Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methods Done. Other Procedures Deemed Applicable To The Experiment Such As The Winkler Method, Which
Uploaded by
JaneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methods Done. Other Procedures Deemed Applicable To The Experiment Such As The Winkler Method, Which
Uploaded by
JaneCopyright:
Available Formats
In the 1960s how estuaries flushed themselves was being studied, and one of the variables was how
the BOD of
the water in the estuary was progressively reduced by the flushing. The Delaware Estuary study was a large project
to show how the effects of pollutants (and their control) would affect water quality. As a part of this study, a group
of young interns were to run up and down the estuary taking samples at specified locations, bring these samples
back to the laboratory, and run the BODs.
As the first large batch bottles came in, the intern assigned to the laboratory measured the initial dissolved oxygen
in all of the bottles and placed them into an incubator. Five days later, he took the bottles out and measured the
final DO. Much to his surprise, the final DO numbers were higher than the initial DO values. Suspecting chemical
error, he remixed all the chemicals very carefully, following exactly the procedures in Standard Methods. But the
results did not change. The final DOs are still higher, and many bottles were actually supersaturated with oxygen.
Enumerate possible reasons for this occurrence and suggest remediation steps to ensure accurate results from the
tests.
- One possible major error would be regarding the incubator, since its main purpose is to provide an energy
source through its’ light for the algae in the bottles to produce oxygen. Therefore, it was possible that the
light bulb in the incubator was faulty. Thus, providing errors in the result.
- Another possible error at the same time possibly an ineffective method would be the procedure of standard
methods done. Other procedures deemed applicable to the experiment such as the Winkler method, which
is known to determine the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water samples, should also be considered.
You might also like
- Baltazar, Daniel Janz: Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument1 pageBaltazar, Daniel Janz: Environmental Science and EngineeringLucienne IrianaNo ratings yet
- CS#4 BOD TestingDocument1 pageCS#4 BOD TestingJohn Andrae MangloNo ratings yet
- Liver Smoothie Enzyme PaperDocument4 pagesLiver Smoothie Enzyme Paperapi-582915120No ratings yet
- Activity Journal (Experiment #1)Document3 pagesActivity Journal (Experiment #1)Abraham MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen Research PaperDocument7 pagesDissolved Oxygen Research Paperfvjebmpk100% (1)
- Lab Report Bio150Document4 pagesLab Report Bio150ahmadalifimran777No ratings yet
- Caso # 2Document6 pagesCaso # 2Catherine RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Hydro Prot DoDocument18 pagesHydro Prot DoPonraj ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Wqi & E-ColiDocument18 pagesWqi & E-ColiAkram ShamsulNo ratings yet
- Labreportclairelarson 1Document5 pagesLabreportclairelarson 1api-239316362No ratings yet
- Biological Oxygen Demand Research PaperDocument4 pagesBiological Oxygen Demand Research Paperafnhkvmnemelfx100% (1)
- Carbon Dioxide 3 - TeacherDocument9 pagesCarbon Dioxide 3 - Teacheralxgc821206No ratings yet
- Elodea Lab Experiment Report EditedDocument5 pagesElodea Lab Experiment Report Editedapi-253293388No ratings yet
- 4500 O2 DisueltoDocument8 pages4500 O2 DisueltoPenelope MeloNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project: Topic-How Fast Do Hydrogen Ions Diffuse Through WaterDocument2 pagesInvestigatory Project: Topic-How Fast Do Hydrogen Ions Diffuse Through WaterShifa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Tecnica WinklerDocument6 pagesTecnica WinklerAzul ScaloniNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of BeetrootDocument8 pagesLiterature Review of Beetrootggsmsyqif100% (1)
- Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide Experiment CourseworkDocument4 pagesCatalase and Hydrogen Peroxide Experiment Courseworkbcr9srp4100% (1)
