture-12 - Introduction & Theoritical Background - Electrical MethodIkhsan Parinduri100% (1)
- Applied Geophysics For The Hydrocarbon Exploration: Electrical and Electromagnetic MethodsDocument26 pagesApplied Geophysics For The Hydrocarbon Exploration: Electrical and Electromagnetic MethodsbrunoNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Survey Using Terrameter SAS 4000 SystemDocument7 pagesResistivity Survey Using Terrameter SAS 4000 SystemSheikh Akiil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Expt 04Document2 pagesExpt 04hod eeNo ratings yet
- Summary of Allowable Bearing CapacityDocument1 pageSummary of Allowable Bearing CapacityparthNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 Disturbed SamplesDocument1 page2.1.1 Disturbed SamplesparthNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument1 page5 PDFparthNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument1 page5 PDFparthNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4parthNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument1 page3 PDFparthNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Soil StratificationsDocument1 page4.0 Soil StratificationsparthNo ratings yet
- 18 Jun 2019 Adi To MMCT TicketDocument1 page18 Jun 2019 Adi To MMCT TicketparthNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument1 page1 PDFparthNo ratings yet
- Amreli B-112 (BH-4)Document5 pagesAmreli B-112 (BH-4)parthNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-03-08Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-03-08parthNo ratings yet
- Amreli B-112 (BH-1)Document2 pagesAmreli B-112 (BH-1)parthNo ratings yet
- Etrex 10 Quick Start ManualDocument12 pagesEtrex 10 Quick Start ManualzulkifliharahapNo ratings yet
- Program Program Program: Day 1: Sun Feb 17, 2019 Day 1: Sun Feb 17, 2019 Day 1: Sun Feb 17, 2019Document1 pageProgram Program Program: Day 1: Sun Feb 17, 2019 Day 1: Sun Feb 17, 2019 Day 1: Sun Feb 17, 2019parthNo ratings yet
- Brief Biodata of NNBhuptaniDocument3 pagesBrief Biodata of NNBhuptaniparthNo ratings yet
- 5 Jul MeDocument2 pages5 Jul MeDivakar VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Palakkad Ph.D. Ordinances and RegulationsDocument15 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Palakkad Ph.D. Ordinances and RegulationsparthNo ratings yet
- Ja 14025Document3 pagesJa 14025Gordon NicolasNo ratings yet
- Vishal Bhayani ResumeDocument2 pagesVishal Bhayani ResumeparthNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Palakkad Ph.D. Ordinances and RegulationsDocument15 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Palakkad Ph.D. Ordinances and RegulationsparthNo ratings yet
- Information Brochure 2018 1Document29 pagesInformation Brochure 2018 1Prakash AsNo ratings yet
- Excavation LookbackDocument69 pagesExcavation LookbackparthNo ratings yet