- Activity 1 Oh My Gas!: Hydrilla SprigDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Oh My Gas!: Hydrilla SprigFe Pakias GullodNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Lab ReportDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Lab Reportapi-253363927100% (3)
- Eutrophication ExperimentsDocument6 pagesEutrophication ExperimentsBiancaNo ratings yet
- Iodine Clock Method CourseworkDocument5 pagesIodine Clock Method Courseworkbcrqs9hr100% (2)
- AP Biology Primary Productivity Lab ReportDocument9 pagesAP Biology Primary Productivity Lab ReportVictor Martin100% (1)
- Engerer 1999Document2 pagesEngerer 1999fluna1No ratings yet
- DissolvedoxygenlabDocument7 pagesDissolvedoxygenlabapi-242403741No ratings yet
- Experiment BODDocument6 pagesExperiment BODMuhd Fadzril100% (1)
- Changes in Densities of Fecal Indicator Bacteria (FIB) Over Differing Tidal Flows in The Ballona Wetlands, Los AngelesDocument1 pageChanges in Densities of Fecal Indicator Bacteria (FIB) Over Differing Tidal Flows in The Ballona Wetlands, Los AngelesuhfsteNo ratings yet
- 2010 Role Kaqun Water in VitroDocument6 pages2010 Role Kaqun Water in Vitromarjan sharabianiNo ratings yet
- Casestudies: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering S.Y. 2013-2014Document6 pagesCasestudies: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Engineering Department of Industrial Engineering S.Y. 2013-2014Patrick SibalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Handout-01: NSC 1110 - BiologyDocument7 pagesLaboratory Handout-01: NSC 1110 - BiologyEmsy MukukaNo ratings yet
- An in Vitro Study of The PH of Three CalciumDocument5 pagesAn in Vitro Study of The PH of Three CalciumRamona MateiNo ratings yet
- WQI & E-COLI ReportDocument18 pagesWQI & E-COLI ReportAkram Shamsul100% (1)
- Organic Groups LaboratoryDocument8 pagesOrganic Groups LaboratoryAna Sofia Guzman FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportNUR AISHAH MOHAMADNo ratings yet
- Investigating Dissolved OxygenDocument10 pagesInvestigating Dissolved OxygenormattNo ratings yet
- Lab Report BioDocument9 pagesLab Report BioArissa SyaminaNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Pembubuhan Kaporit Dalam Menurunkan Kadar Zat Besi (Fe) Pada Air Sumur Gali Tahun 2013Document10 pagesEfektivitas Pembubuhan Kaporit Dalam Menurunkan Kadar Zat Besi (Fe) Pada Air Sumur Gali Tahun 2013arifNo ratings yet
- ID Efektivitas Pembubuhan Kaporit Dalam MenDocument10 pagesID Efektivitas Pembubuhan Kaporit Dalam MenVirdaYuandhaNo ratings yet
- Pack David J 2005Document242 pagesPack David J 2005a_abbaspourNo ratings yet
- Abstract / Summary: Alam. The Method Comprises Mainly Three Stages, Which AreDocument14 pagesAbstract / Summary: Alam. The Method Comprises Mainly Three Stages, Which Aregeek3112No ratings yet
- Effects of A Corrosion Inhibitor On BacteriaDocument11 pagesEffects of A Corrosion Inhibitor On Bacteriaingmetal9104No ratings yet
- Research Paper PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Photosynthesiszepewib1k0w3100% (1)
- Copper and Acetic AcidDocument3 pagesCopper and Acetic AcidCrinita Draconibus OraNo ratings yet
- MR - Skinner: The Committeeon Editing Methodsofanalysis, MR - DoolittleDocument4 pagesMR - Skinner: The Committeeon Editing Methodsofanalysis, MR - DoolittledavidcasNo ratings yet
- INVESTIGATORY PROJECT OF ChetanDocument13 pagesINVESTIGATORY PROJECT OF ChetanDevesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio150 Lab Report - Nurul Alya Binti MokhidinDocument4 pagesBio150 Lab Report - Nurul Alya Binti MokhidinAlya MokhidinNo ratings yet
- Experimental Organic ChemistryDocument229 pagesExperimental Organic ChemistryHamad Mohamad100% (7)
- Cod Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCod Lab ReportNizam AmirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: Gravimetric AnalysisDocument18 pagesChemistry Project: Gravimetric AnalysisTirth BatraNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document16 pagesLab 6신재호No ratings yet
- An Introductory Course of Quantitative Chemical Analysis: With Explanatory NotesFrom EverandAn Introductory Course of Quantitative Chemical Analysis: With Explanatory NotesNo ratings yet
- Retardation of Evaporation by Monolayers: Transport ProcessesFrom EverandRetardation of Evaporation by Monolayers: Transport ProcessesVictor K. La MerRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Methods for Oxidation of Organic Compounds V1: Alcohols, Alcohol Derivatives, Alky Halides, Nitroalkanes, Alkyl Azides, Carbonyl Compounds Hydroxyarenes and AminoarenesFrom EverandMethods for Oxidation of Organic Compounds V1: Alcohols, Alcohol Derivatives, Alky Halides, Nitroalkanes, Alkyl Azides, Carbonyl Compounds Hydroxyarenes and AminoarenesNo ratings yet
- Standard methods for the examination of water and sewageFrom EverandStandard methods for the examination of water and sewageNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Monitoring Handbook for Coal and Oil Shale DevelopmentFrom EverandGroundwater Monitoring Handbook for Coal and Oil Shale DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Advanced Environmental Purification Processes of Water: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandChemistry of Advanced Environmental Purification Processes of Water: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Reactions: C + O Co 1 4 O 1 2 H O: Composition % Dry Mass (G) Molecular Weight (G/mol) MolesDocument1 pageReactions: C + O Co 1 4 O 1 2 H O: Composition % Dry Mass (G) Molecular Weight (G/mol) MolesJaneNo ratings yet
- 8 1 PDFDocument1 page8 1 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- MP3 B PDFDocument1 pageMP3 B PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- 'Enter Length of Rectangle:' 'Enter Width of Rectangle:'Document2 pages'Enter Length of Rectangle:' 'Enter Width of Rectangle:'JaneNo ratings yet
- MP3 CDDocument1 pageMP3 CDJaneNo ratings yet
- 8 2 PDFDocument1 page8 2 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- Clean Water Is Hard To Find. Thus, Making It A More Reliable Matter in This SituationDocument1 pageClean Water Is Hard To Find. Thus, Making It A More Reliable Matter in This SituationJaneNo ratings yet
- Machine ProblemDocument1 pageMachine ProblemJaneNo ratings yet
- A. Relational ExpressionsDocument2 pagesA. Relational ExpressionsJaneNo ratings yet
- Instructions A. More On Arrays and Array OperationsDocument1 pageInstructions A. More On Arrays and Array OperationsJaneNo ratings yet
- B. Working With ArraysDocument7 pagesB. Working With ArraysJaneNo ratings yet
- E. Working With ProgramsDocument1 pageE. Working With ProgramsJaneNo ratings yet
- Machine ProblemDocument1 pageMachine ProblemJaneNo ratings yet
- C. Solving Systems of Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesC. Solving Systems of Linear EquationsJaneNo ratings yet
- Result: X 1 y 1 Z - 2Document3 pagesResult: X 1 y 1 Z - 2JaneNo ratings yet
- MP2 D PDFDocument1 pageMP2 D PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- SLIDE 2 Soda-LimeDocument4 pagesSLIDE 2 Soda-LimeJaneNo ratings yet
- MP1 PDFDocument1 pageMP1 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- A. Answer: - 106 CommandDocument1 pageA. Answer: - 106 CommandJaneNo ratings yet
- MP1 2 PDFDocument1 pageMP1 2 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- Instructions A. Usual Functions in A Scientific CalculatorDocument1 pageInstructions A. Usual Functions in A Scientific CalculatorJaneNo ratings yet
- Instructions A. Opening and Closing MatlabDocument1 pageInstructions A. Opening and Closing MatlabJaneNo ratings yet
- 10 2 PDFDocument1 page10 2 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- 11 4Document1 page11 4JaneNo ratings yet
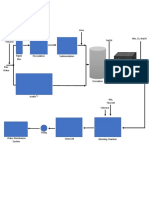
- Lime Ferric, Acid, Polymer Naoh NH, CL NaohDocument1 pageLime Ferric, Acid, Polymer Naoh NH, CL NaohJaneNo ratings yet
- 11 1 PDFDocument1 page11 1 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- 9 2Document1 page9 2JaneNo ratings yet
- 9 3Document1 page9 3JaneNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument1 page8 PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- 9 1Document1 page9 1JaneNo ratings yet